Tomato yellowing-to-green gene SlRHBDD2 and application thereof
A tomato yellow and gene technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as limitations, and achieve the effect of simplifying the screening steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
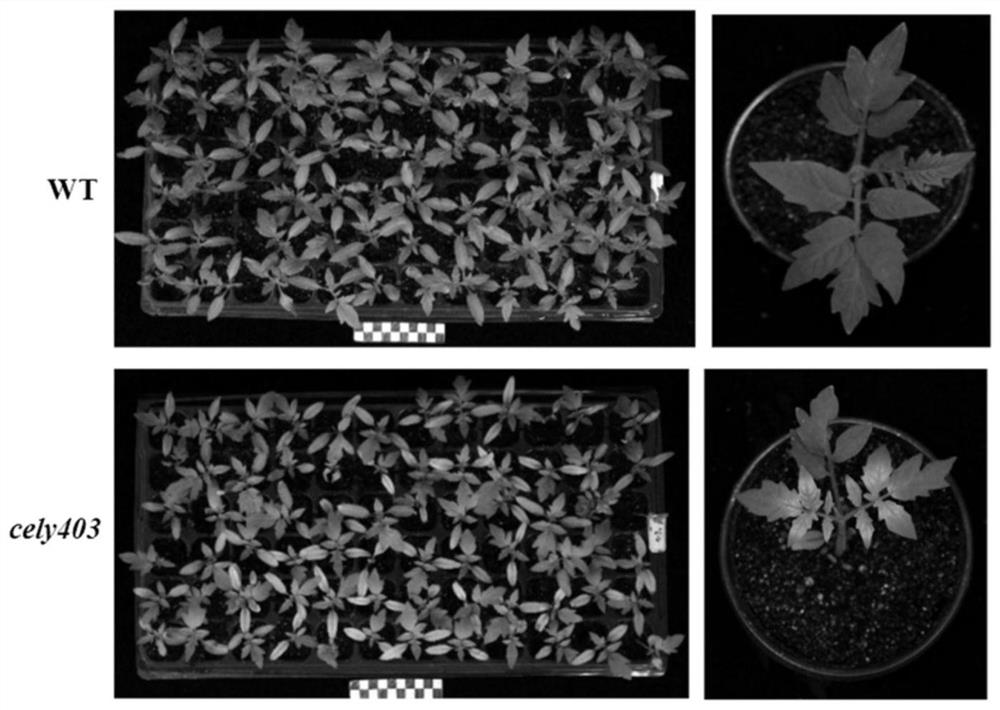
[0023] Example 1. Acquisition and Character Identification of Tomato Yellow-to-Green Leaf Color Mutant "cely403"
[0024] 1. Acquisition of tomato yellow-turned-green leaf color mutant "cely403"
[0025] The tomato yellow-to-green leaf color mutant was derived from the high-generation inbred line "T12404" of the American tomato germplasm resource bank (TGRC) "LA3320". A mutant plant with natural leaf color was found during field planting. The cotyledons turn yellow, the heart leaves are yellow-green at the seedling stage, and the leaves gradually turn green and return to normal at the later stage. Mutant plants were self-seed to obtain mutant lines. After multiple generations of self-propagation and selection, the mutant traits have been stabilized. The mutant was named "cely403" (Cotyledon and EarlyLeaf Yellowing). The Tomato Research Group of the Technical College saves and makes available to the outside world.
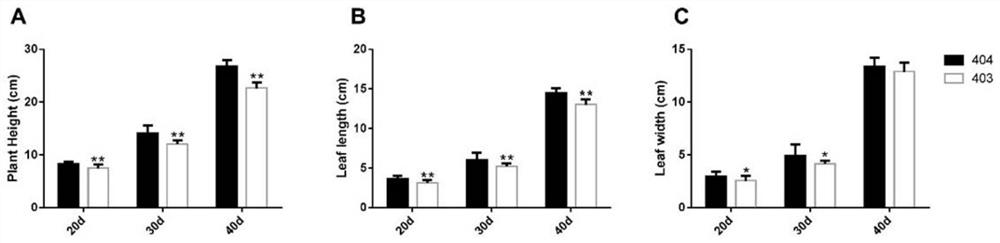
[0026] 2. Character identification of tomato yellow-to-green...
