Halophilic brevibacterium linum strain capable of efficiently degrading ammonia nitrogen and application of same
A technology for degrading ammonia nitrogen and Brevibacterium, applied in bacteria, microorganism-based methods, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve the effect of good tolerance, strong ammonia nitrogen degradation ability, and short treatment time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1: screening isolated bacterial strains
[0029] Selective solid medium: tryptone 5.00g / L; yeast extract 1.00g / L; sodium chloride 19.45g / L; anhydrous MgCl5.90g / L; 2 SO 4 10H 2 O 3.24g / L; CaCl 1.80g / L; KCl 0.55g / L; NaHCO 3 0.16g / L;H 3 BO 3 22mg / L; Na 2 HPO 4 8mg / L; agar 15g / L.
[0030] The strains were selected from the high-salt sewage of a factory in Lishui. Take 50mL of sewage, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10min, discard the supernatant, add water to 1mL and mix well. Add 9 mL of water to form 10 -1 diluent. from 10 -1 Add 1mL of the diluted solution to 9mL sterile water to make 10 -2 Dilution, and so on, make a series of gradient dilutions on the finally obtained bacterial solution, and take 0.1mL to spread on the separation medium, and incubate at a constant temperature of 30°C until a single colony grows. Separation and purification of single colonies with different colors and shapes were carried out, and 6 single colonies were picked. After...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2: Ammonia nitrogen degradation ability test of bacterial strains
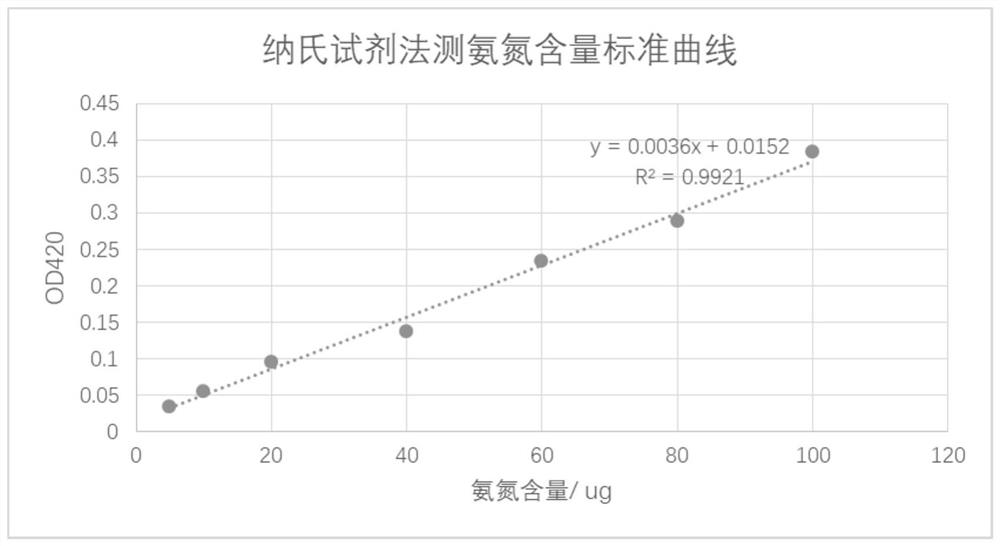
[0032] 1 Ammonia nitrogen standard curve
[0033] In eight 50mL volumetric flasks, add 0.00mL, 0.50mL, 1.00mL, 2.00mL, 4.00mL, 8.00mL, and 10.00mL of ammonia nitrogen standard working solution, and the corresponding ammonia nitrogen contents are 0.0μg, 5.0μg, 10.0μg, 20.0μg, 40.0μg, 60.0μg, 80.0μg and 100μg, add water to the marked line. Add 1.0mL potassium sodium tartrate solution, shake well, then add 1.0mL Nessler's reagent, shake well. After standing for 10 minutes, at a wavelength of 420nm, use a 10mm cuvette and use water as a reference to measure the absorbance. The absorbance after blank correction is taken as the ordinate, and the corresponding ammonia nitrogen content (μg) is used as the abscissa to draw a calibration curve. The obtained standard curve is as figure 2 shown.
