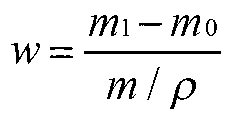Patents
Literature
105results about How to "Stability determination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
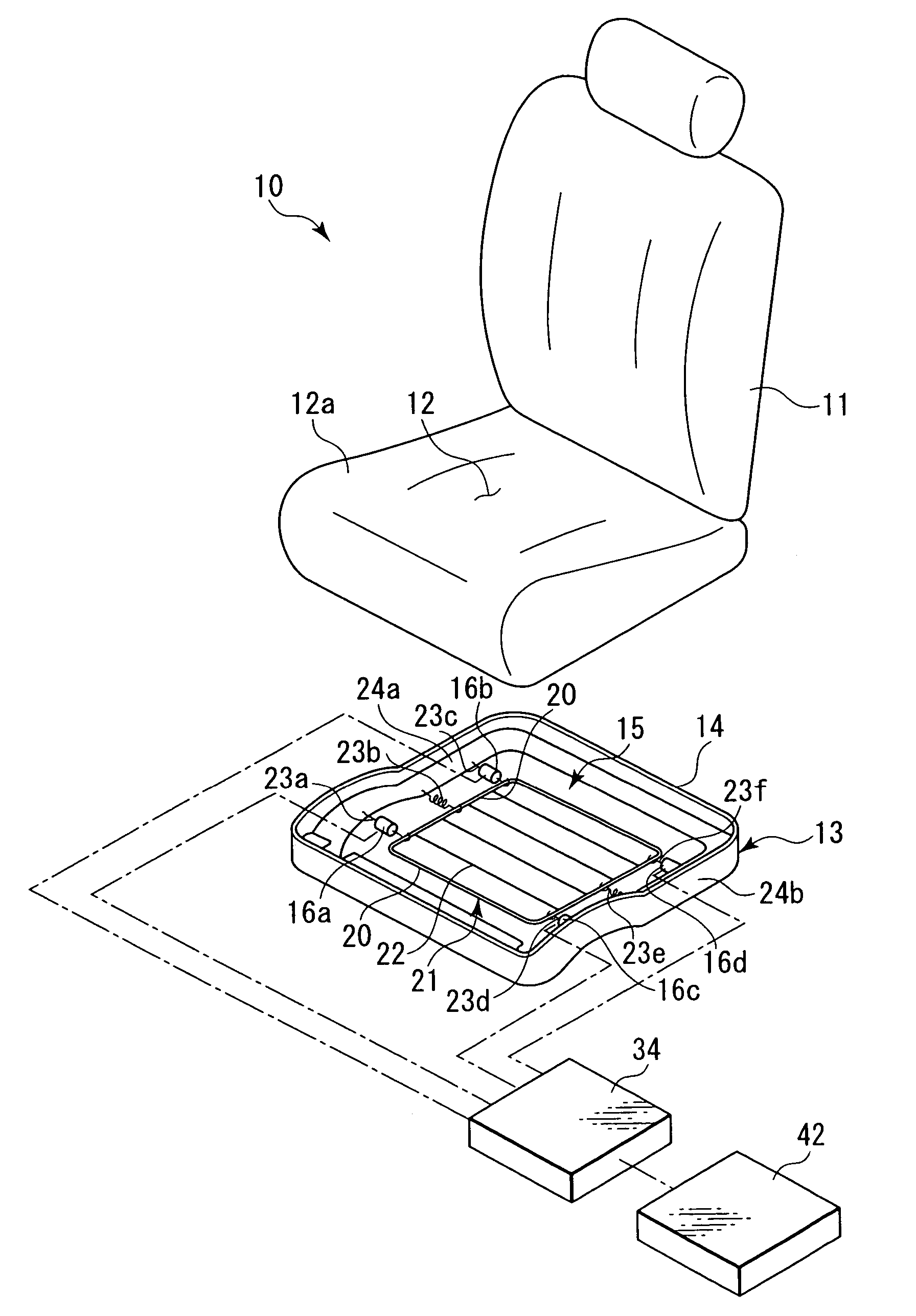
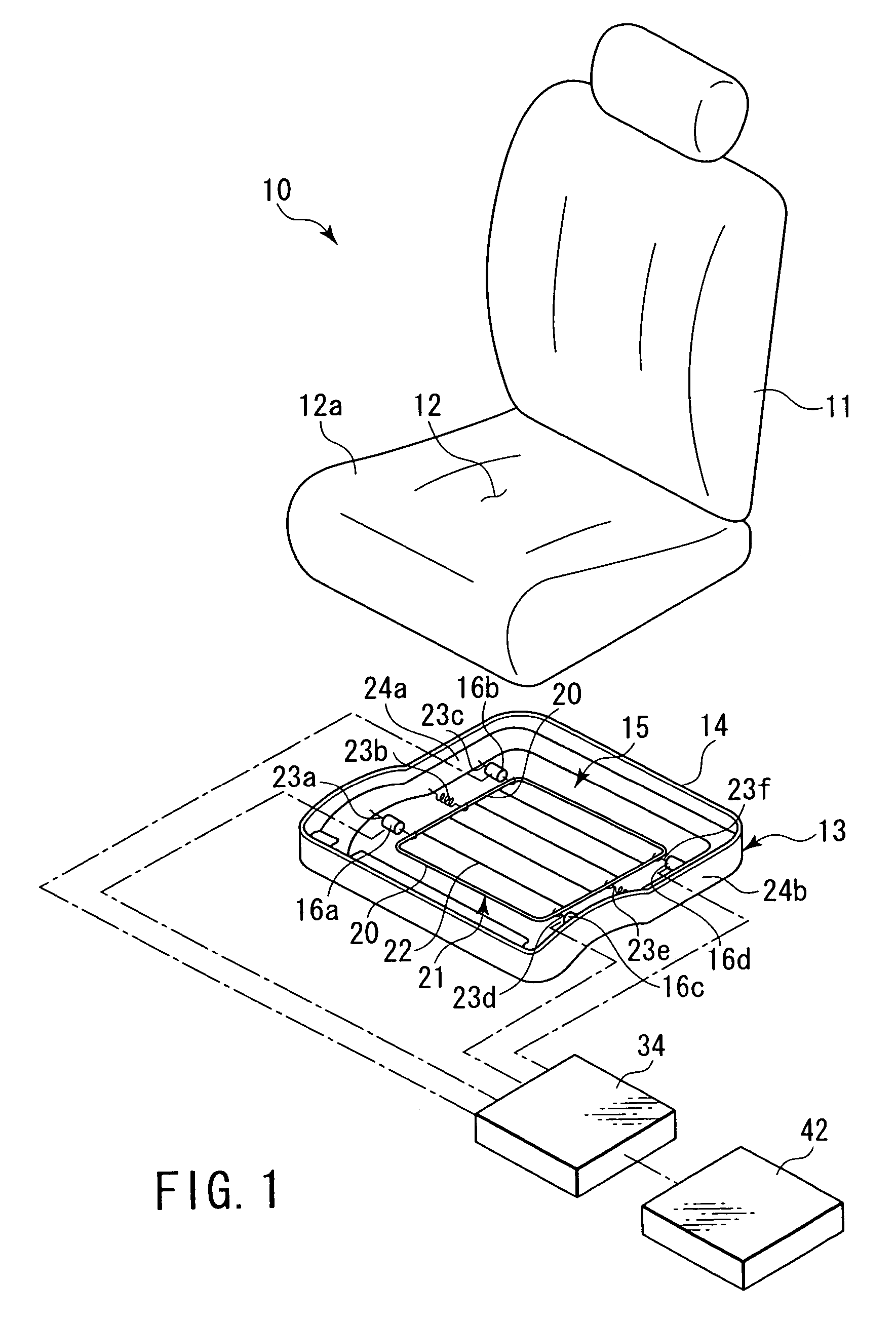
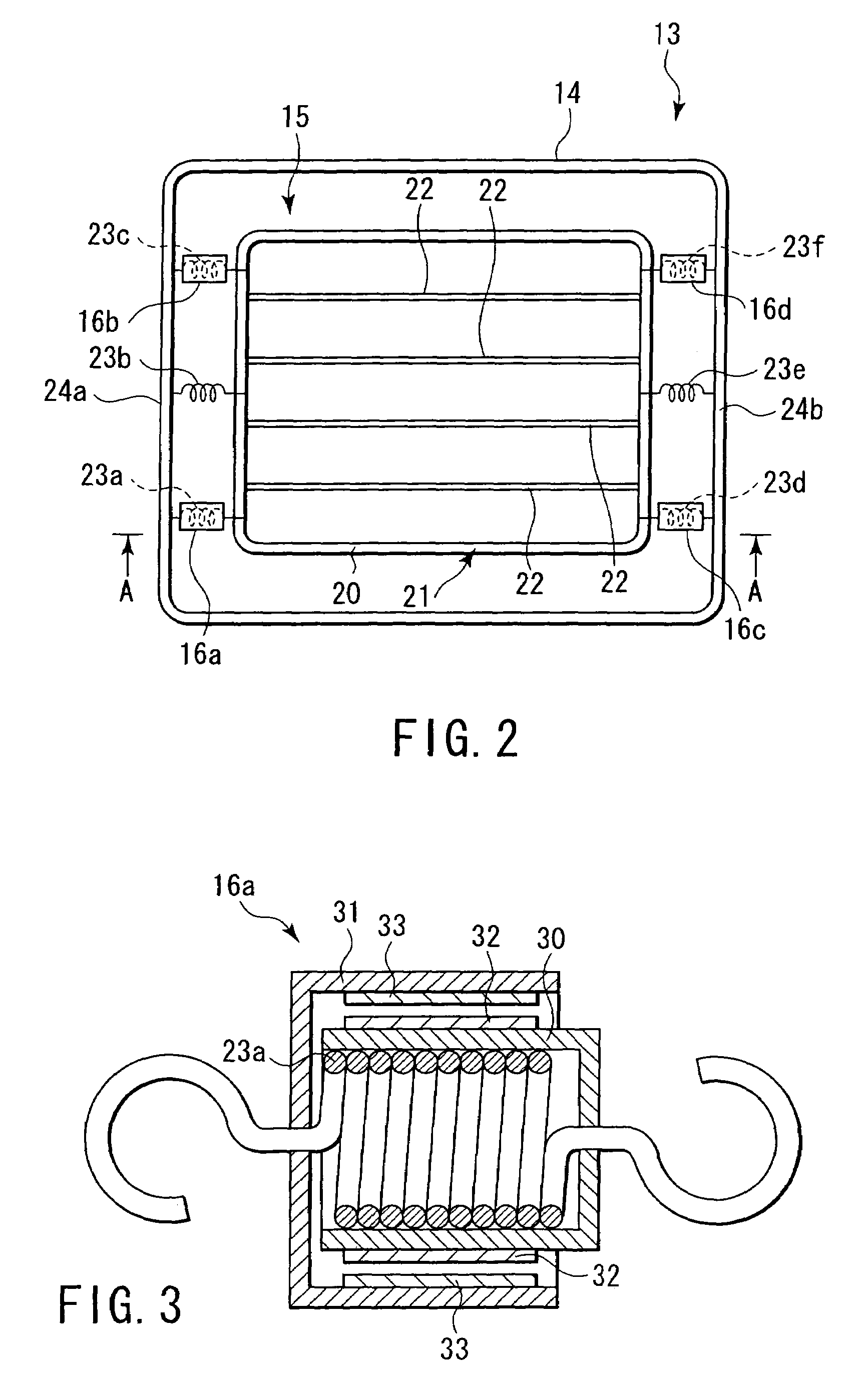
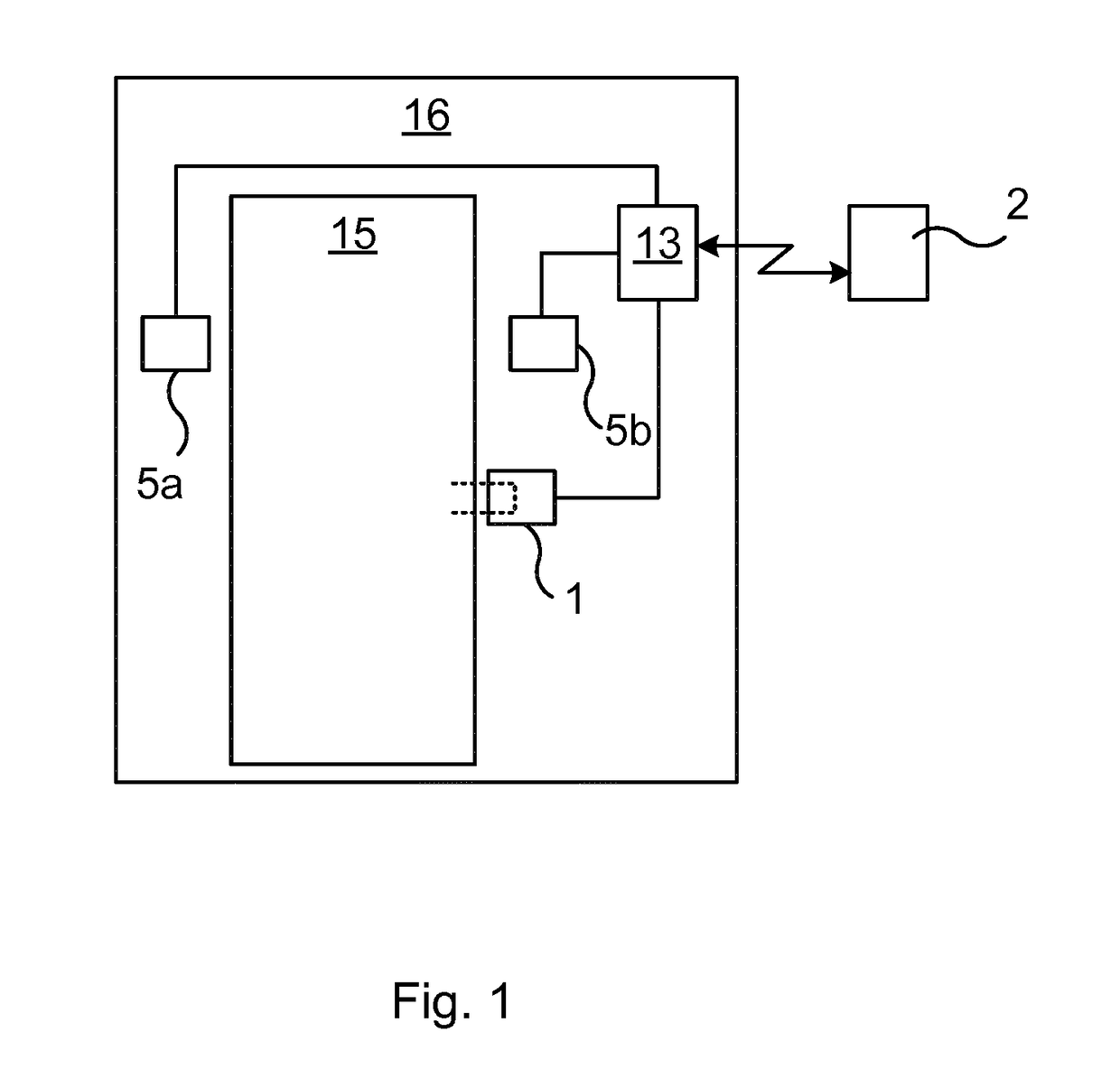
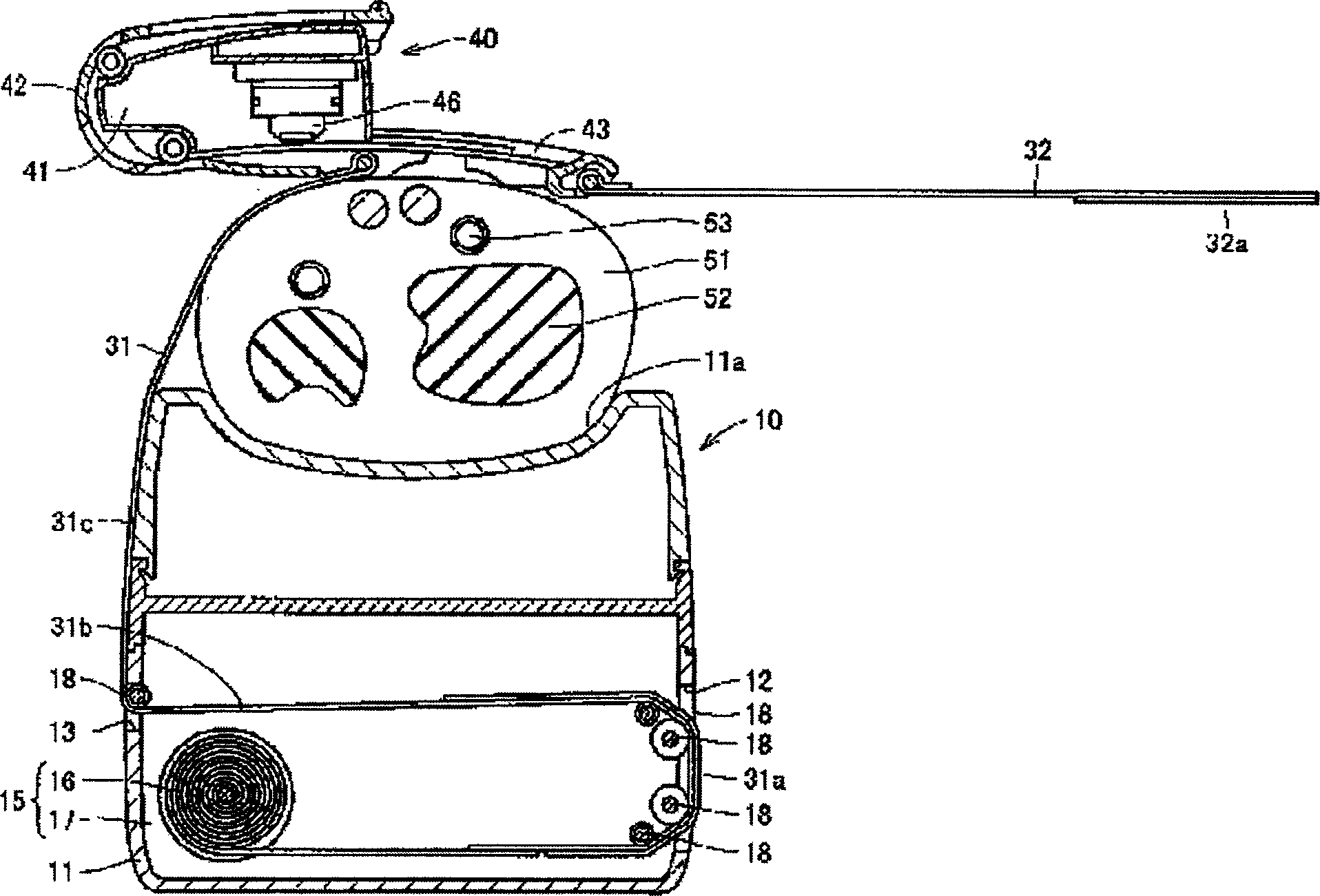
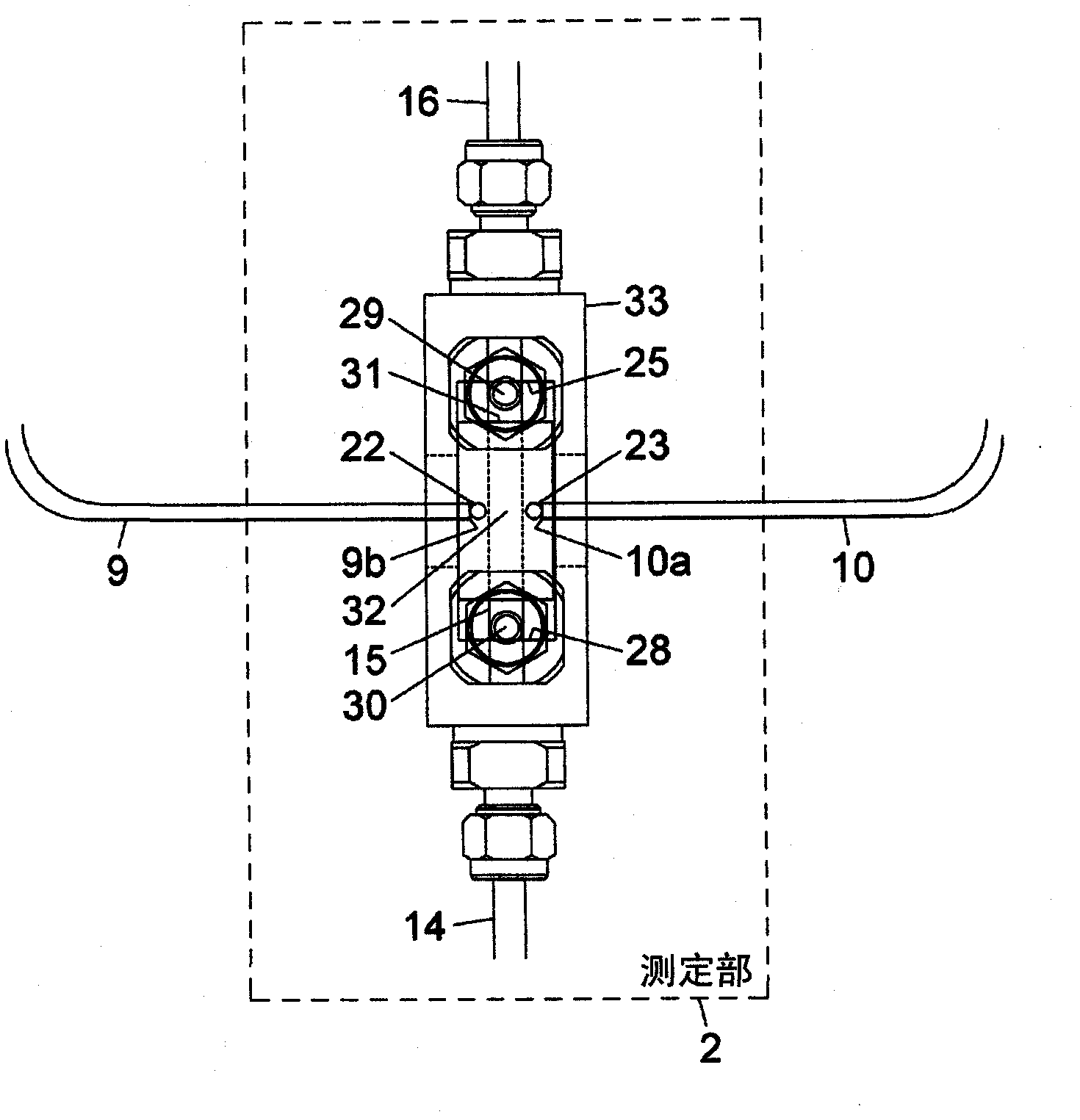
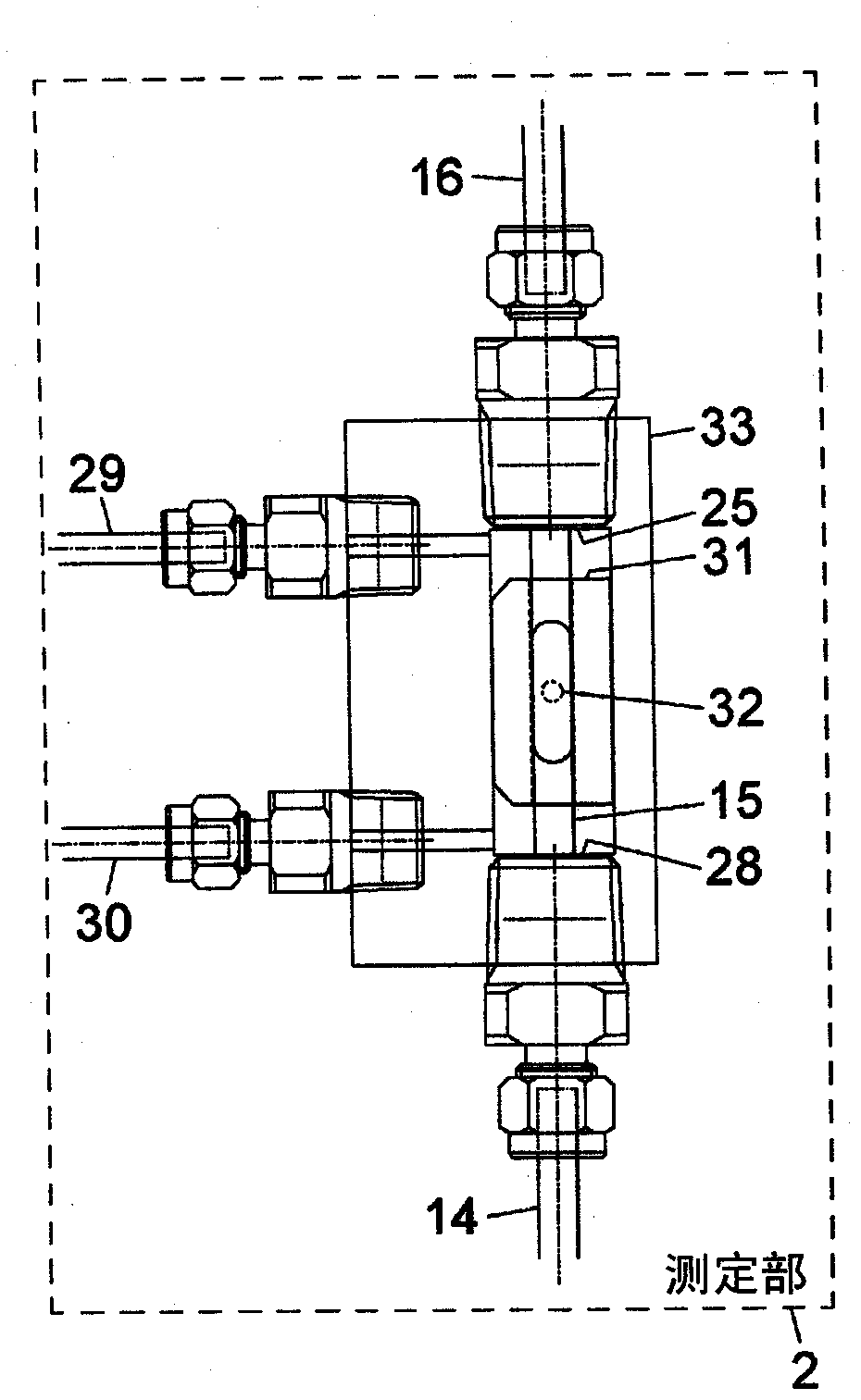
Occupant discriminating method for vehicular seat
InactiveUS7131513B2Incorrect determinationStability determinationVehicle seatsElectric devicesStage determinationEngineering
A flat spring of a vehicular seat is elastically supported by means of supporting springs that extend in accordance with the load of an occupant. The seat has displacement sensors, first-stage determination step, second-stage determination step, and third-stage determination step. The displacement sensors output electrical signals corresponding to the respective elongations of the springs. The first-stage determination step determines the occupant in the seat in accordance with voltage values delivered from the displacement sensors. The second-stage determination step determines whether or not the result of determination by the first-stage determination step is maintained for a given period of time. The third-stage determination step compares the result of determination by the second-stage determination step with the preceding result of determination and specifies the occupant in accordance with the result of the comparison.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
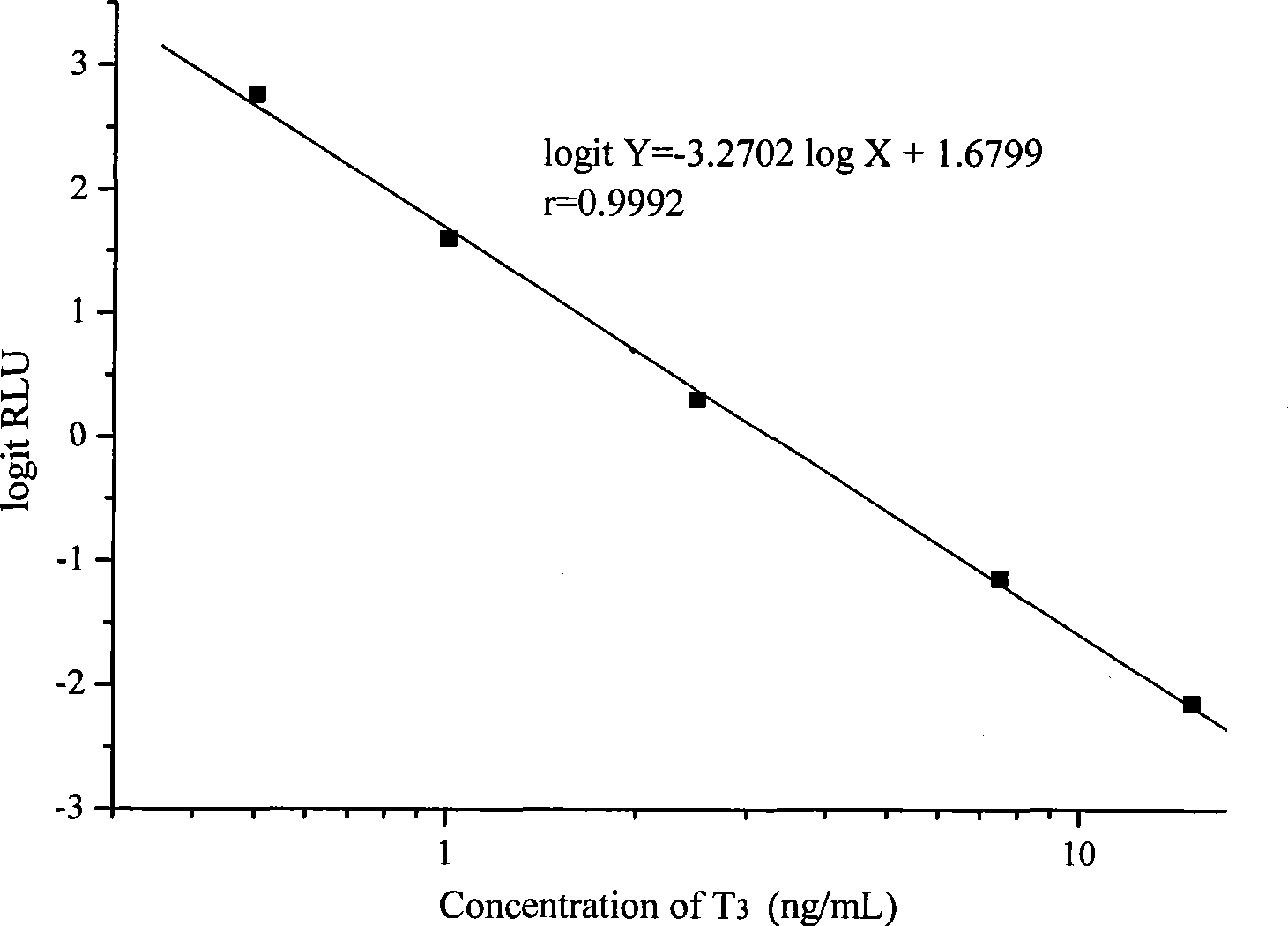
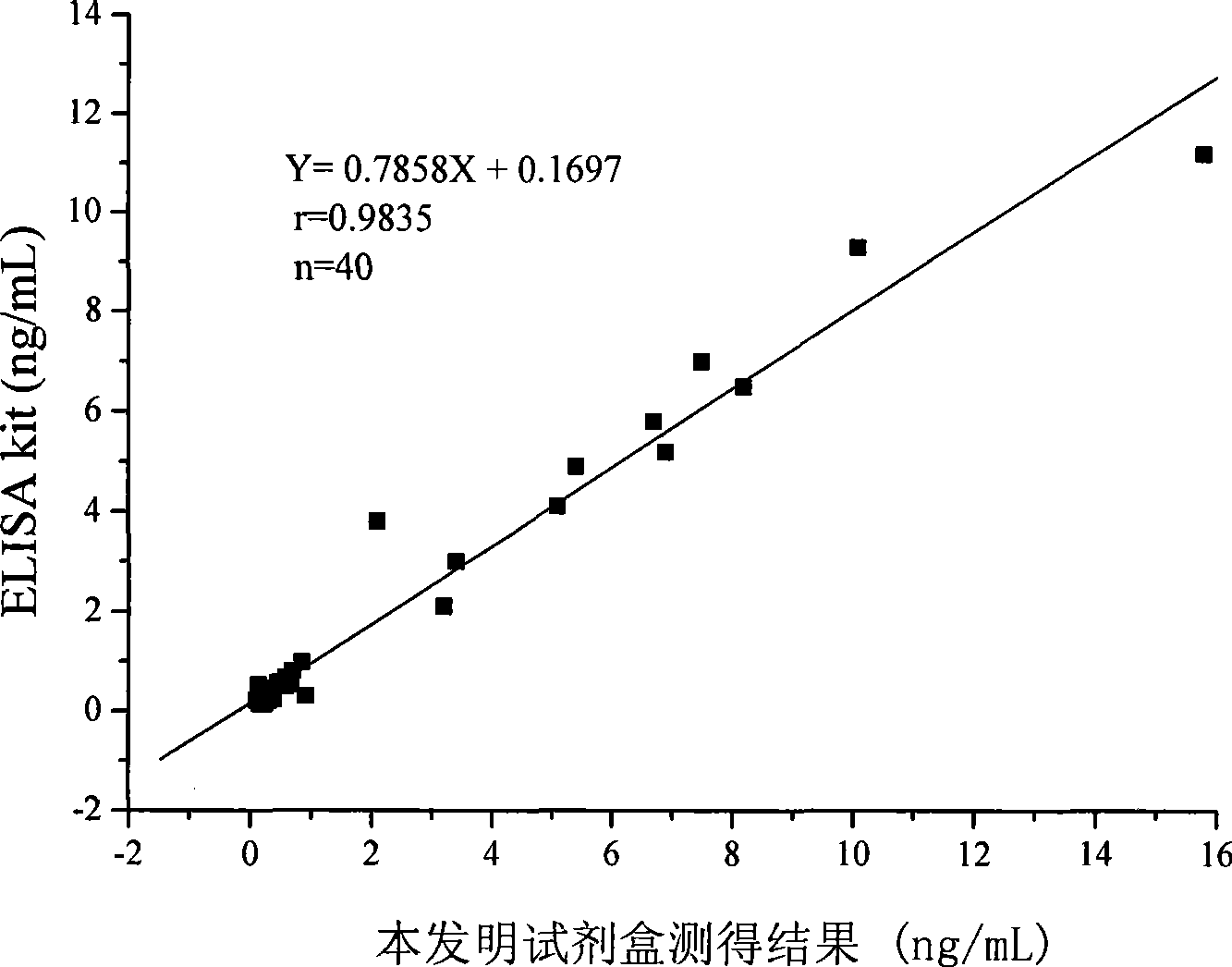
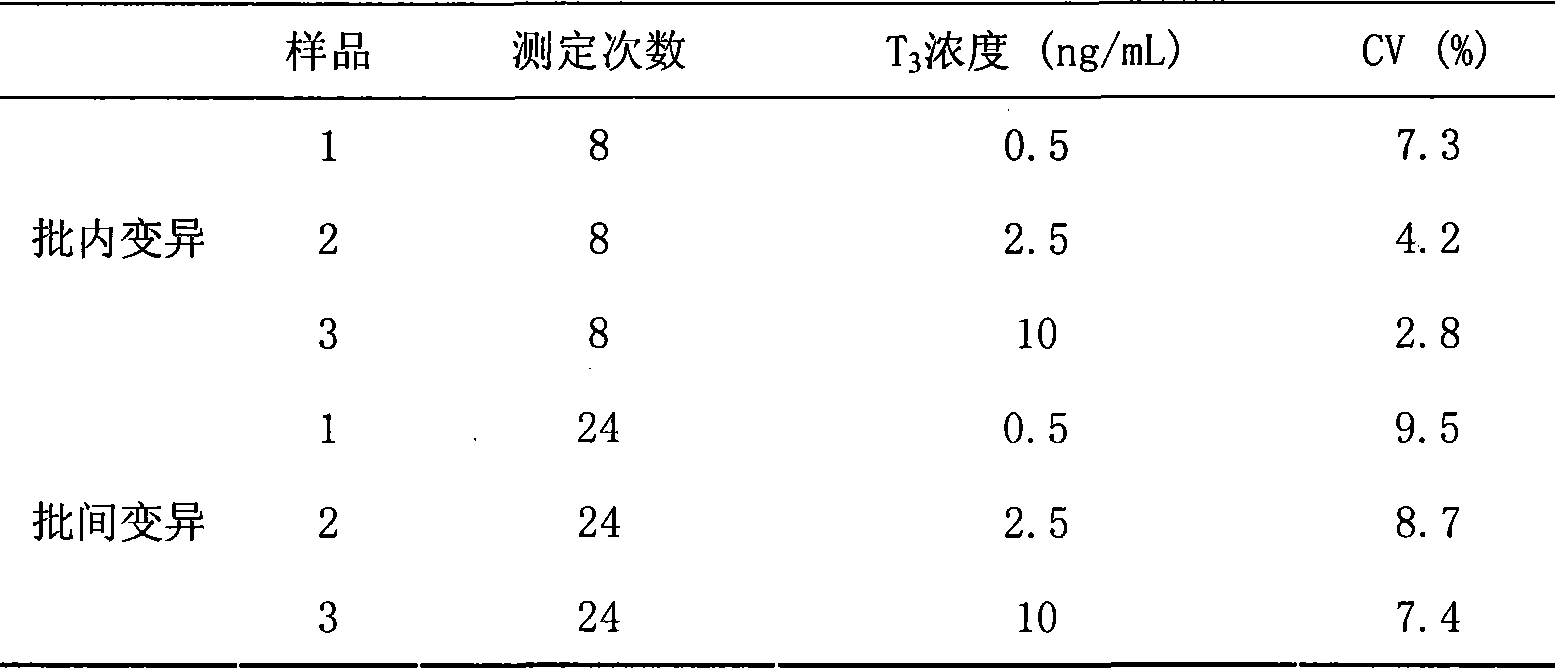
Chemoluminescence immunoassay measuring kit and preparation method thereof for triiodothyronine magnetic particles
InactiveCN101545913AEasy to measureStability determinationChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingBiotin-streptavidin complexAntigen
