Patents
Literature
54results about How to "Short recycling process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for recycling lithium from lithium ion battery waste electrolyte
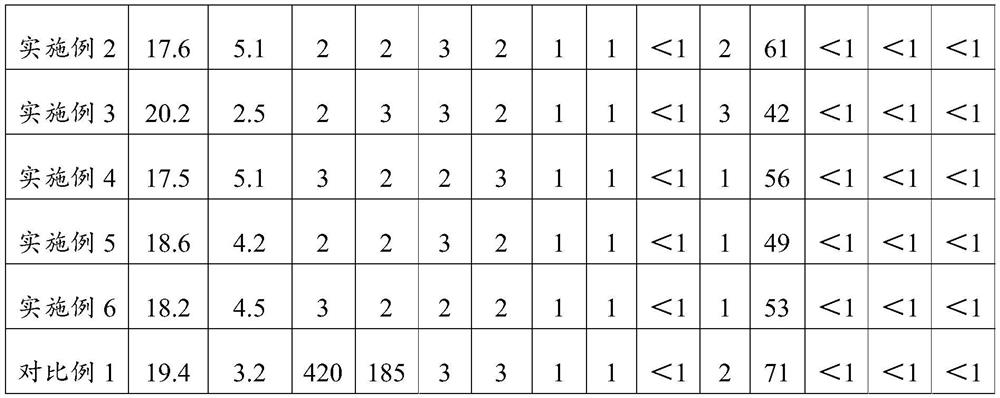
ActiveCN108155434AClean and efficient useEfficient use ofWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingLithium carbonatePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a method for recycling lithium from a lithium ion battery waste electrolyte, and belongs to the technical field of resources cyclic utilization. The invention aims to providethe method for recycling the lithium from the lithium ion battery waste electrolyte. The method is mainly characterized by mixing and reacting the waste electrolyte and a halogenide solution containing a large positive ionic radius, wholly separating PF6- in the electrolyte, deeply purifying the lithium-containing solution after separation, and precipitating the lithium to obtain lithium carbonate, so that the aim of cleanly and high-efficiently utilizing the lithium ion battery waste electrolyte is achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
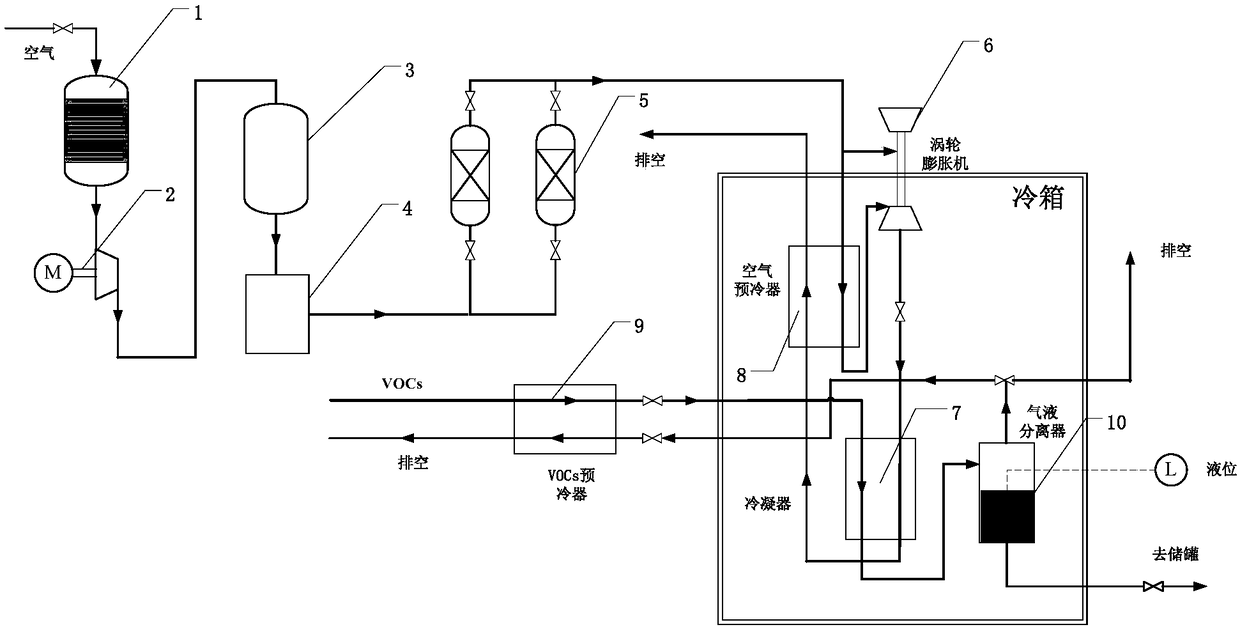
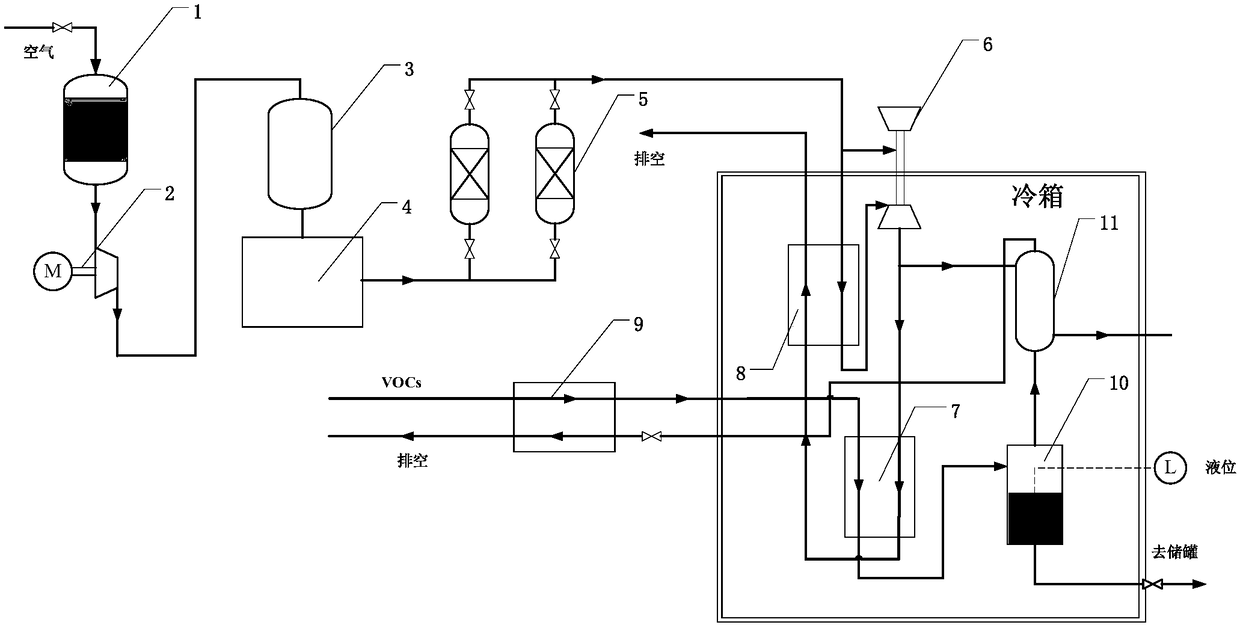
VOCs recovery system using air copious cooling
ActiveCN108452632ALow running costImprove cooling effectSolidificationLiquefactionAtmospheric airAir filter
The invention relates to an efficient and low-cost VOCs recovery system using air copious cooling. The recovery system comprises a gaseous air purification system, an air liquefaction system, a VOCs recovery cold box and the like, wherein the gaseous air purification system comprises an air filter, a freezing dryer and an air purifier; the air liquefaction system comprises an air compressor, an air storage tank, a turbo expander and an air precooler; and the VOCs recovery cold box comprises a VOCs precooler, a VOCs condenser and a gas-liquid separator. According to the recovery system providedby the invention, air is used as a cooling medium in a VOCs recovery process, so that VOCs are condensed and separated. The treated VOCs gas meets national emission standards and can be directly discharged into the atmosphere. Compared with a traditional condensation method, this method can greatly improve the recovery rate of organic gases, effectively shorten the recovery process and simplify the recovery process. At the same time, the use of the method is not limited by the concentration and composition of a source gas, and the application range is wider.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV +1
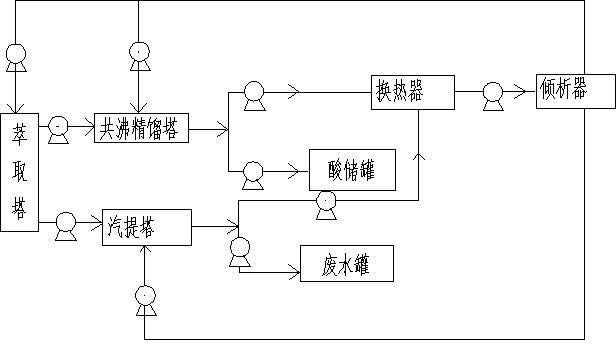
Process and equipment for purifying dilute acetic acid solution
InactiveCN102432453AReduce consumptionShort recycling processCarboxylic compound separation/purificationPhase splittingWastewater
The invention discloses a process and equipment for purifying a dilute acetic acid solution. The process comprises the following steps of: extraction, phase splitting, azeotropic distillation, vapor condensation and separation, extracting agent recovery, and the like. The equipment comprises an extraction tower, an azeotropic distillation tower, a stripping tower, a heat exchanger, an acid storage tank, a decanter and a wastewater tank. The invention has the advantages that: the dilute acetic acid solution is concentrated by an extraction process, and the concentrated solution is purified by an azeotropic distillation method, so that steam consumption is reduced, the solvent recovery process is shortened, and the consumption and secondary pollution of a solvent are reduced; and the concentration of acetic acid after separation is more than or equal to 99.0 percent, the concentration of the acetic acid in the discharged water is less than 0.2 percent, the recovery rate of the acetic acid is more than or equal to 95 percent, the consumption of an extracting agent is less than or equal to 0.15 percent, and the steam consumption is less than or equal to 4t / h.
Owner:ANQIU LUAN PHARMA
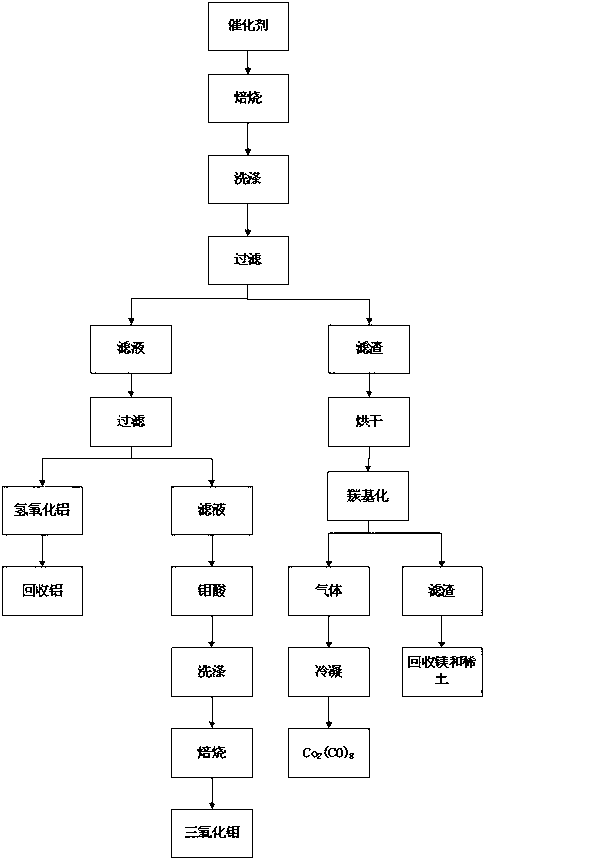
Method of recovering molybdenum and cobalt from waste cobalt-molybdenum catalyst
ActiveCN103074494AEasy to getShort recycling processProcess efficiency improvementPtru catalystAluminium hydroxide
The invention provides a method of recovering molybdenum and cobalt from a waste cobalt-molybdenum catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: adding alkali into the waste cobalt-molybdenum catalyst, then roasting the waste catalyst, carrying out washing and filtering, adding an acid into an obtained filtrate to adjust a pH value, filtering a reacted solution, with filter residue being aluminum hydroxide for recovery of aluminum and a filtrate being a molybdenum-containing solution, adjusting the pH value of the molybdenum-containing solution to obtain molybdic acid deposition, washing the molybdic acid deposition with distilled water to wash out impurities adhering on molybdic acid and carrying out roasting so as to obtain molybdenum trioxide; and adding alkali for roasting, drying washed filter residue, introducing carbon monoxide gas after moisture is totally removed and introducing tail gas into a collection container after condensation at the same time, wherein carbonyl cobalt is condensed to form a solid, which allows metal cobalt to be recovered, the tail gas is cyclically used, and reacted filter residue after introduction of carbon monoxide gas can be used for recovery of carriers like magnesium and rare earth. According to the method, used raw materials are cheap, which is beneficial for cost control; steps of the method are simple, so recovery flow of metal cobalt and molybdenum is shortened, and a recovery rate is increased.
