Antibacterial nano material with high biocompatibility and preparation method thereof, cell membrane extraction method and membrane-coated particle preparation method
A nanoparticle and nanomaterial technology, applied in the field of antibacterial materials, can solve the problems of reducing treatment efficiency and short blood retention time, and achieve high bactericidal effect and high biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
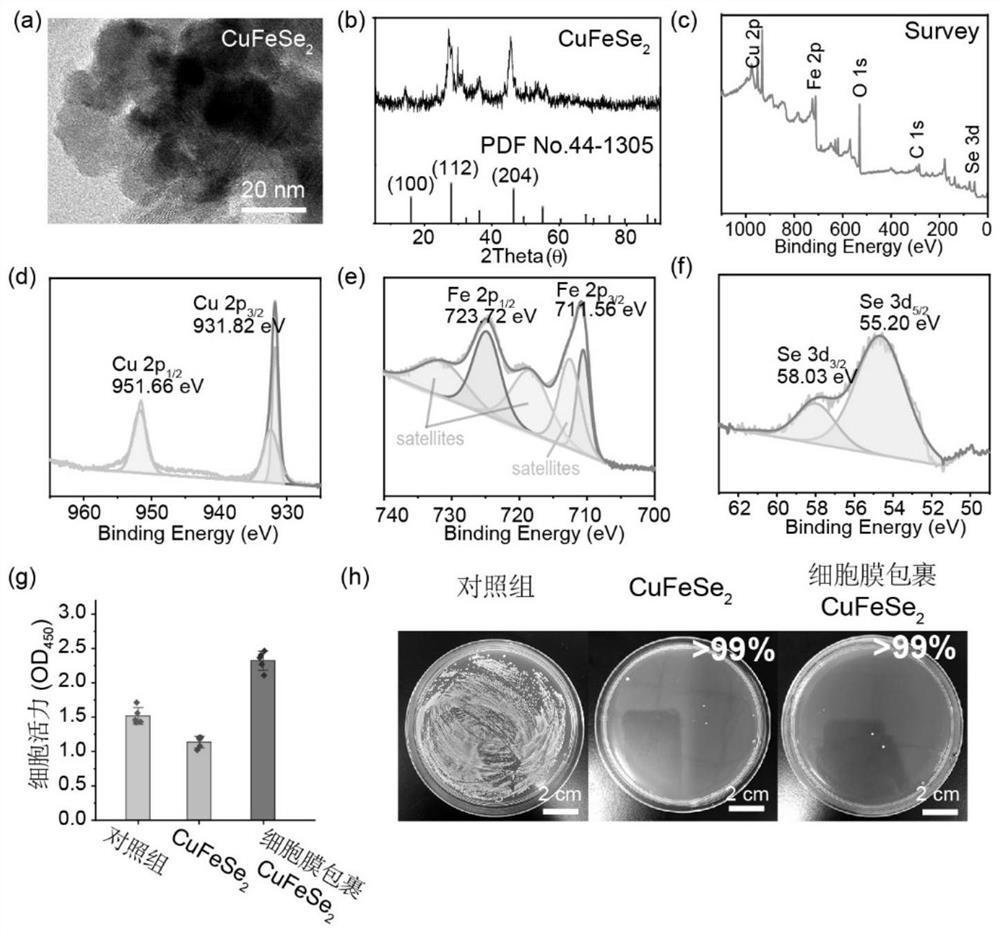
[0040] Bacterial culture: Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923) was cultured in Tryptone Broth (TSB). A single colony of Staphylococcus aureus on solid TSB agar plate was transferred to TSB liquid medium and cultured at 37°C for 16 hours. Then 10 μL of the overnight cultured bacterial suspension was resuspended in 1 mL of TSB medium, and grown at 37°C for 6 hours to obtain a bacterial suspension for use.
[0041] Preparation of antibacterial nanoparticles: under continuous stirring, 39.48 mg of selenium powder was dispersed in 100 mL of ultrapure water, and then 50 mg of sodium borohydride was added for reduction under nitrogen protection. Separately prepare 5 mL of CuCl 2 2H 2 O (42.62mg) dispersion and 5mL FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O (69.75mg) dispersion solution was simultaneously injected into the reduced selenium powder solution after 30 minutes. Collect CuFeSe by filtration through a 0.1 µm membrane filter 2 , freeze-dried to obtain CuFeSe 2 powder.
[0042] Cell m...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Bacterial culture: Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923) was grown in nutrient broth (LB). A single colony of Staphylococcus aureus on solid LB agar plate was transferred to LB liquid medium and cultured at 37 °C for 16 h. Then resuspend 10 μL of overnight cultured bacterial suspension in 1 mL of LB medium, and grow at 37°C for 8 hours to obtain a bacterial suspension for use.
[0050] Preparation of antibacterial nanoparticles: Disperse 98.7 mg of selenium powder in 250 mL of ultrapure water under constant stirring, then add 125 mg of sodium borohydride and reduce it under nitrogen protection. Separately prepare 12.5 mL of CuCl 2 2H 2 O (106.55mg) dispersion and 12.5mL FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O (174.375mg) dispersion liquid was injected into the reduced selenium powder solution at the same time after 30 minutes. Collect CuFeSe by filtration through a 0.1 µm membrane filter 2 , freeze-dried to obtain CuFeSe 2 powder.
[0051] Cell membrane separation and extract...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Bacterial culture: Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923) was grown in nutrient broth (LB). A single colony of Staphylococcus aureus on solid LB agar plate was transferred to LB liquid medium and cultured at 37 °C for 12 h. Then resuspend 10 μL of overnight cultured bacterial suspension in 1 mL of LB medium, and grow at 37°C for 6 hours to obtain a bacterial suspension for use.
[0057] Preparation of antibacterial nanoparticles: under continuous stirring, 40.23 mg of selenium powder was dispersed in 100 mL of ultrapure water, and then 50.19 mg of sodium borohydride was added for reduction under nitrogen protection. Separately prepare 5 mL of CuCl 2 2H 2 O (43.47mg) dispersion and 5mL FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O (68.11mg) dispersion solution was simultaneously injected into the reduced selenium powder solution after 30 minutes. Collect CuFeSe by filtration through a 0.1 µm membrane filter 2 , freeze-dried to obtain CuFeSe 2 powder.
[0058] Cell membrane separation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com