The invention provides a chemoluminescence immunoassay measuring kit and a preparation method thereof for quantificationally detect triiodothyronine (T3) magnetic particles. The kit mainly comprises a triiodothyronine serial calibration sample, magnetic particle solution coated by an anti-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) monoclonal antibody, a T3 antigen marked by biotin, T3 monoclonal antibody marked by FITC, streptavidin marked by alkaline phosphatase, chemoluminescence substrate solution and 20-time concentrated washing solution. The invention adopts a competitive-method reaction mode, effectively utilizes the chemoluminescence technology combined with magnetic particles and biotin-avidin immunity magnifying technology principle to quantificationally detect the content of T3 in blood serum and blood plasma samples of human bodies and ensure the sensitivity of the detection. The kit is simple, convenient, fast, sensitive and stable to use, and provides a very valuable detection method for clinic diagnosis and scientific research works.
Owner:北京科美东雅生物技术有限公司
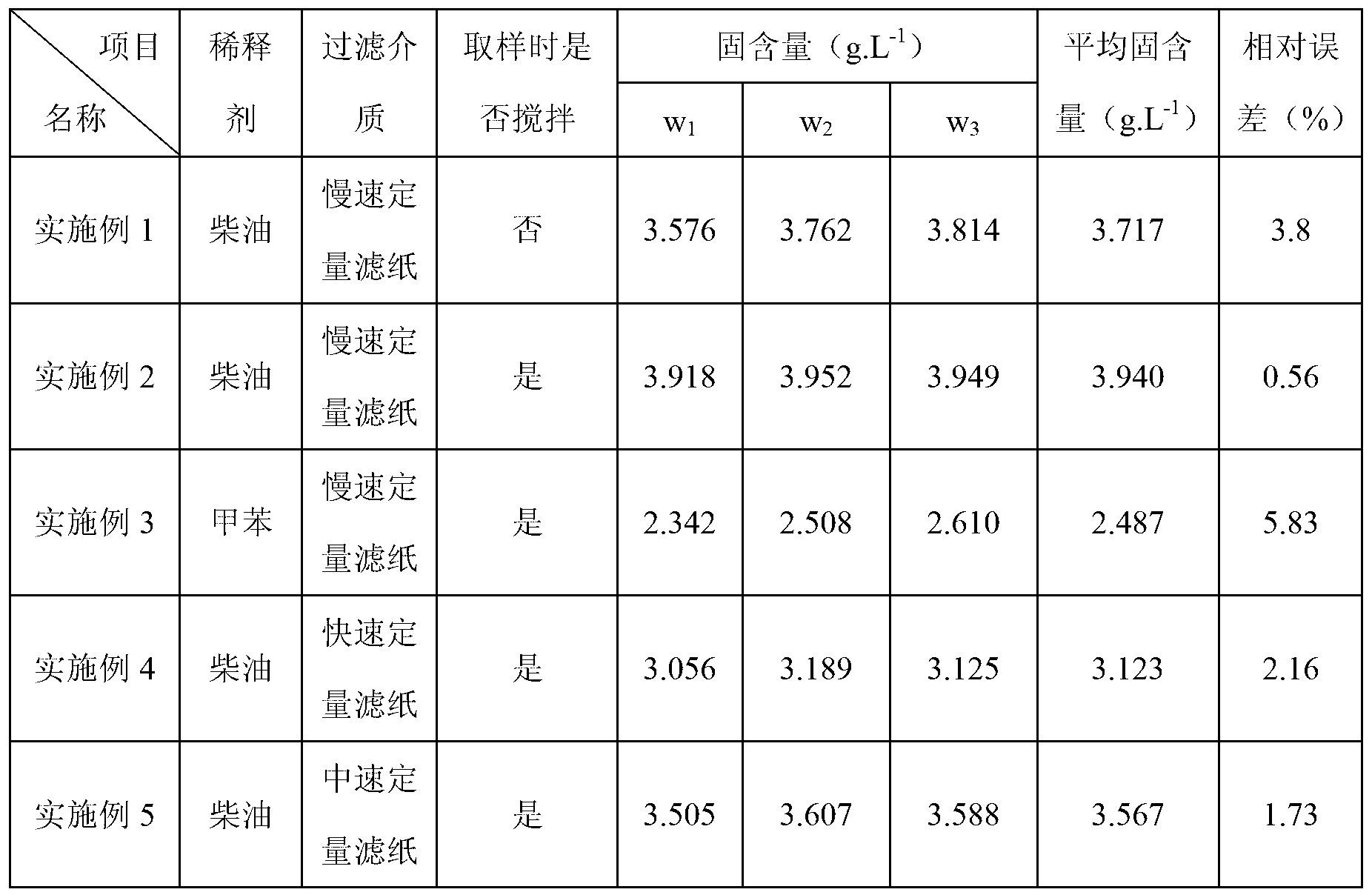
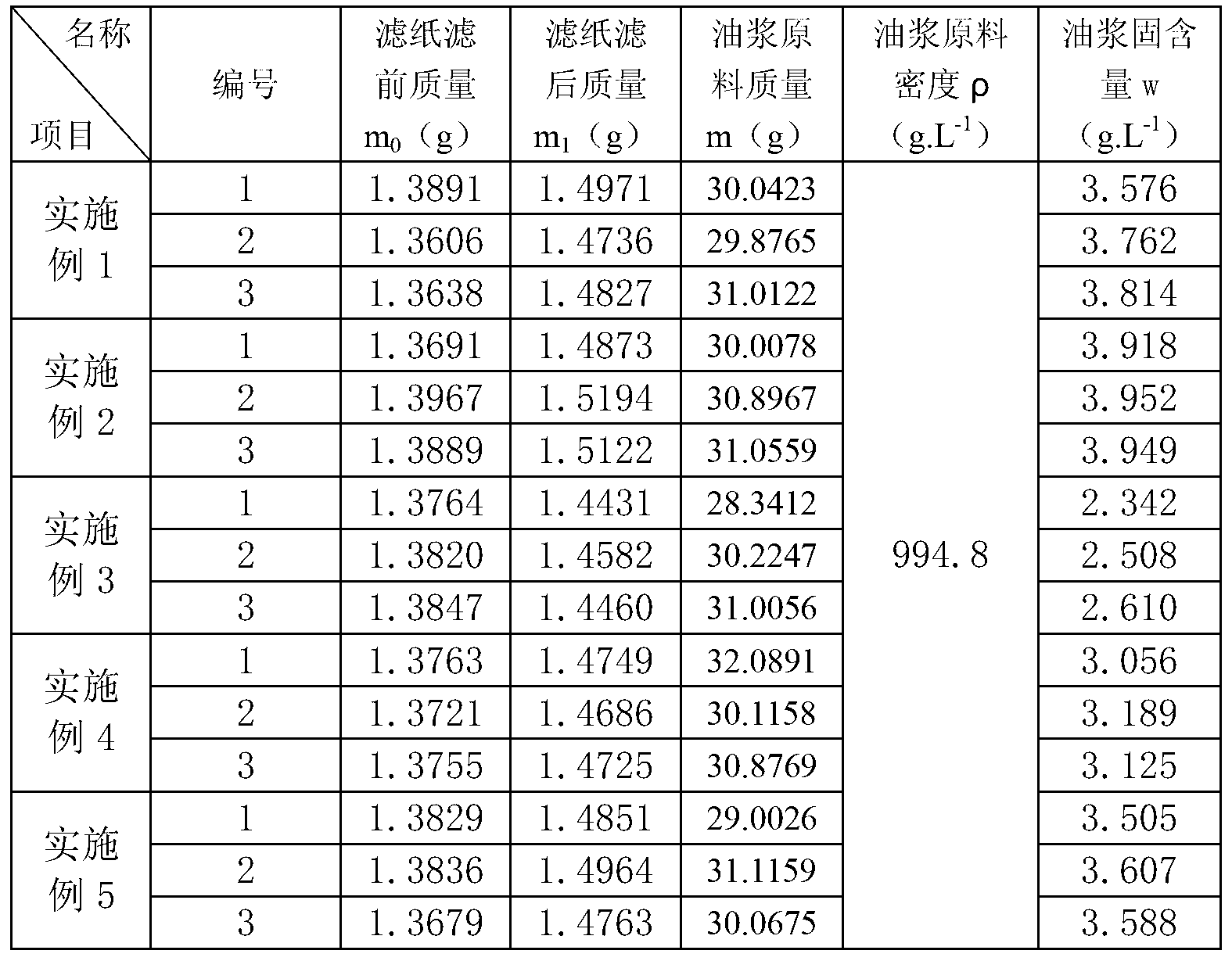
Measuring method of catalytic cracking slurry solid content
The invention relates to a measuring method of the catalytic cracking slurry solid content. The measuring method comprises the following steps of: preheating, stirring and sampling the slurry, adding certain amount of preheated diluent in the slurry and uniformly stirring; carrying out vacuum filtration on the mixed oil sample, and filtering out undissolved substances on a piece of filter paper; extracting the filtered filter paper by using toluene till an extracting solution is colourless; and carrying out vacuum drying, cooling and weighing on the filter paper after extracting, and figuring out the solid content in the tested slurry according to the mass variation of the filter paper. The measuring method of the catalytic cracking slurry solid content provided by the invention realizes the purpose of stably and accurately measuring the solid content of slurry, and solves the problems of low precision and poor stability in actual measurement of the catalytic cracking slurry solid content, thus providing technical support for purification and utilization of slurry and monitoring on safe and stable operation of a catalytic cracking unit.
