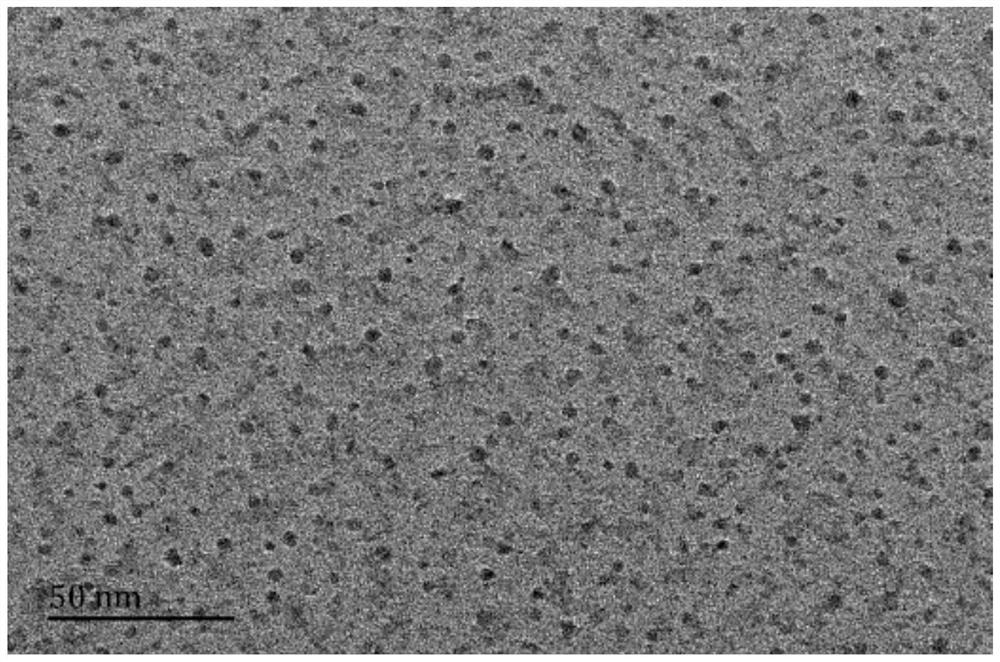
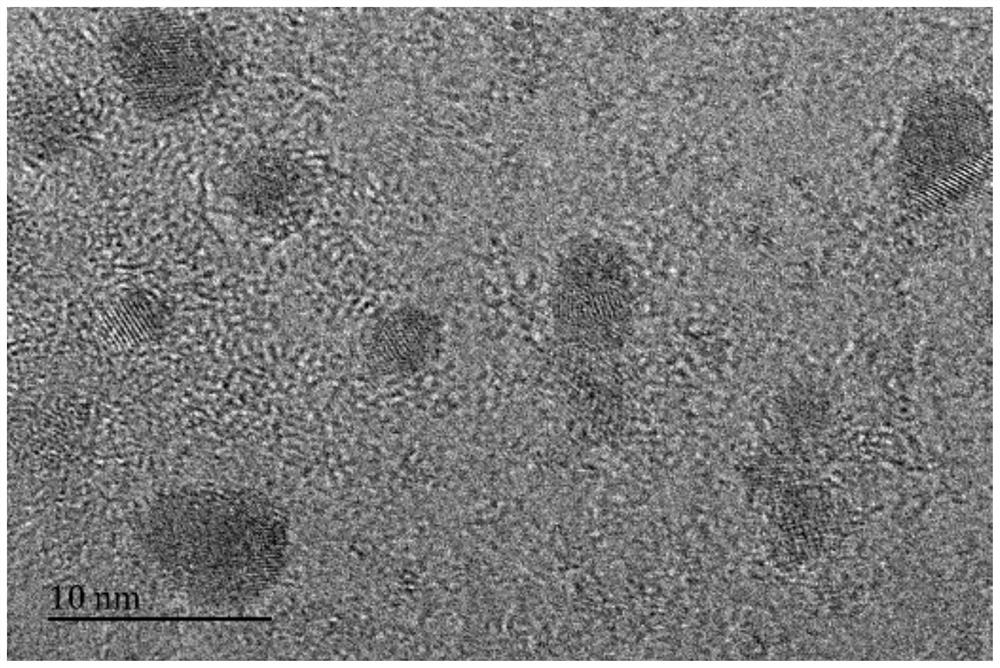
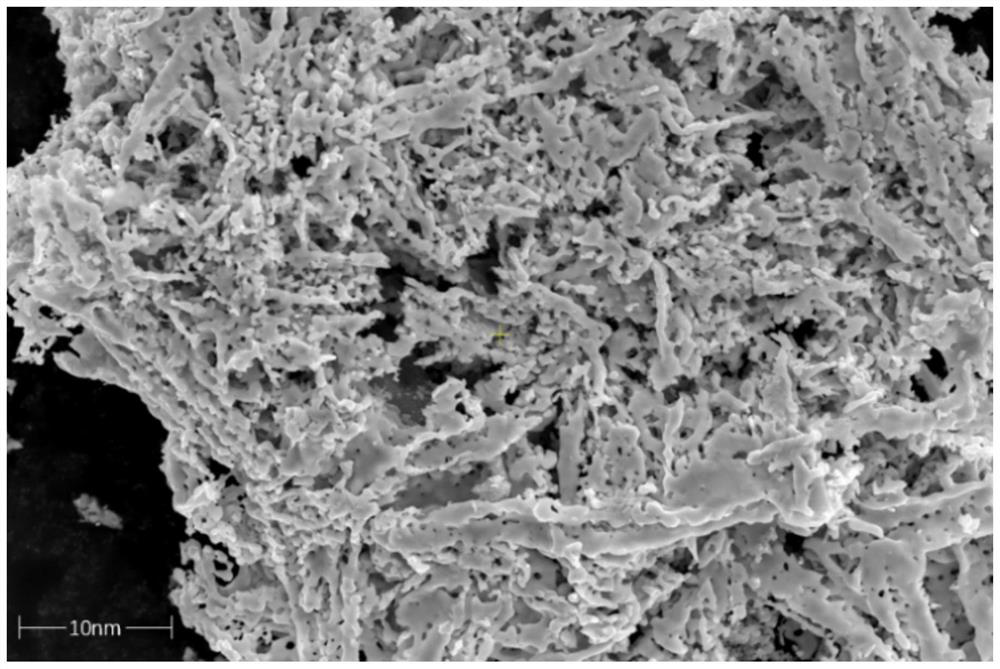
A nanometer zero-valent iron-carbon material and its preparation method and application
A nano-zero-valent iron and carbon material technology, applied in the field of nano-materials, can solve the problems of easy agglomeration and passivation of materials, complex preparation process, uneven particles, etc., and achieve the effect of promoting electron transfer, simple preparation and uniform dispersion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] A nanometer zero-valent iron-carbon material, the preparation method comprising the following steps:
[0050] (1) Ferrous acetate and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid are placed in a ball mill at a mass ratio of 3:1, zirconia grinding balls with a diameter of 7 mm and 5 mm are added, and ground at a rotating speed of 300 rpm for 3 hours to obtain a mixture;
[0051] (2) Place the mixture of step (1) in a tube furnace, raise the temperature to 800° C. at a heating rate of 5° C. / min under a nitrogen gas atmosphere, and calcinate for 3 hours;
[0052] (3) obtain after cooling the material obtained in step (2).
Embodiment 2
[0054] A nanometer zero-valent iron-carbon material, the preparation method comprising the following steps:
[0055] (1) ferrous sulfate and aminotriacetic acid are placed in a ball mill in a mass ratio of 4:1, adding diameters of 10mm and 5mm stainless steel grinding balls, and grinding for 4 hours at a rotating speed of 350rpm to obtain a mixture;
[0056] (2) Place the mixture of step (1) in a tube furnace, raise the temperature to 900° C. at a heating rate of 8° C. / min under a nitrogen gas atmosphere, and calcinate for 5 hours;
[0057] (3) obtain after cooling the material obtained in step (2).
Embodiment 3
[0059] A nanometer zero-valent iron-carbon material, the preparation method comprising the following steps:
[0060] (1) Put ferrous nitrate and diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid in a ball mill at a mass ratio of 2:1, add zirconia grinding balls with a diameter of 5 mm and 2 mm, and grind for 4 hours at a rotating speed of 350 rpm to obtain a mixture ;
[0061] (2) Place the mixture of step (1) in a tube furnace, and raise the temperature to 900° C. at a heating rate of 10° C. / min under a nitrogen gas atmosphere, and calcinate for 2 hours;
[0062] (3) obtain after cooling the material obtained in step (2).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com