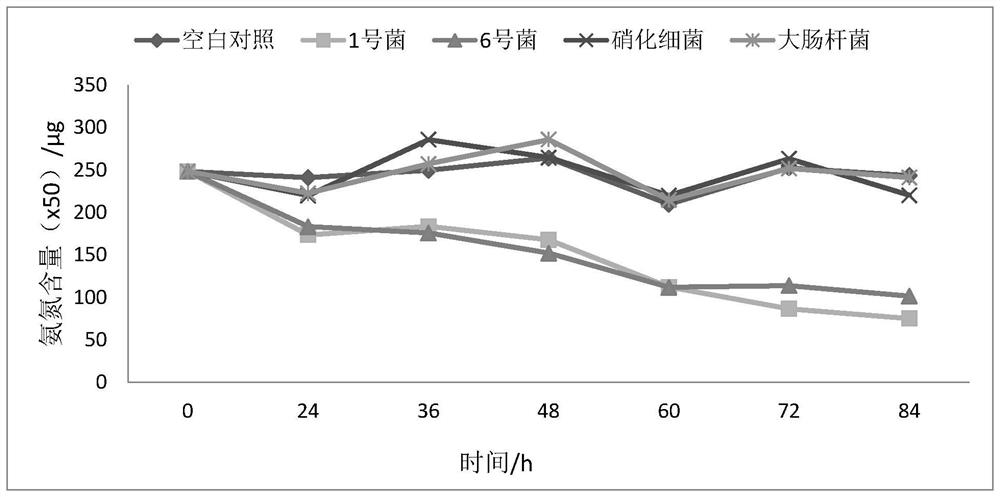
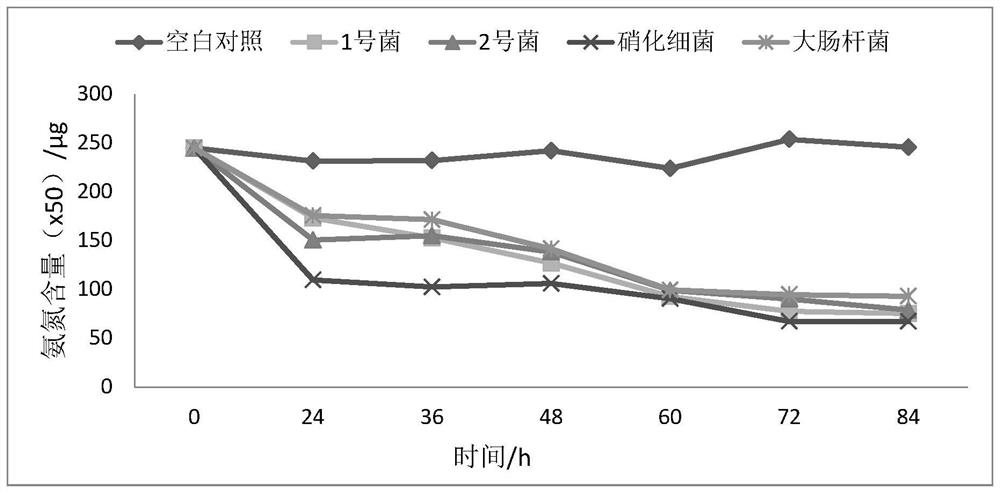
[0034] Ammonia nitrogen degradation ability of 2 strains
[0035] Pick a single colony from the plate and...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment 3: No. 1, No. 6 bacterial strains salt tolerance test
[0052] 1 Growth curves under different salinity
[0053] The growth curves of No. 1 bacterial strain and No. 6 bacterial strain were detected respectively under 1%, 4%, 7%, and 10% salinity, and the results were as follows: Figure 4 shown. From Figure 4 It can be seen that both strain No. 1 and strain No. 6 can grow and reproduce at a salinity of 1%-10%.
[0054] 2 Ammonia nitrogen degradation capacity under different salinity
[0055] Inoculate No. 1 and No. 6 strains into liquid LB medium, and culture them on a shaker at 220 rpm at 30°C for 1 day. Take 2 mL of the bacterial solution and centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min, add 1 mL of deionized water to resuspend, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min, discard the supernatant, and repeat for 4 groups. The sediment was resuspended with artificial water samples with salinity of 1%, 4%, 7% and 10%, respectively, and then 100 mL of corresponding artific...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com