Owner:济宁矿业集团有限公司 +2
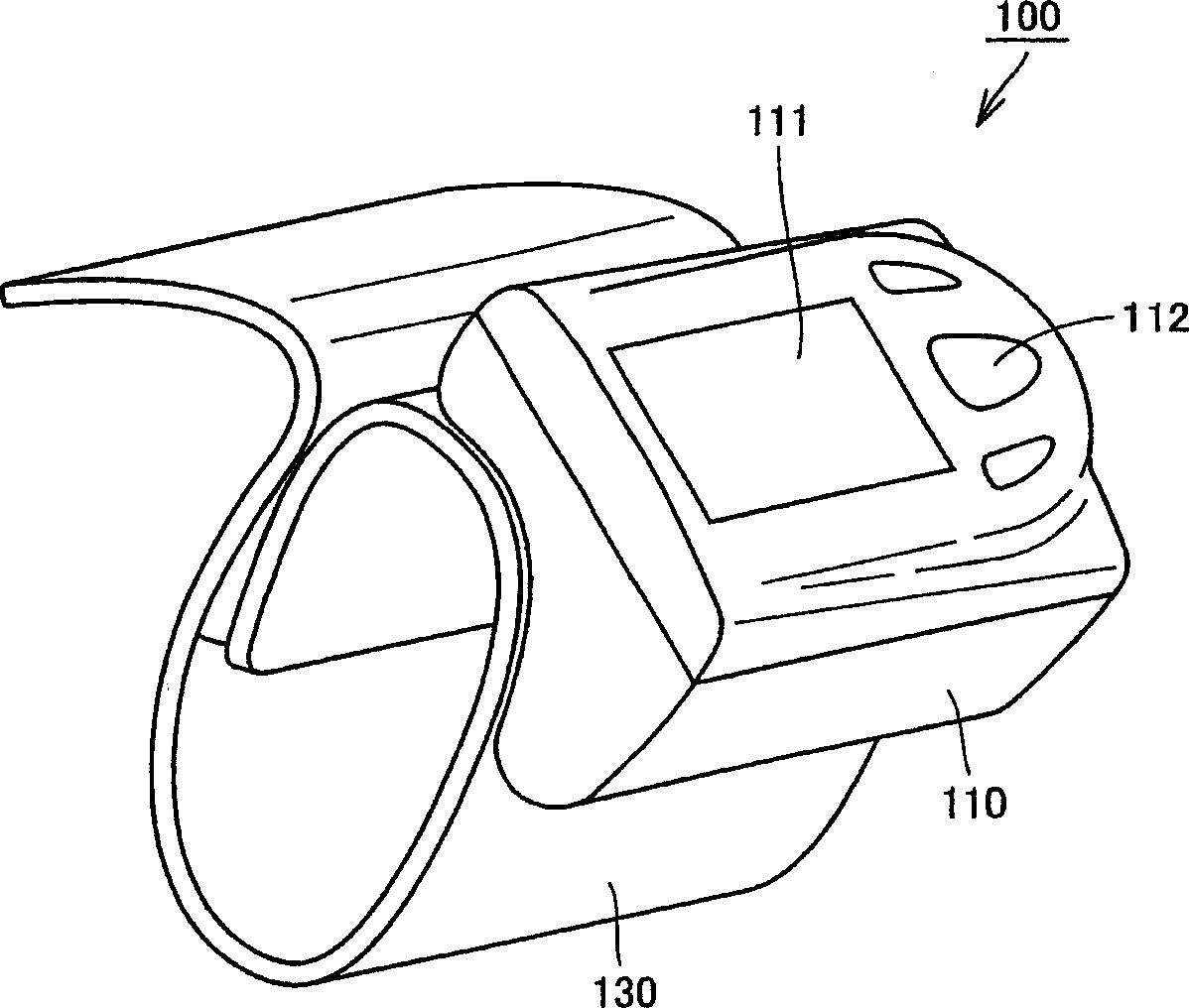
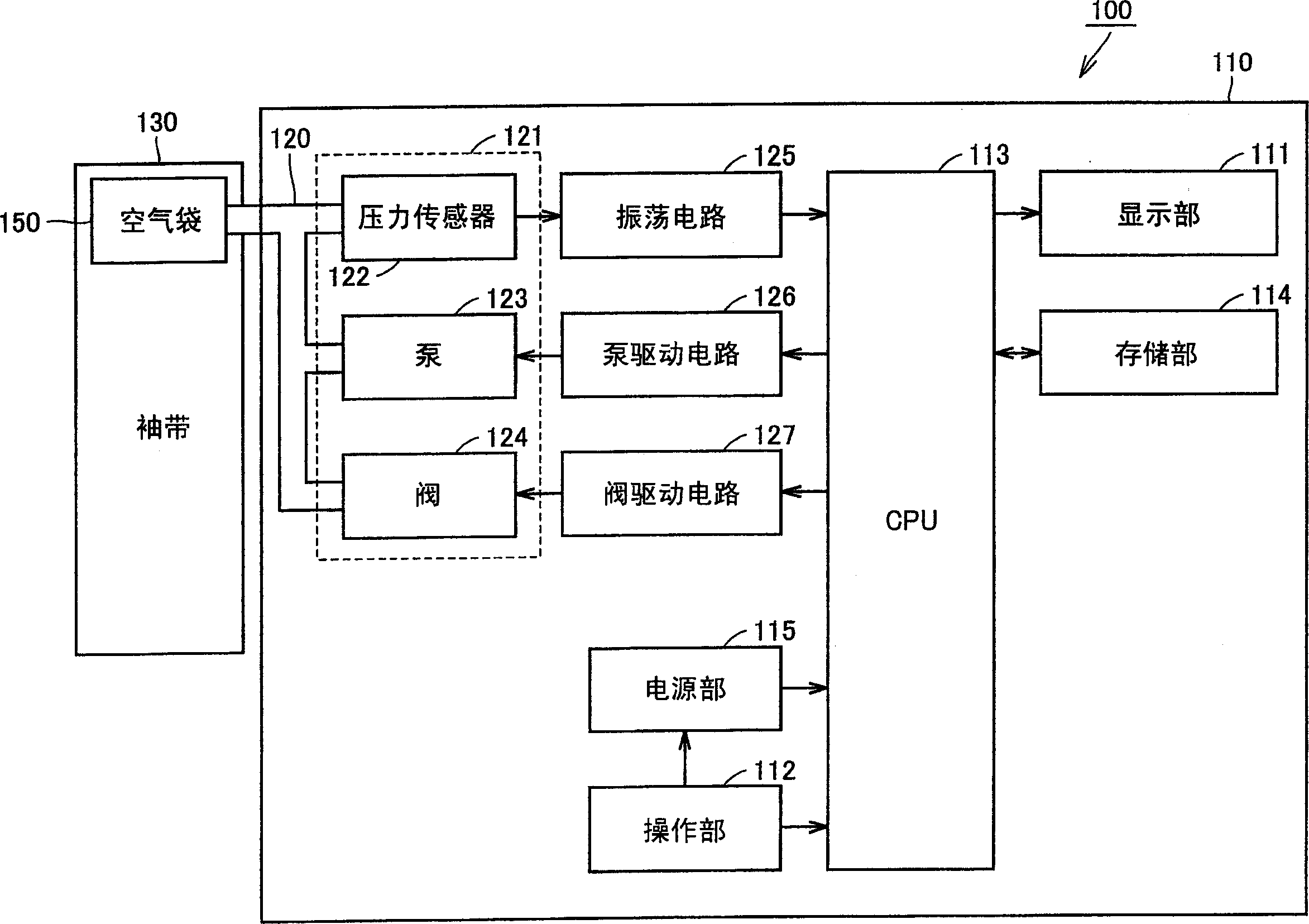
Wrist securing device for pulse wave measuring apparatus, and pulse wave measuring apparatus
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
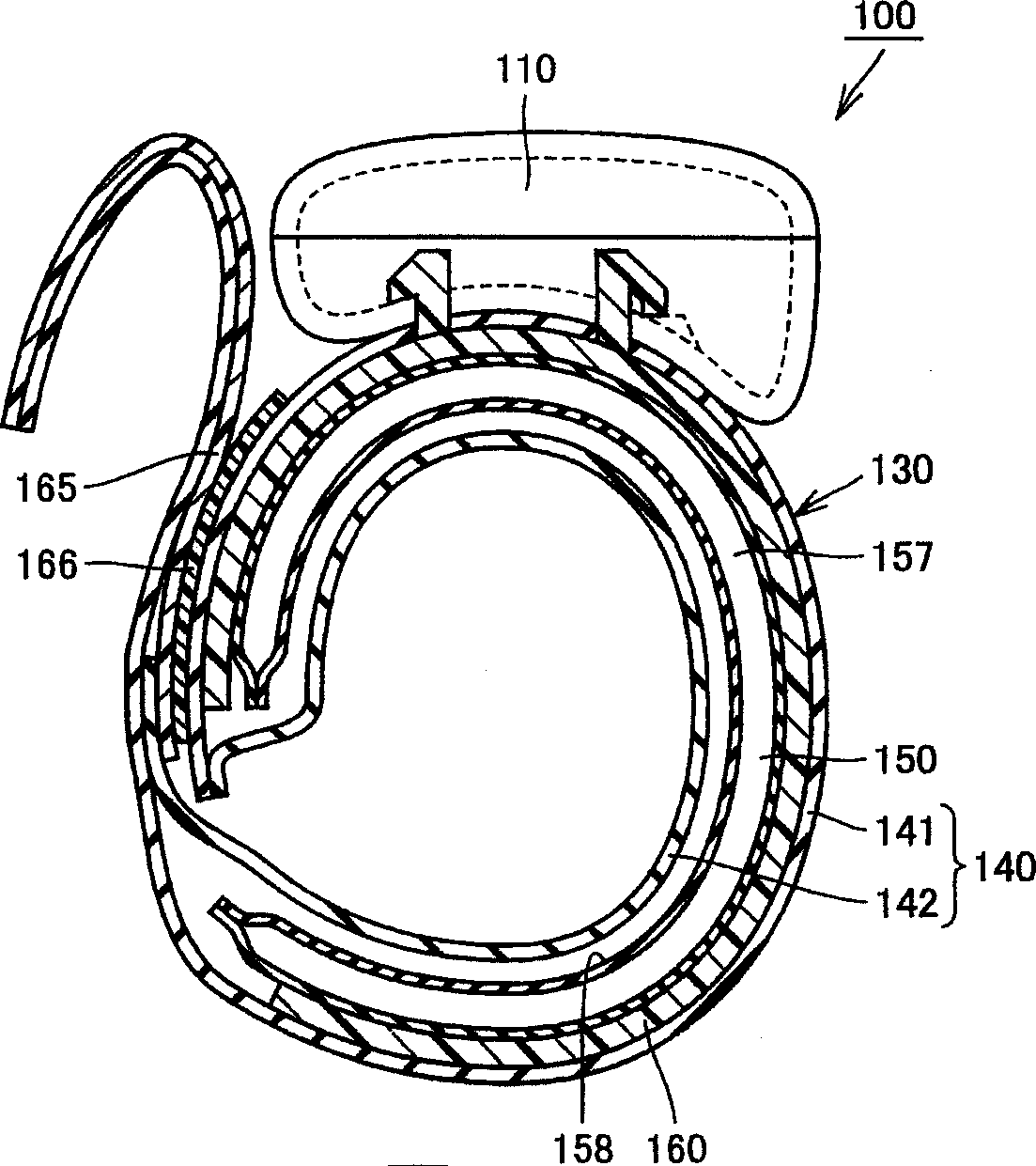
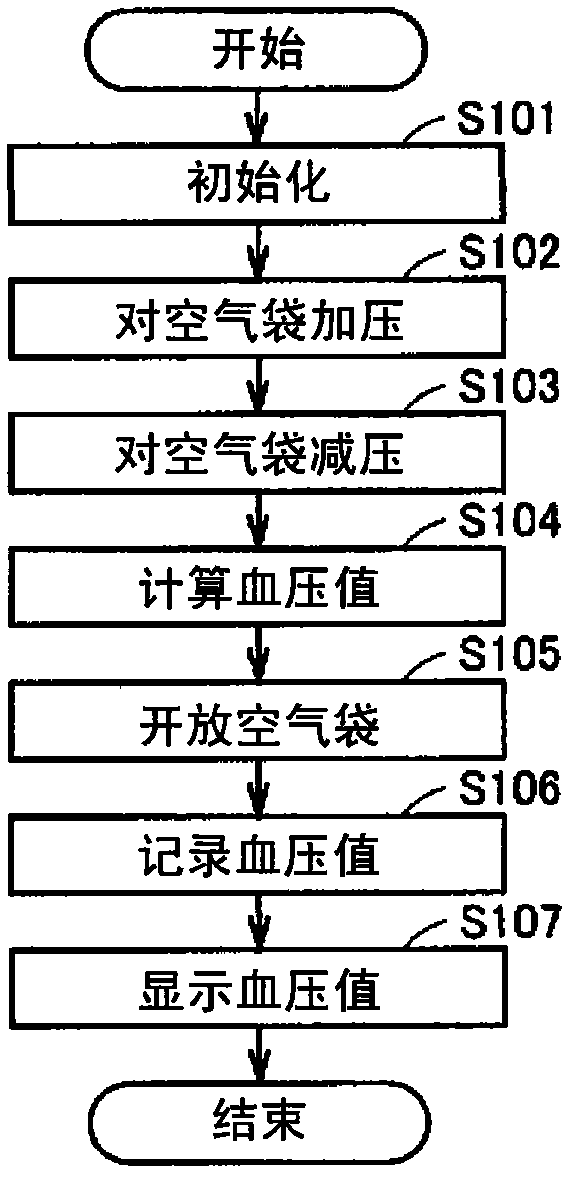
Blood pressure monitor and corresponding cuff
InactiveCN1820702APrecise compressionStability determinationBristleEvaluation of blood vesselsBlood Pressure DeterminationsBlood pressure monitors
An air bag (150) being inflated and deflated as air comes in and out is included. The air bag (150) is formed of a flexible sheet material. The air bag (150) has at least an inner circumferential sheet (162) positioned inside when a blood pressure monitor cuff is wrapped around a living body, and an outer circumferential sheet (161) positioned on the outer circumferential side of the inner circumferential sheet (162). The sheet material forming the air bag (150) has a thickness of 0.15 mm or less. Therefore, big deep wrinkles appearing on the inner surface of the fluid bag fitted on a living body can be reduced, which may otherwise give an adverse effect on blood pressure measurement.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
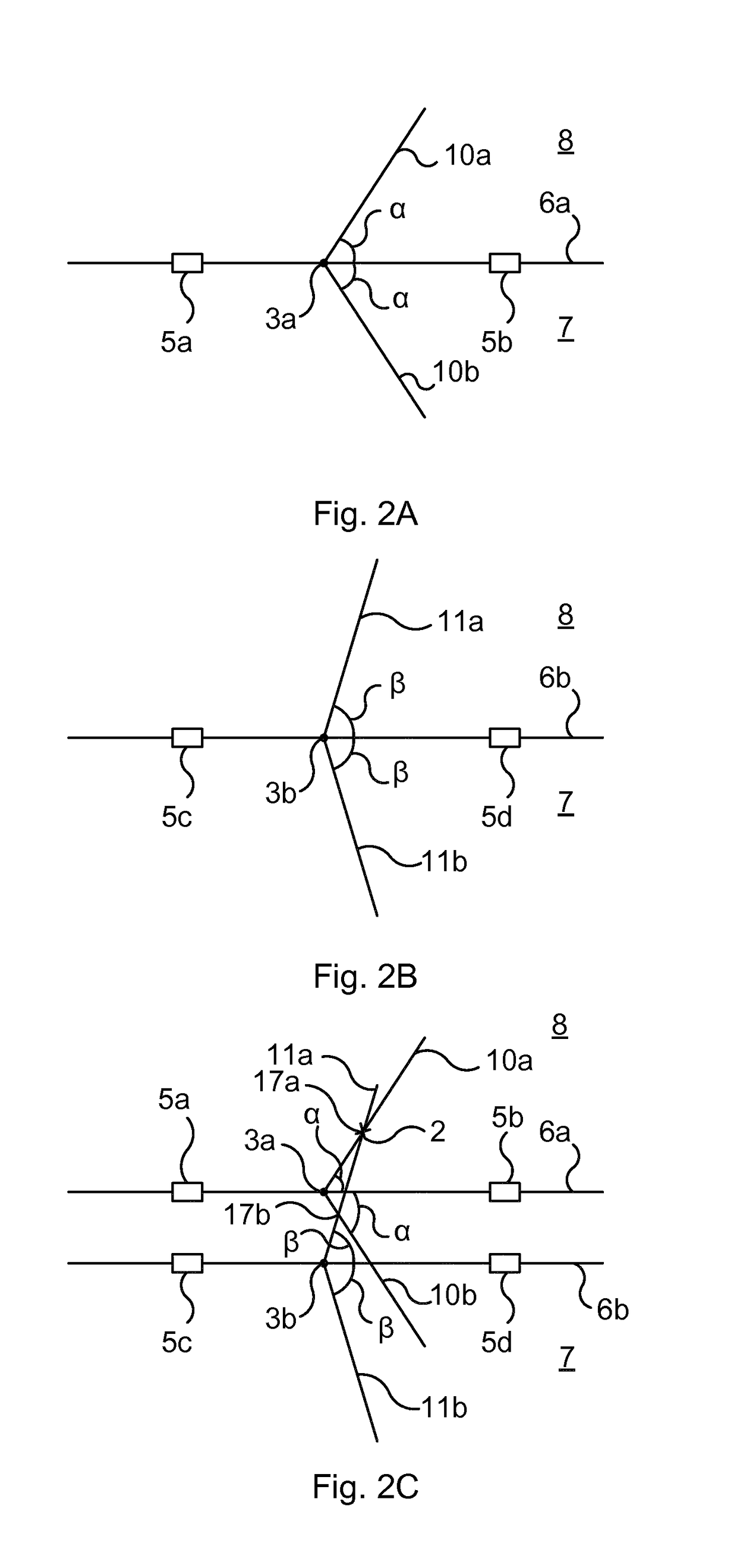
Method, device, computer program and computer program product for determining whether a portable key device is located in an active area in relation to a barrier
ActiveUS20180052217A1Improve accuracyPreventing inadvertent unlockingBuilding locksPosition fixationComputer hardwareComputer program
It is presented a method for determining whether a portable key device is located in an active area in relation to a barrier. The method is performed in an access control device and comprising the steps of: detecting a first angle of arrival of a wireless signal from the portable key device using a first pair of separated antennas; detecting a second angle of arrival of a wireless signal from the portable key device using a second pair of separated antennas; determining a first pair of directions based on the first angle of arrival; determining a second pair of directions based on the second angle of arrival; determining a position of the portable key device to be where one of the first pair of directions intersects one of the second pair of directions; and determining whether the portable key device is located in the active area based on the position.
Owner:ASSA ABLOY AB
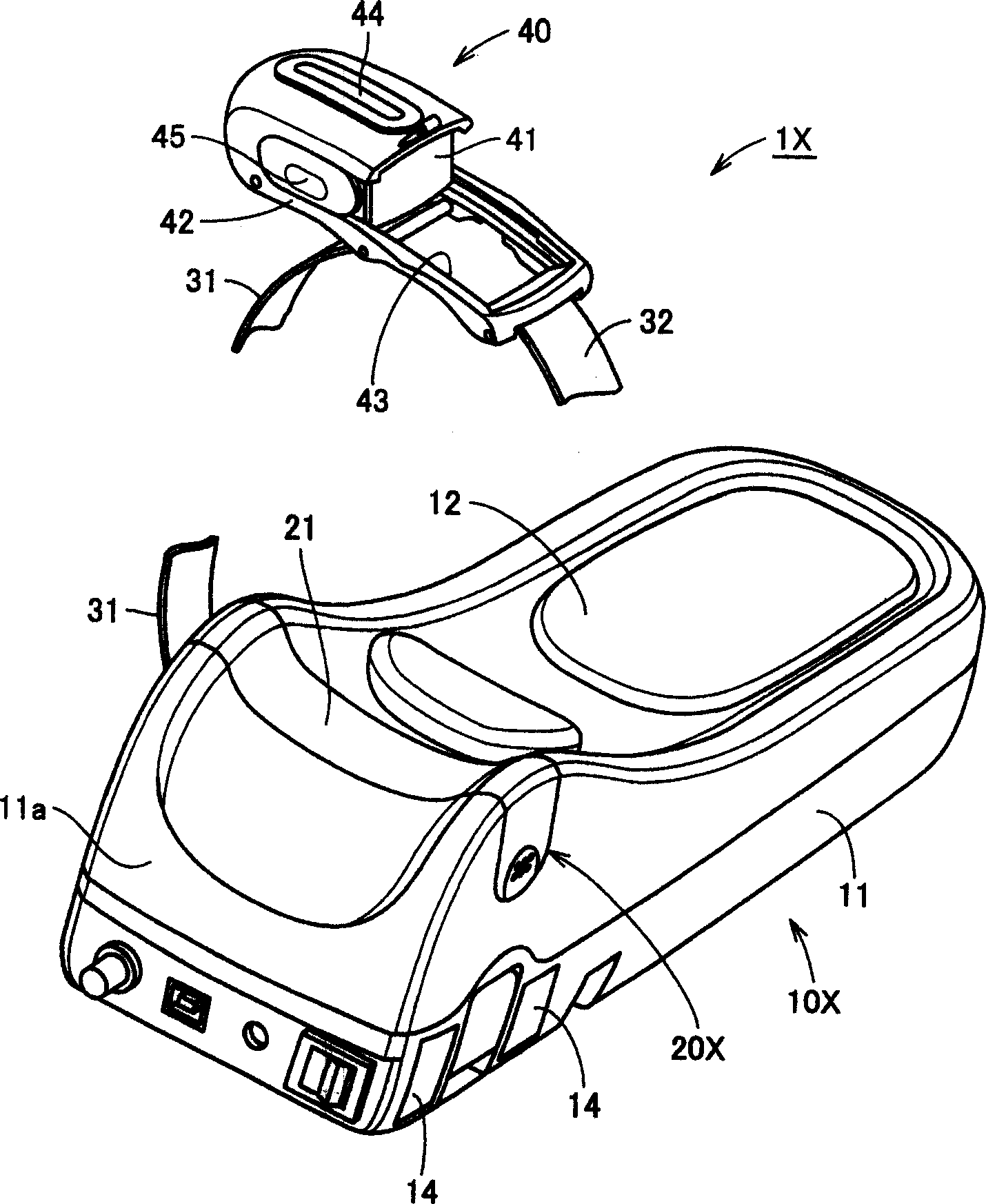
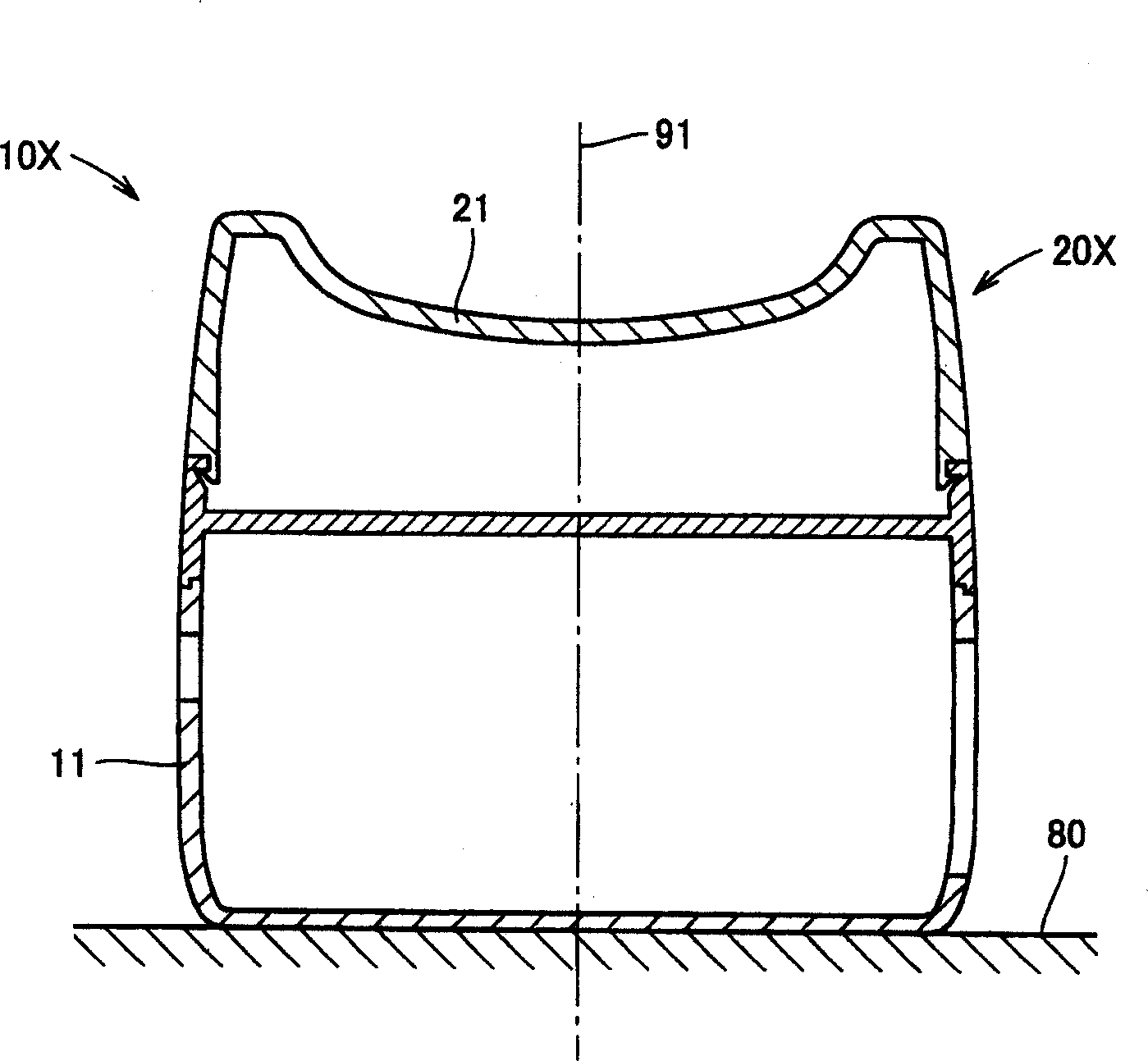
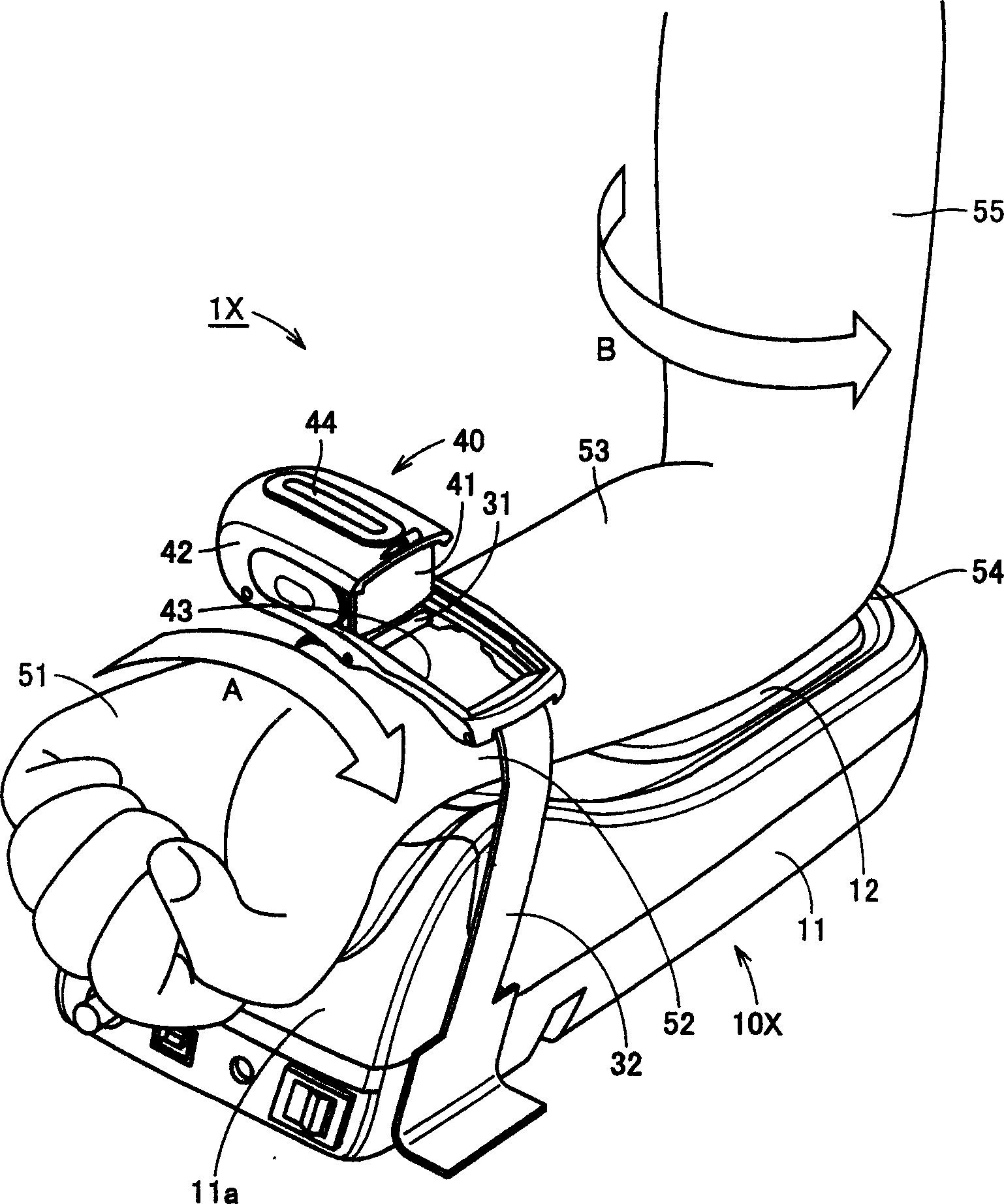
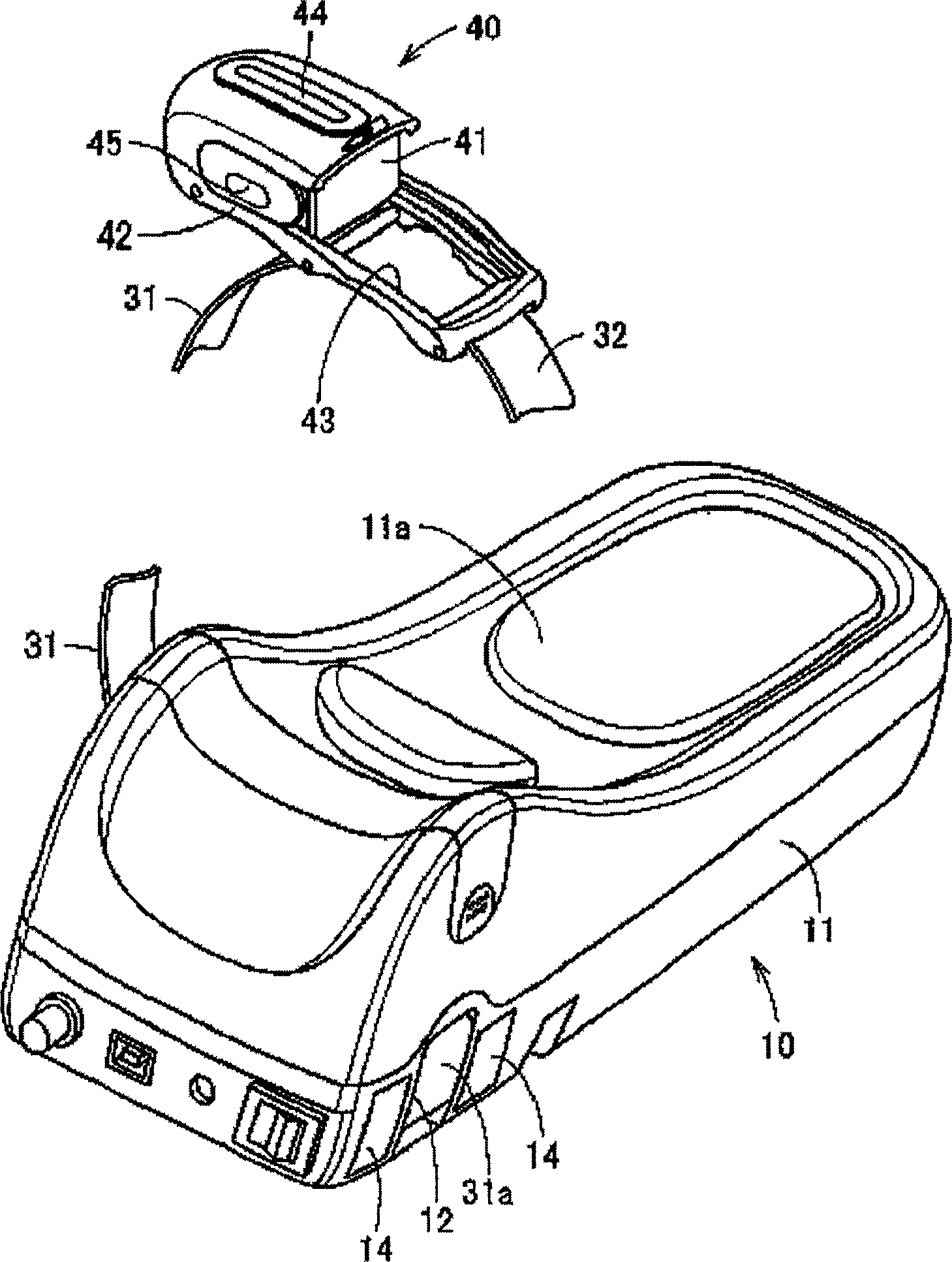
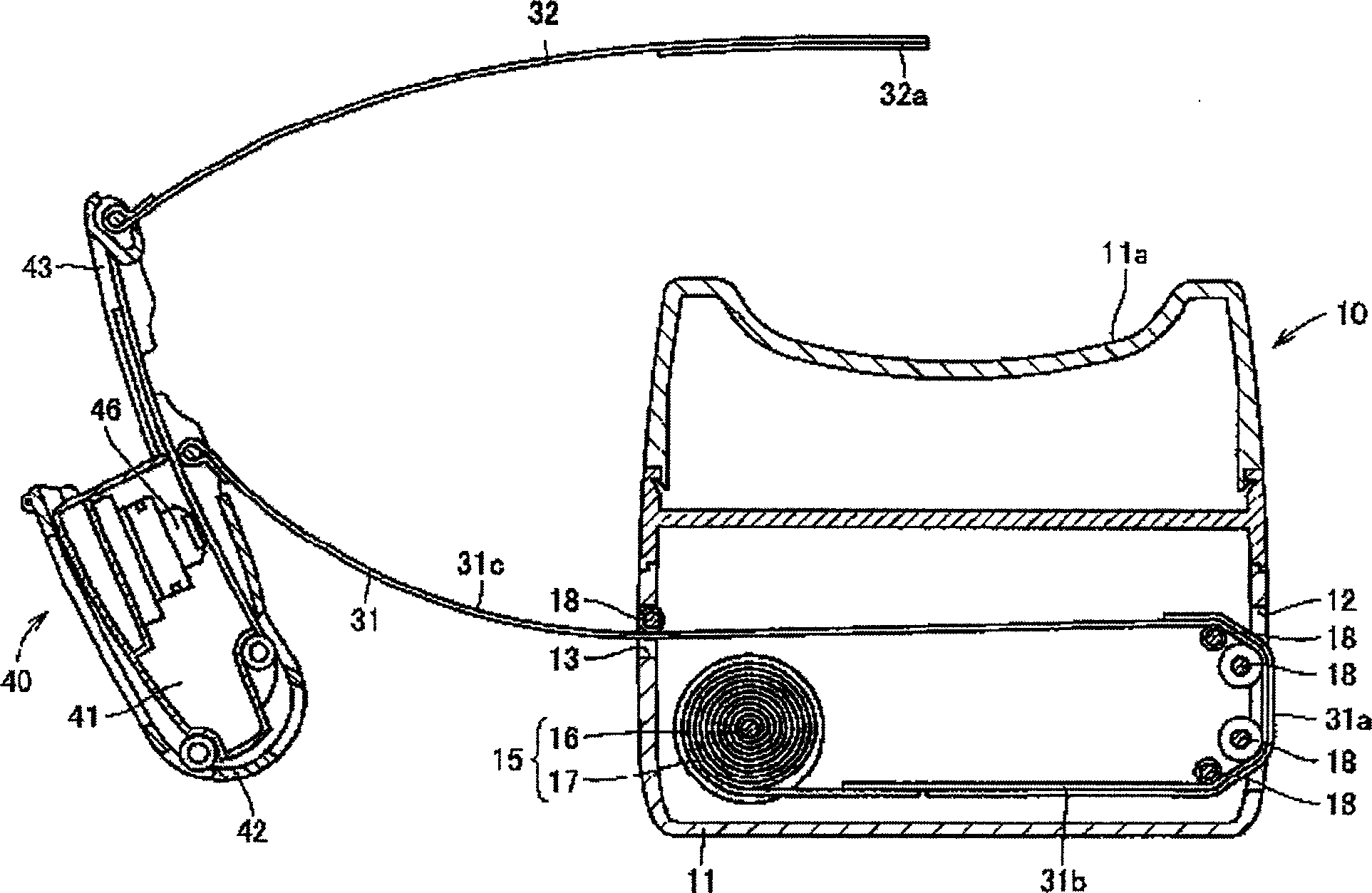
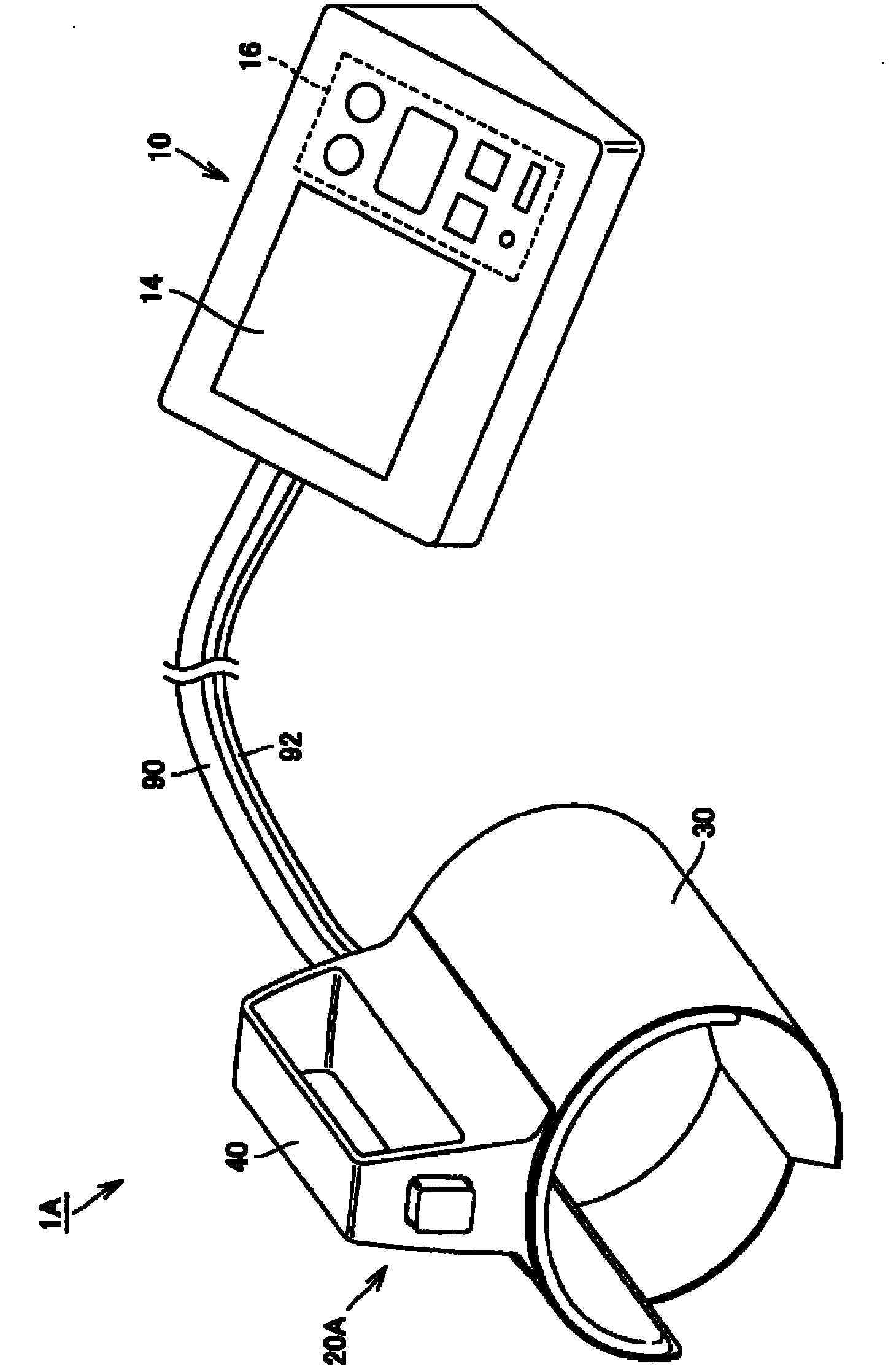
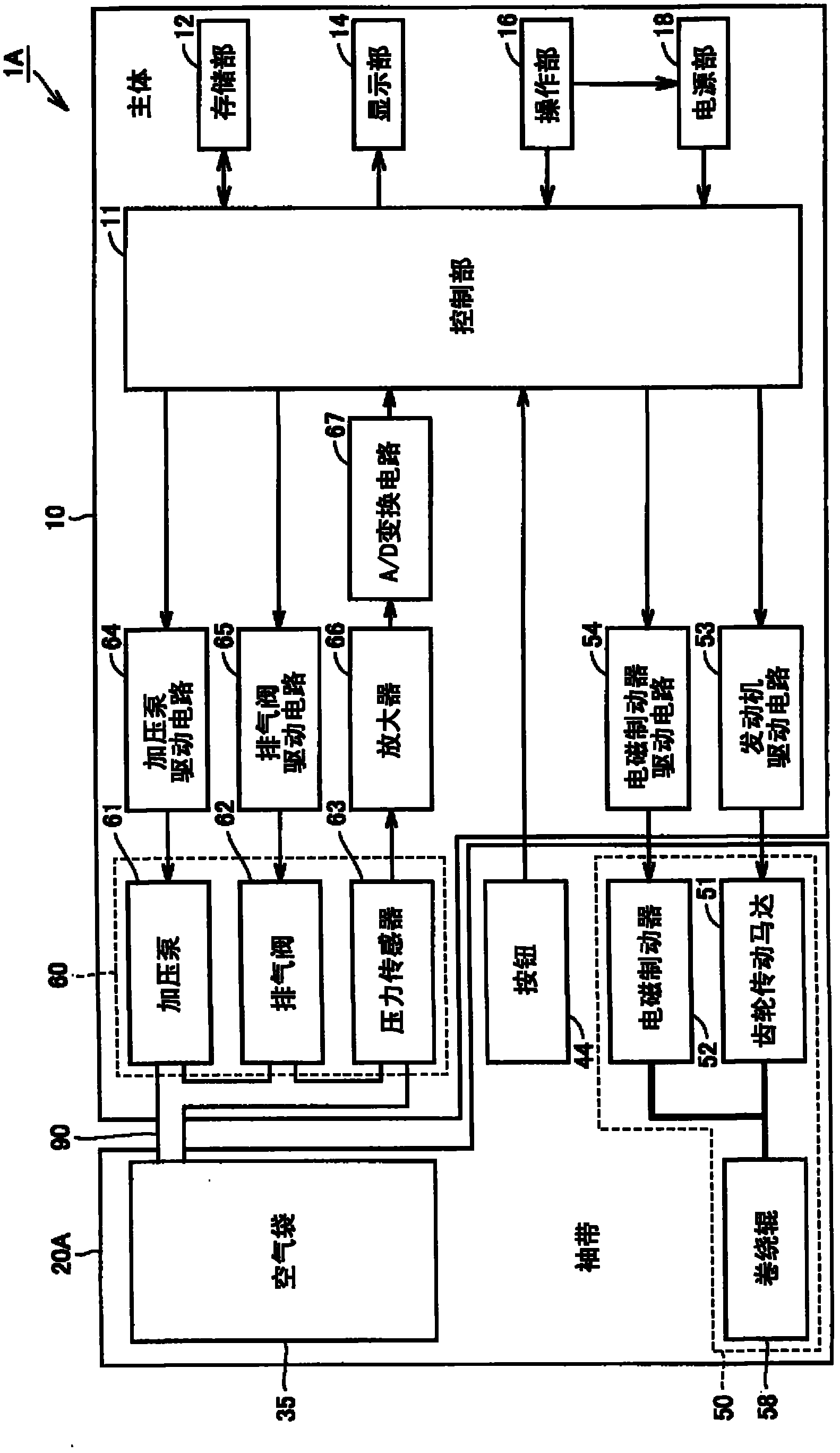
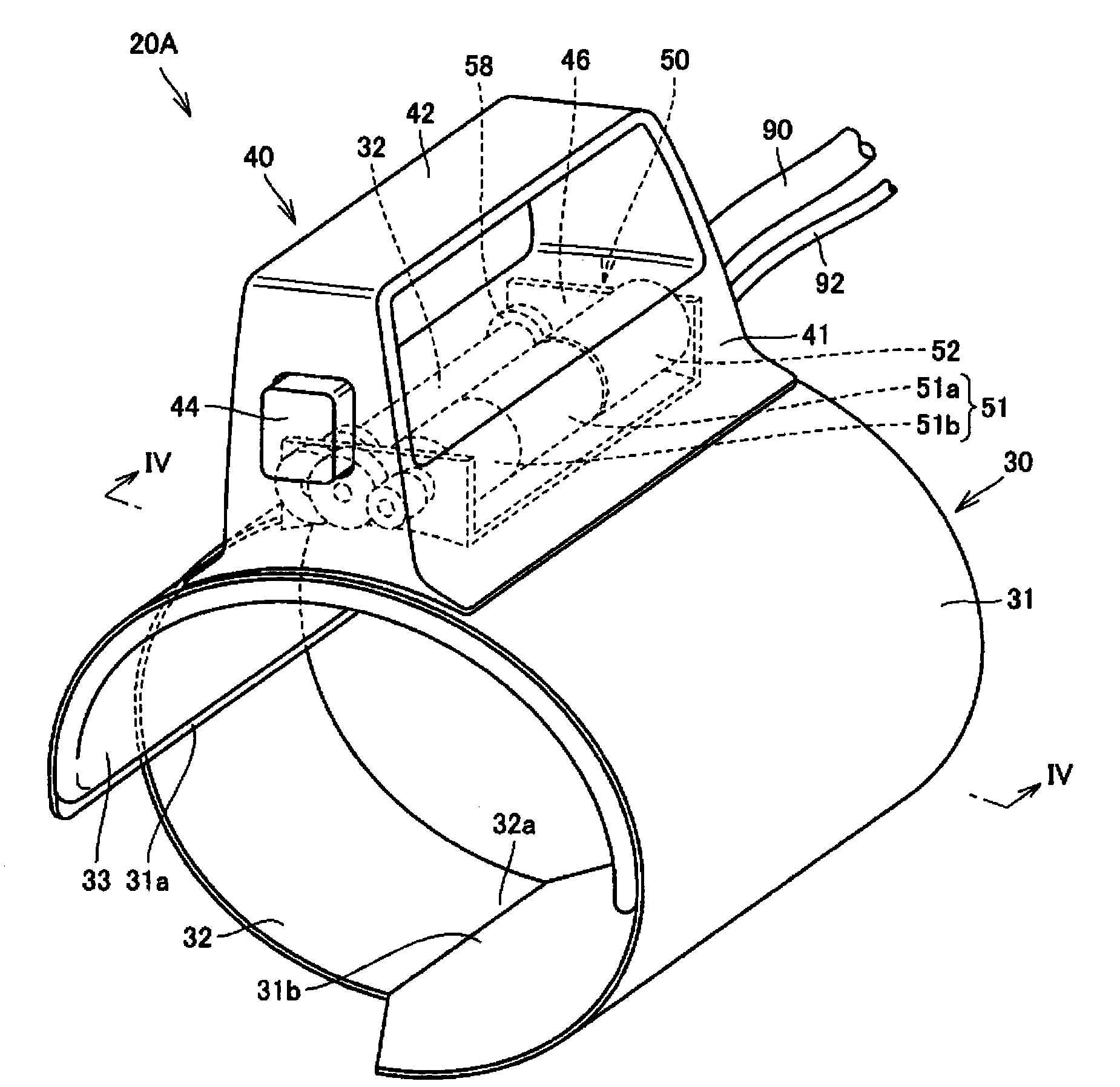
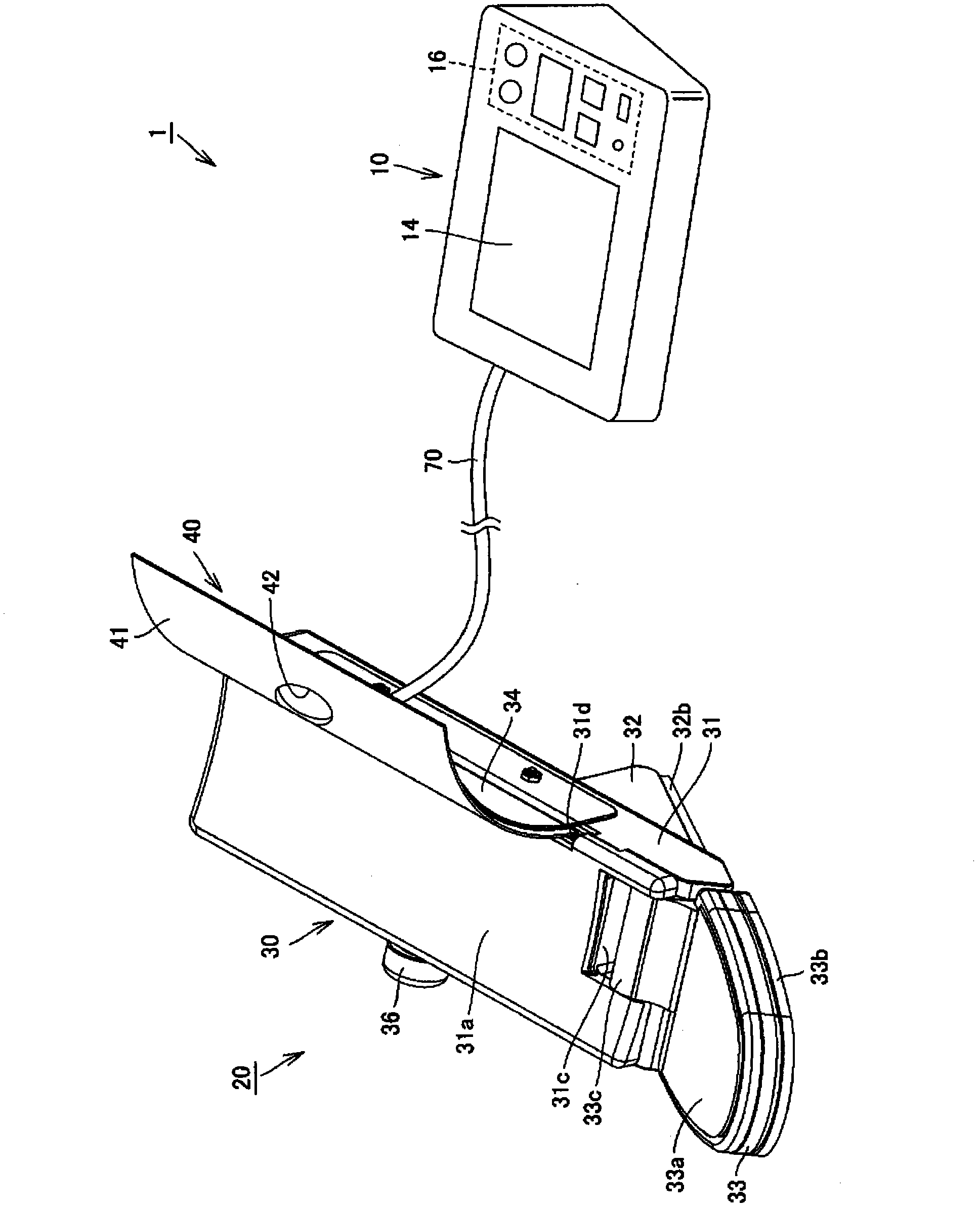
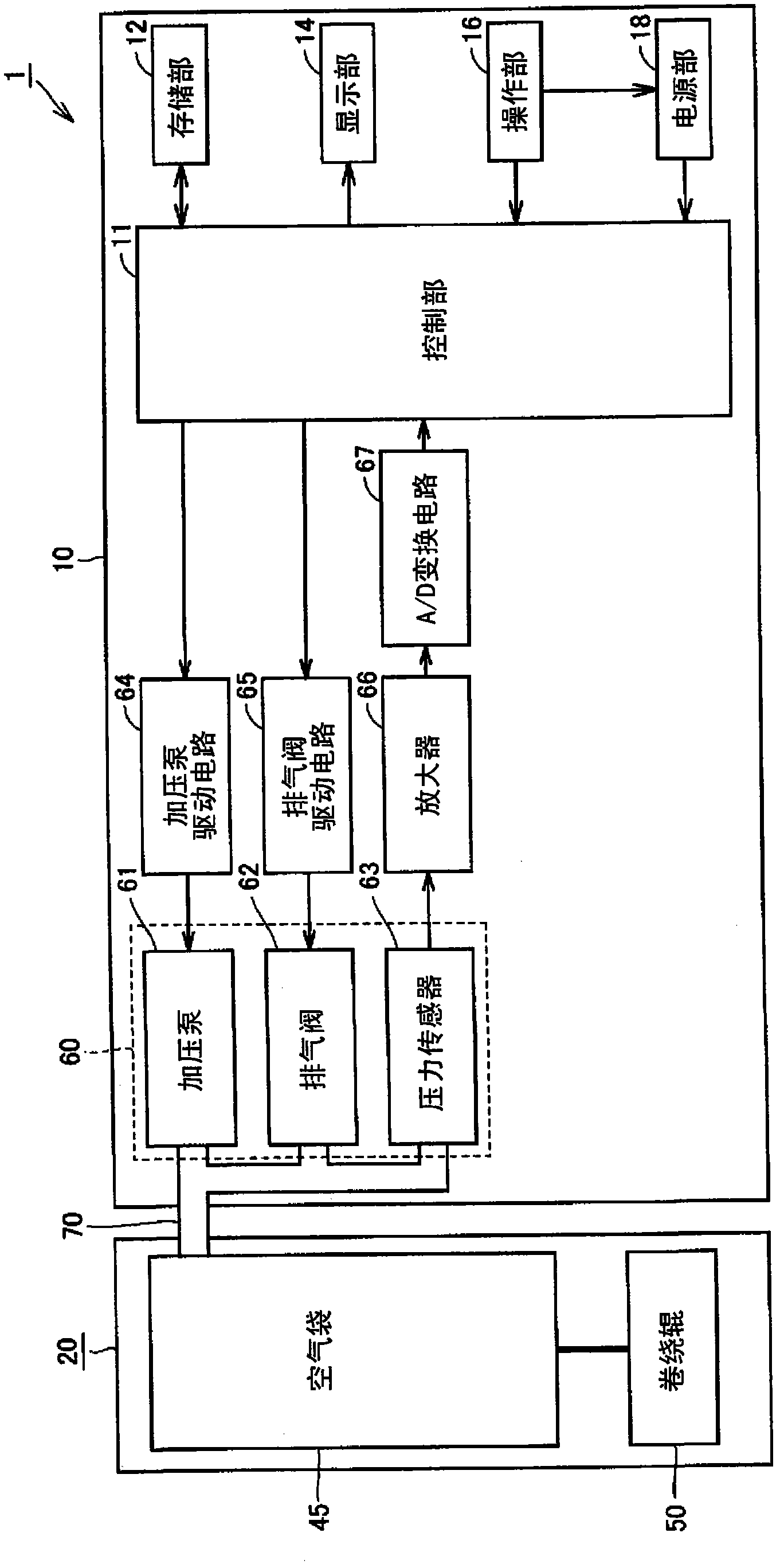
Pulse wave measuring apparatus
ActiveCN1517064AStability determinationHigh precisionMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateConstant forcePulse wave
