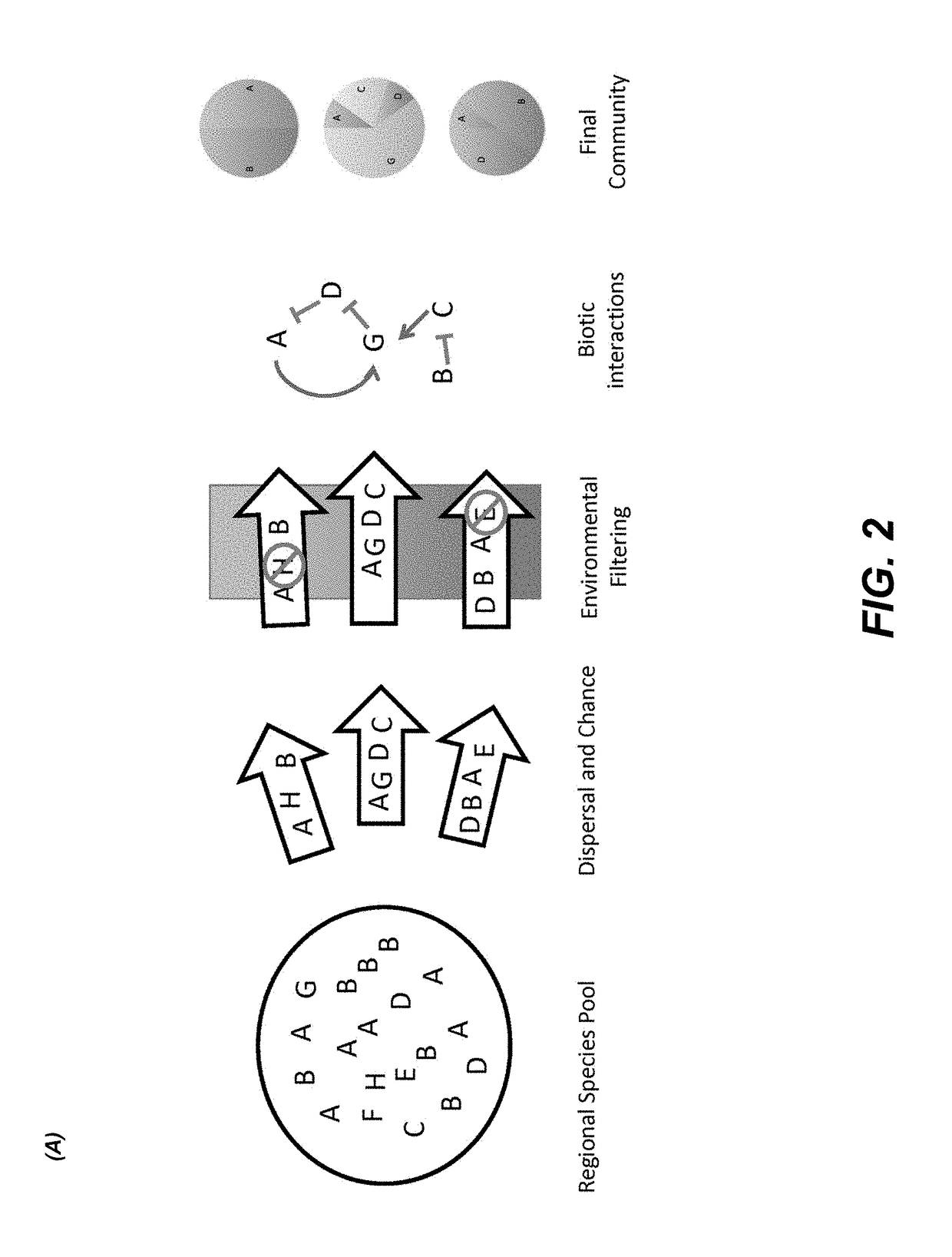
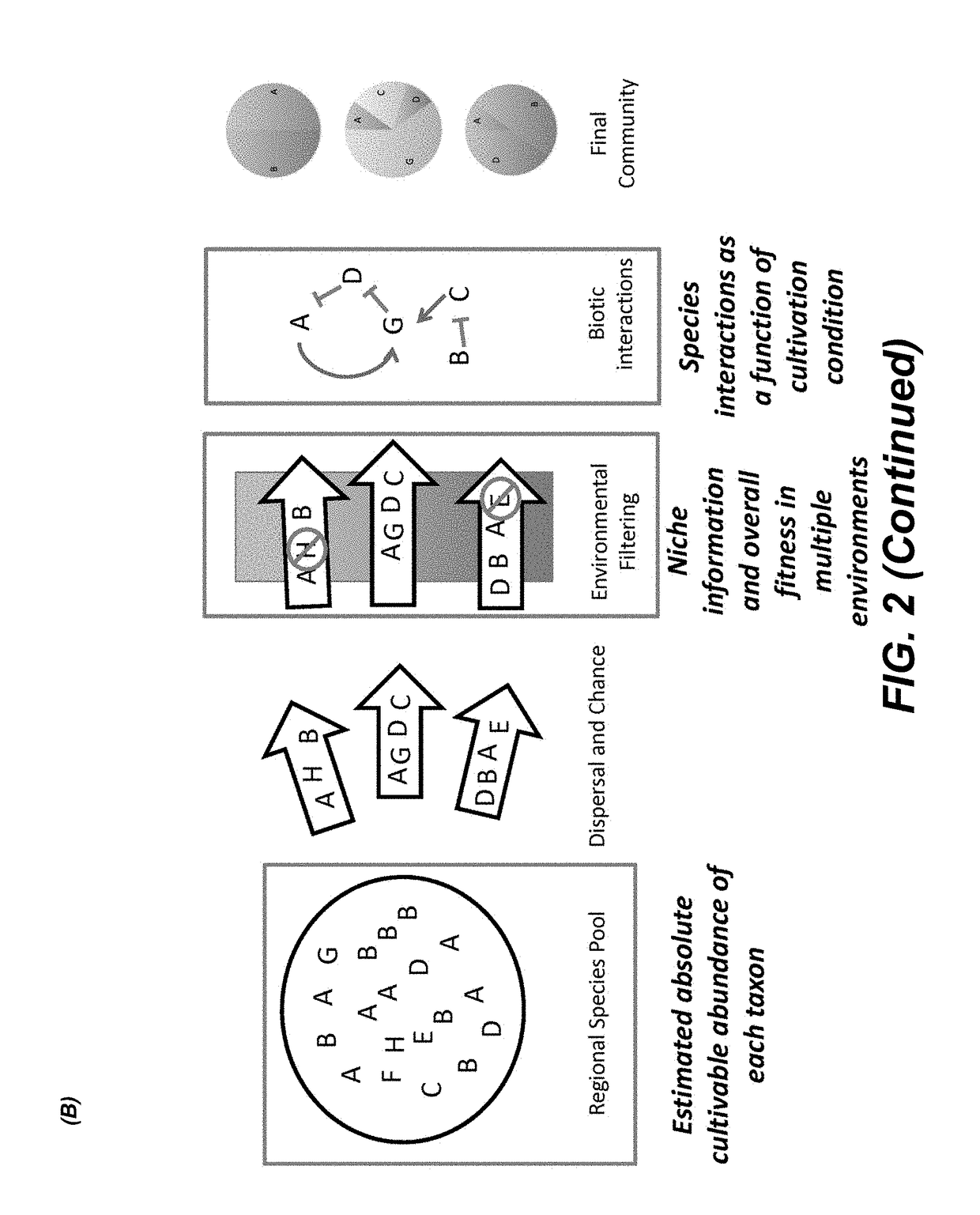
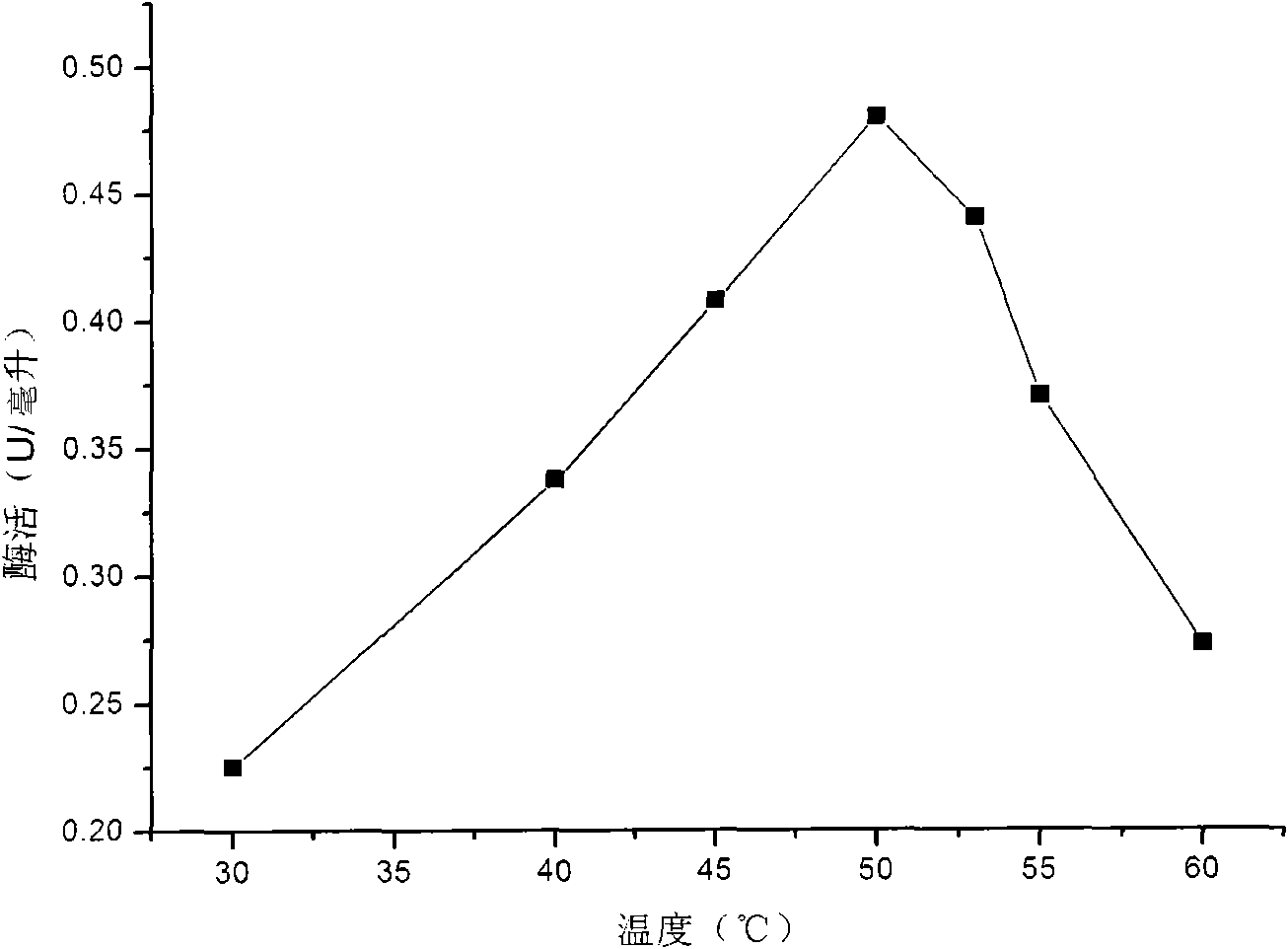
