Microsphere-based stent as well as preparation method and application thereof
A microsphere matrix and microsphere technology, which is applied in medical science, tissue regeneration, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of weak combination of drug-loaded microspheres and 3D printing scaffolds, poor drug release performance, and complex preparation processes. , to achieve the effect of strong drug release ability, increase surface adhesion, and improve dispersion performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
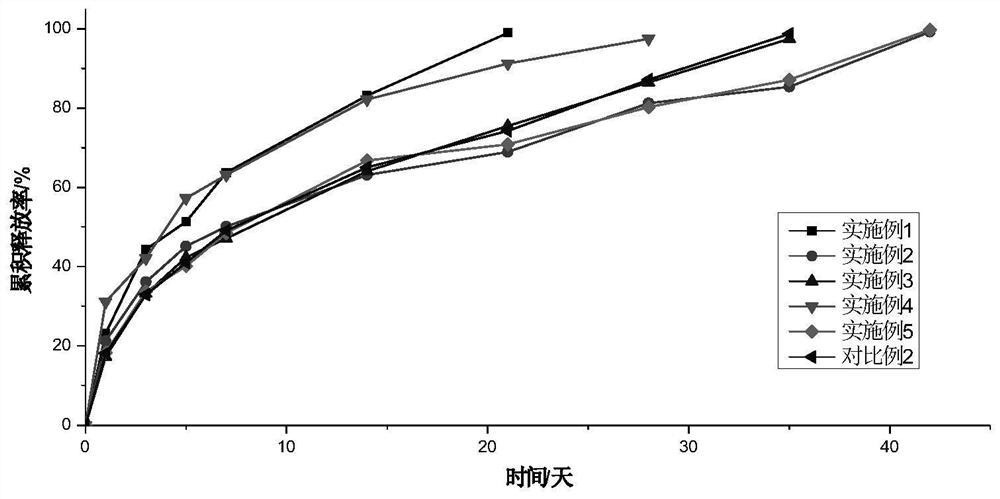
[0035] This embodiment provides a microsphere-based scaffold, which is prepared according to the following steps:
[0036] Use 650 mesh and 1600 mesh standard sieves to sieve polybutylene succinate (molecular weight: 15,000 Dalton) microspheres loaded with VEGF (hereinafter referred to as "drug-loaded microspheres") to obtain 10-21 μm loaded microspheres. drug microspheres. Dissolve 12g of gelatin in 30mL of 70°C deionized water and keep it warm for 2 hours to obtain a gelatin solution with a concentration of 40% as a dispersant solution; dissolve 0.6g of methylcellulose in 6mL of deionized water to obtain a concentration of 10% methylcellulose solution, as a binder solution; after the gelatin solution is cooled, disperse the drug-loaded microspheres in the above-mentioned dispersant solution, stir at 3000rpm for 10min, and then drain the drug-loaded microspheres; Add the drug microspheres to the above binder solution, and continue to stir for 10 minutes to obtain a uniform s...
Embodiment 2
[0038] This embodiment provides a microsphere-based scaffold, which is prepared according to the following steps:
[0039] Use 100-mesh and 140-mesh standard sieves to sieve BMP-7-loaded polylactic acid (molecular weight: 60,000 Daltons) microspheres (hereinafter referred to as "drug-loaded microspheres") to obtain drug-loaded microspheres of 104-150 μm . Dissolve 35g of gelatin in 50mL of 70°C deionized water, keep it warm for 2 hours to obtain a gelatin solution with a concentration of 70%, and use it as a dispersant solution; Polyvinyl alcohol 124 solution, as the binder solution; after the gelatin solution is cooled, disperse the drug-loaded microspheres in the above-mentioned dispersant solution, ultrasonically disperse at 25KHZ, 800W for 3min, then drain the drug-loaded microspheres; stir at 1000rpm Next, add the drained drug-loaded microspheres to the above binder solution, and continue stirring for 30 minutes to obtain a uniform slurry of extrudable drug-loaded micros...
Embodiment 3
[0041] This embodiment provides a microsphere-based scaffold, which is prepared according to the following steps:
[0042] Use standard sieves of 270 mesh and 1600 mesh to sieve the polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (molecular weight is 30,000 Daltons) microspheres loaded with alendronate sodium (hereinafter referred to as "medicine-loaded microspheres") to obtain 10 ~53 μm drug-loaded microspheres. Dissolve 3g polyethylene glycol 400 in 20mL deionized water to obtain a polyethylene glycol 400 solution with a concentration of 15% as a dispersant solution; dissolve 1.0g polyvinyl alcohol 1799 in 2mL 90°C deionized water, and keep it warm for 2 hours to obtain the concentration 50% polyvinyl alcohol 1799 solution, as the binder solution; disperse the drug-loaded microspheres in the above-mentioned dispersant solution, stir at 500rpm for 15min, then drain the drug-loaded microspheres; under stirring at 500rpm, drain the Add the dry drug-loaded microspheres to the above bin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com