A pulse wave measuring apparatus is disclosed, in which a sensor unit can be fixed easily under an appropriate pressure at an appropriate position on a living organism. With the living organism fixed by a living organism fixing device, a pressure sensitive portion arranged on the sensor unit is pressed against the living organism thereby to measure the pulse wave. The living organism fixing device includes a fixing stand for fixing the living organism in position, and fastening bands for connecting the fixing stand and the sensor unit and fastening the living organism fixedly to the fixing stand while at the same time activating by pressing the sensor unit against the living organism. The fastening bands include a first band portion with one end mounted on the sensor unit and the other end mounted on the fixing stand and a second band portion with one end mounted on the sensor unit and the other end removably mounted on the fixing stand. The fixing stand has a constant force spring for pulling the other end of the first band portion with a constant force.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Sensor unit, electronic apparatus, and moving object
ActiveCN104344820AStability determinationImprove reliabilityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed/acceleration/shock instrument detailsEngineeringBiomedical engineering
A sensor unit includes a substrate provided with a first sensor device as an inertia sensor and a connector connected to the first sensor device, and a mount on which the substrate is placed and which includes an opening through which the connector is exposed. A gap is provided between the substrate and the mount, and the first sensor device is provided in a position that falls within the gap in a plan view.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
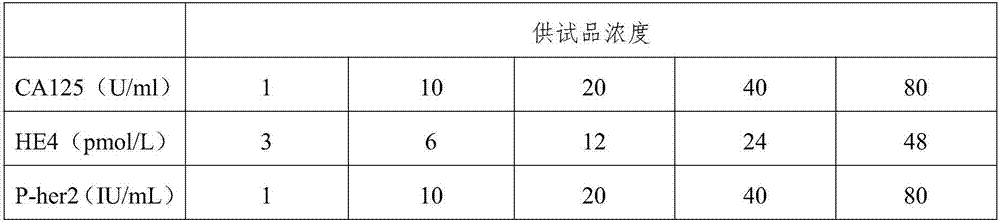
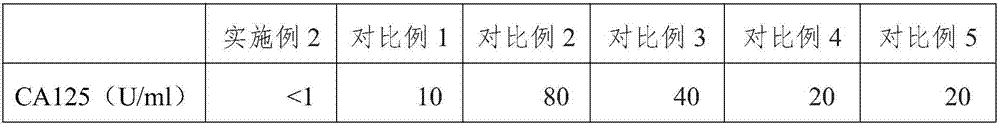
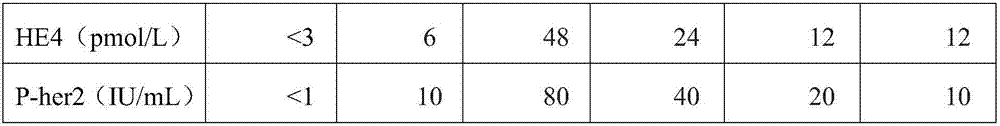
Triple test diagnostic kit for breast cancer
ActiveCN105866418AHigh sensitivityPlay the role of multi-stage amplificationMaterial analysisPositive controlEarly breast cancer
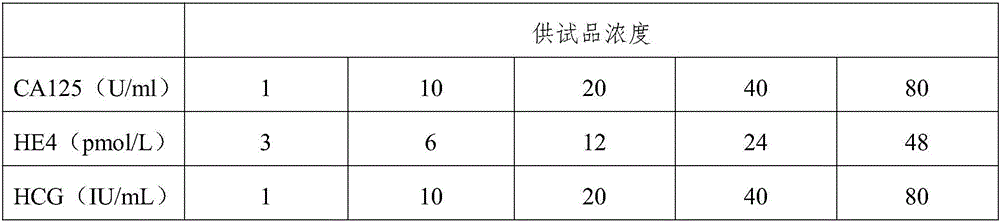
The invention belongs to the field of biological detection and specifically relates to a triple test diagnostic kit for breast cancer of tumor serum markers CA125, HE4 and P-her2. The triple test diagnostic kit for breast cancer provided by the invention mainly comprises an abzyme elisa plate, a biotin antibody enveloped plate, bovine serum albumin, serum diluent, horse radish peroxidase, tetramethyl benzidine, sulfuric acid, negative control liquid and positive control liquid. The triple test diagnostic kit for breast cancer provided by the invention can be used for detecting the expression levels of CA125, HE4 and P-her2 in the body of the patient after operative treatment or the relapsing and metastatic tumor patient; the triple test diagnostic kit for breast cancer has important significance in clinical diagnosis of breast cancer; the triple test diagnostic kit for breast cancer provided by the invention can reduce the interference of other matters in serum, can greatly increase the accuracy and stability of detection result and is beneficial to the early diagnosis and prognosis treatment of the patient suffering from breast cancer.