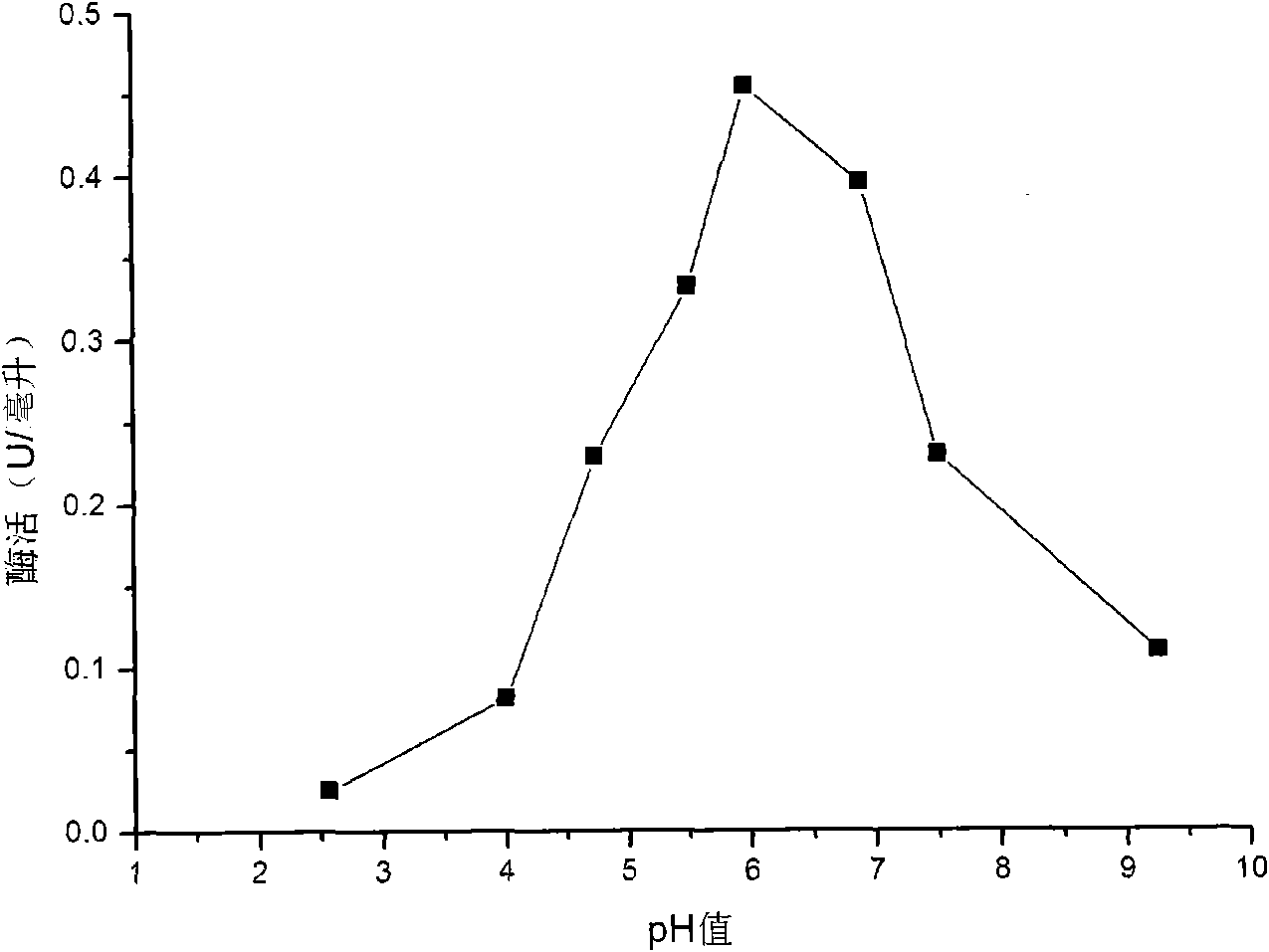
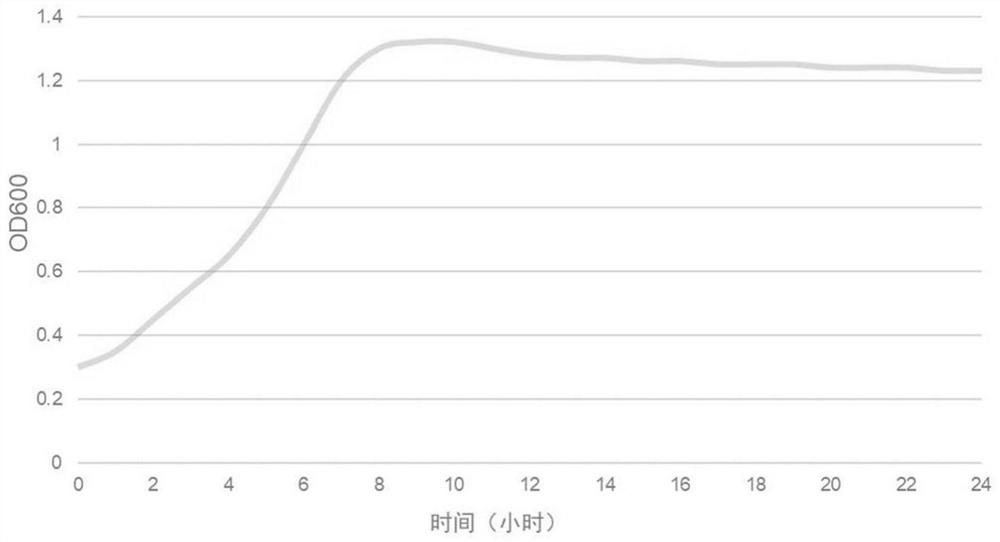
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