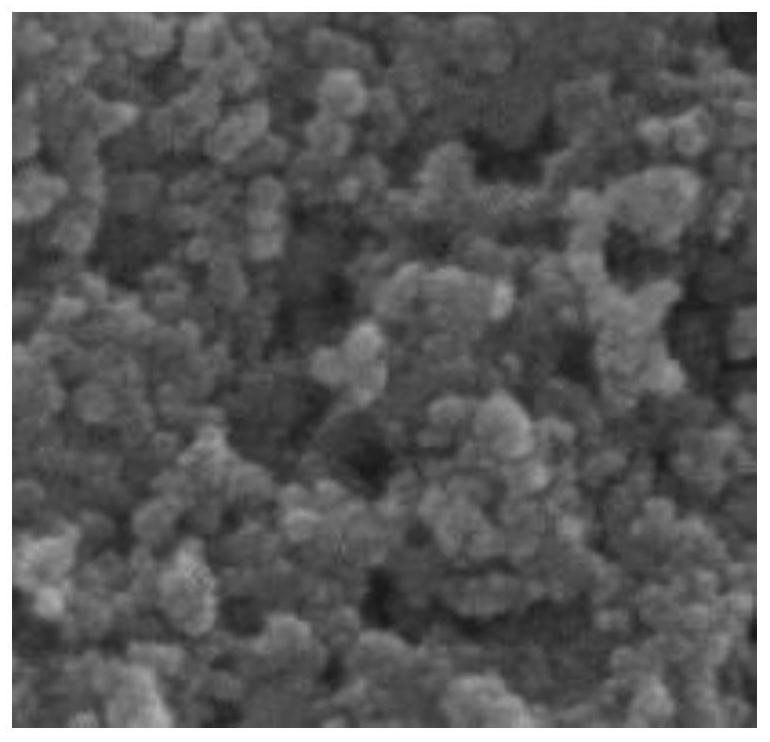
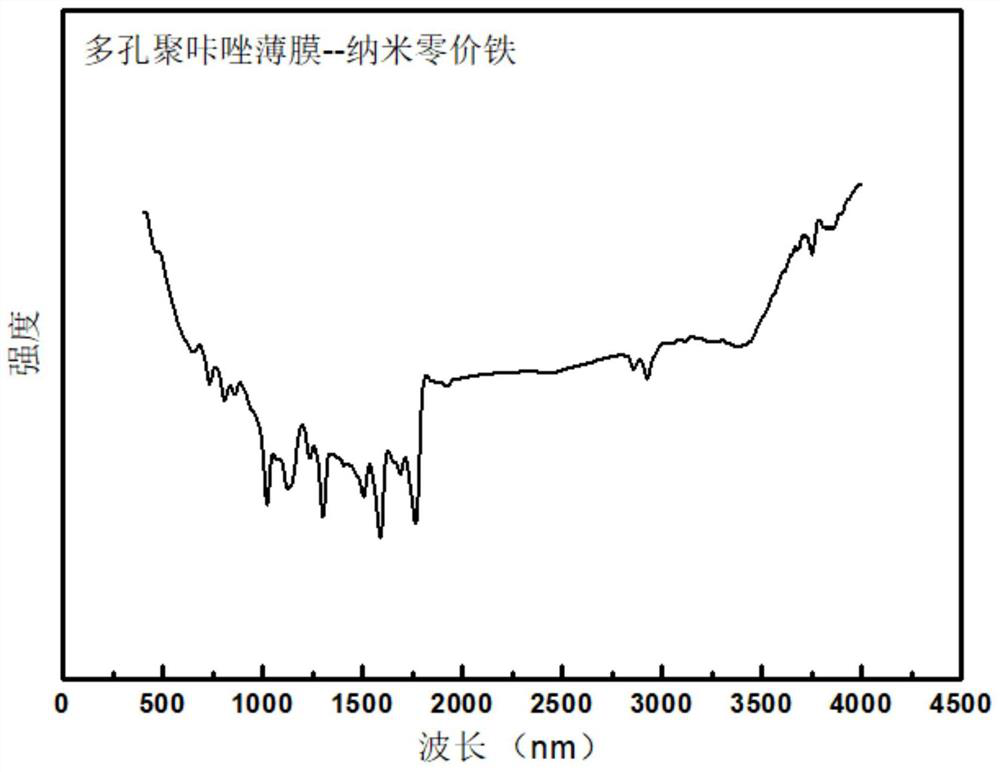
Porous polycarbazole nano-film loaded with nano zero-valent iron as well as preparation method and application of porous polycarbazole nano-film
A technology of nano-zero-valent iron and nano-film, which is applied in the fields of application, chemical instruments and methods, and organic fertilizers, and can solve problems such as poor monodispersity, easy agglomeration, and easy oxidation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] The invention provides a preparation method of a porous polycarbazole nanofilm loaded with nano zero-valent iron, comprising the following steps:
[0033] (1) Preparation of porous polycarbazole nanofilms by combining electrochemical polymerization and chemical oxidation;
[0034] (2) The porous polycarbazole nano-film loaded with nano-zero-valent iron was prepared by liquid phase reduction method.
[0035] In the present invention, by loading nano-zero-valent iron on the porous polycarbazole nano-film, on the one hand, it can greatly limit the loss of nano-zero-valent iron. The degree of "effective oxidation" maintains the high reactivity of nano-zero-valent iron, prevents it from being oxidized by non-target pollutants in the environment such as water, and prolongs its service life. At the same time, the loading of the porous polymer nano-film can effectively prevent its agglomeration, improve the dispersion, mechanical strength and adsorption effect of nano-zero-val...
Embodiment 1
[0048] The preparation process of the porous polycarbazole nanofilm loaded with nanometer zero-valent iron is as follows:
[0049] (1) Preparation of porous polycarbazole nanofilms by combining electrochemical polymerization and chemical oxidation
[0050] Polycarbazole film was prepared by cyclic voltammetry electropolymerization on CHI-660 electrochemical workstation, during which MnO 2 as an oxidizing agent. Under the three-electrode system, a platinum plate electrode is used as an auxiliary electrode, a saturated calomel electrode is used as a reference electrode, and the electrolyte is a mixed solution of carbazole and dilute sulfuric acid (concentration: 0.21mol / L). The electrochemical polymerization conditions are: the polymerization voltage is 0.5V, the scanning rate is 8mV / s, and the scanning cycle is 26 cycles. The polymerization conditions are: add 2.4mL carbazole monomer to 400mL dilute sulfuric acid (concentration: 0.21mol / L), Then add 1.2g MnO 2 After the poly...
Embodiment 2
[0055] The preparation process of the porous polycarbazole nanofilm loaded with nanometer zero-valent iron is as follows:
[0056] (1) Preparation of porous polycarbazole nanofilms by combining electrochemical polymerization and chemical oxidation
[0057] Polycarbazole film was prepared by cyclic voltammetry electropolymerization on CHI-660 electrochemical workstation, during which MnO 2 as an oxidizing agent. In the three-electrode system, a platinum sheet electrode was used as an auxiliary electrode, a saturated calomel electrode was used as a reference electrode, and the electrolyte was a mixed solution of carbazole and dilute sulfuric acid (concentration: 0.8 mol / L). The electrochemical polymerization conditions are: the polymerization voltage is 0.5V, the scanning rate is 2.5mV / s, and the scanning cycle is 20 cycles. Then add 1.6g MnO 2 After the polymerization, take out the working electrode, wash it with dilute hydrochloric acid, ethanol and distilled water in turn,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com