Owner:赛特斯(海南)生物医学有限公司
Reagent for assaying antigen and method of assaying antigen
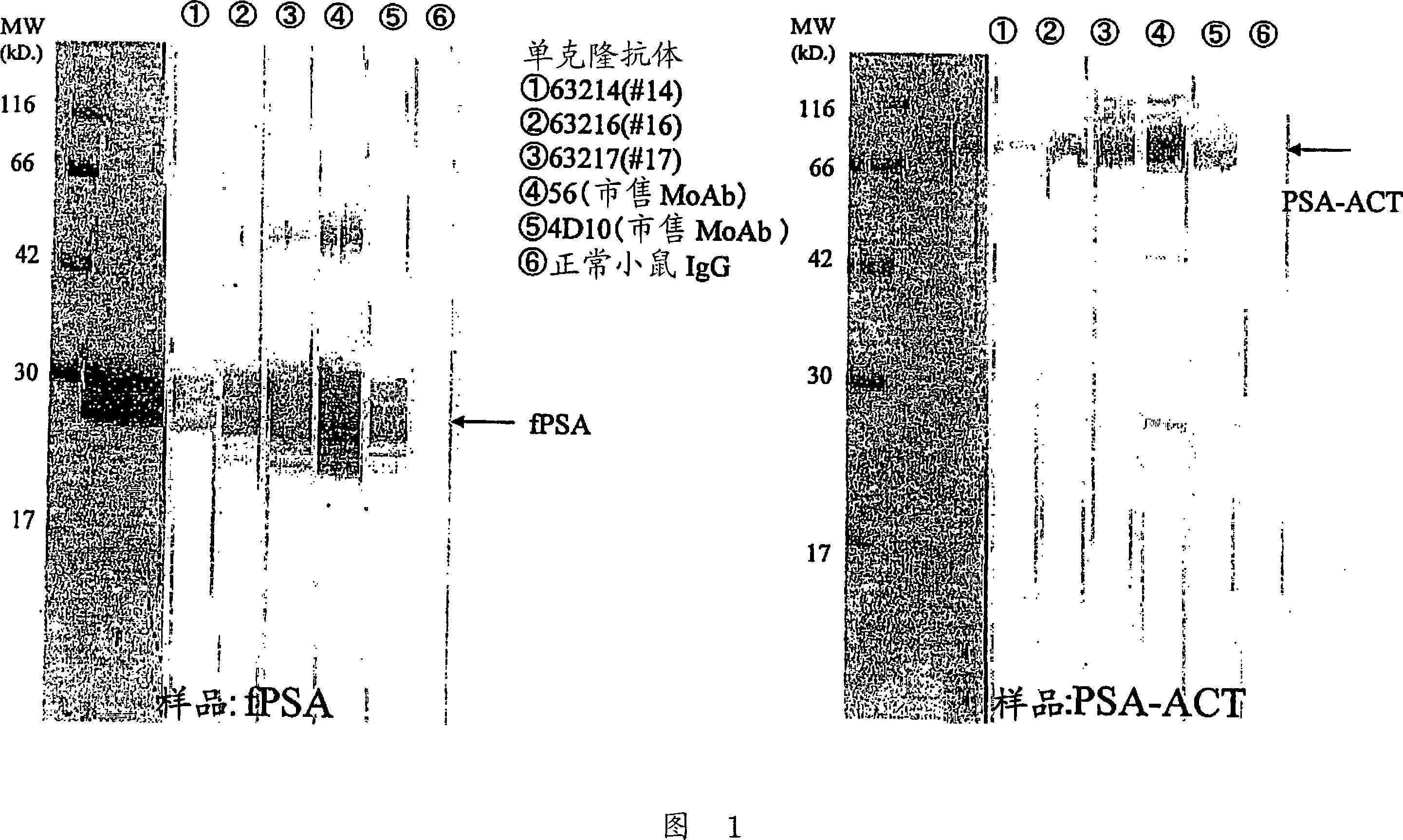
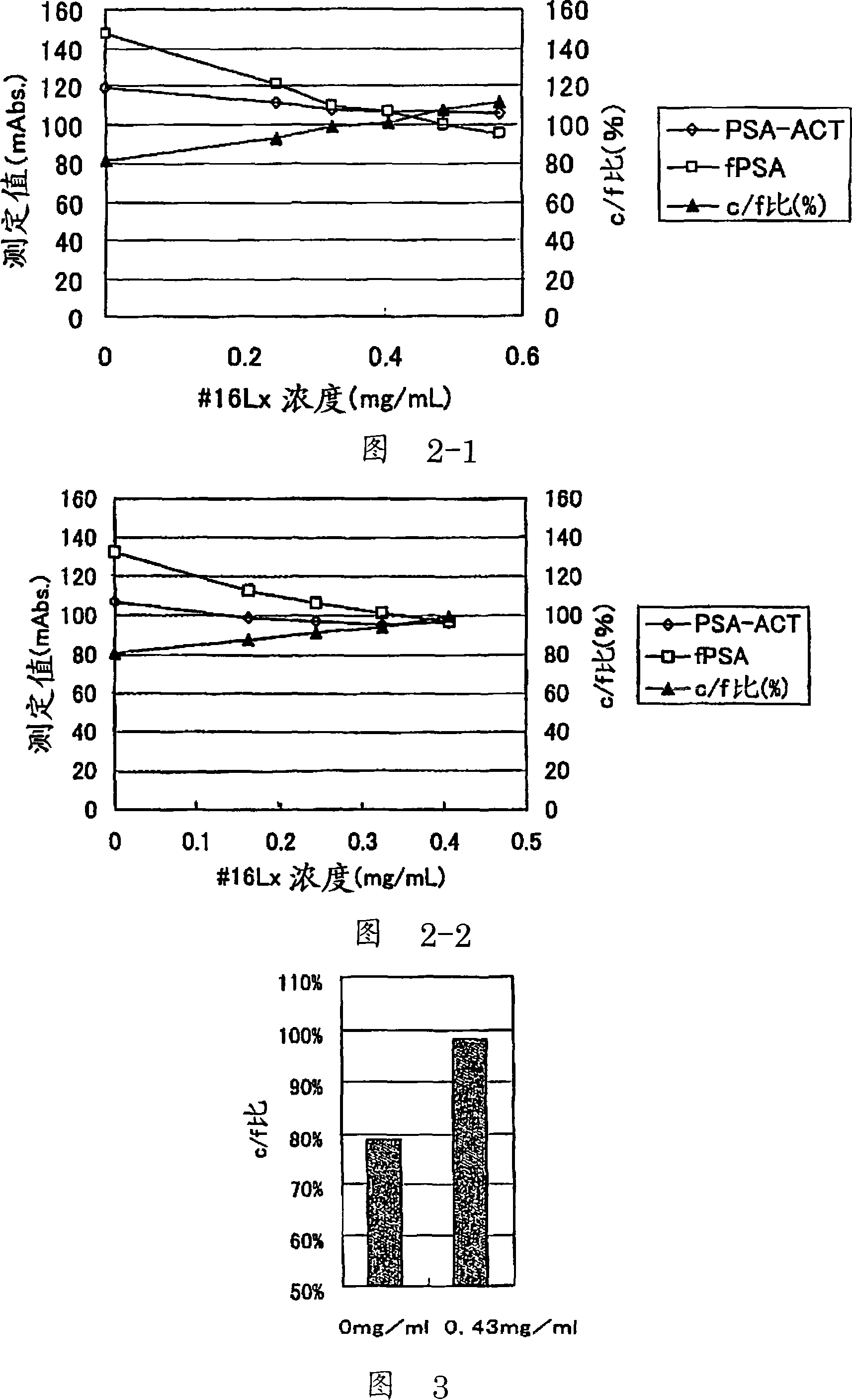
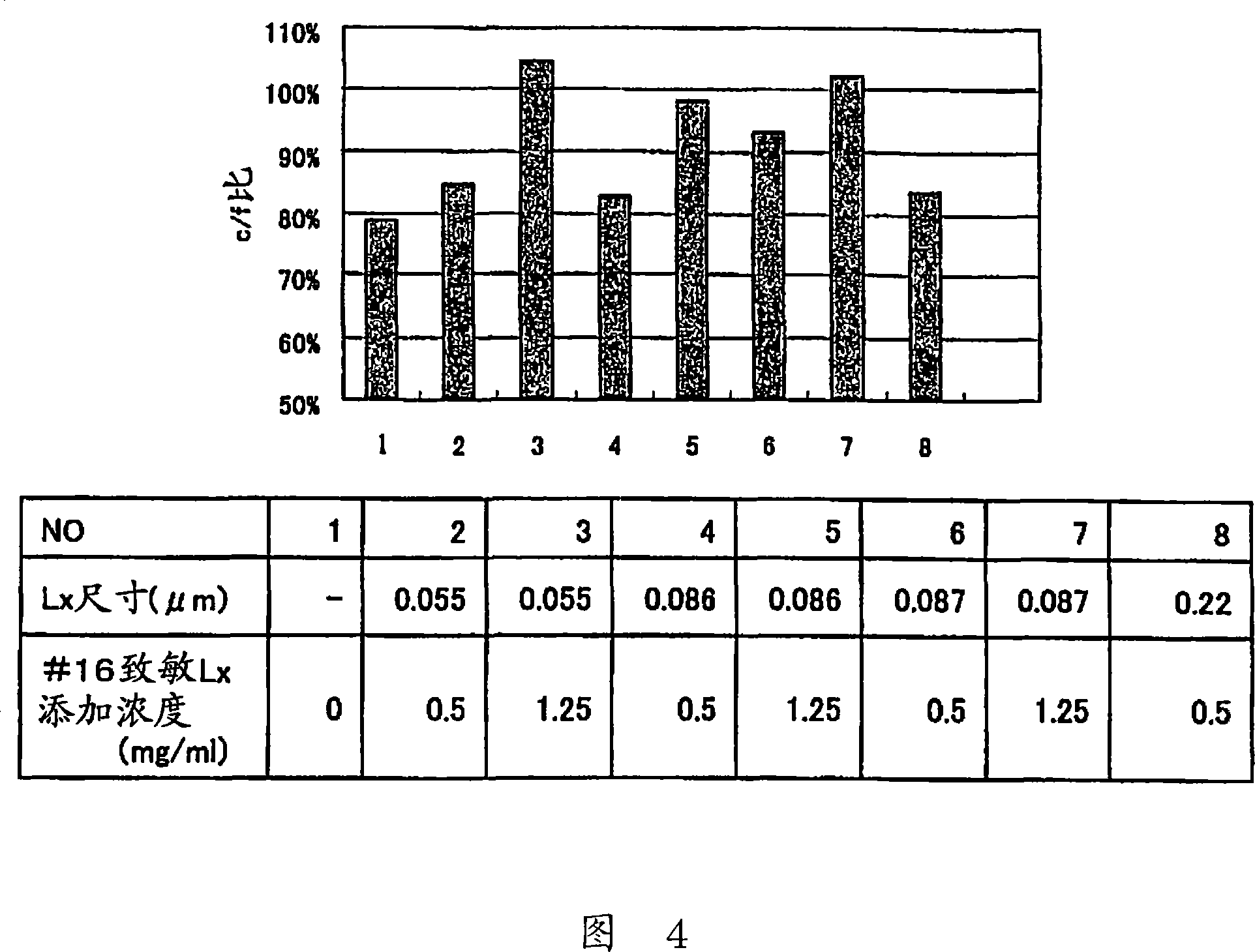
ActiveCN101088010AImprove stabilityStable Quality ManagementMaterial analysisAntigenMonoclonal antibody
Owner:SEKISUI MEDICAL CO LTD
Blood pressure information measurement device
ActiveCN101977547AEasy to wearReliable windingEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographySphygmomanometerMeasurement device
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Stability determination method and device and application in demulsification and stability evaluation
ActiveCN102954983AStability determinationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectric fieldPeak value
The invention discloses a stability determination method of an oil-water emulsion, and the determination method comprises the following steps: preparing the oil-water emulsion; applying an electric field to the oil-water emulsion; measuring a response time period tA from the application of the electric field to the generation of current in the electric field, and / or measuring a peak tail current value IE when the current in the electric field converges into a constant value after a current peak value Imax; and using the response time period tA and / or the peak tail current value IE as the stability determination results of the oil-water emulsion. The invention also discloses an application of the stability determination method of the oil-water emulsion provided in the invention in demulsification effect evaluation of a demulsifier, an application of the stability determination method of the oil-water emulsion provided in the invention in crude oil demulsification performance evaluation, and a stability determination device (100) of the oil-water emulsion.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
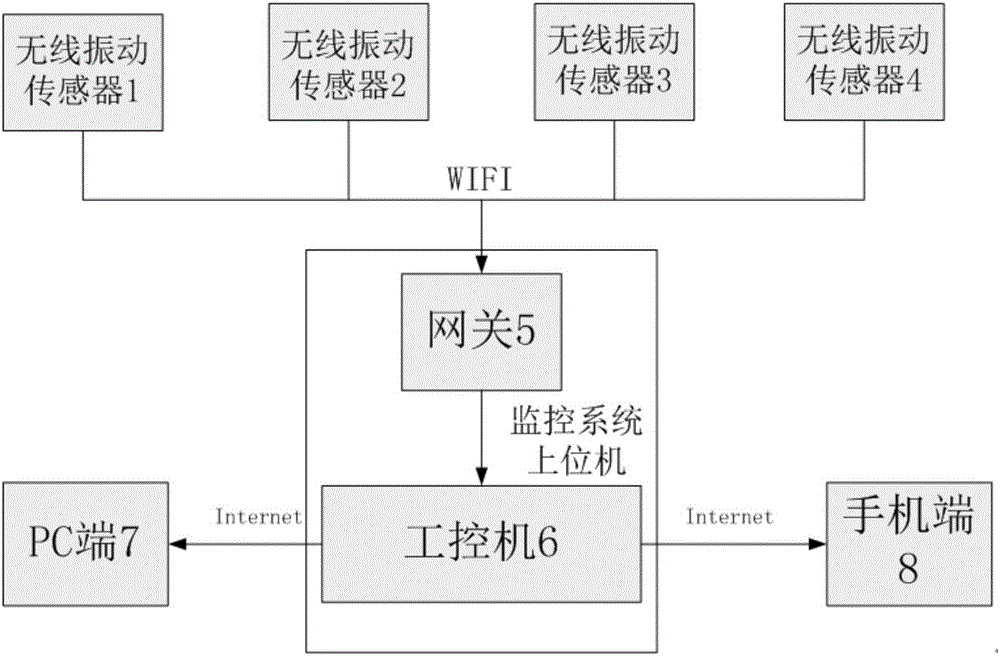
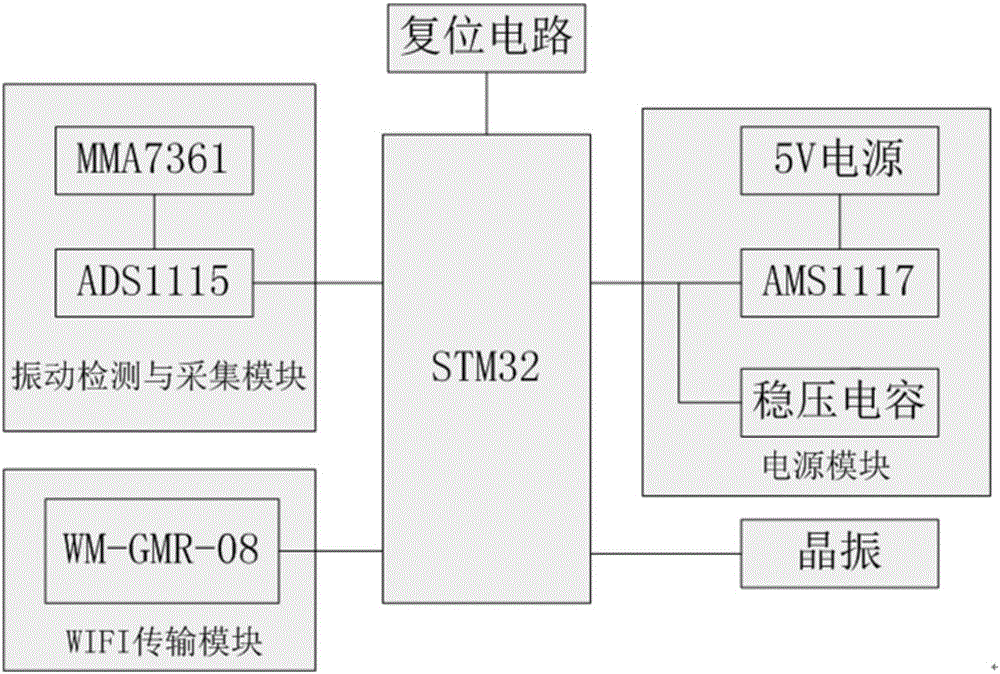
Vibration sensor tunnel on-line monitoring system based on wireless network transmission
InactiveCN106802181AReduce energy consumptionLow costSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing electrical meansOccupancy rateVibration control
The present invention relates to a vibration sensor tunnel on-line monitoring system based on wireless network transmission. The system comprises a monitoring system upper computer, at least four wireless vibration sensors and a mobile device terminal. The wireless vibration sensor is installed on the tunnel, and the monitoring system upper computer is connected with the wireless vibration sensor and the mobile device terminal; and the wireless vibration sensor records the vibration data of two directions of the tunnel in real time, the data is transmitted to the monitoring system upper computer through the wireless network, the monitoring system upper computer stores and displays the actual engineering data of the vibration signals, and the monitoring system upper computer makes out the real-time line chart of the vibration system according to the collection data, and a mobile terminal employs the wireless network to remotely access the monitoring system upper computer and reads the collected monitoring data. Compared to the prior art, the vibration sensor tunnel on-line monitoring system based on the wireless network transmission can couple the vibration signals of the two directions, actually reflect the vibration condition in the tunnel, and is fast in response time and low in resource occupancy rate, etc.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for measuring hematocrit value of blood sample, method for measuring concentration of analyte in blood sample, sensor chip and sensor unit
ActiveCN101529236AStability determinationSufficient detection sensitivityBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesPhysicsBlood cell
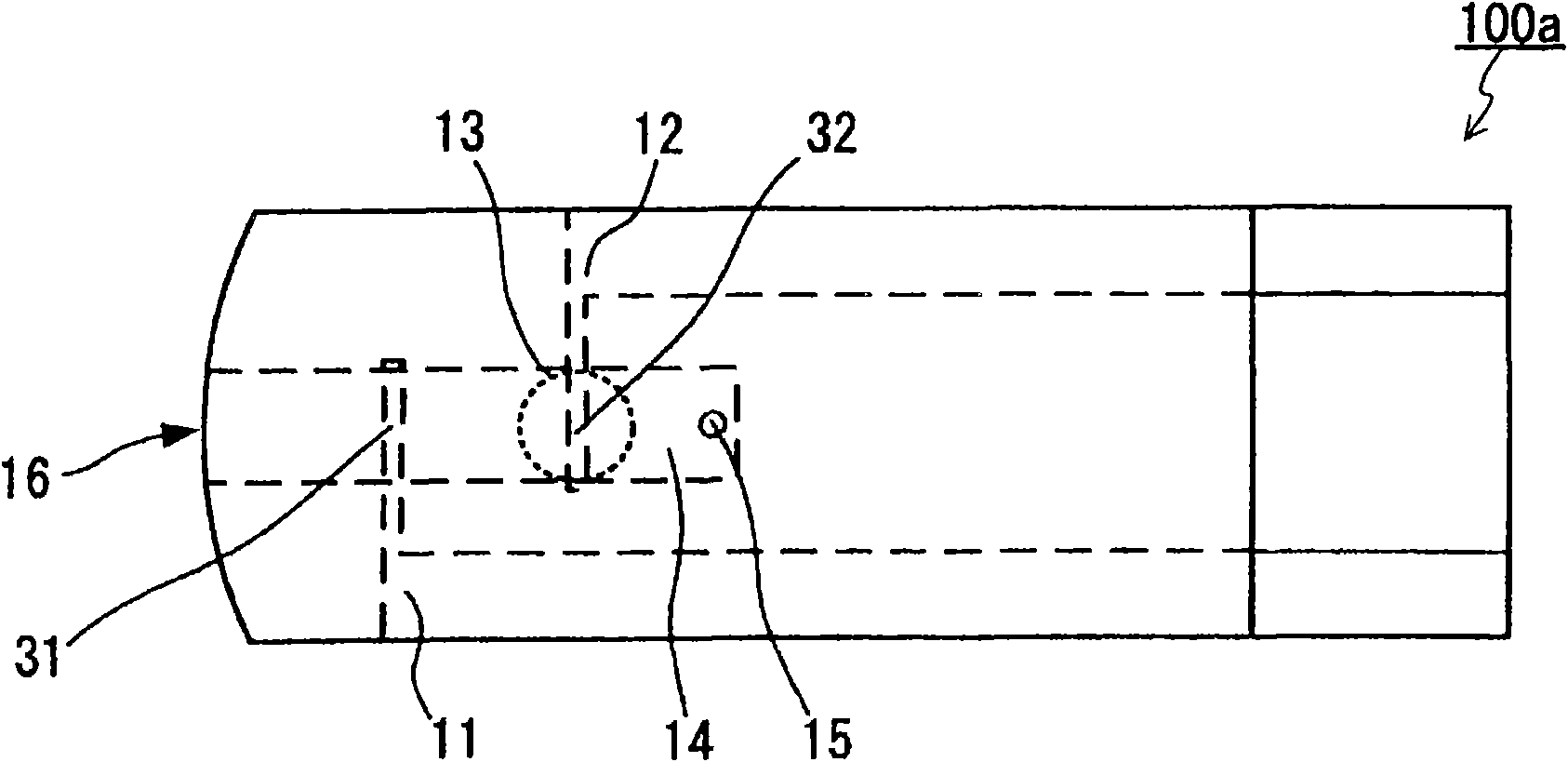
Voltage is applied across a counter electrode and a working electrode, with which a blood sample is in contact, in such a state that an oxidant in a redox substance is in contact with the counter electrode but is substantially not in contact with the working electrode, whereby an easily electrolytically oxidizable metal constituting at least a part of the surface of the working electrode is oxidized, and the oxidant in contact with the working electrode is reduced to measure current produced upon the oxidation and reduction. According to the above constitution, while lowering the voltage applied across the working electrode and the counter electrode, the hematocrit value of the blood sample can be measured stably with a satisfactory detection sensitivity. This measurement can be carried out, for example, with a sensor chip comprising a working electrode (11), a counter electrode (12), and a blood sample holding part (14) in communication with a blood sample introduction port (16). Theposition of the working electrode (11) in its part (31) is nearer to the blood sample introduction port (16) than the counter electrode in its part (32). The surface of the part (31) contains an easily electrolytically oxidizable metal. A reagent (13) containing an oxidant is disposed in contact with the part (32).