Owner:JINGMEN GEM NEW MATERIAL
Dry recycling technology for MOX fuel pellet waste
ActiveCN106782736AHigh recovery rateShort recycling processRadioactive decontaminationMOX fuelWaste product
The invention belongs to the field of nuclear fuel. In order to solve the problem that an MOX fuel pellet waste wet recycling technology has many defects, the invention provides a dry recycling technology for MOX fuel pellet waste. The technology comprises the following steps of 1, burning MOX fuel pellet waste; 2, crushing by using a crusher; 3, screening; 4, ball milling; and 5 recycling. According to the technology provided by the invention, powdering of the MOX fuel pellet waste is achieved by crushing-ball milling technologies, so that the technology is fundamentally different from a dry recycling technology for UO2 fuel pellet waste using an oxidized crushing technology. Practical application shows that the MOX fuel pellet waste wet recycling technology provided by the invention has the advantages of high recycling rate, short recycling technical process, high in speed, simple in equipment, low in cost, and being free from generating radioactive liquid waste, and can be recycled in an MOX combustion manufacturer; the recycled power has similar sintering performance with the common MOX raw material powder, and can be mixed with common raw materials for preparing MOX fuel pellets.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
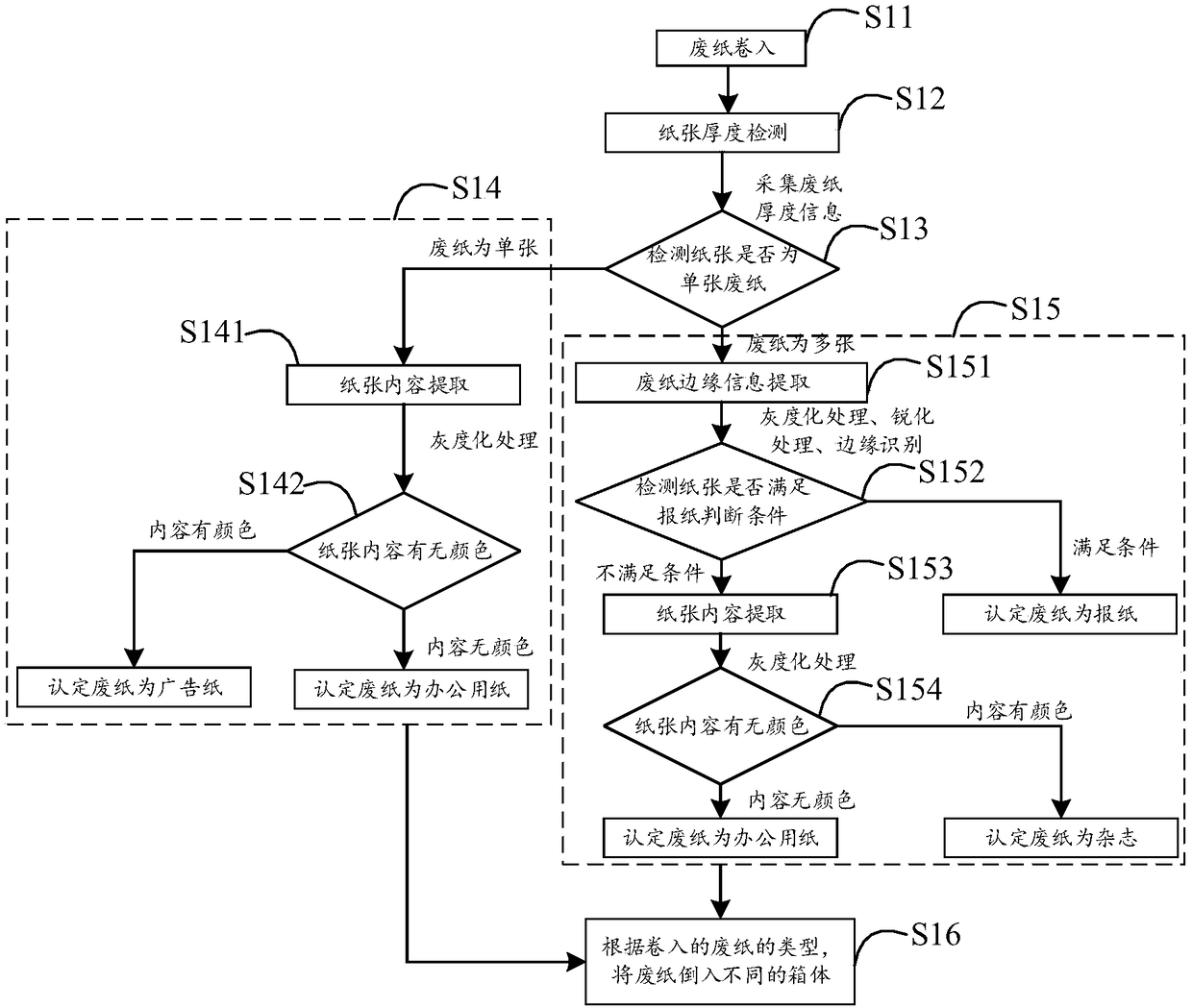
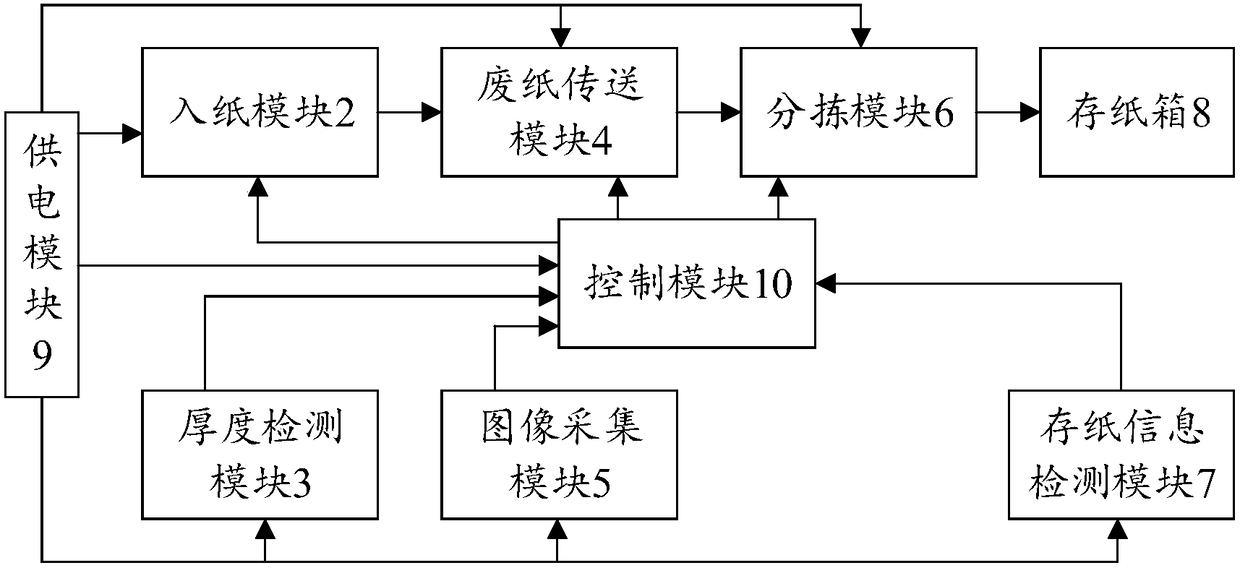
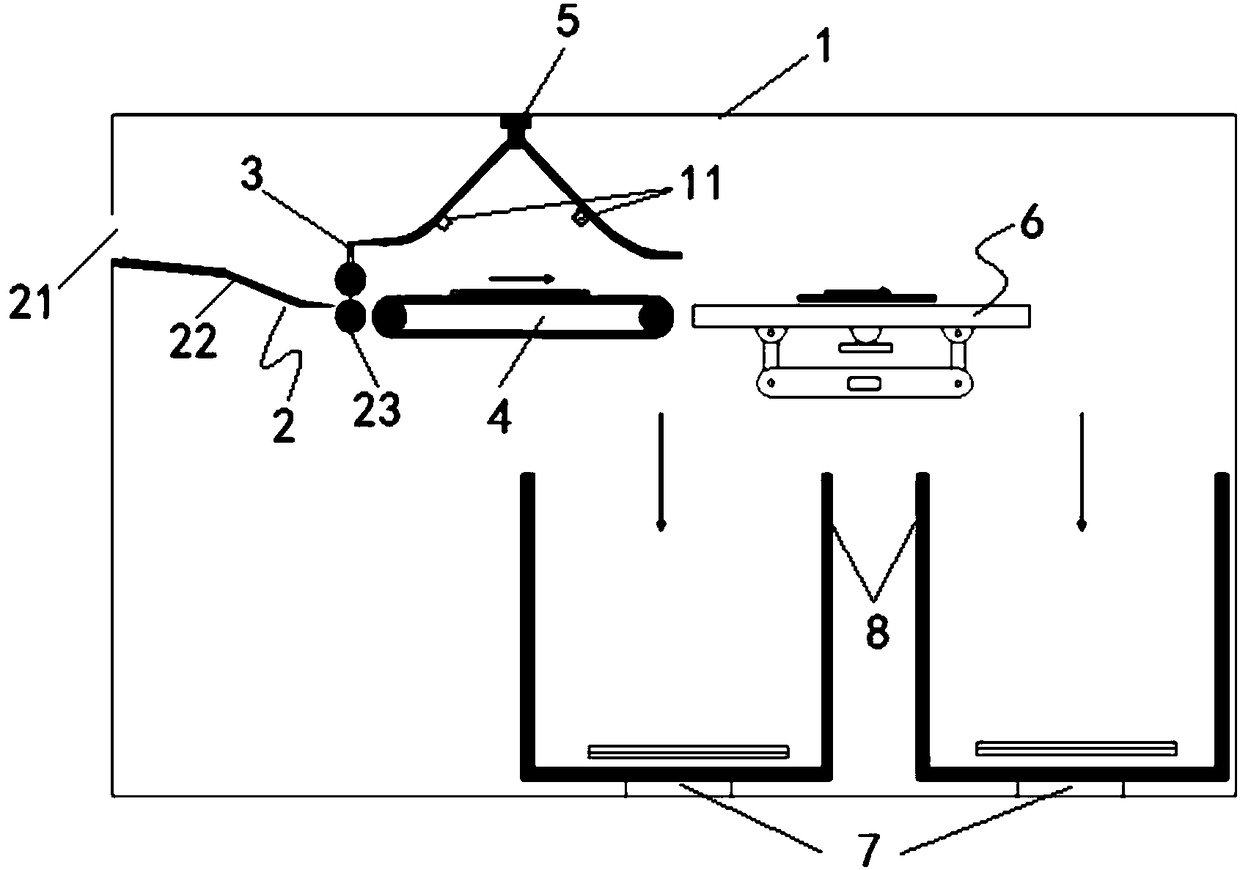
Waste paper classification recycling method, recycling terminal and recycling system
ActiveCN108339755AImprove recycling ratesLow costCharacter and pattern recognitionSortingRecovery methodEconomic benefits
The invention relates to a waste paper classification recycling method, a recycling terminal and a recycling system. The waste paper classification recycling method comprises the steps of winding waste paper; detecting the thickness of the winded waste paper; judging whether the paper is a single waste paper sheet or multiple waste paper sheets according to a detection result; if judging the paperis the single waste paper sheet, determining the type of the winded single waste paper sheet; if judging the paper is the multiple waste paper sheets, determining the type of the winded multiple waste paper sheets; and recycling the waste paper according to the type of the winded waste paper. According to the waste paper classification recycling method provided by the invention, the waste paper is classification recycled, so that the waste paper recycling utilization ratio can be effectively improved, the environment pollution is reduced, the recycling quality is high, and a favorable renewable resource recycling environment can be built. The waste paper classification recycling method provided by the invention can be beneficial to shortening a recycling process and reducing the waste paper recycling cost, and has a great help to the improvement of the economic benefit of a papermaking industry.