Microorganism classification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
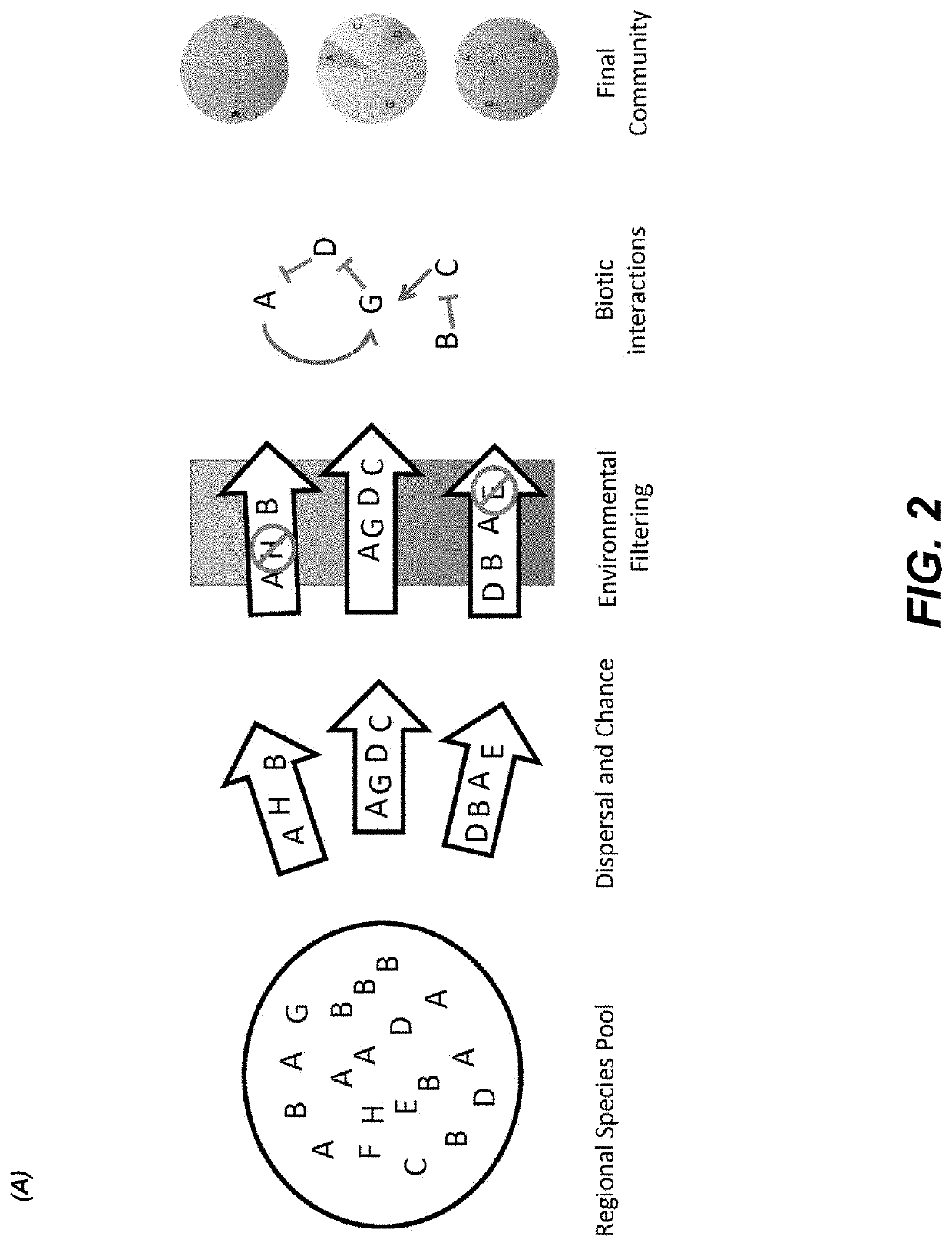