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
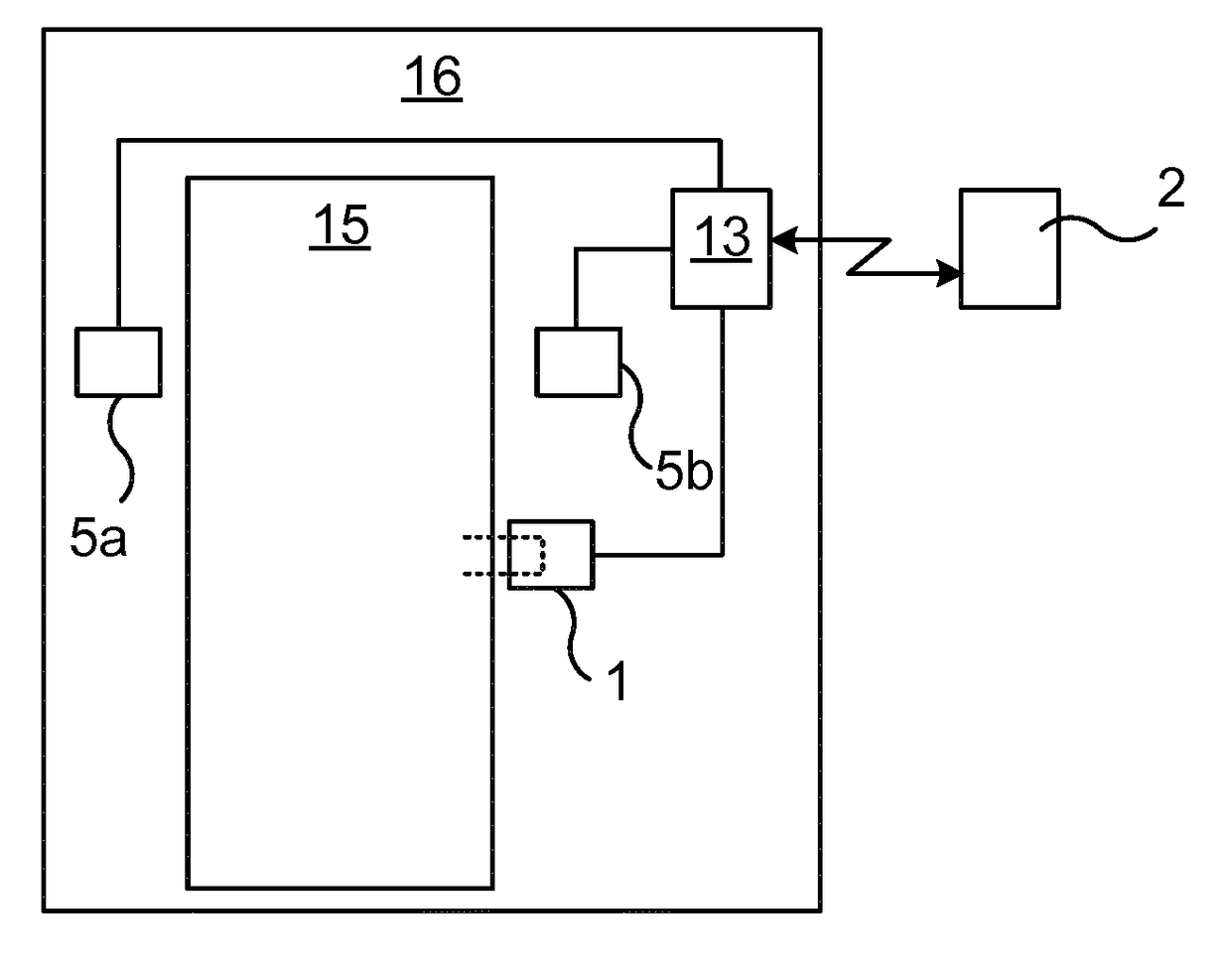
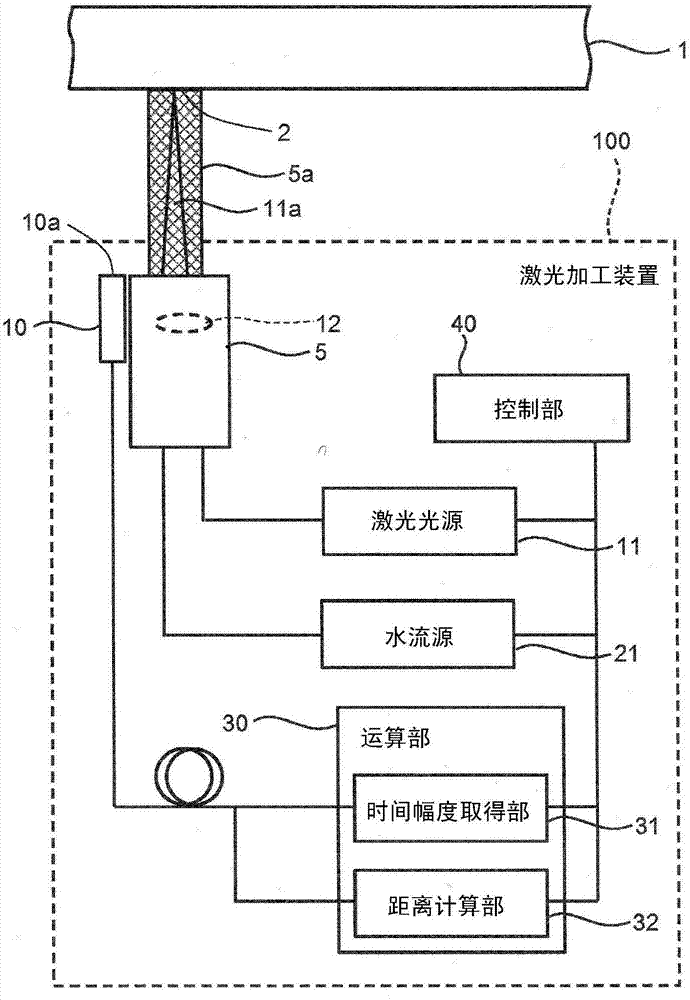
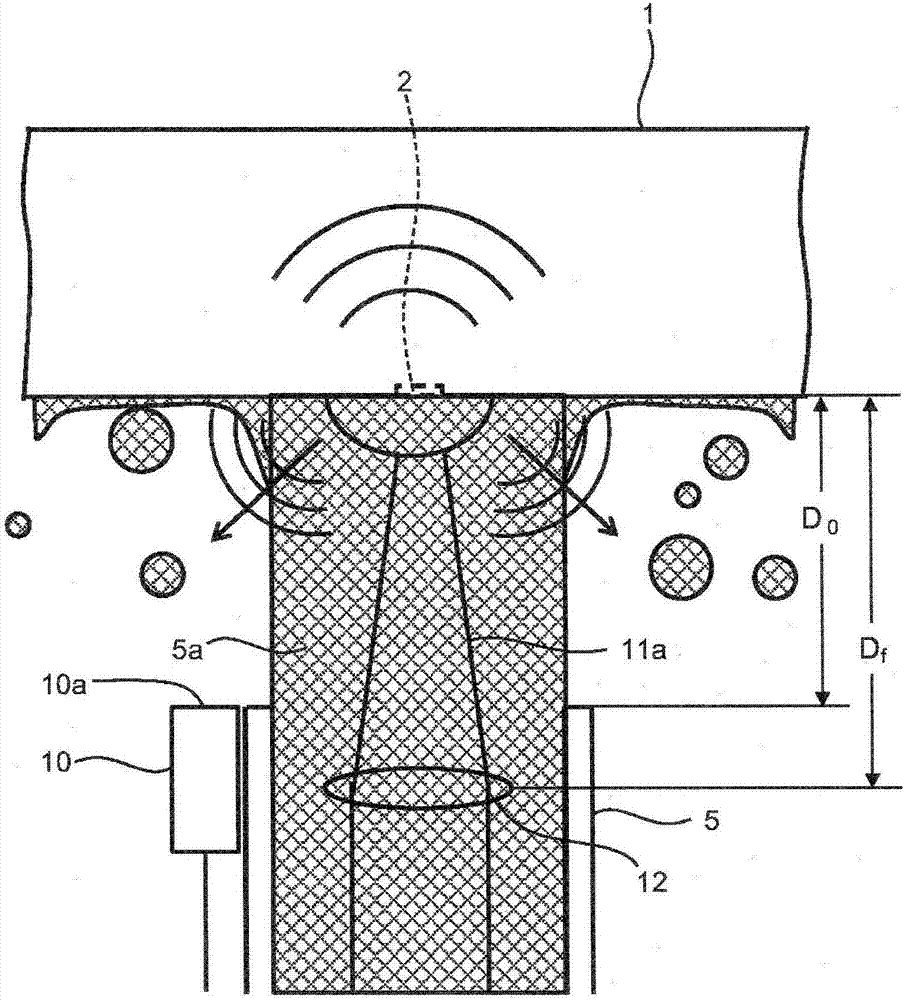
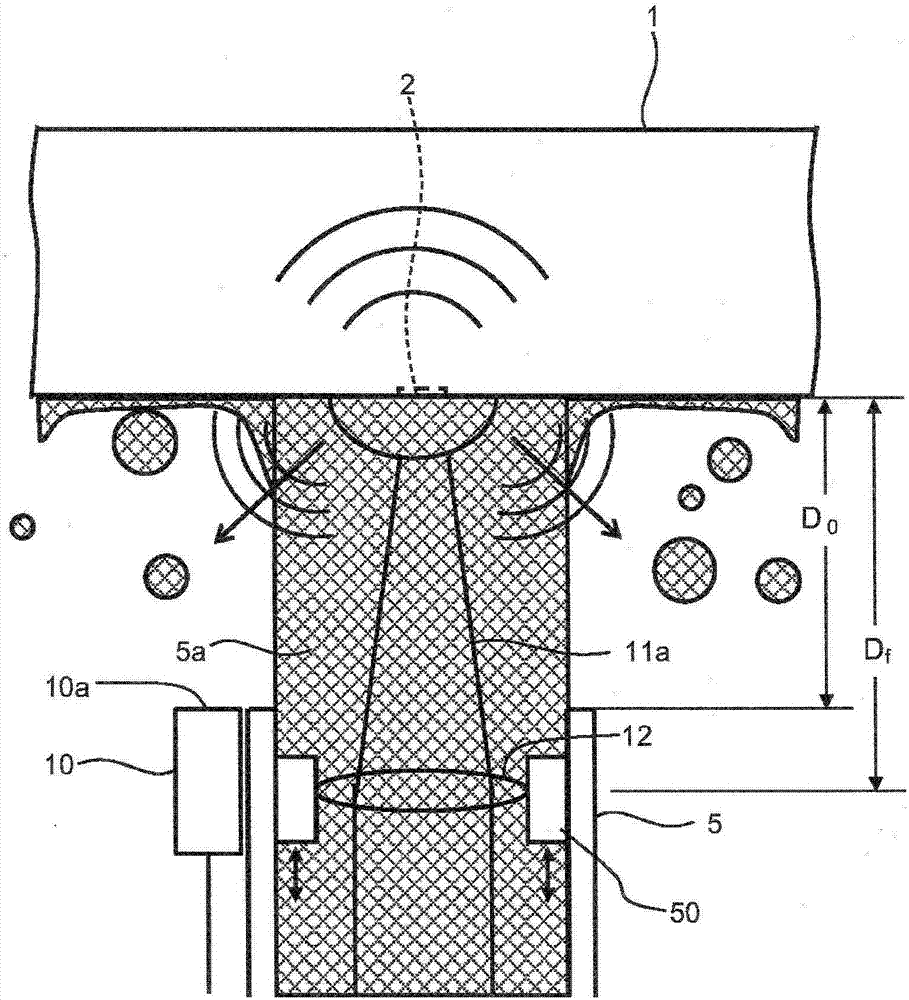
Laser processing apparatus, laser processing method and distance measurement method
ActiveCN106944742AStability determinationUsing reradiationLaser beam welding apparatusLaser lightCalculator
According to an embodiment, a laser processing apparatus (100) has: a laser light source (11); a light collector (12); a water transmitter (5); a sound sensor (10); a time-width acquirer (31); and a distance calculator (32). The laser light source (11) emits the laser light (11a). The light collector (12) collects the laser light (11a) on a workpiece (1). The water transmitter (5) supplies a water stream (5a) to a surface to be treated of the workpiece (1). The sound sensor (10) is provided at a predetermined position relative to at least one of the water transmitter (5) and the light collector (12), and receives a sound coming from the surface to be treated. The time-width acquirer (31) detects time width from a reference time point to a time point when the sound sensor (10) receives the sound. The distance calculator (32) calculates a distance from one of the water transmitter (5) and the light collector (12) to the surface to be treated.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for determining concentration of stable dispersion water solution C60
ActiveCN103712937AGood dispersionStability determinationPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsEmulsionLiquid state
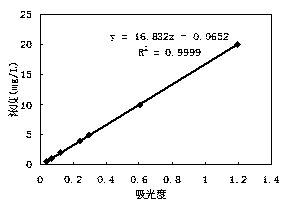
The invention relates to a method for determining the concentration of stable dispersion water solution C60. The method comprises the steps of firstly, preparing different concentrations of C60-Toluene standard solution, determining the absorbance at the wavelength of 334-336nm, performing linear regression to the concentration values and corresponding absorbance value, thus obtaining a standard curve; then taking stable dispersion water solution C60 to be determined, adding calcium chloride solution and toluene, wherein the ratio of the stable dispersion water solution to calcium chloride solution to toluene is 1:(0.5-1):(0.5-2); sealing, performing ultrasonic dispersion for 10-15min to form white emulsion, oscillating and standing to obtain a two-layer solution, freezing for 30-60min in the condition of minus 20 DEG C so as to entirely condense the water phase to be in a solid state and keep an organic phase under a liquid state; entirely absorbing the organic phase solution, determining the absorbance, and calculating the concentration of the C60 according to the standard curve; repeating the steps, adding the concentrations of the C60 obtained by twice extraction, thus obtaining the final determined concentration of the stable dispersion water solution C60 to be determined. The method is simple and fast to operate, and capable of performing batch determination.
Owner:江苏皓海检测技术有限公司
Oncoprotein P185 detection kit
ActiveCN103698536AHigh affinityHigh binding constantDisease diagnosisBiological testingSerum igeMonoclonal antibody
The invention discloses an oncoprotein P185 detection kit. The oncoprotein P185 detection kit comprises oncoprotein P185 monoclonal antibodies, an elisa plate, a positive reference substance, a negative reference substance, cleaning liquor, a stop buffer, horse radish peroxidase-chain avidin and a developing substrate thereof, wherein the oncoprotein P185 monoclonal antibodies comprise an oncoprotein P185 monoclonal antibody enveloped on the elisa plate and the oncoprotein P185 monoclonal antibody marked by biotin. The oncoprotein P185 detection kit disclosed by the invention can be adopted for effectively and stably measuring oncoprotein P185 level in human serum, is high in sensitivity and precision, and good in test repeatability.
Owner:ANHUI ANKE BIOTECHNOLOGY (GRP) CO LTD
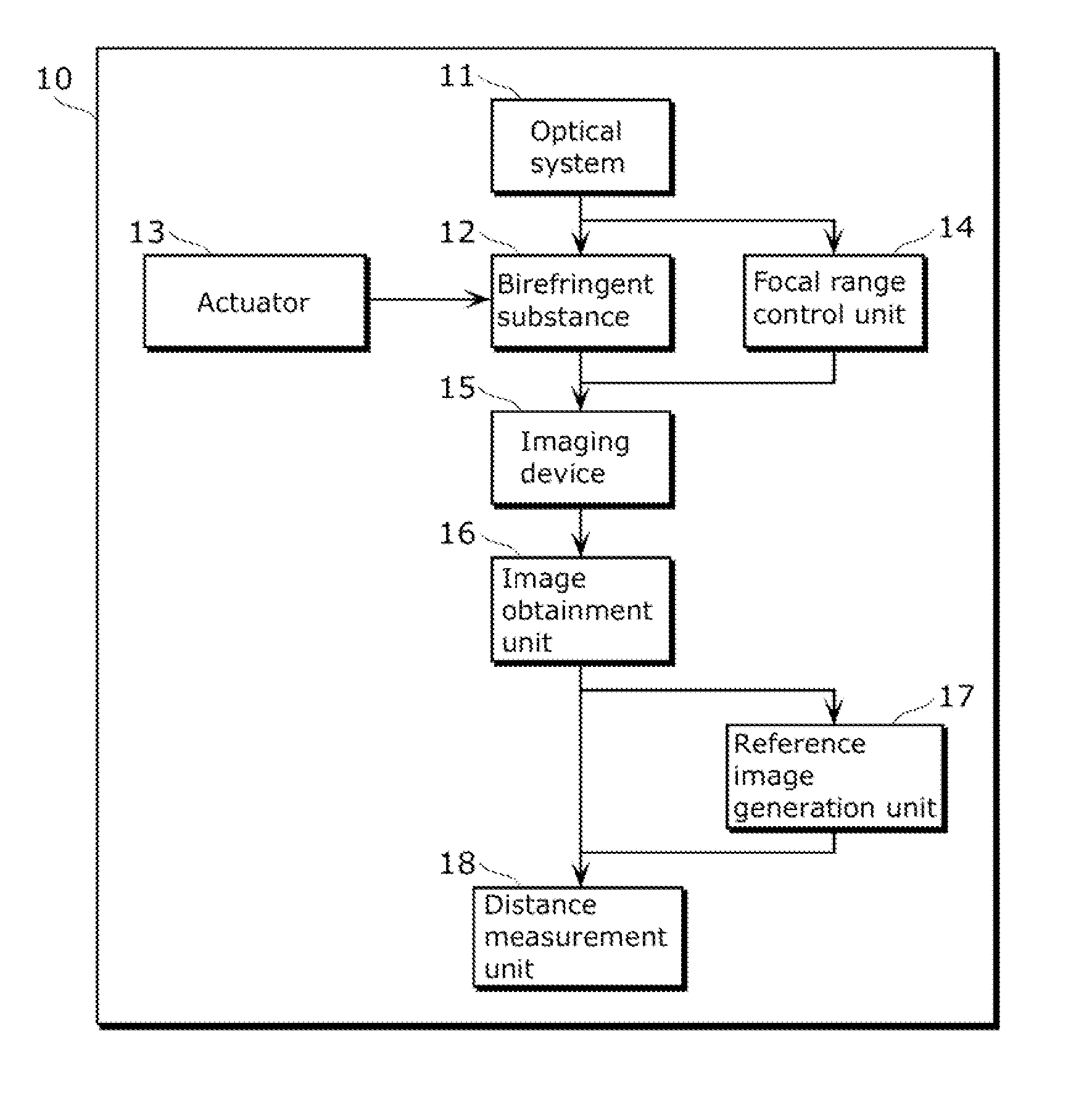
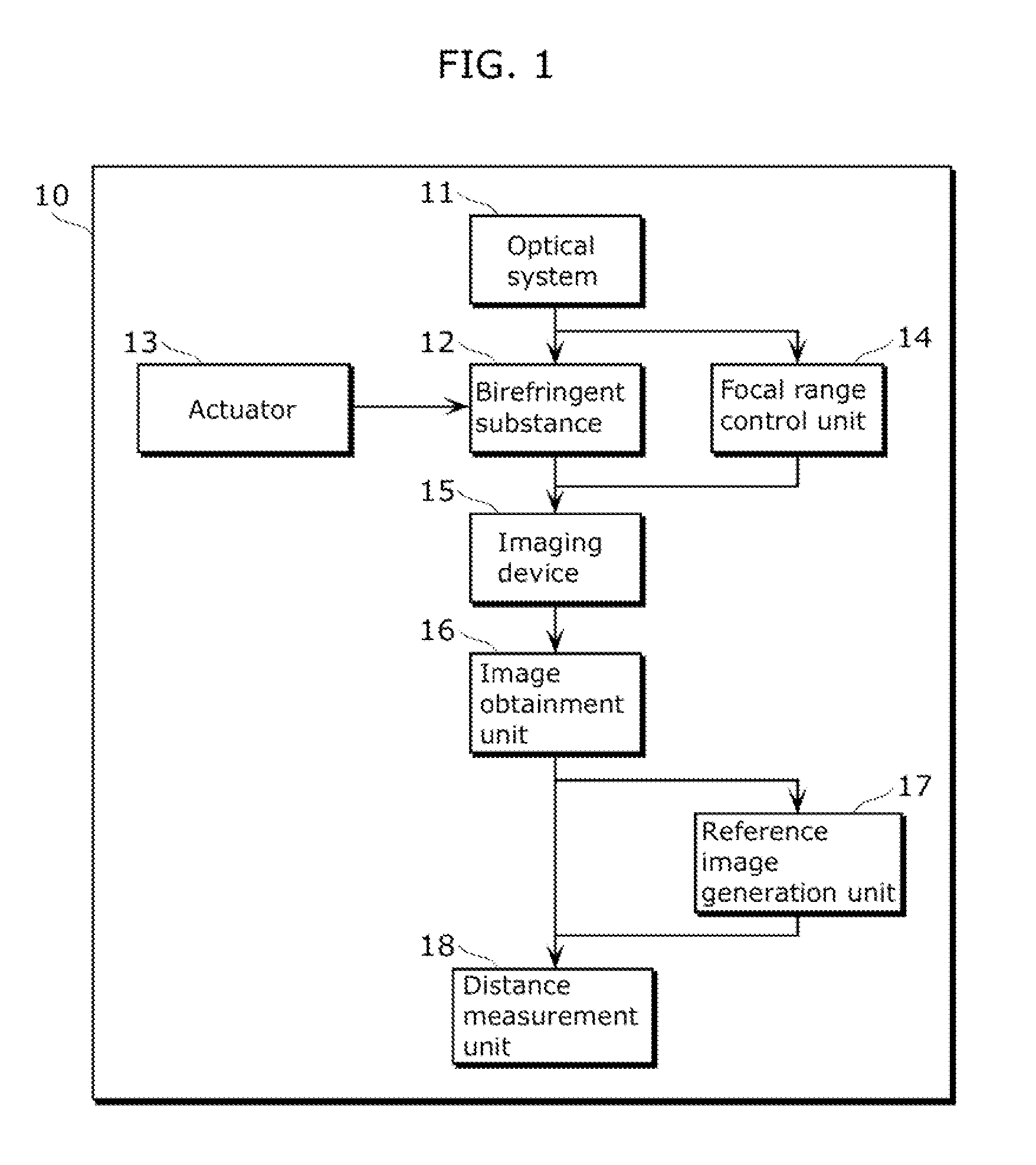
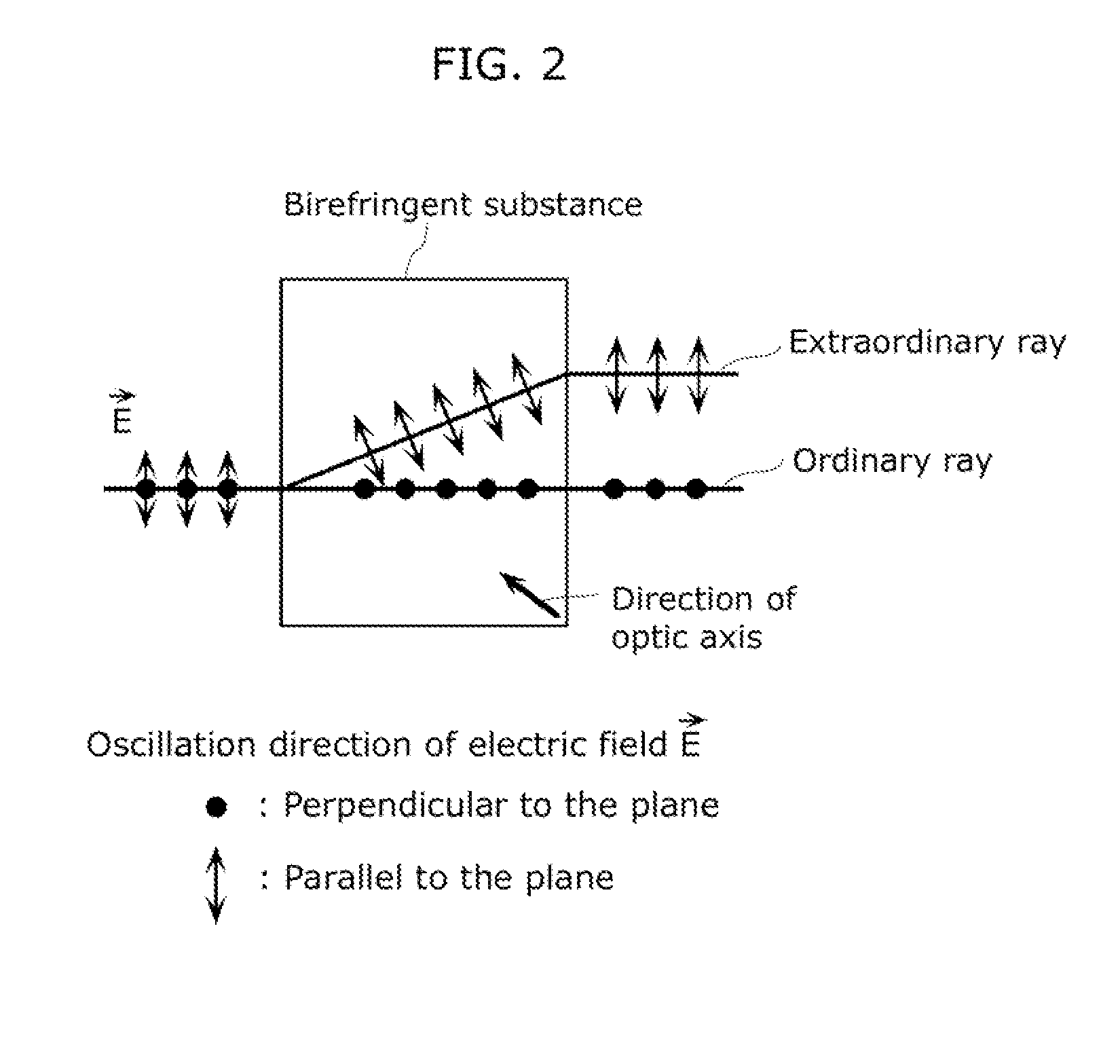
Imaging apparatus, imaging method, program, and integrated circuit
InactiveUS20120314061A1Stability determinationOptical rangefindersColor television detailsDiffusion functionPoint spread function
Ambiguous distinction of PSFs between positions in front of and behind an imaging point corresponding to a distance to an object is eliminated without decreasing the amount of light to be exposed, and the distance to the object is estimated from a small number of captured images. An imaging apparatus includes: an imaging device which captures an image; an optical system for forming an image of an object on the imaging device; a birefringent substance having a birefringence effect; and a distance measurement unit which measures a distance from the imaging device to the object, using the captured image and a point spread function having a form changed by the optical element between positions in front of and behind an image point corresponding to the distance to the object.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
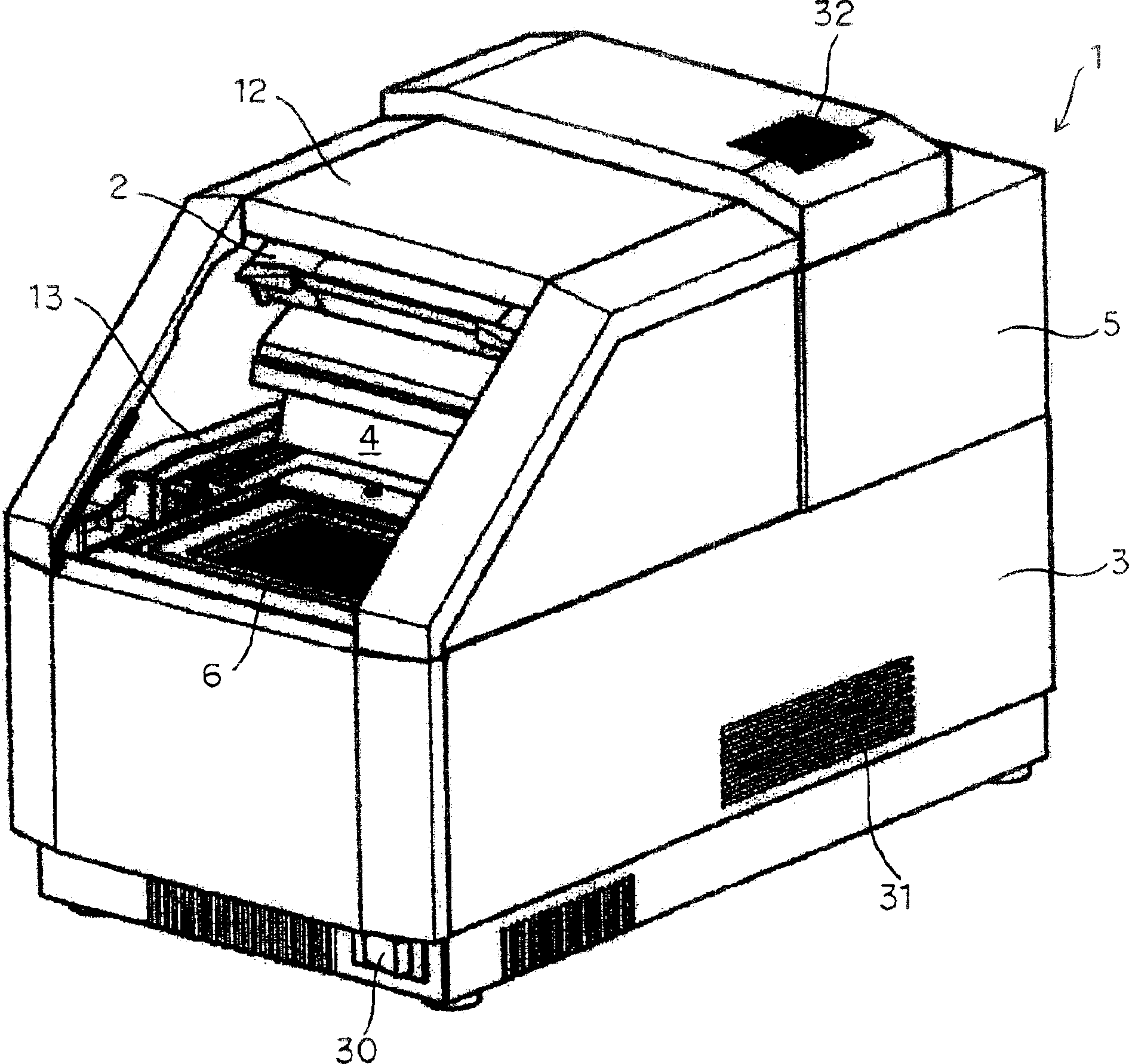
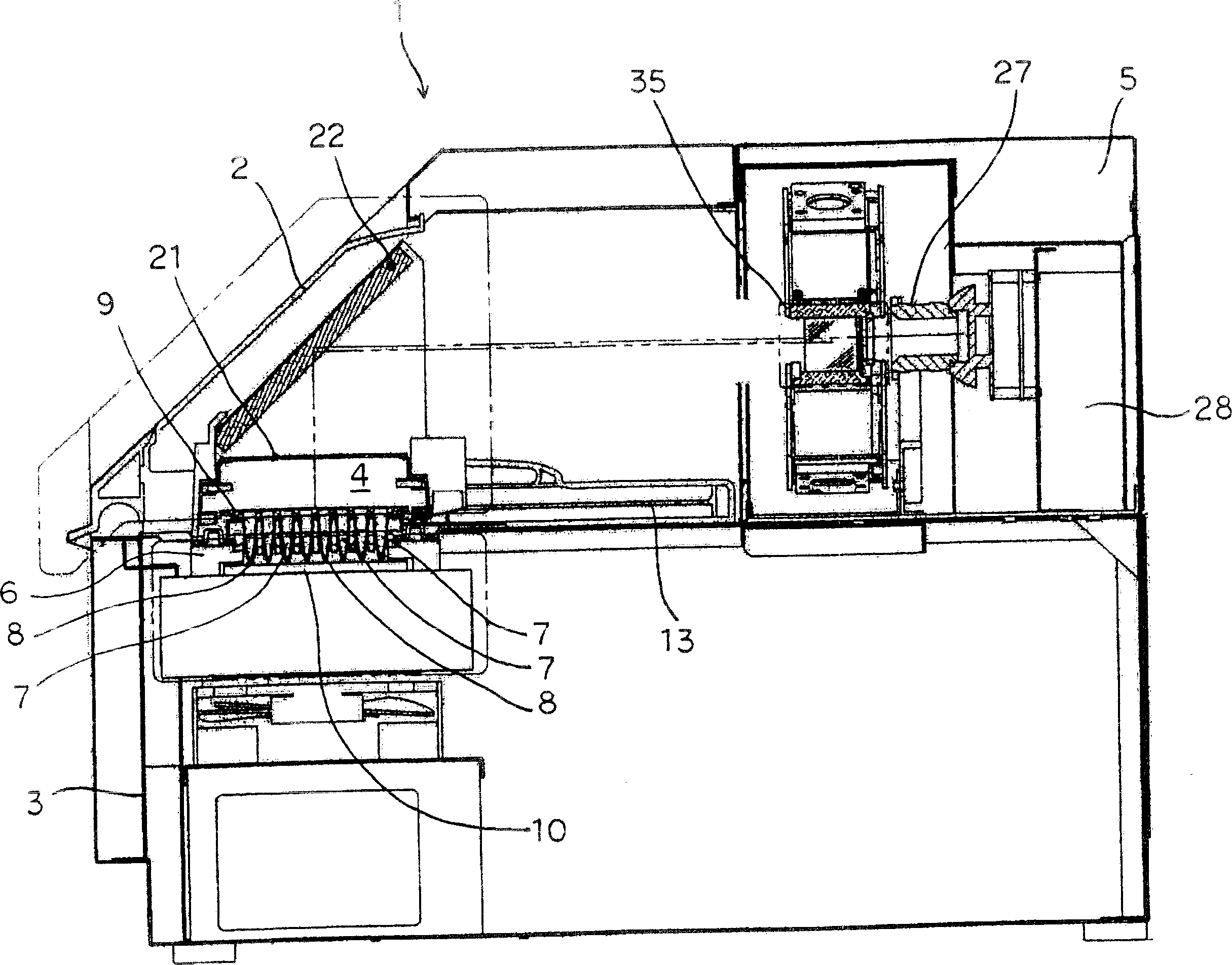
Reaction detecting device
ActiveCN1908153AMinimize variation in assay sensitivityReduce the overall heightBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceReaction chamber
An object is to provide a reaction detecting device in which a height dimension of the device itself can be set to be small to realize space saving, unevenness of measurement sensitivity for each reaction container is minimized, and high-sensitivity and high-precision reaction detecting is possible, the device includes: a reflective plate disposed above a temperature controllable reaction block disposed in a reaction chamber constituted in a main body to reflect light; and a light source lamp and a camera arranged in the main body, the light from the light source lamp is reflected by the reflective plate to enter each reaction container from above, and light such as fluorescence directed upwards from a reaction specimen is reflected by the reflective plate to enter the camera.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