Owner:向霄
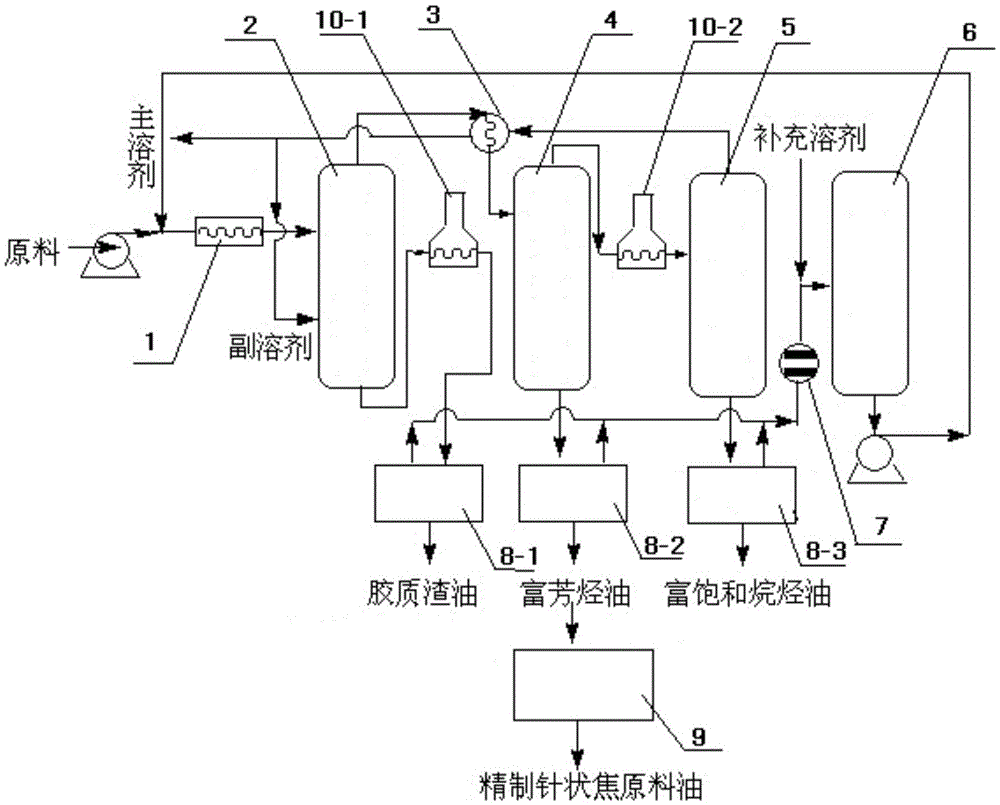
System device for producing needle coke crude oil through catalytic slurry oil
InactiveCN105482850AHigh aromaShort recycling processTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrocarbon oils treatment productsAlkaneThermodynamics
The invention belongs to the field of catalytic slurry oil deep processing and particularly relates to a system device for producing needle coke crude oil through catalytic slurry oil. According to the device, a mixer 1, the top of a catalytic slurry oil extraction tower 2, the top of an aromatic-hydrocarbon-rich oil separation tower 4 and the top of an aromatic-alkane-rich oil separation tower 5 are sequentially connected through pipelines. The bottom of the catalytic slurry oil extraction tower 2 is connected with a gas stripping tower A8-1. The bottom of the aromatic-hydrocarbon-rich oil separation tower 4 is directly connected with a gas stripping tower B8-2. The bottom of the aromatic-alkane-rich oil separation tower 5 is connected with a gas stripping tower C8-3. A gas outlet of the gas stripping tower A8-1, a gas outlet of the gas stripping tower B8-2 and a gas outlet of the gas stripping tower C8-3 are sequentially connected and then connected with a condenser 7 and a solvent tank 6, and the bottom of the gas stripping tower B8-2 is connected with a hydrofining reactor 9. The device fully utilizes petroleum resources and turns waste into wealth, the catalytic slurry oil can be utilized at high value, and the produced needle coke crude oil can serve as needle coke raw materials high-additional-value products.
Owner:GUANGXI HONGDA BIO ENERGY TECH
Method for fabricating NdFeB magnet from waste NdFeB magnet
ActiveCN106328364AShort recycling processMeet the needs of environmental protectionInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRecycling and recovery technologiesHeat treatedNeodymium iron boron
The invention provides a method for fabricating an NdFeB magnet from a waste NdFeB magnet. The method comprises the steps of providing first powder, wherein the first powder is formed from the waste NdFeB magnet; providing second powder, wherein the second powder is formed from an alloy thin strip; mixing the first powder and the second powder to form mixed powder, wherein the first powder relative to the weight of the mixed powder accounts for 90-99wt%; and sequentially performing magnetic field pressing and matching, vacuum sintering and thermal processing on the mixed powder to form the NdFeB magnet.
Owner:CHINA STEEL
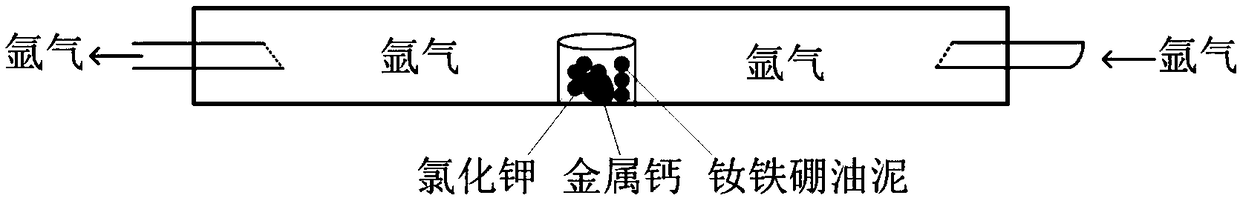
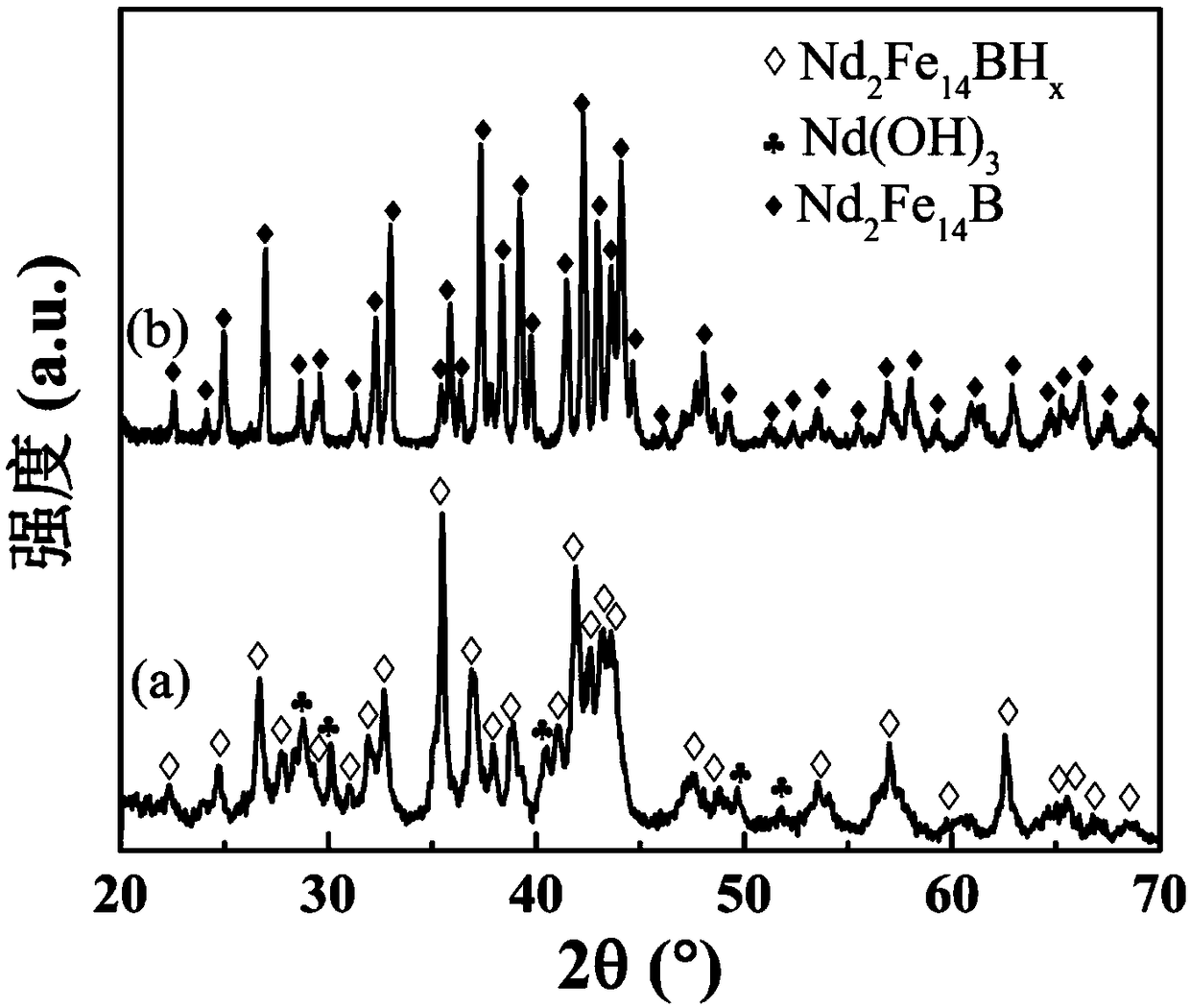
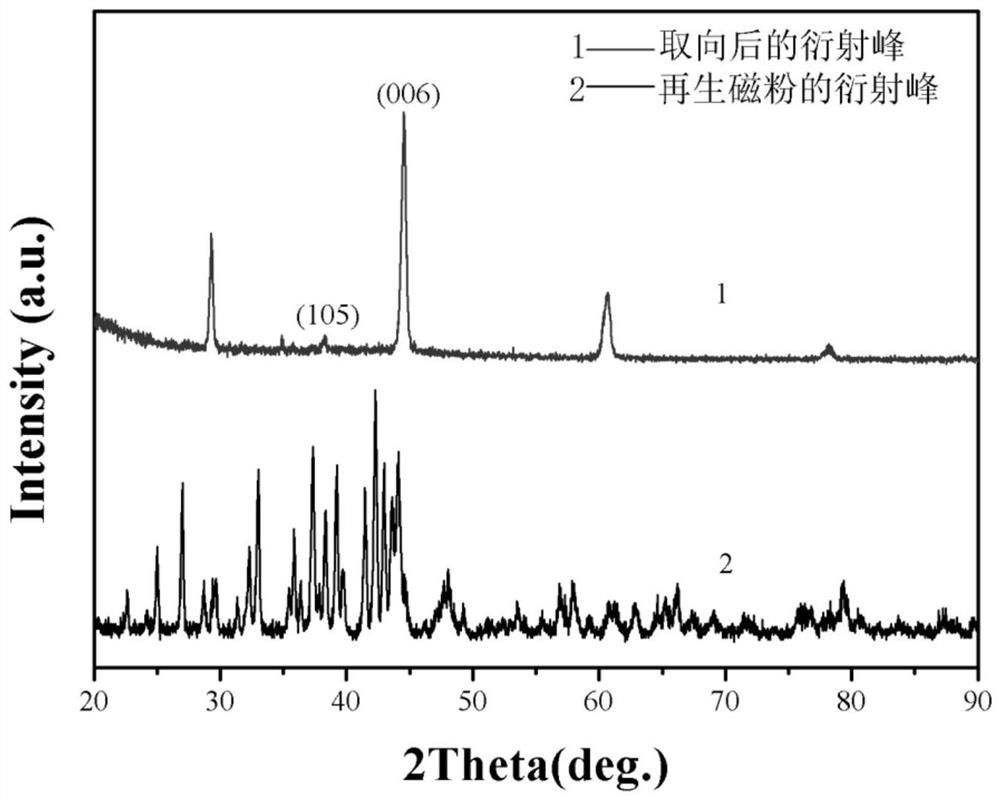
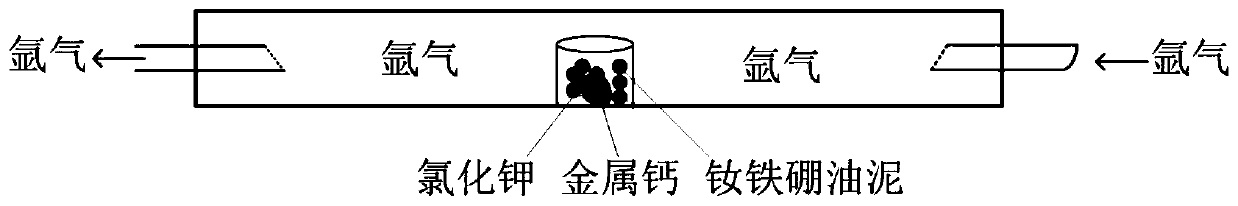
Method for recovering neodymium iron boron trepanning oil sludge waste through Ca-chloride reduction diffusion technology
ActiveCN109338113AHigh recovery rateAchieve recyclingTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusSintered magnetsOil sludge
The invention discloses a method for recovering neodymium iron boron trepanning oil sludge waste through a Ca-chloride reduction diffusion technology, and belongs to the technical field of recycling of rare-earth permanent-magnet industrial solid waste. The method includes the technological processes of drying of the oil sludge waste containing sintered neodymium iron boron, Ca-chloride reductiondiffusion, low-temperature soaking and calcium removal, doping of rare-earth-rich alloy powder, sintering, heat treatment and the like. The neodymium iron boron trepanning oil sludge waste serves as araw material, Ca-KCl is used for direct reduction diffusion to obtain regenerated neodymium iron boron magnetic powder, the powder is recycled, and a regenerated sintered magnet is prepared through the sintering technology. In the method, potassium chloride serves as a low-melting-point auxiliary agent so that the reaction temperature can be reduced, the reaction time can be shortened, the recycling rate is increased, and the use amount of metal calcium is reduced. Low-temperature calcium removal is adopted, the powder can be prevented from being oxidized, and the calcium removal efficiency is improved. By using the rare-earth-rich alloy, rare earth can be supplemented, and component adjustment and industrial production are facilitated. According to the method, the purposes of shorteningthe recycling technology, reducing the recycling cost, reducing the environmental burden and increasing the waste utilization rate are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for recovering lithium from waste lithium battery positive electrode material and application
ActiveCN112366381AShort recycling processSimple technical circuitWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingPhysical chemistryElectrode material
The invention provides a method for recovering lithium from a positive electrode material of a waste lithium battery and application, and relates to the technical field of comprehensive recovery of waste lithium battery resources. The method for recovering lithium from the waste lithium battery positive electrode material comprises the steps that the waste lithium battery positive electrode material is leached and separated in a soluble sulfide solution to obtain a lithium-containing solution, the pH of a leaching system is 5-10, the leaching temperature is 20-100 DEG C, the leaching time is 1-6h, and the ratio of the volume of the soluble sulfide solution to the mass of the positive electrode material of the waste lithium battery is 1-20mL / g; and a precipitant is added into the lithium-containing solution to recover the lithium-containing precipitate. According to the method for recovering lithium from the waste lithium battery positive electrode material, the technical problems thatin the prior art, energy consumption is high, management and operation cost is high, selective recycling cannot be achieved, the technical route is relatively complex, and the recycling rate and purity are not high are solved, the loss of valuable metal is avoided, and the harm of waste lithium batteries to the environment is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING MINING & METALLURGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD
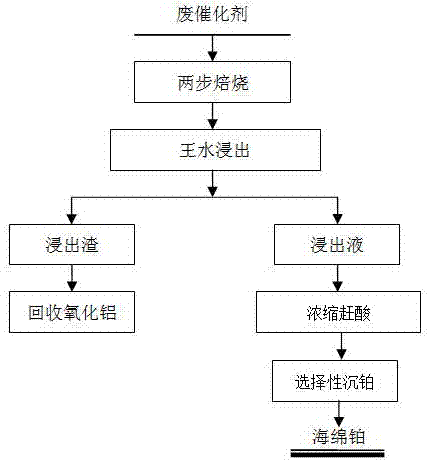
Method for short-flow recovery of platinum group metal from waste catalysts
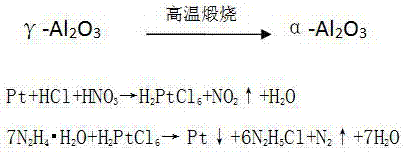