Embodiment 2
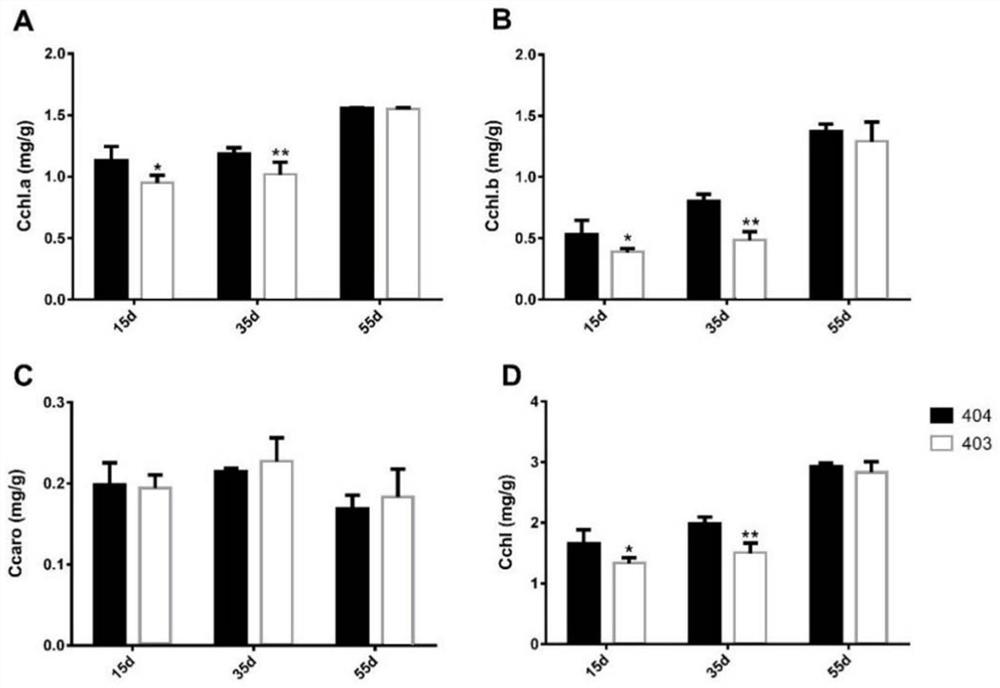
[0028] Embodiment 2, comparison of chlorophyll content and photosynthetic characteristics of tomato yellowing to green leaf color mutant
[0029] At different periods after sowing, randomly select 12 individual plants with the same growth from the mutant and the wild type, select the second true leaf that is fully expanded under the growth point, cut it into 2-3cm, weigh 0.2g and soak it in 25mL A mixture of acetone and ethanol (volume ratio 95% acetone: absolute ethanol = 2:1), sealed and protected from light, and cultured at 26° C. in the dark for 24 hours. Measure the OD value of the extract solution at three wavelengths of 470nm, 645nm and 663nm with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, and repeat 3 times. According to the Arnon calculation method improved by Livchtenthaler, the contents of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoids were calculated respectively, and the total chlorophyll content was the sum of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The results showed that, compa...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3, Genetic Analysis and Gene Mapping of Tomato Yellowing to Green Leaf Color Mutation Character
[0032] 1. Genetic analysis of the mutation trait of tomato from yellow to green leaf color
[0033] Crossing mutant cely403 with wild-type 404 yielded F 1 Generation, self-crossing to get F 2 Generation, using F 2 Genetic analysis of segregating populations. The results showed that F 1 The leaf color of the generation plant is green, which is the wild-type phenotype; sowing F 2 In this generation, the leaf color of 483 plants was counted, and the number of plants with normal leaf color and yellowed leaf color was 378 and 105, and the chi-square test results (X 2 =2.572 0.05,1 =3.84) in line with the segregation ratio of 3:1, the above results were repeated three times, and the experimental results all showed that the mutant trait was controlled by a recessive single gene.
[0034] 2. Gene mapping of tomato yellow to green leaf mutation trait
[0035] Use F ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com