Method for determining content of potassium polyaspartate in grape wine by using high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection method
A high-performance liquid chromatography and aspartic acid technology, applied in the field of potassium polyaspartate analysis in wine, can solve the problems affecting the sensory evaluation of wine, visual defects, etc., and achieve the effect of promoting technological progress and accurate sample dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] 1. Instruments and reagents
[0027] High-performance liquid chromatography system (including a quaternary pump, autosampler, column chamber with thermostat and FLD), electric heating plate, 4mL brown vial, 0.1-1.0mL pipette, 0.2μm cellulose acetate filter membrane, electronic balance , Volumetric flask, Milli-Q ultrapure water system preparation.
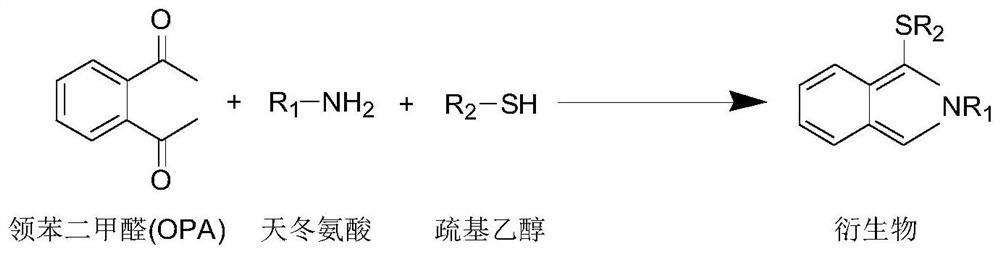
[0028] Aspartic Acid (DL-Aspartic Acid C 4 h 7 NO 4 , purity ≥99%, CAS: 617-45-8), sodium metabisulfite (Na 2 S 2 o 5 , CAS: 7681-57-4), hydrochloric acid solution (HCl, CAS: 7647-01-0); sodium hydroxide (NaOH, CAS: 1310-73-2), aminocaproic acid (C 6 h 13 NO 2 , purity ≥ 99%, CAS: 60-32-2), sodium tetraborate decahydrate (solid, purity > 99%, CAS: 1303-96-4), o-phthalaldehyde (OPA) (C 8 h 6 o 2 , purity ≥99%, CAS: 643-79-8), mercaptoethanol (C 2 h 6 OS, purity ≥99%, CAS: 60-24-2)
[0029] 2. HPLC-FLD conditions
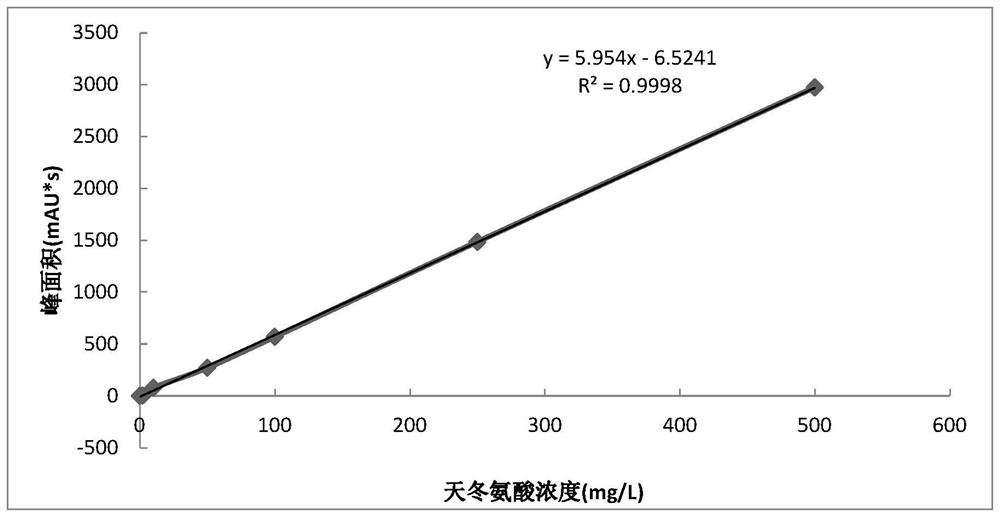
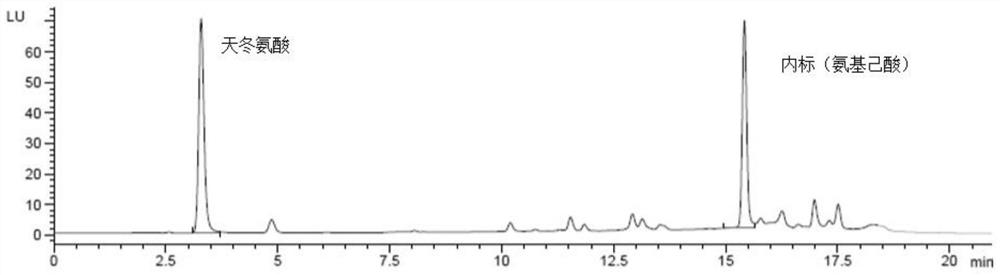
[0030]The chromatographic column is a C18 polar column (such as: Syncronis aQ 4.6×250mm, 5μm); col...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com