Magnetic control gear shifting hub
A technology of shifting wheels and hubs, which is applied in the field of wheel power transmission devices and magnetically controlled shifting hubs, can solve the problems of insufficient power, stuck reverse carts, and small size.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
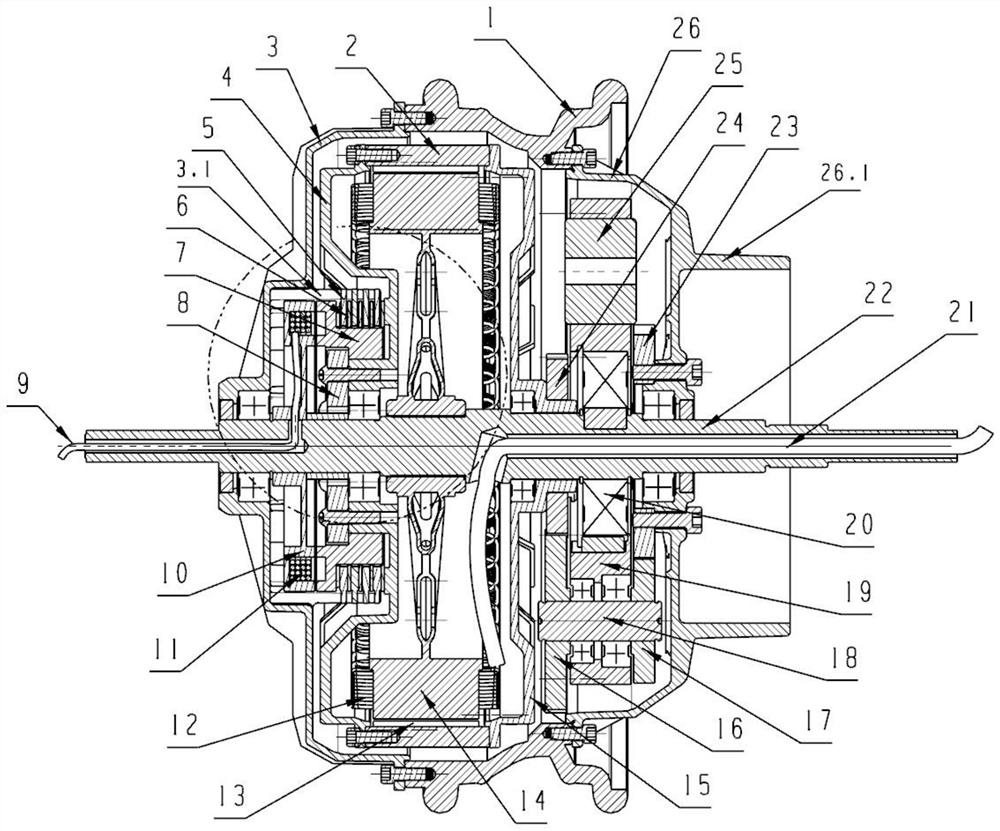
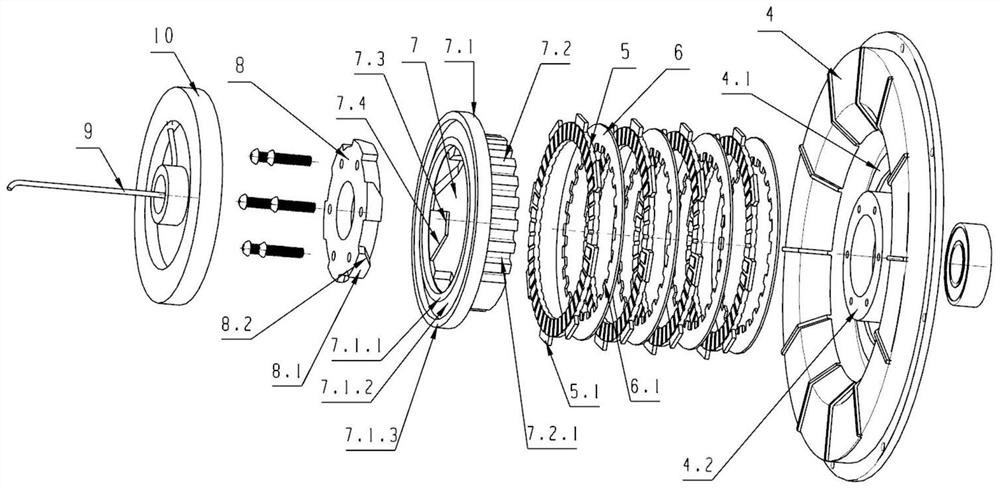
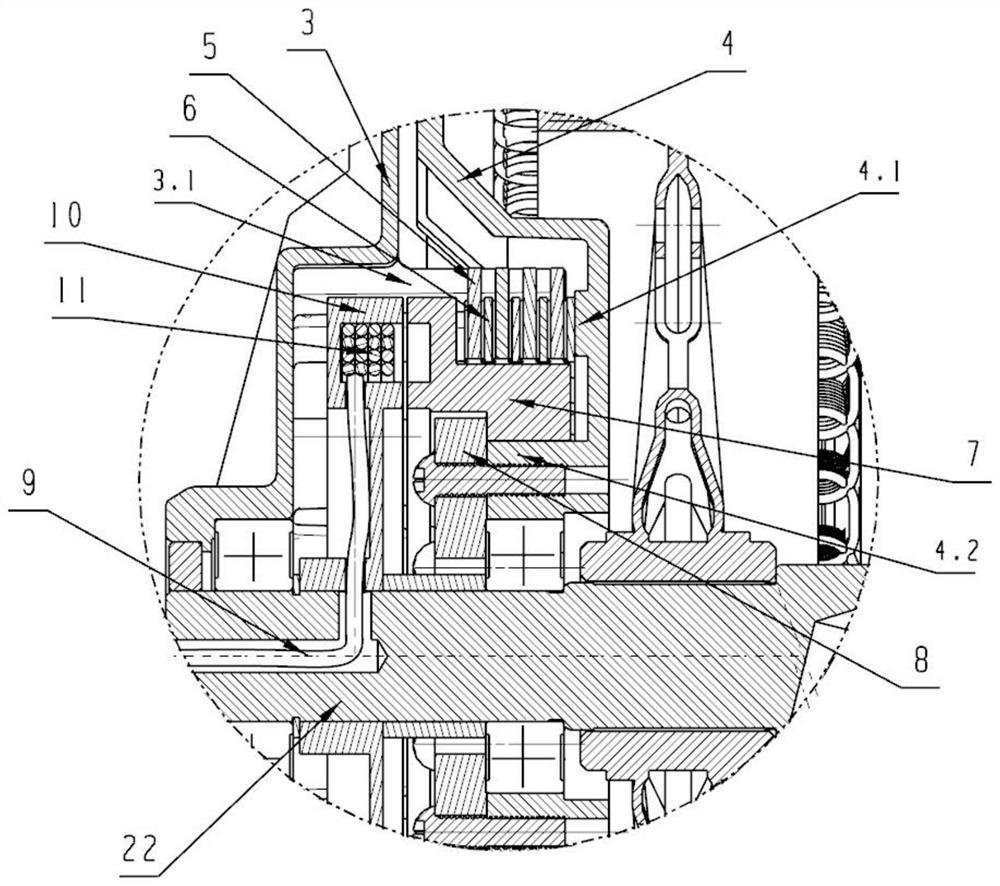
[0040] see Figure 1 to Figure 12, a magnetically controlled shifting hub, comprising a motor spindle 22 and a hub steel ring 1, the two ends of the hub steel ring 1 are respectively installed with a hub left cover 3 and a hub right cover 26, and a motor is provided on the motor spindle 22, and the motor includes a rotor 2 And the stator 14, the motor winding 12 is laid on the stator 14, the magnetic steel sheet 13 is provided between the rotor 2 and the stator 14, the motor two ends are respectively the motor left cover 4 and the motor right cover 15, the motor left cover 4 and the motor right cover 15 is fixedly connected with the rotor 2, the motor wire 21 is led out from the shaft hole at the right end of the motor main shaft 22, the gearbox body is formed in the hub cavity, the clutch and the gear set are arranged in the gearbox body, and the shaft hole end of the motor left cover 4 is provided with a boss 4.2, the clutch is set on the boss 4.2 with the driven hub 7 and t...
Embodiment 2
[0053] see Figure 13 to Figure 20 , the similarity between it and Embodiment 1 will not be repeated here, the difference lies in the position of the motor clutch.