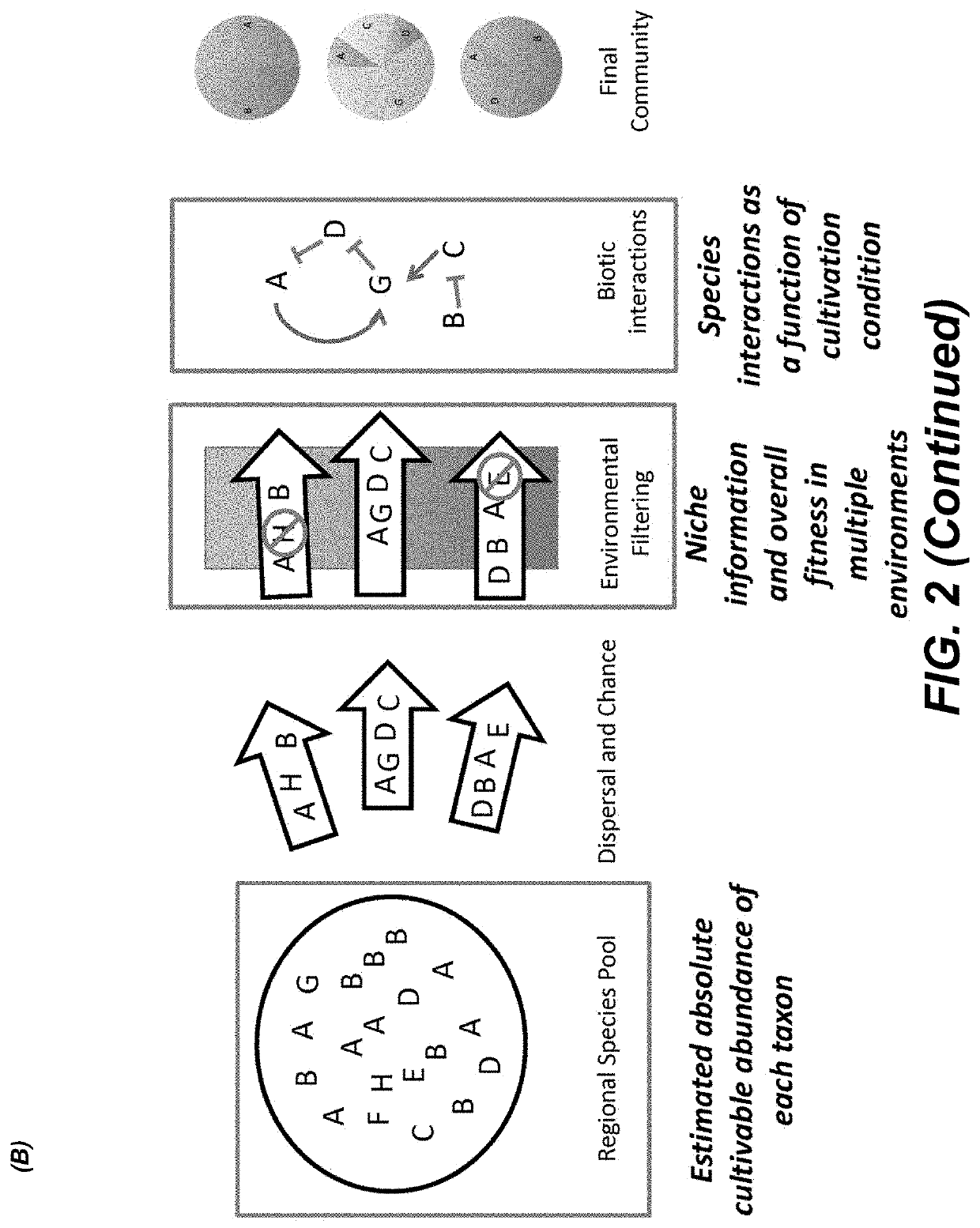
Taxonomic or other systematic or hierarchical microorganism classification systems.