Cuff for blood pressure gauge, and blood pressure gauge having the cuff
ActiveCN101977548AEasy to wearReliable windingEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographySize differenceBlood pressure
Provided is a blood pressure gauge cuff (20) comprising an upper arm supporting bed (30) which can support an upper arm, and an arm band (40) which can be wound on the upper arm. The upper arm supporting bed (30) includes an upper arm supporting face (31a) for supporting the upper arm applied thereto, a take-up mechanism which is enabled, by pulling one end portion of the arm band (40) in the take-up direction, to take up a portion near the one end portion of the arm band (40), and a hook (36) capable of retaining the portion near the other end portion of the arm band (40) extracted from the take-up mechanism against the tension of the take-up mechanism. The upper arm, which is supported on the upper arm supporting bed (30), is fastened, while the portion near the other end portion of thearm band (40) is being retained by the hook (36), by the upper arm supporting face (31a) and the arm band (40) of the portion extracted from the take-up mechanism. The blood pressure gauge cuff thus constituted can be easily mounted on the upper arm as a measurement region having a size difference, and its reliable winding on the upper arm can be repeated at each time of measurement.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
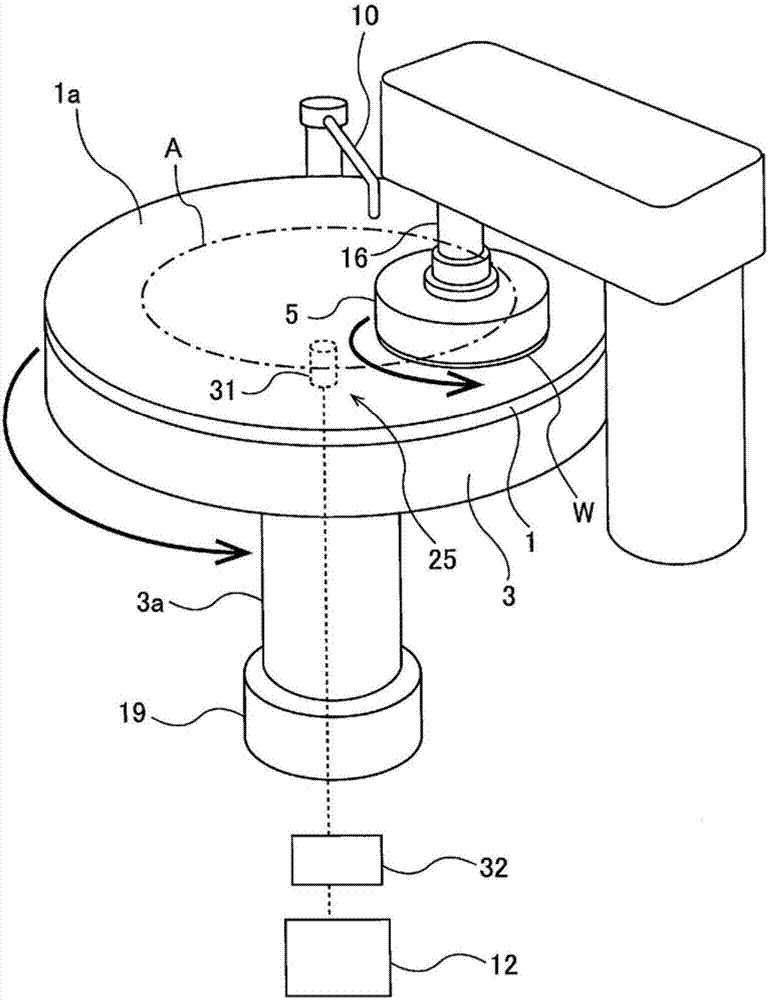
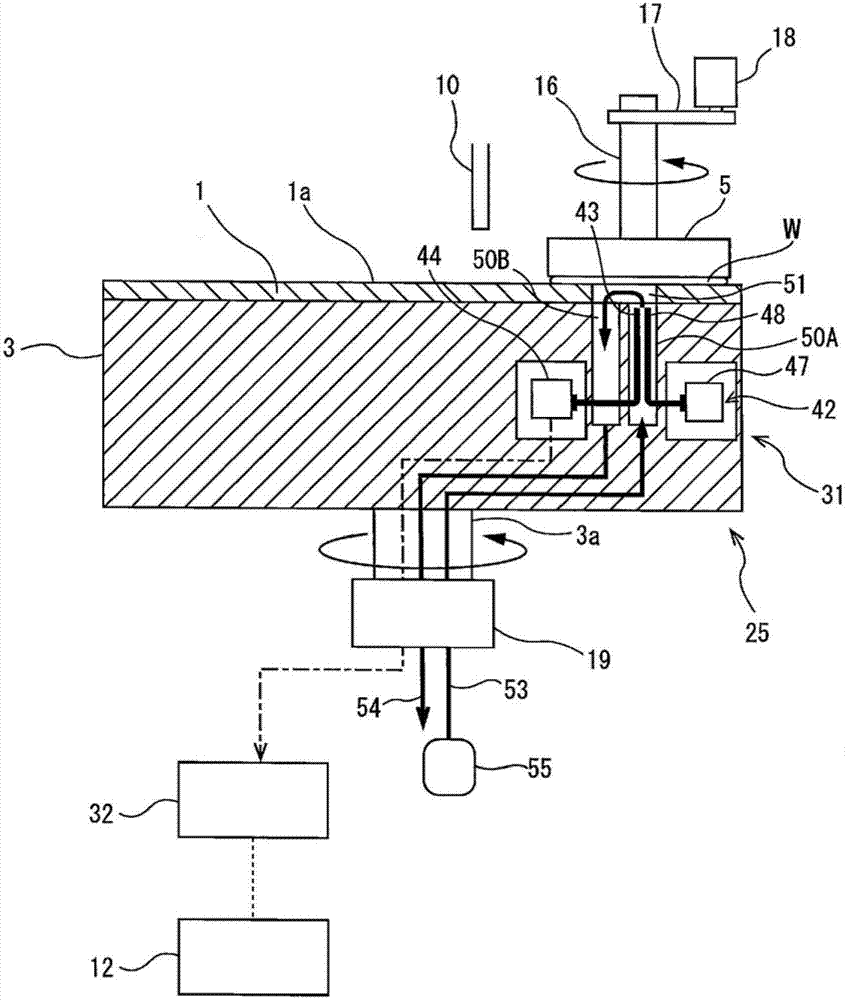
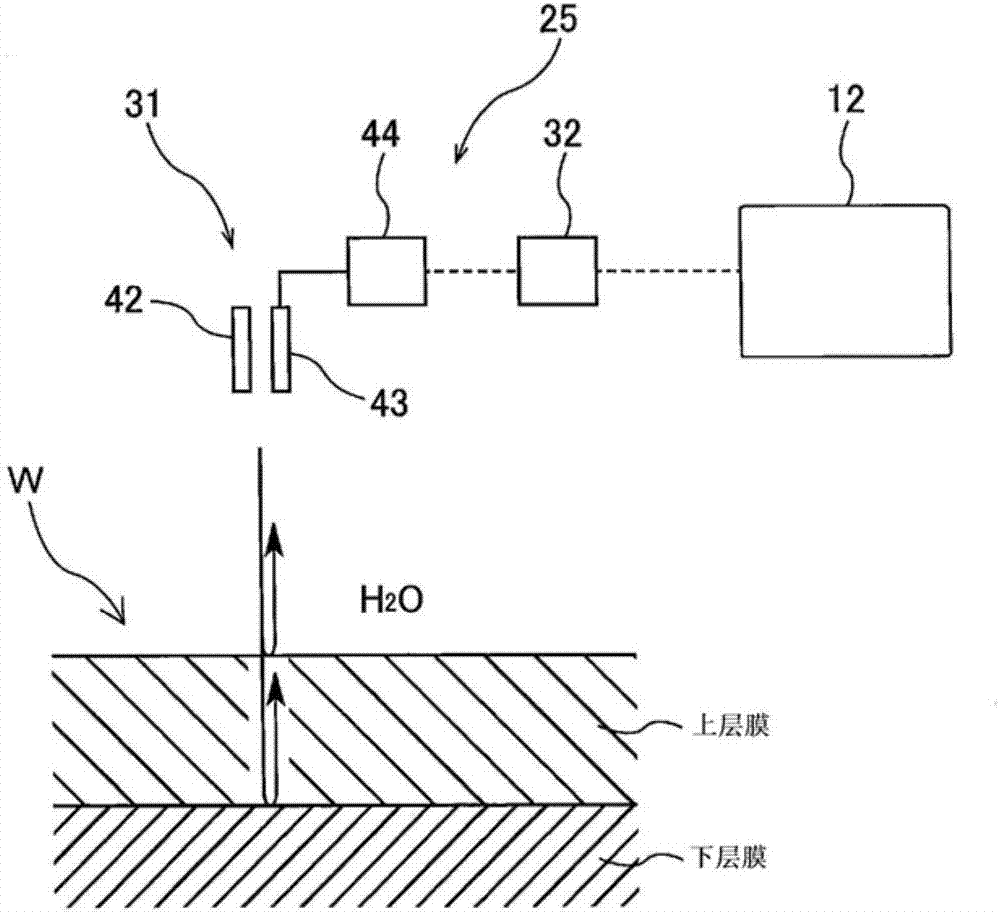
Film thickness measuring method, film thickness measuring device, polishing method, and polishing device
ActiveCN107429989AStability determinationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLength waveUltimate tensile strength
The present invention relates to a film thickness measuring method that detects a film thickness by analyzing optical information contained in light reflected from a substrate. The film thickness measuring method includes the steps of generating a spectral waveform showing the relationship between the strength and wavelength of the reflected light from the substrate (W), determining the intensity of the frequency component and corresponding film thickness by performing a Fourier transformation process on the spectral waveform, determining the plurality of maximal values (M1, M2) of the intensity of the frequency component, and selecting one film thickness according to a selection standard from film thicknesses (t1, t2) corresponding respectively to the maximal values (M1, M2). The selection standard is either selecting the Nth largest film thickness or selecting the Nth smallest film thickness, wherein N is a natural number defined beforehand.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Detection apparatus, system and method for photosensitizer concentration
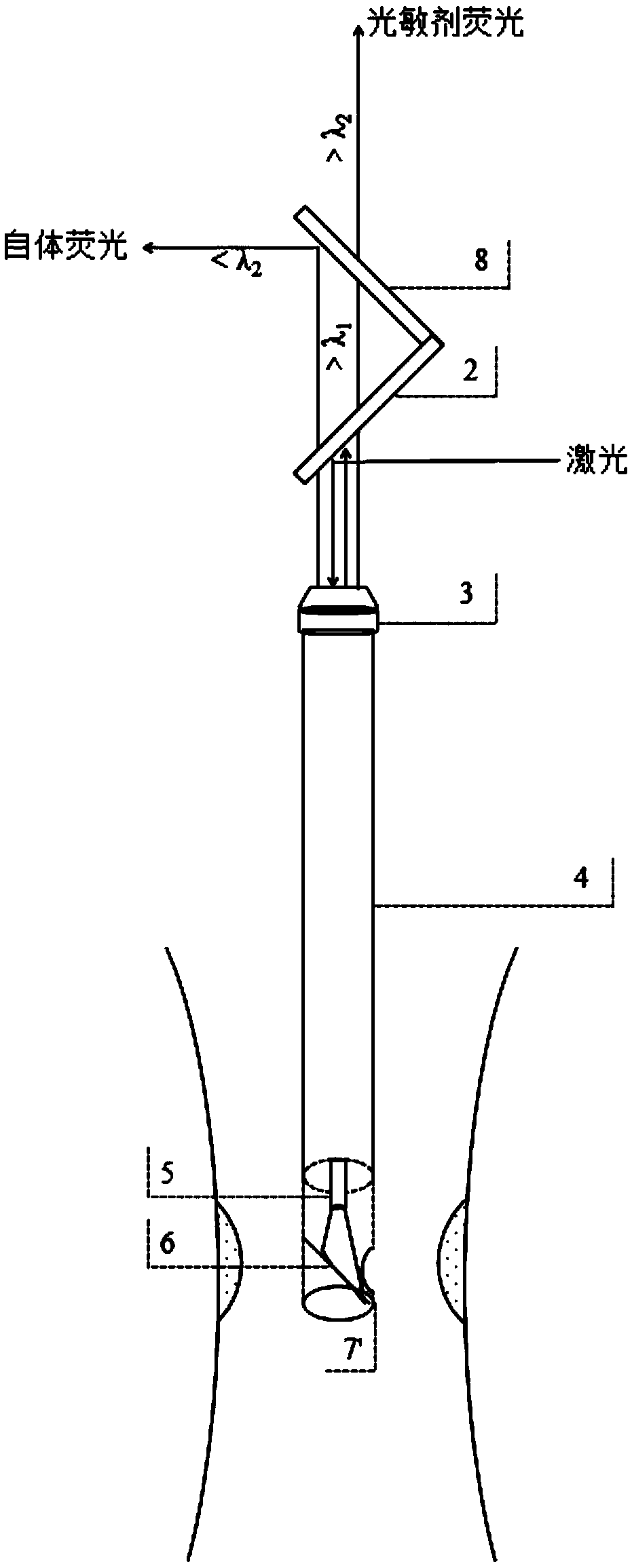
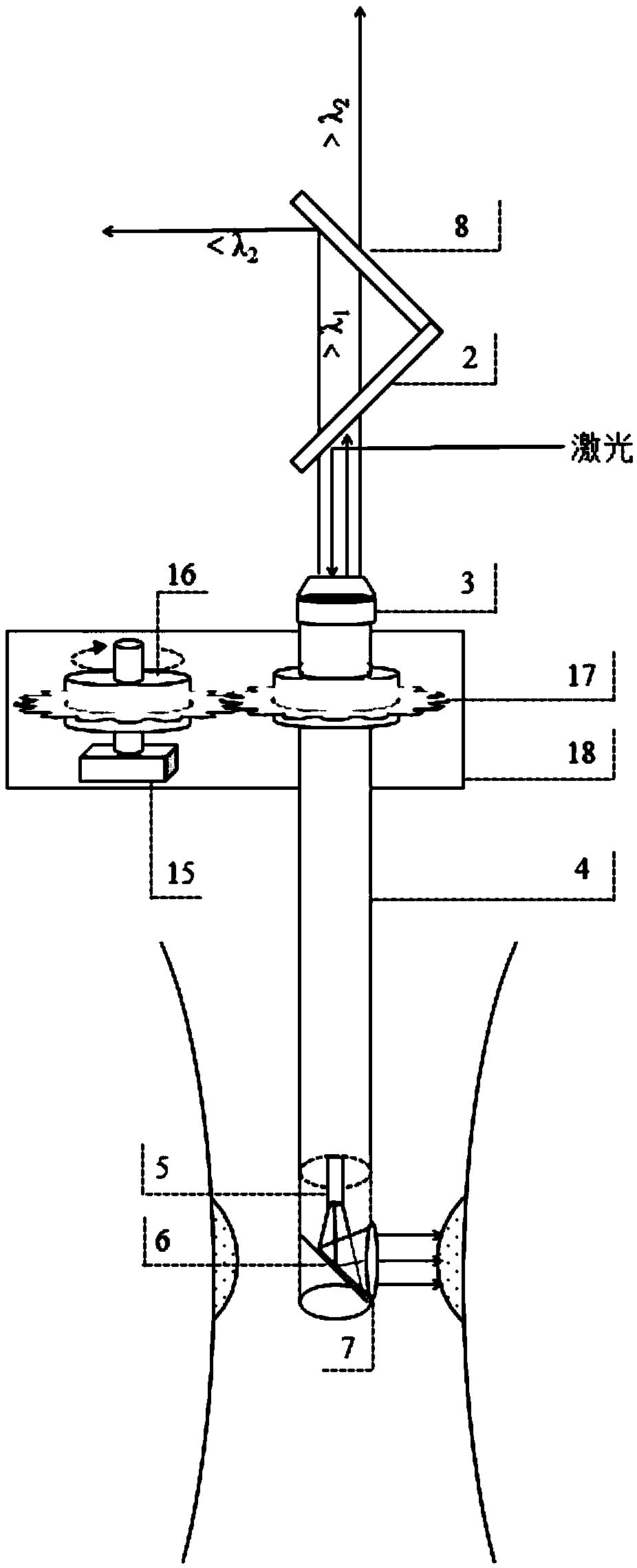
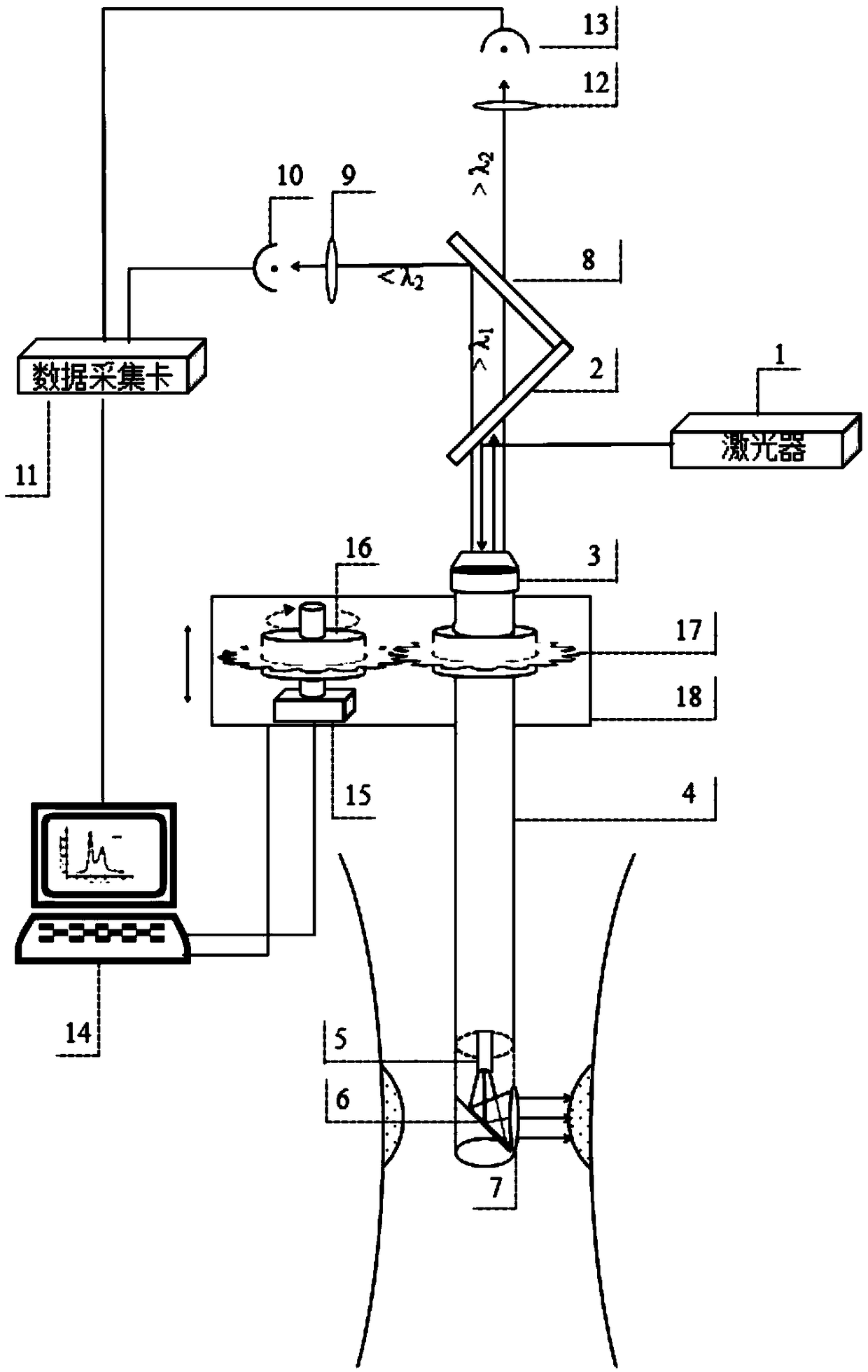
ActiveCN108956564AReal-time accurate detectionIncrease luminous fluxFluorescence/phosphorescencePhotodynamic therapyPhotosensitizer
The invention discloses a detection apparatus, system and method for photosensitizer concentration. The detection apparatus for photosensitizer concentration comprises an optical fiber, a reflector, acoupler, a first dichroic mirror and a second dichroic mirror, wherein one end of the optical fiber is provided with the reflector, and the other end of the optical fiber is connected with the coupler; and the coupler, the first dichroic mirror and the second dichroic mirror are sequentially located on the same straight line. The photosensitizer concentration detection apparatus is applied to thephotosensitizer concentration detection system, can conveniently and accurately capture autofluorescence and the fluorescence signals of a photosensitizer, quickly calculate an integral value and perform concentration analysis, is applicable to a method for calculating the concentration of the photosensitizer based on a fluorescence intensity ratio, greatly improves photodynamic therapy efficiency, reduces cost, and is extremely applicable to real-time in-vivo detection of an endoscope due to small size.
Owner:深圳市优迈医学科技有限公司
Complex of labeled probe and water-soluble carrier
InactiveCN102893151AHigh sensitivityGood reproducibilityBiological testingWater solubleBiotin-binding proteins
Owner:EIKEN KAGAKU +1
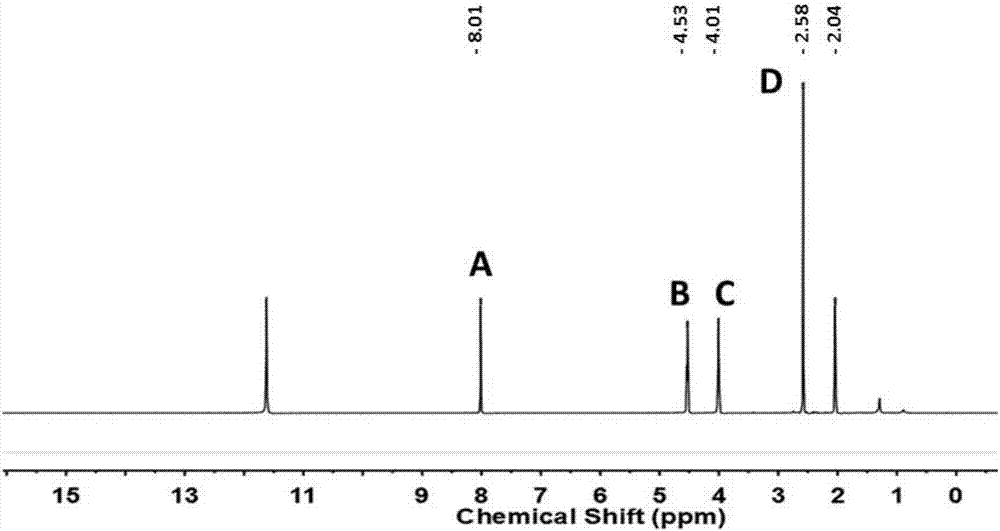
Application of metronidazole as internal standard substance to H-nuclear magnetic resonance technology
InactiveCN107505348AStability determinationAccurate measurementAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceHydrogen
The invention discloses an application of metronidazole as an internal standard substance to an H-nuclear magnetic resonance technology. The specific application of metronidazole comprises at least one of the following 1)-3): 1) structural analysis of a to-be-detected compound; 2) qualitative analysis of the to-be-detected compound; 3) quantitative analysis of the to-be-detected compound. The purity of metronidazole is 99.8% plus or minus 0.4%, and applicable solvents refer to various deuterated solvents. High-purity metronidazole is taken as the internal standard substance, a hydrogen spectrum is simple, quantitative peak range is wider, metronidazole can be dissolved in various deuterated solvents and has the advantage of traceability, and the content of the to-be-detected substance can be determined stably and accurately.