InactiveCN107574315AShort recycling processHigh purityProcess efficiency improvementAluminium oxides/hydroxidesDissolutionTwo step
The invention discloses a method for short-flow recovery of platinum group metal from waste catalysts. The method is determined on the basis of analyzing and researching states and contents of carriers and active components in the waste catalysts; in order to effectively separate the platinum group metal from the carriers, the method uses the characteristics of different acid dissolubility of aluminum trioxide with different crystal forms for controlling the roasting temperature to totally convert gamma-Al2O3 in the waste catalyst carriers to alpha-Al2O3 through two-step roasting, and uses dissolution of aqua regia for leaching out the platinum group metal; the leaching rate of aluminum oxide is lower than 0.2%; after leaching liquid is concentrated to catch acid, and the acidity is adjusted, hydrazine hydrate is used for selective reduction to obtain sponge platinum with a purity of higher than 99%; and the recovery rate of platinum is higher than 99%. The method saves a middle impurity removing link, effectively shortens the recovery flow of the platinum group metal in the waste catalysts, introduces no impurity metal in the whole process, and is high in purity of the sponge platinum and high in refining efficiency.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
TiO2-WO3 composite nano powder and preparation method thereof, SCR denitration catalyst and flue gas denitration method
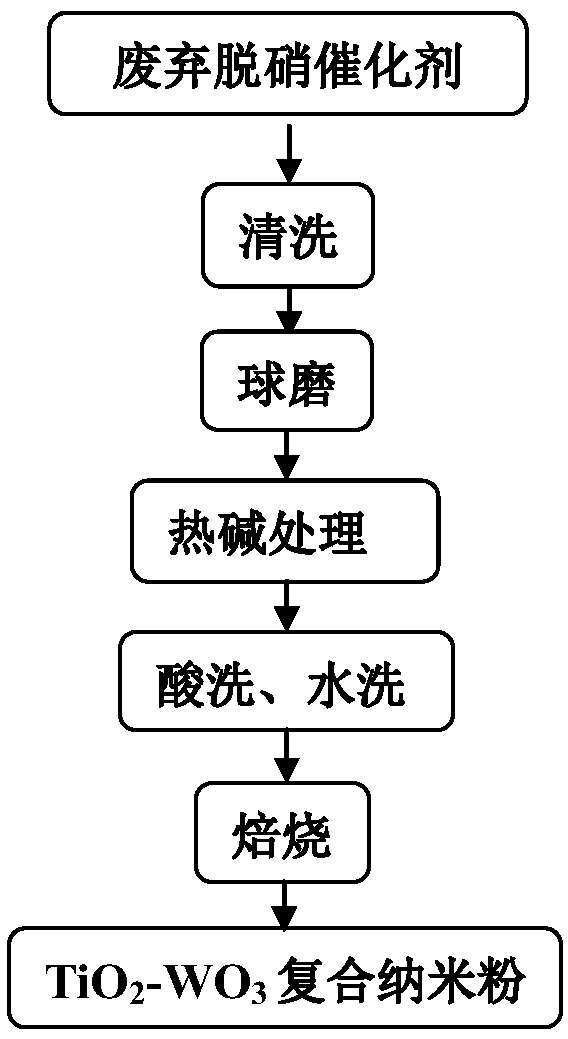
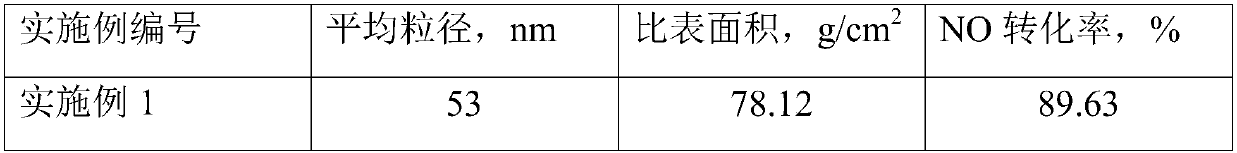
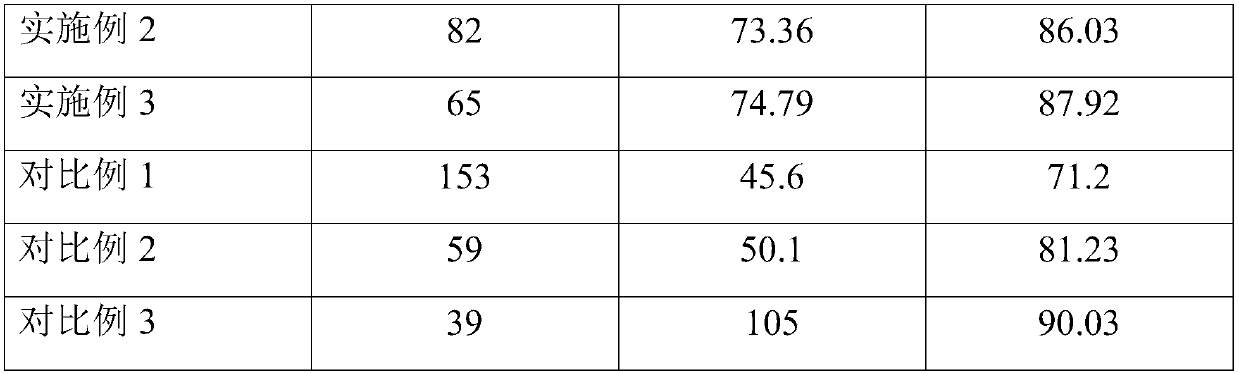
ActiveCN110605113ALarge specific surface areaSimple processGas treatmentDispersed particle separationFiltrationFlue gas
The invention relates to the field of denitration, and discloses TiO2-WO3 composite nano powder, a preparation method thereof, an SCR denitration catalyst and a flue gas denitration method. The preparation method of the TiO2-WO3 composite nano powder comprises the following steps: (1) cleaning and ball-milling a waste denitration catalyst to obtain crushed granules, and adding a strong alkali solution to carry out hot alkali treatment and first filtration to obtain filter residues; (2) carrying out acid pickling and water washing on the filter residues, and carrying out second filtration to obtain titanium-tungsten raw powder; and (3) roasting the titanium-tungsten raw powder to obtain the TiO2-WO3 composite nano powder. The preparation method of the TiO2-WO3 composite nano-powder is simple in process and low in cost and can be achieved at a relatively low temperature and under normal pressure, the prepared TiO2-WO3 composite nano-powder has a relatively high specific surface area, anda denitration catalyst prepared from the composite nano-powder has relatively high denitration efficiency.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +1
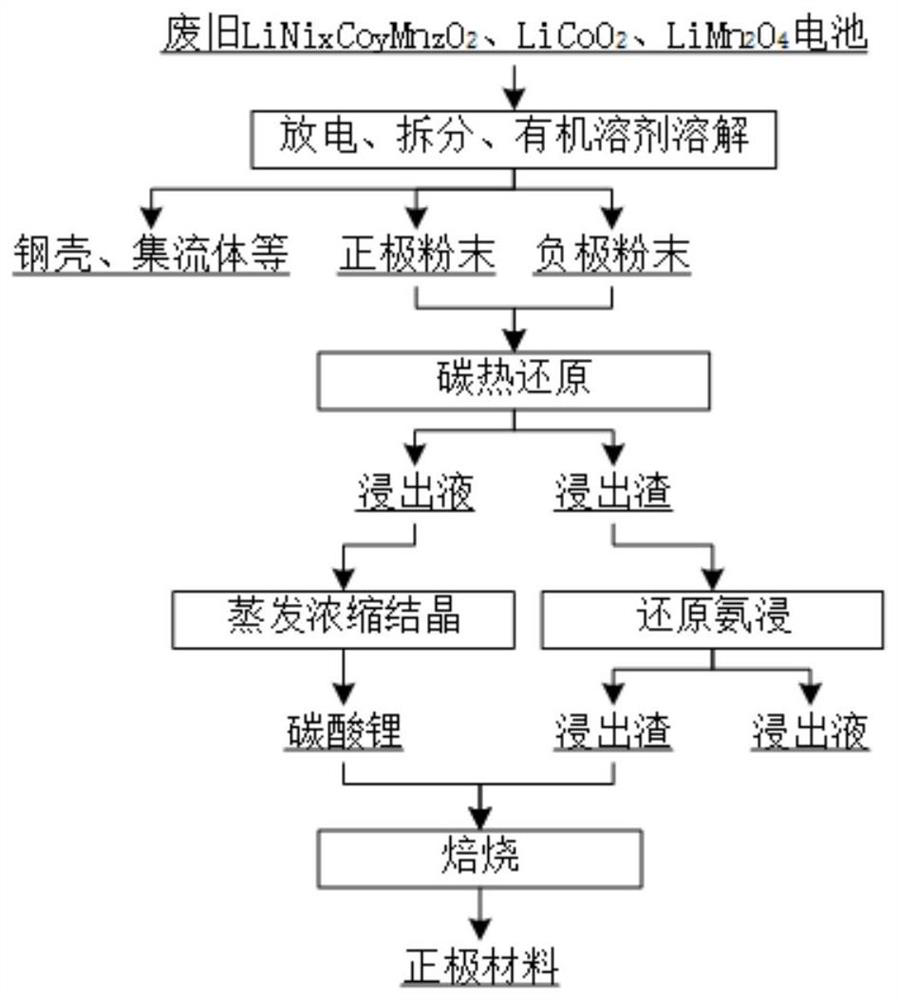
Method for regenerating electrode by using waste lithium battery and leaching residues
InactiveCN113213544AImprove electrochemical performanceTake advantage ofPositive electrodesWaste accumulators reclaimingPregnant leach solutionElectrical battery
The invention discloses a method for regenerating an electrode by using a waste lithium battery and leaching residues. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) discharging and splitting waste LiNixCoyMnzO2, LiCoO2 and LiMn2O4 batteries, and dissolving the batteries with an organic solvent to obtain waste positive electrode mixed powder and negative electrode powder; 2) mechanically mixing the positive electrode powder and the negative electrode powder with a ball mill, and performing carbon thermal reduction treatment; (3) leaching the powder subjected to carbon thermal reduction with water, separating a leaching solution and leaching residues, and evaporating, concentrating and crystallizing the leaching solution to obtain lithium carbonate; (4) leaching the leaching residues by adopting reduced ammonia, and separating ammonia leaching liquid from the leaching residues to obtain a solution rich in high-purity valuable metal nickel and cobalt and manganese oxide leaching residues; and 5) sintering the leaching residues and the regenerated lithium carbonate in the step 2) in a muffle furnace to prepare the LiMn2O4 positive electrode. Based on mixing of multiple waste lithium battery positive and negative electrode materials and full utilization of waste residue regeneration materials in the recovery process, the method has the advantages that the recovery process is green and low in pollution, the recovered waste batteries are wide in source, and the electrochemical performance of regenerated lithium manganate is good.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for separating and recovering silver and palladium from silver-palladium alloy scrap
InactiveCN112501438AInhibit electrolysisEffects of recycling processes such as avoidor restoreProcess efficiency improvementWater chlorinationAlloy
The invention discloses a method for separating and recovering silver and palladium from silver-palladium alloy scrap. The comprises the following steps of dissolving and leaching high-silver low-palladium alloy scrap by using nitric acid; conducting selective palladium precipitation on the leachate by adding a first palladium precipitation agent, and filtering to obtain silver-rich filtrate and palladium-rich salt; preparing high-purity silver powder from the silver-rich filtrate by adopting a reduction method; and after palladium-rich salt oxidation acid leaching, adding a second palladium precipitation agent for further purification and recovery. By adopting the recovery method to recover palladium, the problem of entrainment loss of precious metal ions caused by a traditional chlorination precipitation method is optimized, the tedious step of repeatedly washing silver chloride precipitates to recover the precious metal ions is avoided, the recovery process of the palladium is greatly shortened, the recovery rate and purity of the palladium are remarkably improved, meanwhile, the influence of the palladium on recovery of the high-purity silver powder is avoided, the energy consumption can be effectively reduced, the difficulty in wastewater treatment is reduced, and the method is environment-friendly.