[0054] It is fixedly connected with the first suction disk 27 on the side of the pressure plate on the driven hub 7, the other side of the first suction disk 27 is provided with the fifth magnetic conduction ring 27.1, and the coil ring groove 10.3 of the electric suction disk 10 is set inside. The ring frame 28, the coil 11 is wound on the ring frame 28, the fifth magnetically conductive ring 27.1 is nested in the shaft hole at one end of the ring frame 28, and the shaft hole at the other end of the ring frame 28 contacts the fourth magnetically conductive ring of the electric chuck 10 10.4, there is a certain gap between the fourth magnetic conduction ring 10.4 and the fifth magnetic conduction ring 27.1, the fifth magnetic conduction ring 27.1 is attracted by the fourth magnetic conduction ring 10.4 after the e...
Embodiment 3
[0060] see Figure 21 ~ Figure 23 , the similarities between it and Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 will not be repeated here, the difference lies in the electromagnetic shifting position. Specifically, the second suction disc 29 and the support disc 30 are installed in the hub cavity where the hub left cover 3 is located on the motor main shaft 22, the second suction disc 29 is connected with the first suction disc 27 through a bearing, and the second suction disc 29 is connected with the first suction disc 27 through a bearing. The disk 29 can slide horizontally on the motor shaft 22. The center of the support disk 30 has a shaft hole 30.1. Several electric suckers 10 are installed on the support disk 30. The ring skeleton 28 is set in the electric sucker 10, and the coil 11 is wound on the ring skeleton 28. One end of the shaft hole of the ring frame 28 is installed with a fixed iron core 10.5, and a plurality of moving iron cores 29.1 are installed on the second suction plat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com