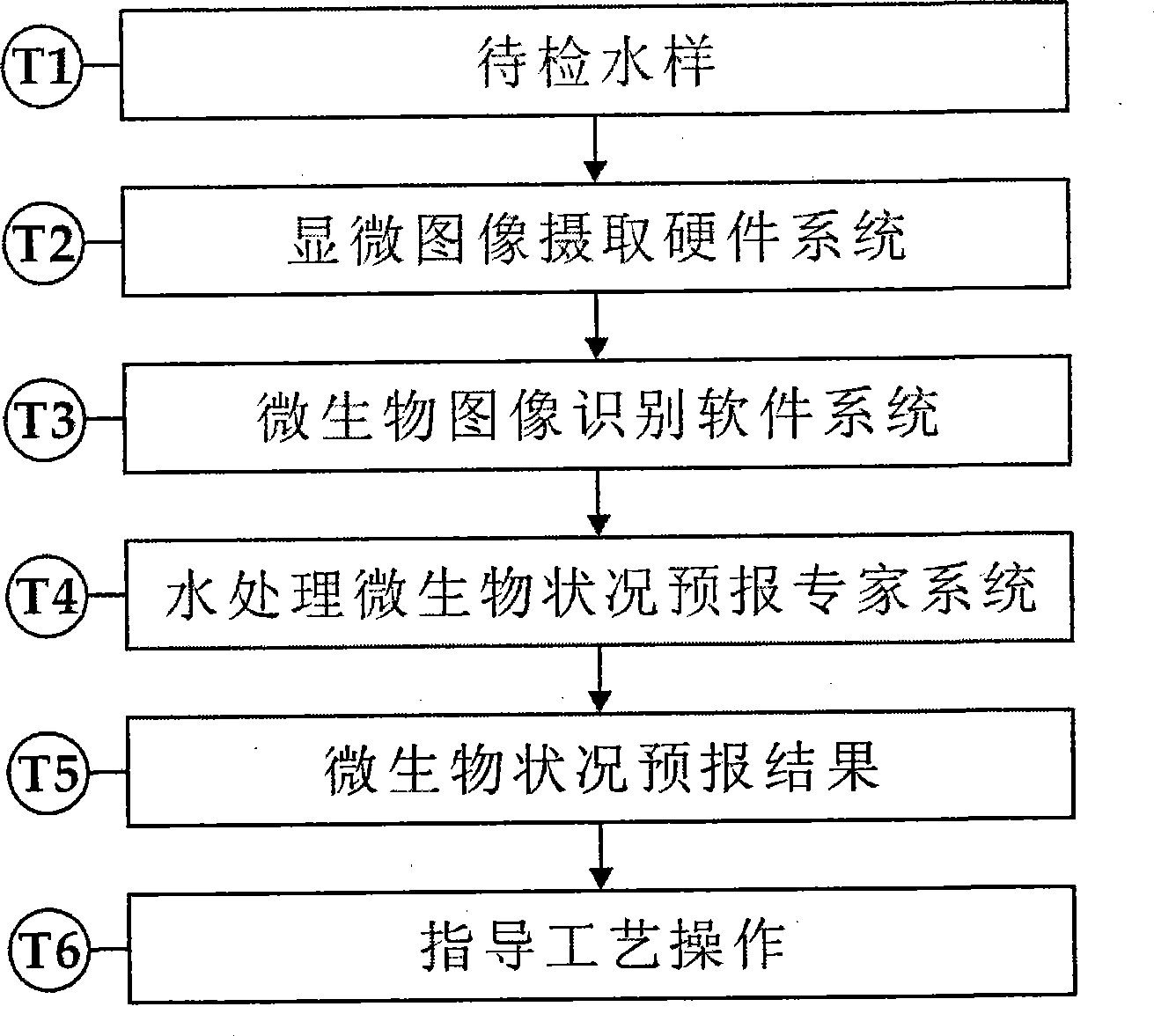
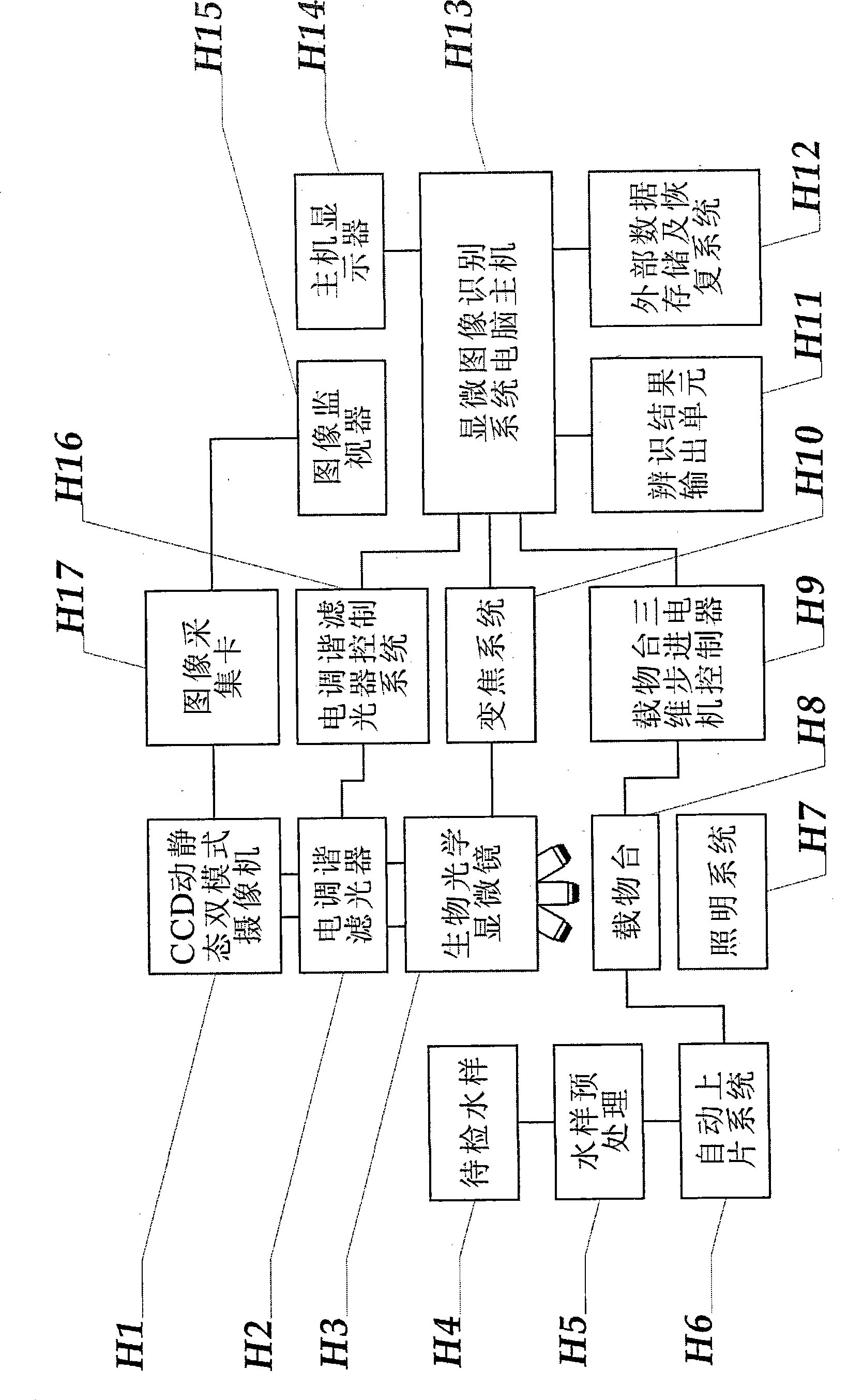
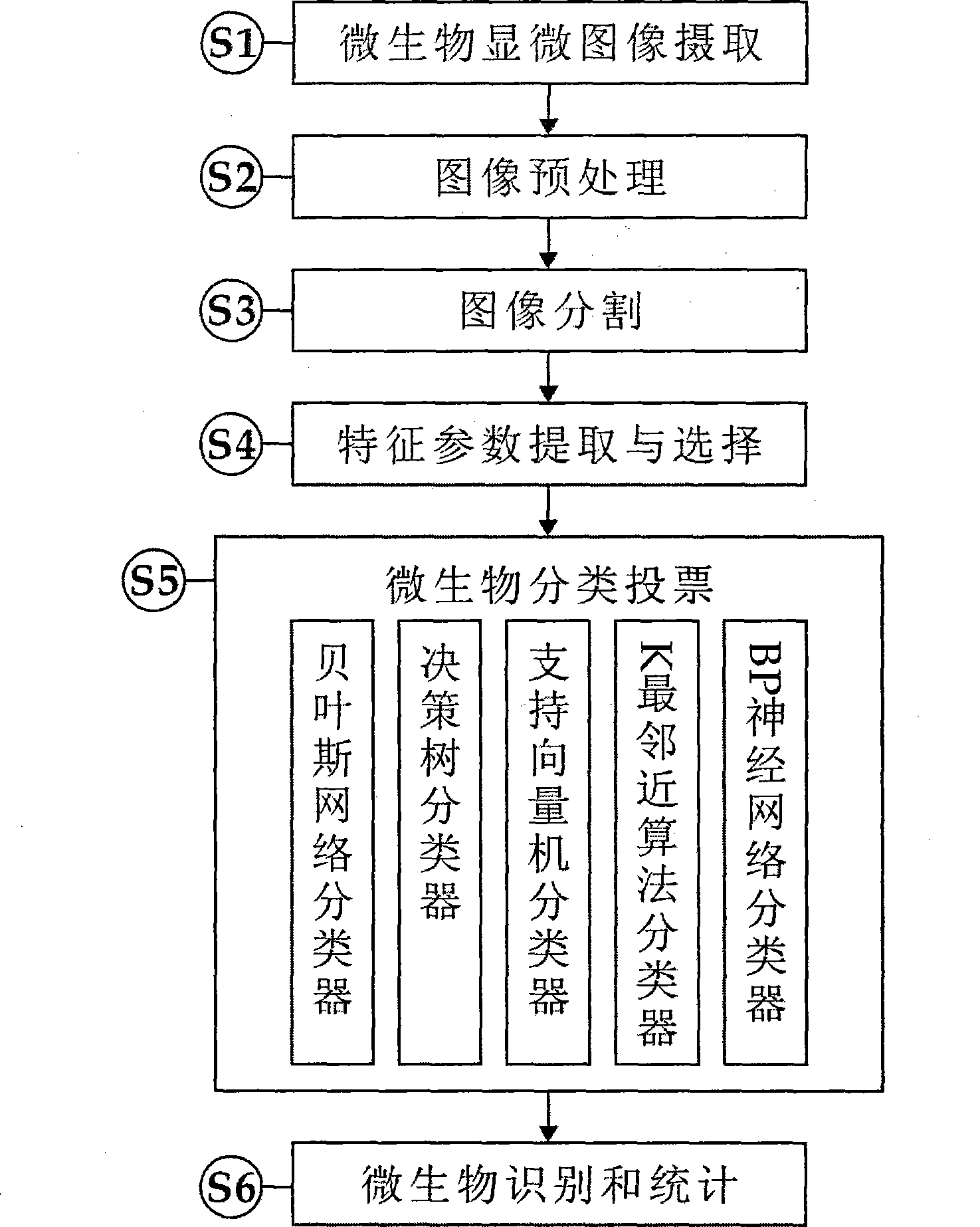