Owner:FIRST RARE MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for simultaneously recycling and preparing carbon-based metal sulfide negative electrode material from waste nickel-cobalt-manganese lithium ion battery positive electrode material and waste cobalt-manganese lithium ion battery negative electrode material
ActiveCN113206227AIncrease contentImprove electrochemical performanceNegative electrodesWaste accumulators reclaimingElectrical batteryManganese
The invention designs a simple, convenient and efficient regeneration process for a waste nickel-cobalt-manganese ternary lithium ion electrode material, so that a waste nickel-cobalt-manganese positive electrode material and a graphite negative electrode material are simultaneously recycled and regenerated into a sodium ion battery negative electrode material, and belongs to the technical field of lithium ion battery material recycling. The method mainly comprises the following steps: 1, mixing waste anode powder, waste cathode powder and sublimed sulfur according to a certain proportion, and carrying out mechanical ball milling to realize uniform compounding; 2, performing high-temperature calcination in a tubular furnace, and achieving the preparation of the carbon-based metal sulfide composite material in one step; 3, extracting lithium from the composite material by water leaching, and drying the leaching residue to directly use the leaching residue as a sodium ion battery negative electrode material. According to the invention, the pressure of environment and resources can be effectively relieved, and huge economic benefits are brought. Meanwhile, the method is simple and efficient in process and beneficial to large-scale preparation.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
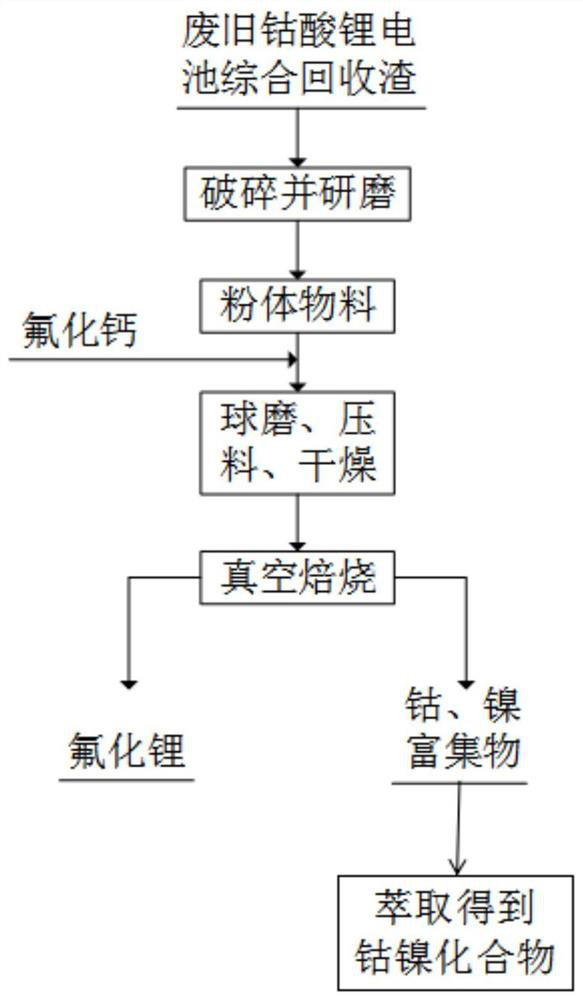
Method for recovering valuable metals from comprehensive recovery slag of waste cobalt acid lithium battery
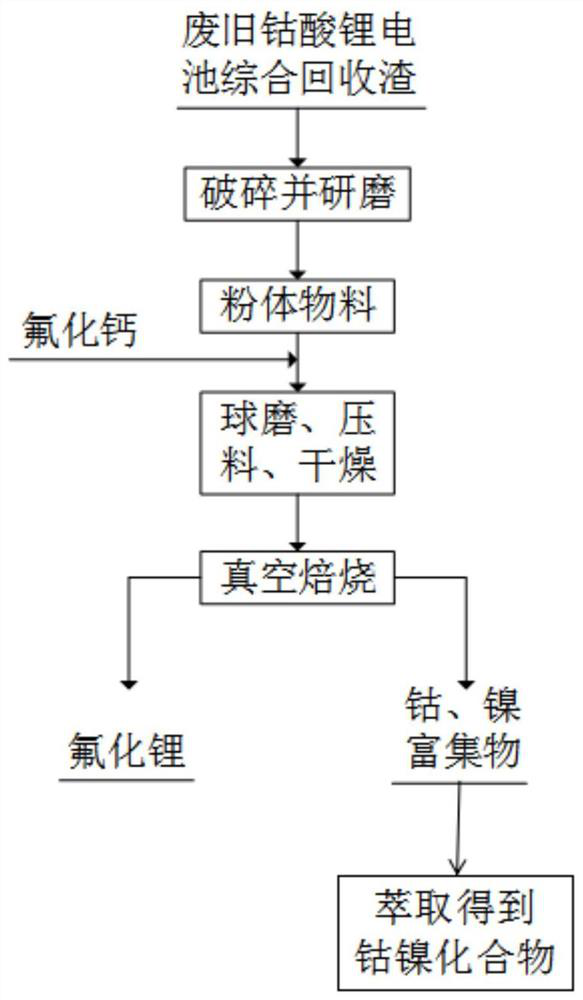
ActiveCN112251604ASimple recycling processShort recycling processProcess efficiency improvementMechanical crushingSlag
The invention is applicable to the technical field of secondary resource recovery, and particularly relates to a method for recovering valuable metals from comprehensive recovery slag of a waste cobalt acid lithium battery. The method specifically comprises the following steps of mechanically crushing and grinding the comprehensive recovery slag of the waste cobalt acid lithium battery to obtain apowder material; adding calcium fluoride powder into the powder material, mixing, ball-milling, briquetting and drying to obtain a dried material; carrying out vacuum heat treatment on the dried material to obtain a volatile product lithium fluoride and residues rich in cobalt and nickel; and extracting the residues rich in cobalt and nickel to obtain a cobalt-nickel compound. The recovery methodis short and simple in technological process, free of strong acid and strong alkali reagents, environment-friendly, capable of directly recovering lithium, cobalt and nickel, economical, efficient and wide in application range.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for separating manganese from ternary lithium ion battery positive electrode leachate
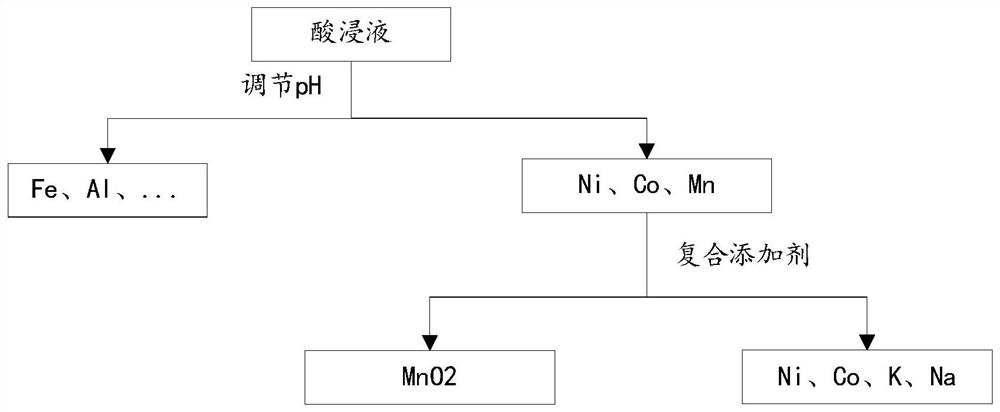
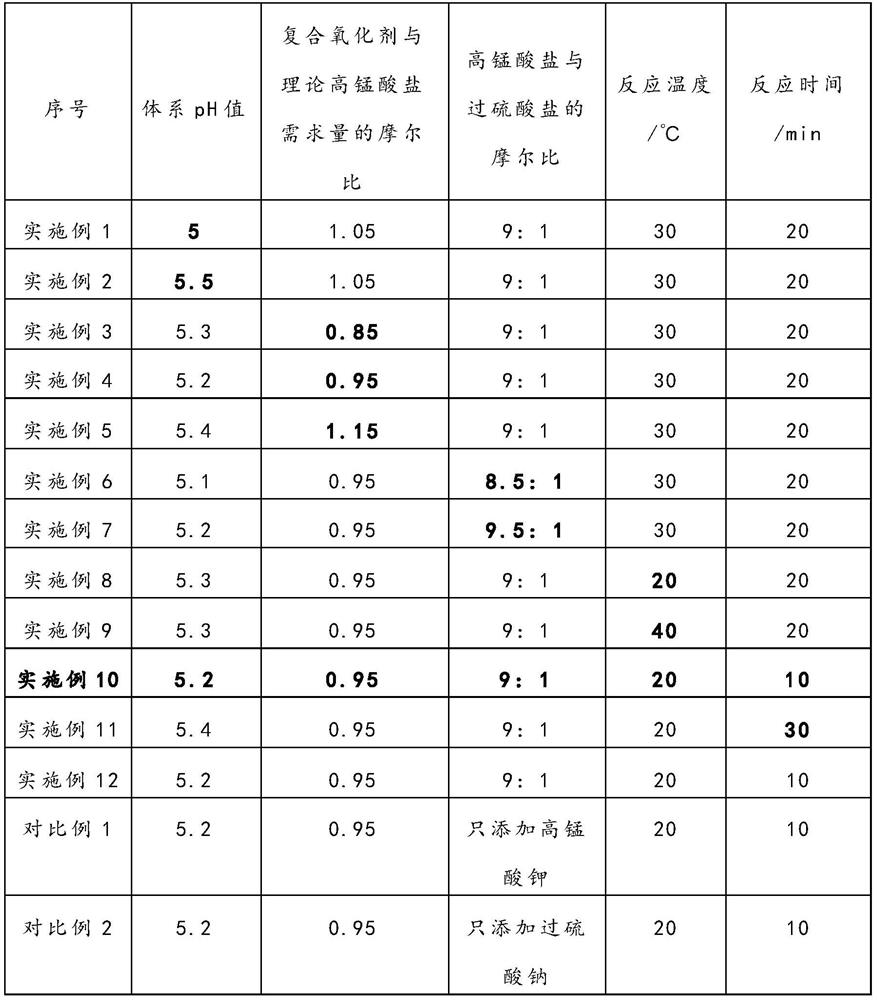
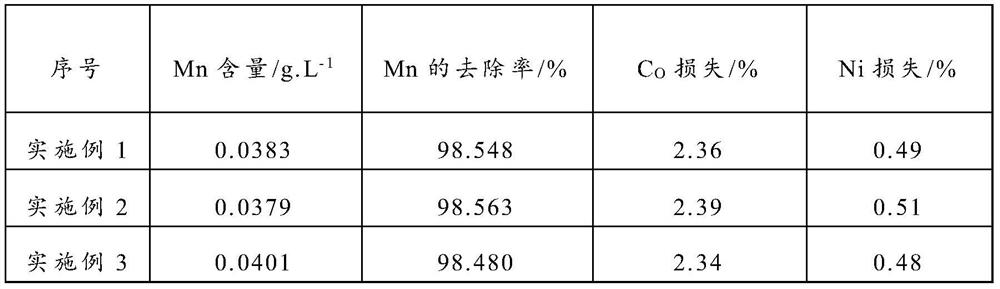
PendingCN113584309AAchieve separationReduce lossesWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementPermanganate saltPersulfate
The invention provides a method for separating manganese from a ternary lithium ion battery positive electrode leachate, which comprises the following steps: adding a composite oxidant into a ternary lithium ion battery positive electrode material leachate, carrying out oxidation reaction on Mn < 2 + >, precipitating in the form of MnO2, and removing a manganese element in the leachate, wherein the composite oxidant is composed of permanganate and persulfate, and the molar ratio of the permanganate to the persulfate is (8.5-9.5): 1. According to the method, the recovery process of the battery positive electrode material is shortened, the product yield is high, the removal rate of manganese is as high as 98.733%, and the loss rates of cobalt and nickel are as low as 2.44% and 0.48% respectively. The impurity content of the separated MnO2 or MnSO4 is low, the required equipment requirement is simple, the experiment condition is mild, the normal-temperature reaction can be adopted, and the method has good environmental protection and economic benefits.