Owner:INST OF QUALITY STANDARD & TESTING TECH FOR AGRO PROD OF CAAS
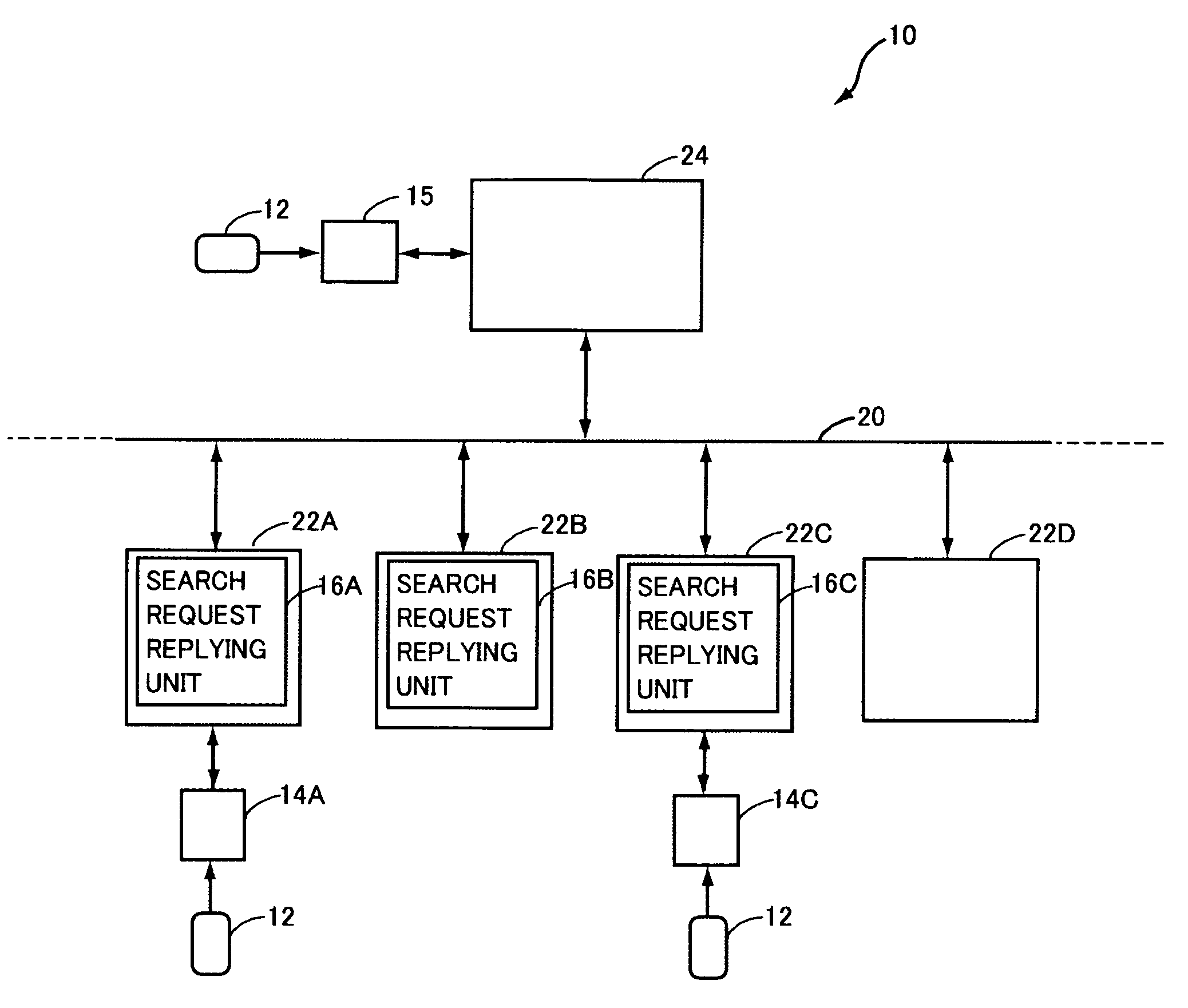
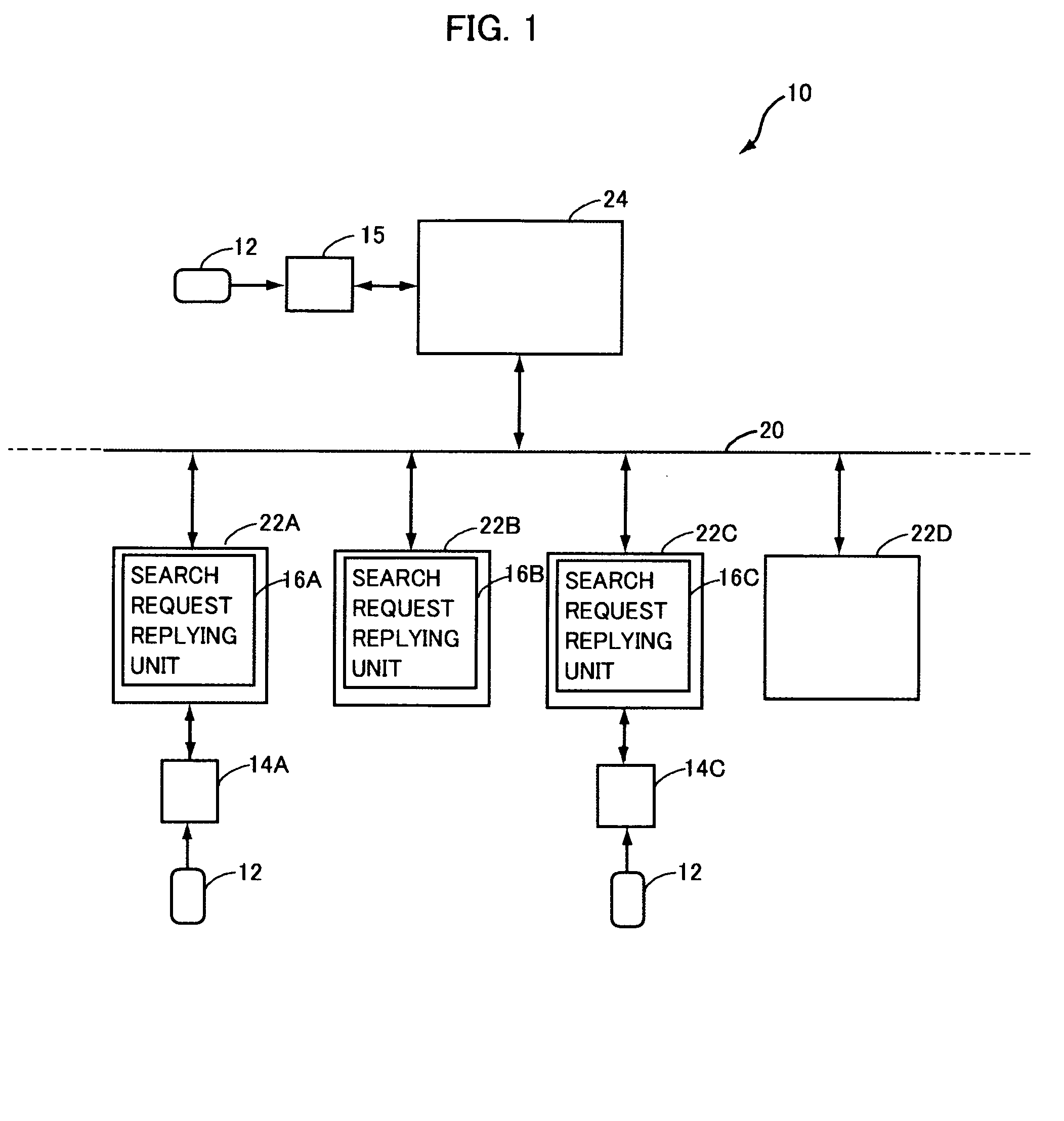
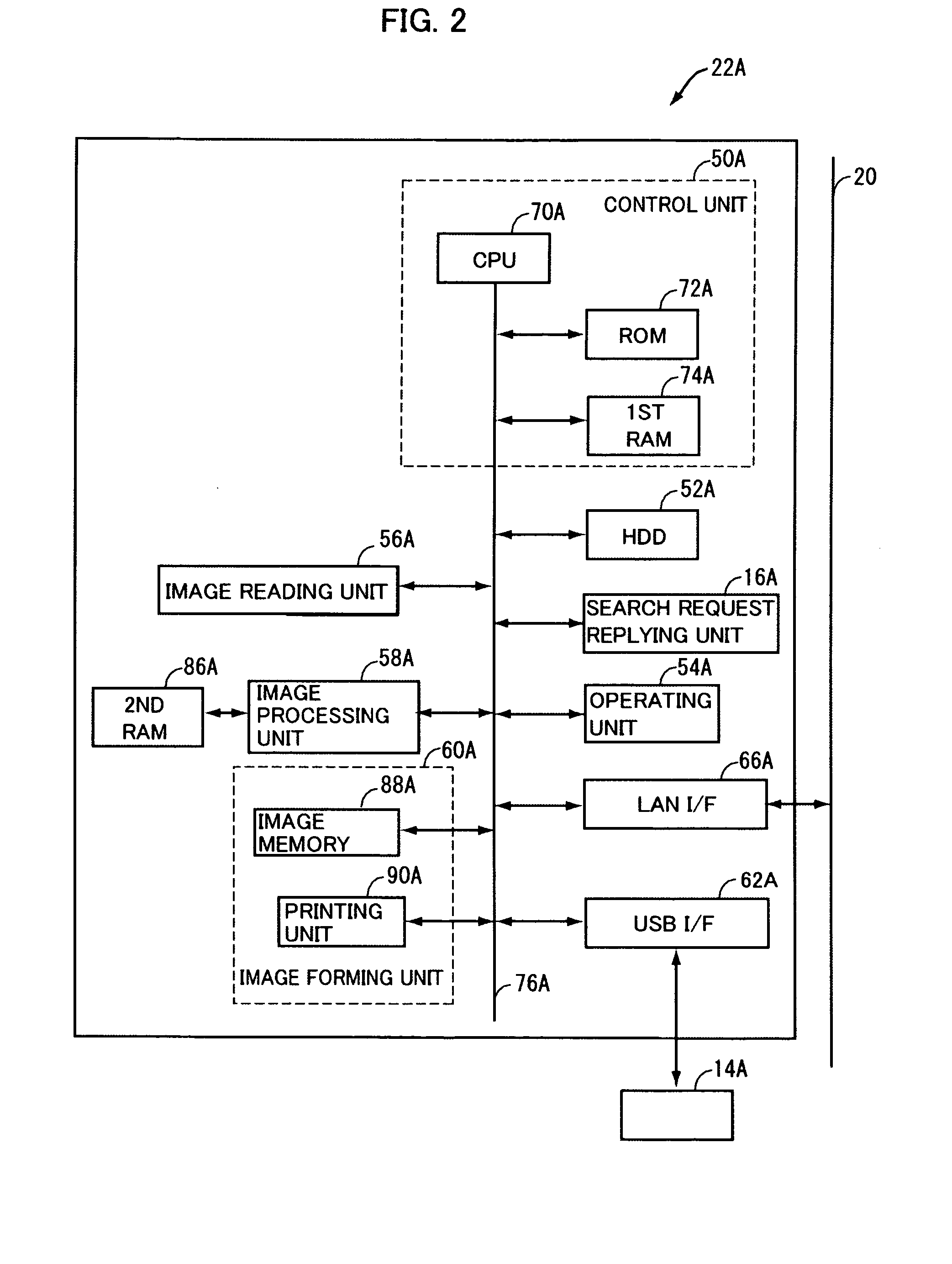
Authentication system, terminal and information processing device, having function of performing stable authentication
ActiveUS20100071047A1Stability determinationSave troubleDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationInformation processingCard reader
To provide an authentication system allowing stable determination as to whether a user is a registered user while saving user's trouble, an information processing device capable of data communication with a plurality of image forming apparatuses extracts an image forming apparatus connected to an IC card reader from the plurality of image forming apparatuses, based on reply signals transmitted from the plurality of image forming apparatuses, and transmits user account information of registered users to the extracted image forming apparatus. The image forming apparatus connectable to the IC card reader performs, if it is determined that the IC card reader is connected to the image forming apparatus, the authentication process based on the user account information of registered users received from the information processing device and on the information read by the IC card reader.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for quickly measuring content of five rare earth elements in edible packing material
InactiveCN105606436AReduce processing timeNo pollutionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRare-earth elementHigh pressure
The invention discloses a method for quickly measuring content of five rare earth elements in an edible packing material. The method comprises the following steps: performing preliminary heating using power of 1200 W through a high-pressure closed microwave digestion method for an HNO3 system, heating to 80 DEG C within 4 min, and stewing for 3 min; performing secondary heating for 1 min to raise the temperature from 80 DEG C to 100 DEG C, and stewing for 2 min; performing third heating to raise the temperature from 100 DEG C to 120 DEG C within 1 min, and stewing for 2 min; performing fourth heating to raise the temperature from 120 DEG C to 180 DEG C within 2 min, and stewing for 15 min. The shortcomings of complicated program, more reagents, long digestion time, pollution to the environment and influence on the health of a human body are overcome; the technical defects of low sensitivity, high detection limit, high spectral interference and incapability of simultaneously measuring the content of various elements are overcome; therefore, the content of the five rare earth elements can be sensitively, efficiently, quickly, synchronously and accurately detected, and the method has great application value.
Owner:新疆出入境检验检疫局检验检疫技术中心
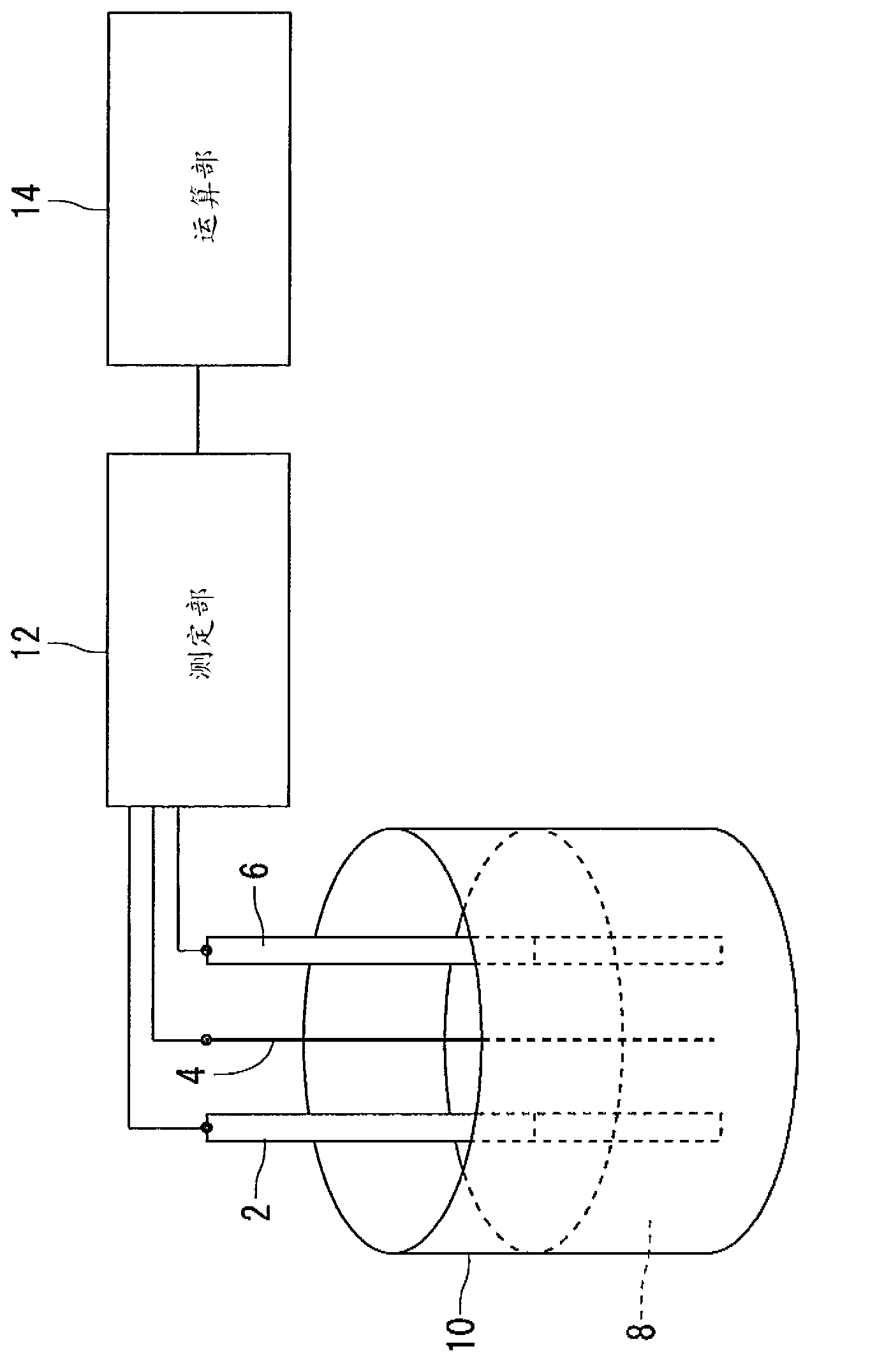
Liquid densitometer
InactiveCN102159935AStability determinationTransmissivity measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsLiquid densityEngineering
A liquid density in a liquid supply tube, through which the liquid is supplied, is stably measured from the outside of the liquid supply tube. A liquid densitometer is provided with a liquid supply tube (14, 16) through which a liquid is supplied, a light transmission unit (15) set at a halfway point of the liquid supply tube (14, 16), a light projection unit (9, 22) that irradiates measurement light to the light transmission unit (15), a light reception unit (10, 23) that receives the measurement light to transmit through the light transmission unit (15), a support member (31) that supports movably the light projection unit (9, 22) and the light reception unit (10, 23) so as to move a measurement position (32) from which the light is irradiated to the light transmission unit (15) and at which the light reception unit (10, 23); receives the light transmitting through the light transmission unit (15), a measurement position moving mechanism (2) that makes the support member (31) move in order for the measurement position (32) to move in a predetermined area of the light transmission unit (15), and a data processing unit that acquires light intensity data which the light reception unit (10, 23) receives at a plurality of measurement positions (32) to calculate a density of the liquid, which flows through the liquid supply tube (14, 16), in accordance with the plurality of the light receiving intensities.
Owner:KURASHIKI BOSEKI KK
Breast cancer triple rapid detection kit
ActiveCN106855575AHigh sensitivityPlay the role of multi-stage amplificationMaterial analysisBiotinSerum dilution
The invention belongs to the biological detection field, and concretely relates to a breast cancer triple rapid detection kit of tumor serum markers CA125, HE4 and P-her2. The breast cancer triple rapid detection kit is mainly composed of an antibody coated well, a biotin antibody coated plate, a serum dilution solution, a horseradish peroxidase, tetramethyl benzidine, hydrochloric acid, a negative reference liquid and a positive reference liquid. The breast cancer triple rapid detection kit can detect the expression level of the CA125, HE4 and P-her2 in postoperative patients or recurrent or metastatic tumor patients, and is of great significance to clinic diagnosis of the breast cancer. The breast cancer triple rapid detection kit reduces interference of other substances in serum, greatly improves the accuracy and the stability of a detection result, and facilitates the early stage diagnosis and the prognosis treatment of the breast cancer patients.
Owner:珠海博美生物科技有限公司
Polarographic residual chlorine sensor
InactiveCN103185742ADetermination of high precision and high residual chlorine concentrationStability determinationMaterial electrochemical variablesResidual chlorinePhysics
The present invention provides a polarographic residual chlorine sensor capable of reducing the change over time of the electrode surface area of a working electrode. The polarographic residual chlorine sensor determiners the residual chlorine concentration by at least immersing the working electrode (2) and a counter electrode in the water to be measured, and measuring the current flow between the working electrode and a counter electrode caused by an oxidation-reduction reaction. The cross-sectional areas of a conductive material (16) constituting the working electrode perpendicular to the axial direction at different positions are the same shape, and are covered by a casing (17) in the manner of leaving axially two end faces, and an end face is immersed in the water to be measured.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for quantitatively detecting glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in blood serum
InactiveCN107102146AHigh single event brightness characteristicsGood water solubilityBiological testingGlial fibrillary acidic proteinDiethylenetriamine
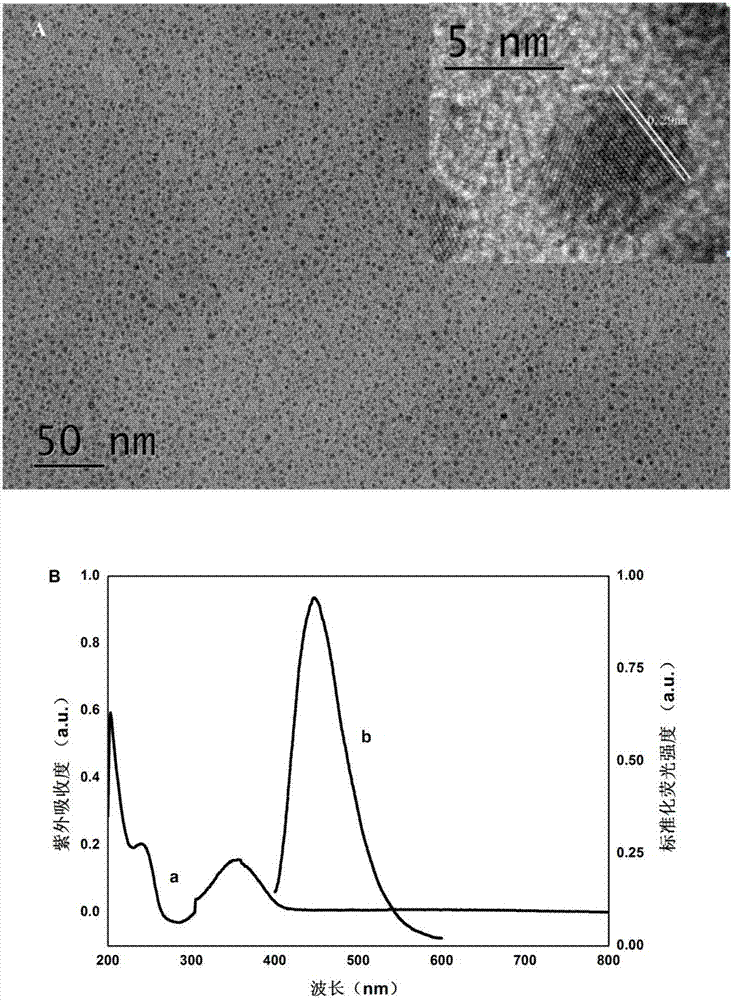
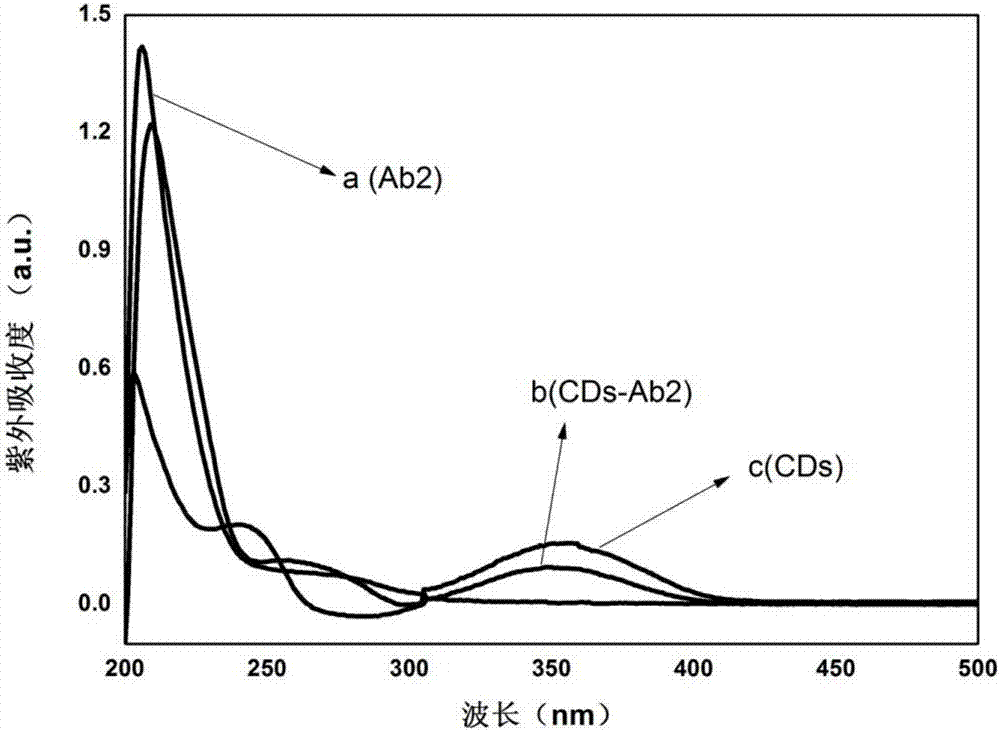
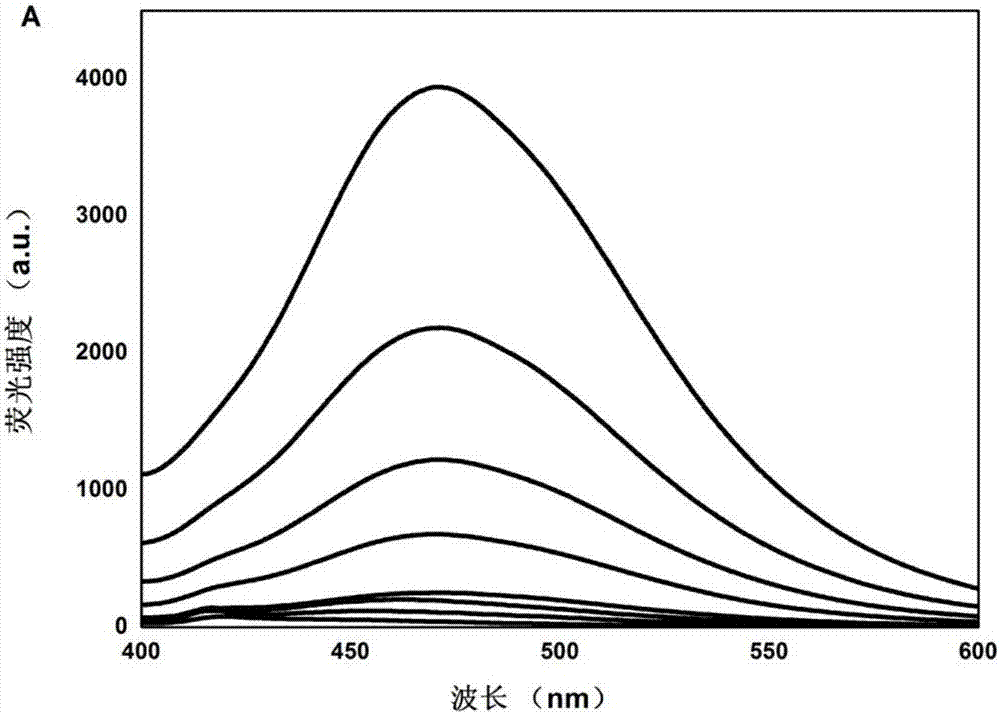
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in a blood serum. The method comprises the steps of firstly, purifying a resin connecting antibody Ab1 through protein A / G agarose, capturing GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein) in the blood serum to form PA / G-Ab1-GFAP, and centrifugally cleaning to achieve the aims of separation and enrichment; secondly, adopting citric acid as a carbon source and diethylenetriamine as a passivator for synthesizing carbon dots (CDs), connecting with an antibody Ab2 through an amido bond, and forming a fluorescence labelled probe CDs-Ab2; then combining the PA / G-Ab1-GFAP and the CDs-Ab2 to form a sandwich structure PA / G-Ab1-GFAP-Ab2-CDs, detecting fluorescence intensity, and obtaining the content of the GFAP in the blood serum according to a standard curve. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity and simplicity and convenience in detection, and the characteristics of high selectivity and high affinity of immunoreaction, and can be directly applied in determining the GFAP in the blood serum.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com