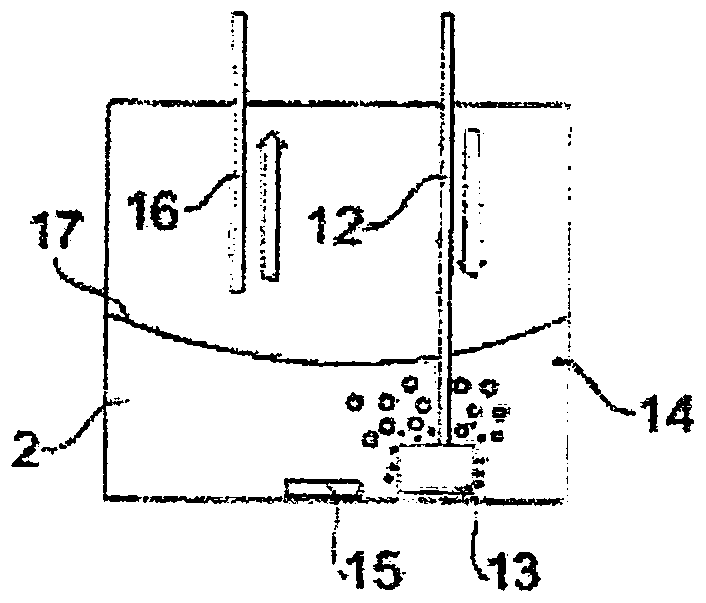
System and method for intelligent water treatment micro-organism