Owner:GUANGDONG JIANA ENERGY TECH CO LTD +1
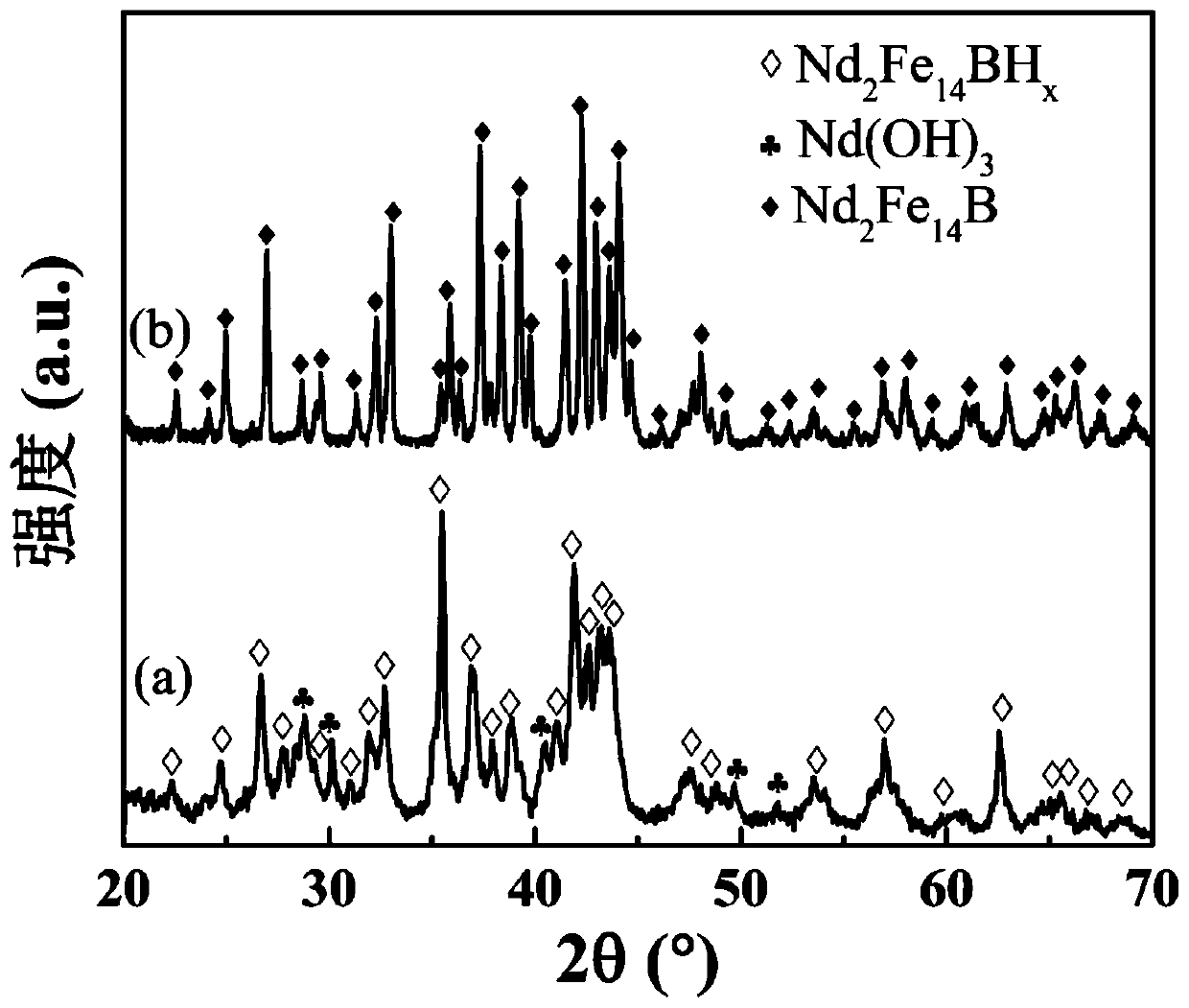
A low-cost method for preparing high-performance anisotropic NdFeB magnetic powder using NdFeB oil-based slice sludge
ActiveCN110157916BAchieve recyclingReduce usageRecycling and recovery technologiesProcess efficiency improvementIce waterOil sludge
The invention relates to a low-cost method for preparing high-performance anisotropy neodymium-iron-boron magnetic powder by using neodymium iron boron oil-based slice oil sludge, and belongs to the technical field of recycling of rare-earth permanent magnet wastes. Firstly, cutting fluid and impurities of oil sludge are removed in a physical and chemical separation mode, so that the content of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and other impurities in the oil sludge can be reduced, and the purification purpose is achieved. The metal calcium (Ca) is taken as a reducing agent to be added and one or morebuffering agents are assisted, namely potassium chloride and calcium chloride are used as the reducing agents, so that a stable reaction system is constructed. According to the reaction system, on thebasis of substantially reducing the use amount of the metal calcium, the reaction can be fully carried out, the grain size and distribution of recycled magnetic powder are greatly improved, and the single crystal proportion and the orientation degree of the recycled magnetic powder are improved; in addition, reactants are pressed into blocks during reaction, so that sufficient and uniform reaction of the reactants is facilitated; a reduction product is ground into powder, the mixture of ice water and the like is used for removing calcium, the oxidation degree of the recovered magnetic powderis reduced, and the speed and the efficiency of calcium removal are improved. The method has the characteristics of economy, high efficiency, environmental protection and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
A method for recovering NdFeB casing sludge waste by ca-chloride reduction diffusion technology
ActiveCN109338113BHigh recovery rateAchieve recyclingTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusSintered magnetsOil sludge
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
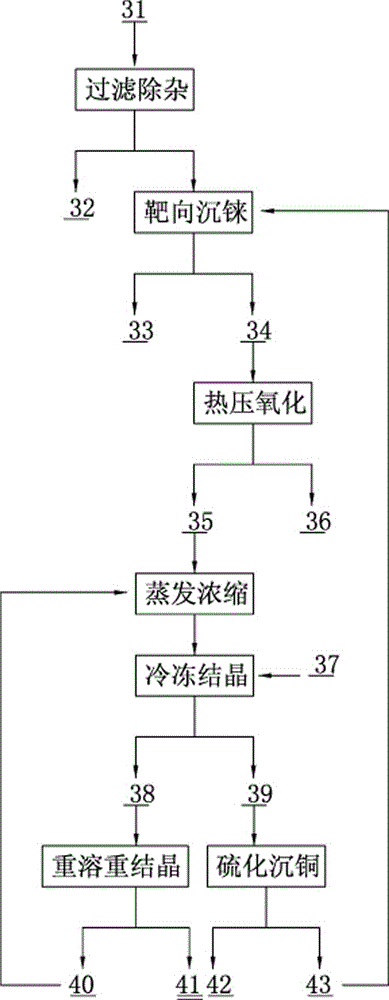
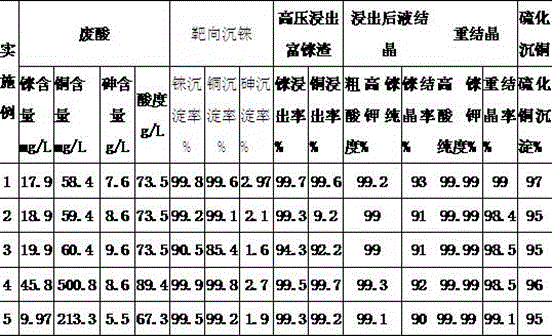
Method for rapidly recovering rhenium, copper and lead from copper smelting waste acid and device for implementing method
ActiveCN105543491AReduce processingImprove protectionProcess efficiency improvementEnvironmental resistanceAnti-gravity
The invention discloses a method for rapidly recovering rhenium, copper and lead from copper smelting waste acid and a device for implementing the method. According to the method, the copper smelting waste acid is subjected to lead removing through filtering, lead residues with the lead content higher than 55% are obtained and taken as lead extraction raw materials, the lead extraction raw materials are subjected to targeted rhenium precipitation, rhenium-rich residues are obtained and are subjected to hot-pressing oxidizing leaching, a rhenium-rich leaching agent is obtained, the rhenium-rich leaching agent after evaporation and concentration is subjected to KCl rhenium precipitation and recrystallization, potassium perrhenate is prepared, and a liquid obtained after rhenium precipitation is vulcanized for copper deposition. The device comprises a rhenium and copper precipitant storage tank, a precipitation tank, a flocculating agent storage tank, a flocculation reaction tank, a reaction kettle, an evaporation-crystallization device, a centrifugal separator, a waste acid anti-gravity-osmosis filter, a rhenium-rich copper residue anti-gravity-osmosis filter, a filter press, a rhenium and copper precipitation tank steam heating system, a copper precipitation tank steam heating system and a slurry pump. The method and the device have the characteristics of low investment, rapid and short procedures, simple and efficient operation, and high recovery rate, and are clean and environment-friendly.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
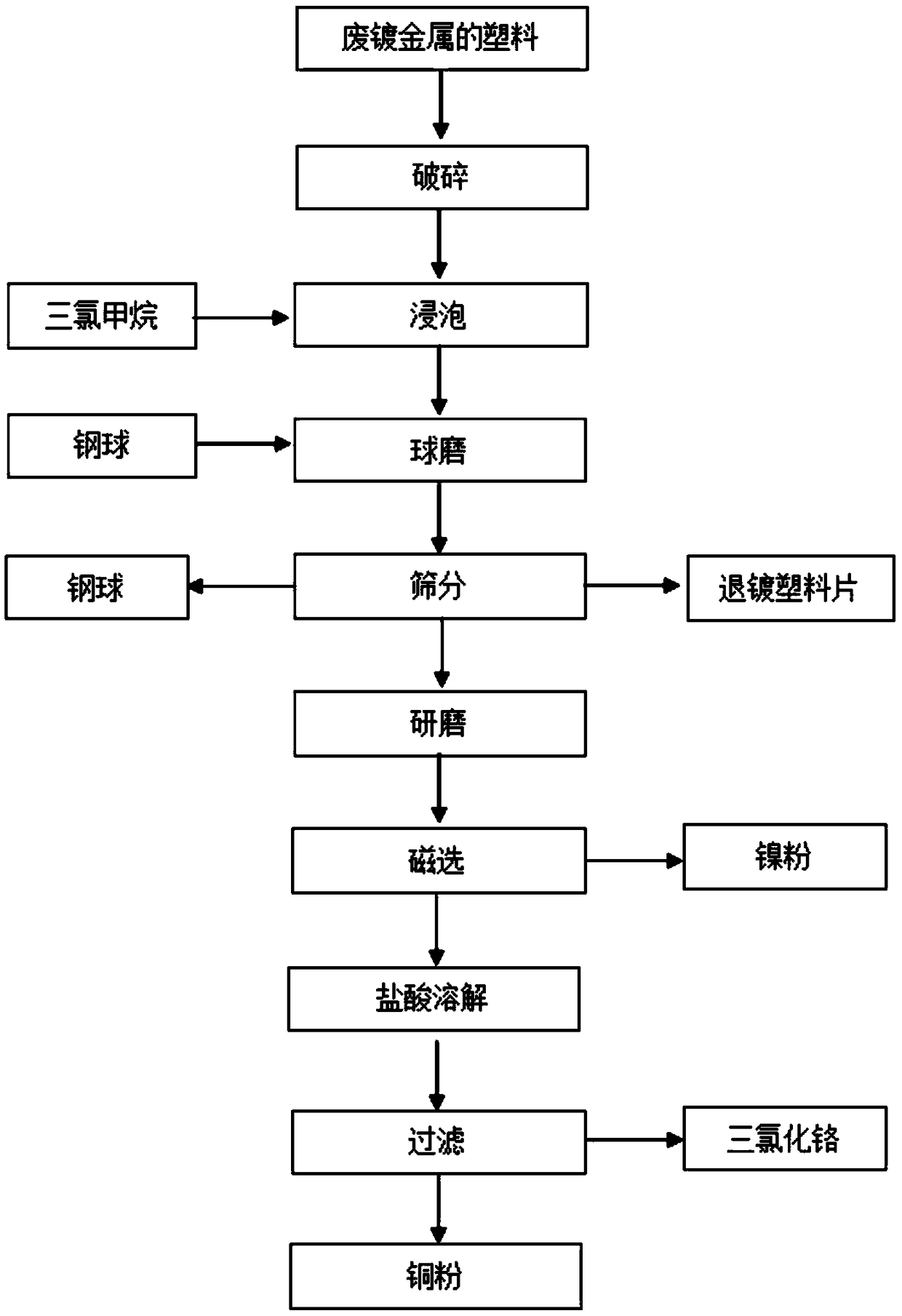
Method for recycling metal and plastics from waste plastics containing metal cladding materials
InactiveCN109352869AEasy to useShort recycling processPlastic recyclingProcess efficiency improvementChromiumMagnet
The invention provides a method for recycling metal and plastics from waste plastics containing metal cladding materials. The method comprises the steps that firstly, the waste plastics containing themetal cladding materials are crushed, 2*2 cm plastic sheets are obtained, and the plastic sheets are soaked in a trichloromethane solution to be processed for 24 hours; the plastic sheets and steel balls are added into a vertical stirring ball mill to be subjected to vacuum ball mill treatment for 20-40 min, and metal cladding materials and stripped plastic sheets are obtained after screening; the metal cladding materials separated from the plastics are further subjected to grinding treatment, copper, nickel and chromium mixed metal powder is obtained, nickel is sucked out through a magnet, and the nickel and the copper and chromium mixed metal powder are obtained separately; and the copper and chromium mixed metal powder is added into diluted hydrochloric acid to react, chromium is dissolved to enter a solution to be converted into a chromium trichloride solution, and copper powder is obtained after filtering. The use device is simple, the recycling process is short in procedure, thecost is low, and industrial production is hopeful to achieve.
