A method for recovering valuable metals from the comprehensive recovery slag of waste lithium cobalt oxide batteries
A technology of old lithium cobalt oxide and valuable metals is applied in the field of secondary resource recovery to achieve the effects of efficient recovery, maximization of economic value and simple recovery process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
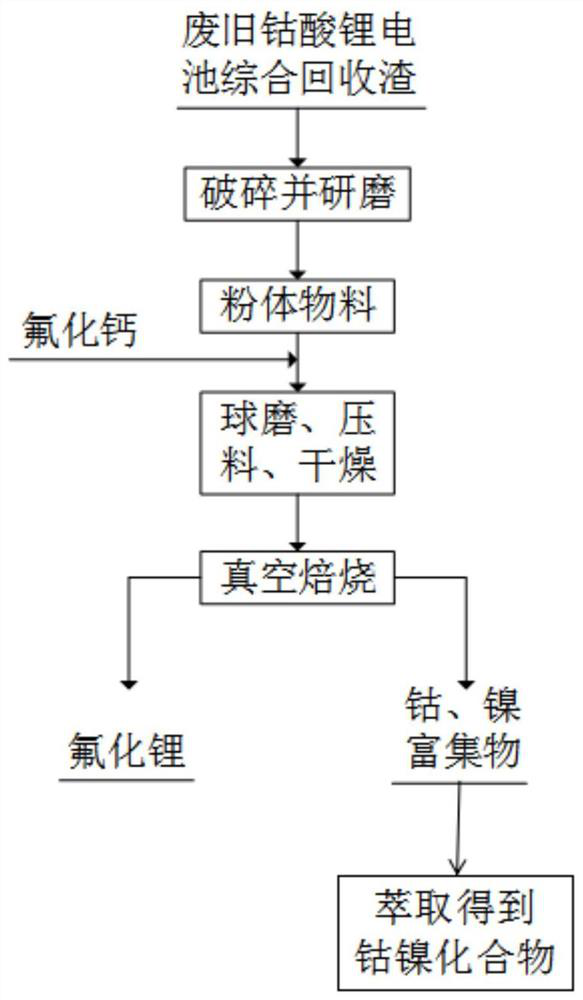
[0032] Mechanically crush and grind the waste lithium cobalt oxide battery comprehensive recovery slag to obtain powder materials;
[0033] The lithium in the powder material and the fluorine in the calcium fluoride powder are ball-milled, pressed and dried at a molar ratio of 1:1.5 to obtain a dry material, which is an experimental sample;
[0034] Take 20g of the experimental sample as the initial raw material and put it into the corundum crucible, and then put the crucible in the heating zone of the vacuum furnace. When the vacuum reaches 50Pa, the vacuum furnace will heat it. When the temperature is 750℃, stop the heating and keep the temperature for 1.5h. After finishing, the vacuum pump continues to run, until the temperature in the furnace is down to room temperature, the vacuum pump is closed, and the volatile product lithium chloride is taken out (wherein, in the vacuum heat treatment, the condensed collection of the volatile material is the prior art, and will not be ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Mechanically crush and grind the waste lithium cobalt oxide battery comprehensive recovery slag to obtain powder materials;
[0038] The lithium in the powder material and the fluorine in the calcium fluoride powder are ball-milled, pressed and dried at a molar ratio of 1:2.0 to obtain a dry material, which is an experimental sample;
[0039] Take 40g of the experimental sample as the initial raw material and put it into the corundum crucible, and then put the crucible in the heating zone of the vacuum furnace. When the vacuum reaches 100Pa, the vacuum furnace is heated. When the temperature is 850℃, it is kept for 2.0h. The vacuum pump continued to run until the temperature in the furnace dropped to room temperature, the vacuum pump was turned off, and the volatile product lithium chloride was taken out. After weighing, its mass was 10.42 g. After calculation, the recovery rate of lithium element was 98.1%, and the purity reached 99.2%. The cobalt and nickel are enrich...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com