Owner:CHANGSHA HUIJU ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
A method for removing fluorine in nickel-cobalt-manganese solution
ActiveCN110669933BGood removal effectGuaranteed recyclableWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementAluminum IonSlag
The invention provides a method for removing fluorine in a nickel-cobalt-manganese solution, belonging to the technical field of solution purification. A method for removing fluorine in a nickel-cobalt-manganese solution, comprising the following steps: separating, crushing, and screening a current collector of a waste lithium-ion battery; dissolving the current collector with an acid to obtain an aluminum-containing solution; adding the aluminum-containing solution to the fluorine-containing nickel-cobalt-manganese The solution is defluorinated to obtain fluorine-containing slag and nickel-cobalt-manganese solution after defluorination. According to the technical scheme provided by the present invention, the concentrations of fluoride ions and aluminum ions in the nickel-cobalt-manganese solution after defluoridation are all less than 0.01g / L; the nickel-cobalt-manganese content in the fluorine-containing slag is all lower than 0.5%; The aluminum-containing solution removes fluorine from the nickel-cobalt-manganese solution, realizing parallel processing of the current collector and battery positive electrode material during lithium-ion battery recycling, shortening the recycling process, and saving recycling costs; after the nickel-cobalt-manganese solution is defluorinated, it enters the subsequent process flow, There is basically no corrosion to the equipment. Moreover, the aluminum content of the nickel-cobalt-manganese solution after defluorination is extremely low, and no aluminum impurities are introduced in the whole defluorination process.
Owner:JINCHI ENERGY MATERIALS CO LTD
Method and equipment for resource utilization of waste resin powder
PendingCN113829534ARealize resource reuseEasy to movePlastic recyclingProcess engineeringWaste management
The invention provides a method and equipment for resource utilization of waste resin powder. The method for resource utilization of the waste resin powder comprises the following steps that S1, the waste resin powder, a curing agent, a release agent and multiple pigments are taken out, and the waste resin powder, the curing agent, the release agent and the multiple pigments are proportioned according to a certain proportion; S2, the various materials proportioned in the S1 are added into a stirrer to be uniformly stirred to obtain a mixture; S3, the mixture stirred in the S2 is injected into a die-casting die, die-casting forming work is conducted through certain pressure, and the mixture is formed; and S4, the formed mixture obtained in S3 is put into curing equipment for natural curing, and a cured product with the waste resin powder as the main component is obtained after a period of time. The method and equipment for resource utilization of the waste resin powder have the advantages that the recycling effect is good, the resource utilization process is simple and clear, and the treatment efficiency is high.
Owner:广州绿邦环境技术有限公司 +1
Method for recovering valuable metal in positive plate of lithium battery
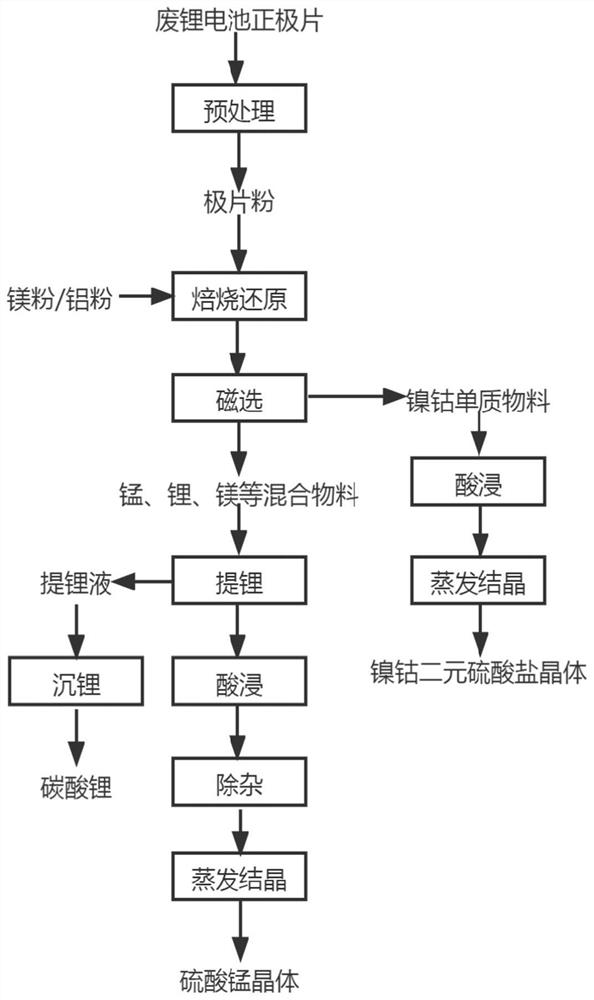
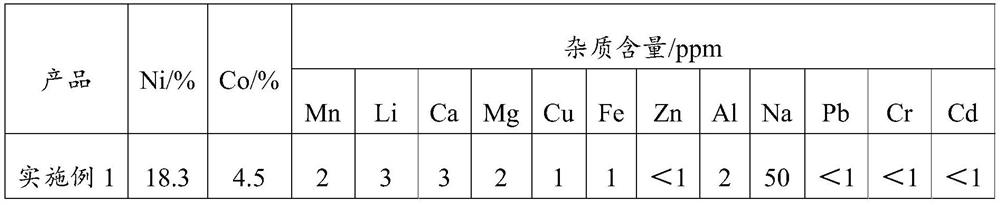
PendingCN114231745AMild leaching conditionsImprove leaching efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsLithium carbonateChemistry
The invention discloses a method for recycling valuable metal in a lithium battery positive plate. The method comprises the following steps: S1, mixing a positive plate material with reducing metal, and roasting; the roasting is carried out under a protective atmosphere; s2, performing magnetic separation on the material obtained in the step S1 to obtain a magnetic component and a non-magnetic component; s3, performing acid dissolution on the magnetic component, concentrating the obtained leachate, and performing cooling crystallization to obtain metal salt A; s4, the non-magnetic component is soaked in water, and sediment and water soaking liquid are obtained; adding carbonate into the water immersion liquid to obtain lithium carbonate; and dissolving the sediment with acid, purifying, and evaporating and crystallizing the obtained dissolved solution to obtain the metal salt B. The recovery method provided by the invention can achieve the purpose of omitting extraction and subsidiary steps thereof through simple impurity removal and separation procedures, simplifies the process flow, and saves the investment cost.
Owner:GUANGDONG BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +2
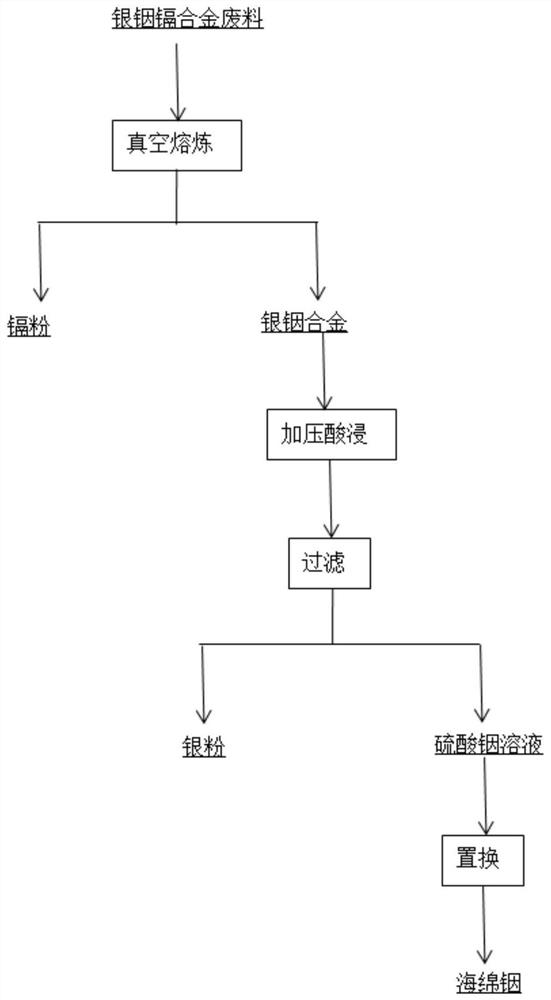
Method for recovering silver, indium and cadmium from silver-indium-cadmium alloy waste
ActiveCN113005292AShort recycling processEnvironmentally friendlyProcess efficiency improvementIndiumSulfuric acid
The invention discloses a method for recovering silver, indium and cadmium from silver-indium-cadmium alloy waste. The method comprises the following steps: I, smelting the silver-indium-cadmium alloy waste under a vacuum condition to obtain cadmium powder and silver-indium alloy; II, carrying out a leaching reaction on the silver-indium alloy and dilute sulfuric acid and filtering to obtain solid residues and leachate; III, eluting the solid residues through acidic deionized water, then washing the solid residues to be neutral through deionized water, and drying to obtain silver powder; and IV, diluting the leachate, and putting an aluminum plate into the diluted leachate for a replacement reaction to obtain sponge indium. Through adoption of the method, the mass purity of the recycled silver powder is not smaller than 99%, the yield of the silver powder is larger than 99.6%, the mass purity of the recycled sponge indium is not smaller than 99%, the yield of the sponge indium is larger than 99%, the mass purity of the recycled cadmium powder is not smaller than 99%, and the yield of the cadmium powder is larger than 98%. The recycled silver, indium and cadmium can be directly used for preparing a silver-indium-cadmium alloy material.
Owner:西安诺博尔稀贵金属材料股份有限公司
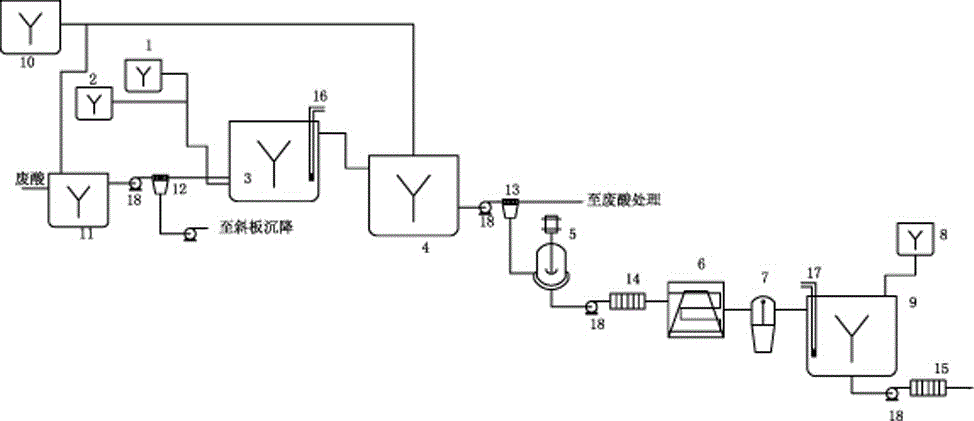
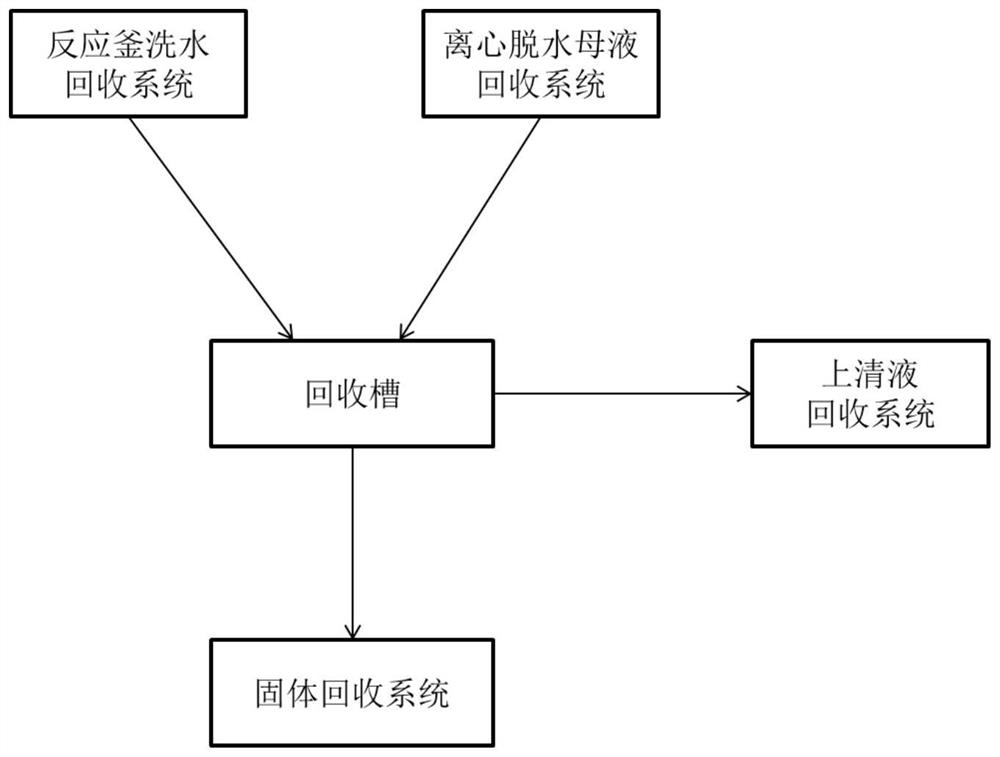
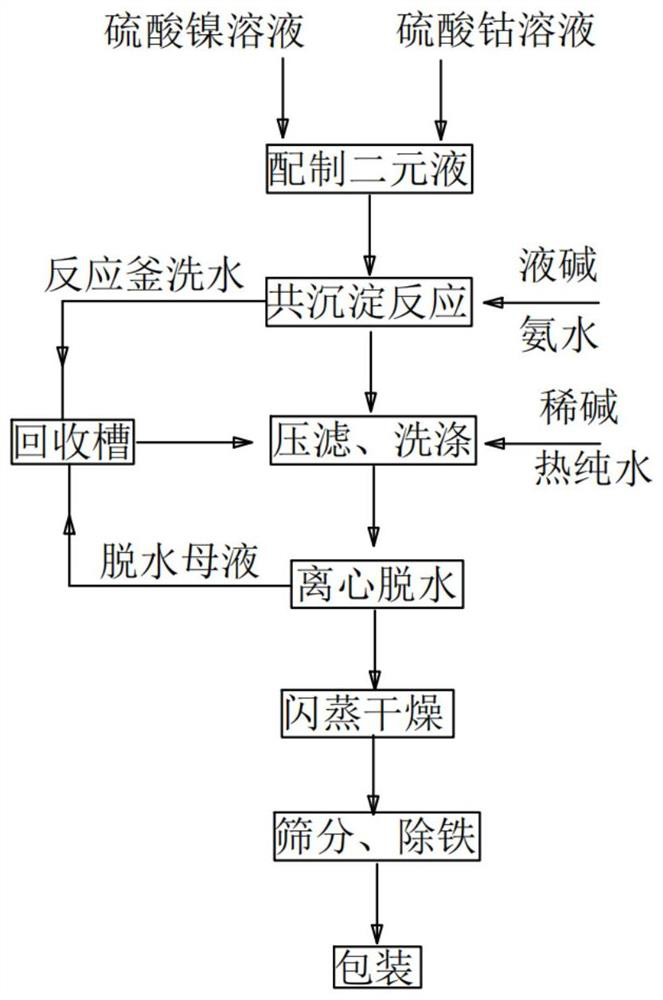
Recovery system and recovery method of nickel-cobalt hydroxide
PendingCN114522966AReduce dosageReduce recycling costsTransportation and packagingSolid waste disposalWash waterProcess engineering
The invention discloses a nickel-cobalt hydroxide recovery system and method, the recovery system comprises a reaction kettle washing water recovery system, a centrifugal dewatering mother liquor recovery system, a recovery tank, a supernatant recovery system and a solid recovery system, a feed inlet of the recovery tank is respectively communicated with the reaction kettle washing water recovery system and the centrifugal dewatering mother liquor recovery system; the supernate outlet is communicated with the supernate recovery system, and the discharge port of the recovery tank is communicated with the solid recovery system. According to the recycling method disclosed by the invention, the reaction kettle washing water and the dewatering mother liquor are independently recycled into the recycling tank, the nickel-cobalt hydroxide is recycled, the recycled nickel-cobalt hydroxide is low in impurity content, and the recycled nickel-cobalt hydroxide is returned to the processes of filter pressing, washing, centrifugal dewatering, flash drying, screening for iron removal and packaging of the product, so that the product quality is improved. The method not only can improve the final yield of the nickel-cobalt hydroxide, but also can save energy consumption, shorten the recovery process and improve economic benefits.
Owner:格林爱科(荆门)新能源材料有限公司
Method for recovering valuable metal from nickel-titanium-palladium target material waste
ActiveCN112501437AShort recycling processHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementTitaniumOxidizing acid
The invention discloses a method for recovering valuable metal from nickel-titanium-palladium target material waste. The method comprises the following steps of S1, conducting preliminary acid leaching; S2, recovering nickel; S3, conducting secondary oxidation acid leaching; S4, recovering titanium; S5, oxidizing and precipitating palladium; S6, washing; and S7, recovering the palladium. Accordingto the method, the precious metal palladium and the valuable metal nickel and titanium can be effectively separated and recycled; (2) the steps of dissolving waste by using nitric acid, conducting subsequent denitration treatment and the like in the traditional process can be effectively avoided, the palladium recovering process is greatly shortened, and the energy consumption and the emission ofsewage and waste gas are effectively reduced; (3) the recovery rate and purity of the palladium are improved; and (4) the whole technological process of the method is simple to operate, less in equipment investment and short in precious metal recovery period.
Owner:FIRST RARE MATERIALS CO LTD
A method for recovering lithium from lithium-ion battery waste electrolyte
ActiveCN108155434BClean and efficient useEfficient use ofWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingElectrolytic agentLithium carbonate
The invention relates to a method for recycling lithium from a lithium ion battery waste electrolyte, and belongs to the technical field of resources cyclic utilization. The invention aims to providethe method for recycling the lithium from the lithium ion battery waste electrolyte. The method is mainly characterized by mixing and reacting the waste electrolyte and a halogenide solution containing a large positive ionic radius, wholly separating PF6- in the electrolyte, deeply purifying the lithium-containing solution after separation, and precipitating the lithium to obtain lithium carbonate, so that the aim of cleanly and high-efficiently utilizing the lithium ion battery waste electrolyte is achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A method for recovering valuable metals from the comprehensive recovery slag of waste lithium cobalt oxide batteries
ActiveCN112251604BSimple recycling processShort recycling processProcess efficiency improvementSlagResource recovery
The present invention is applicable to the technical field of secondary resource recovery, and in particular relates to a method for recovering valuable metals from the comprehensive recovery slag of waste lithium cobaltate batteries, specifically, comprising the following steps: carrying out the comprehensive recovery slag of waste lithium cobaltate batteries Mechanical crushing and grinding to obtain a powder material; adding calcium fluoride powder to the powder material, mixing ball milling, briquetting, and drying to obtain a dry material; vacuum heat treatment of the dry material to obtain a volatile product lithium fluoride and the residue enriched in cobalt and nickel; the residue enriched in cobalt and nickel is extracted to obtain a cobalt-nickel compound. The recovery method of the invention has a short and simple process flow, does not need to use strong acid and strong alkali reagents, is environmentally friendly, can directly recover lithium, cobalt and nickel, is economical and efficient, and has a wide range of applications.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for extracting lithium from waste lithium ion battery and application thereof
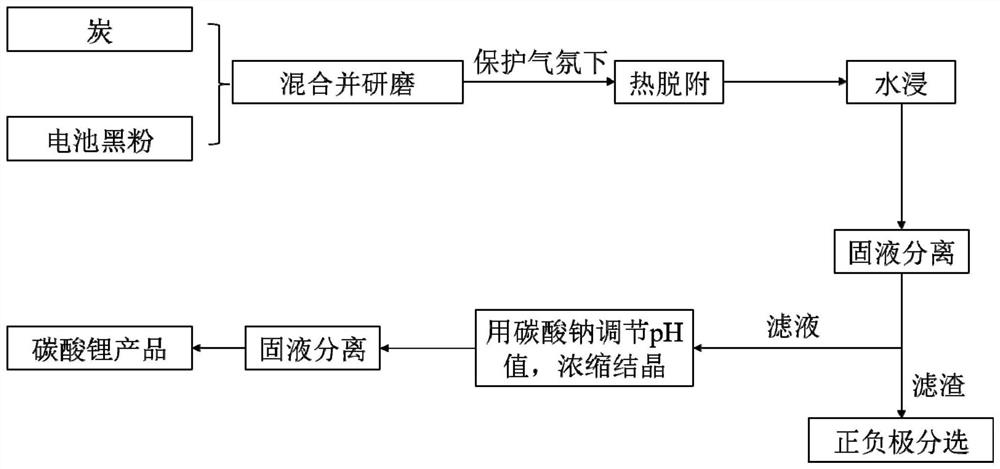
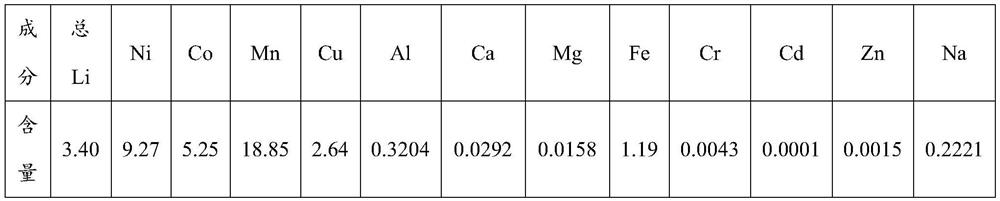
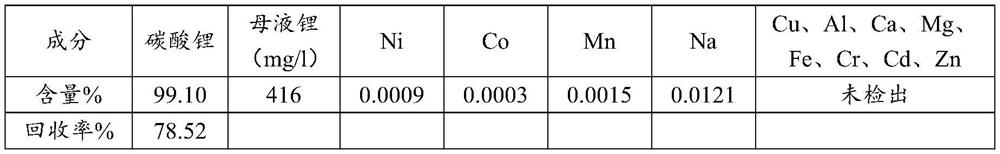
PendingCN114368766AShort recycling processEasy to operateWaste accumulators reclaimingLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesActivated carbonLithium electrode
The invention discloses a method for extracting lithium from a waste lithium ion battery. The method comprises the following steps: mixing battery black powder with carbon, grinding and thermally desorbing; carrying out water immersion on a product after thermal desorption, and filtering to obtain a lithium-containing aqueous solution; and adjusting the pH value of the lithium-containing aqueous solution with sodium salt, concentrating and filtering to obtain a lithium carbonate product. The method for extracting the lithium from the waste lithium ion battery has the advantages that the lithium recovery process is short, the operation is simple, and the recovery rate is high; the active carbon powder is adopted as an extracting agent, lithium is extracted through thermal desorption, the lattice structure of metal oxide is destroyed, dissolution of the cathode material by downstream hydrometallurgy enterprises is facilitated, and no additional additive needs to be added; only the activated carbon powder is added, other chemical substances are not added in the main production line process, no new'three wastes' are discharged, and no secondary pollution is caused.
Owner:威立雅新能源科技(江门)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com