machine vision identification
InactiveCN101477630AEasy to detectSimple dataTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopic imageImage segmentation algorithm
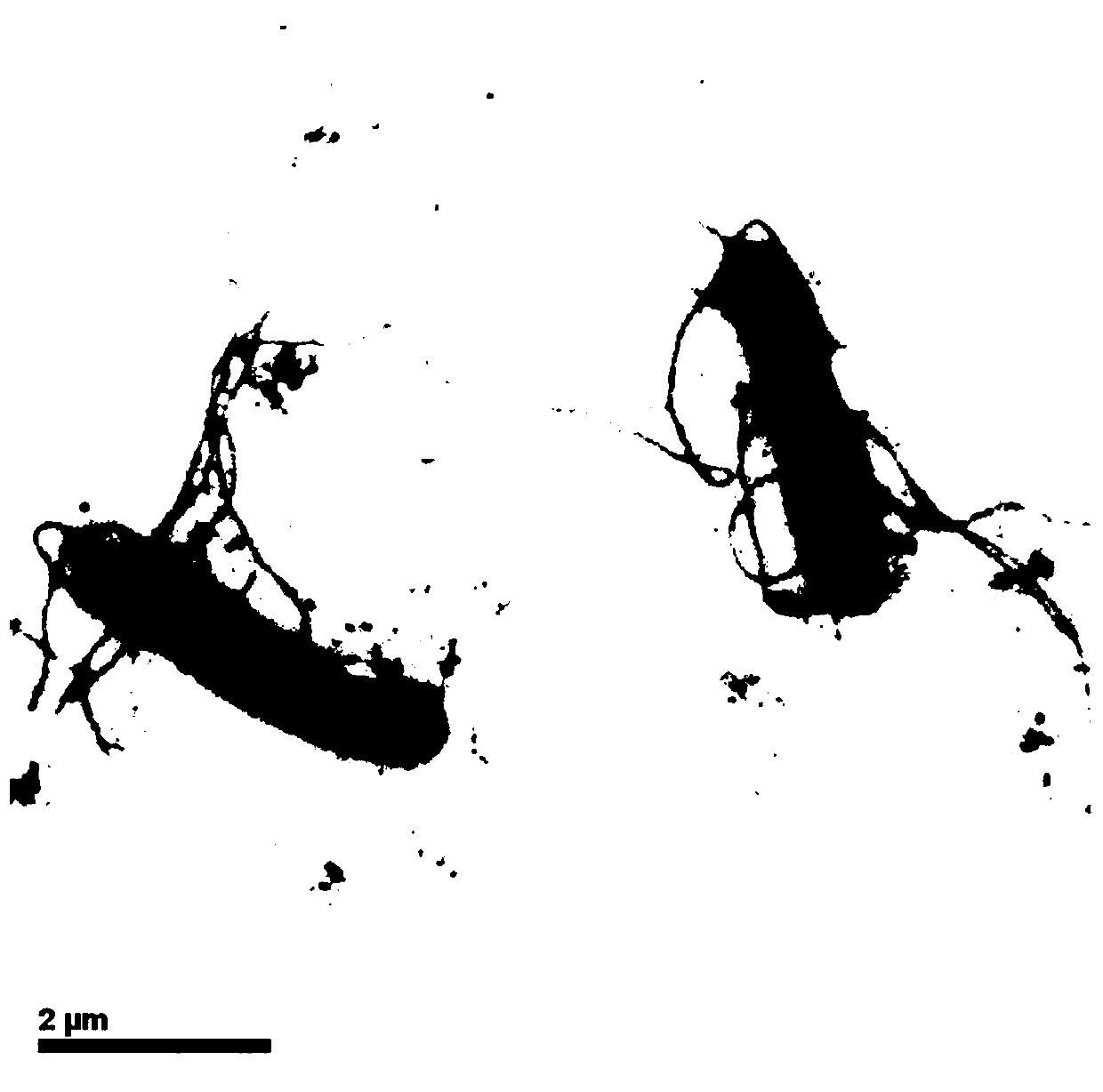
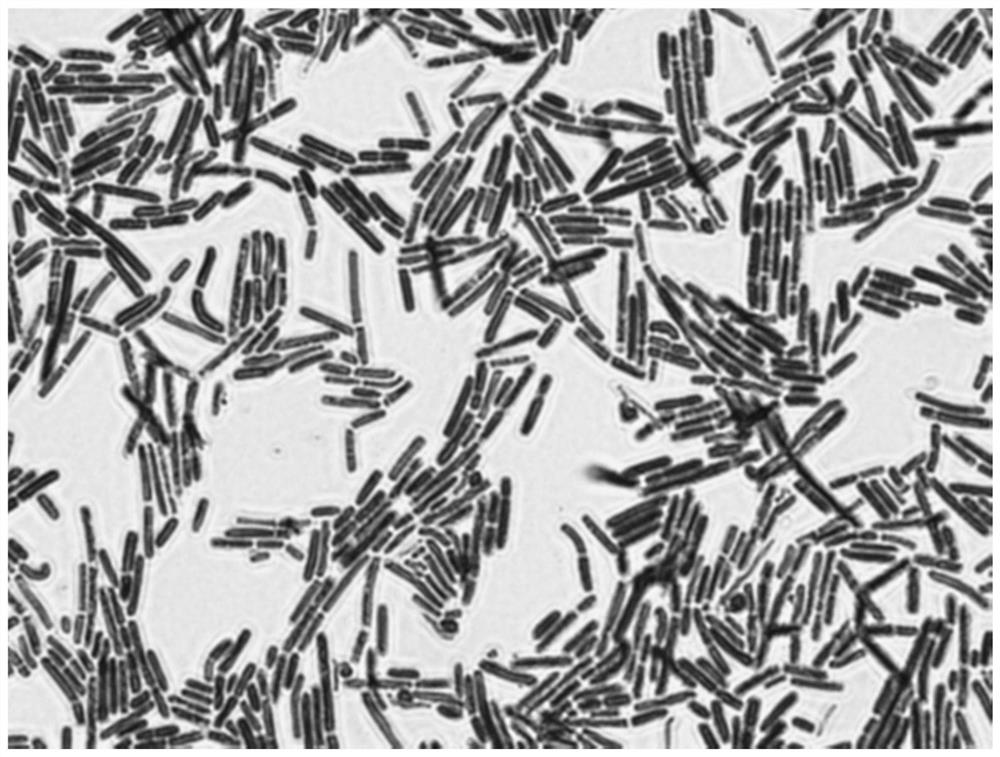
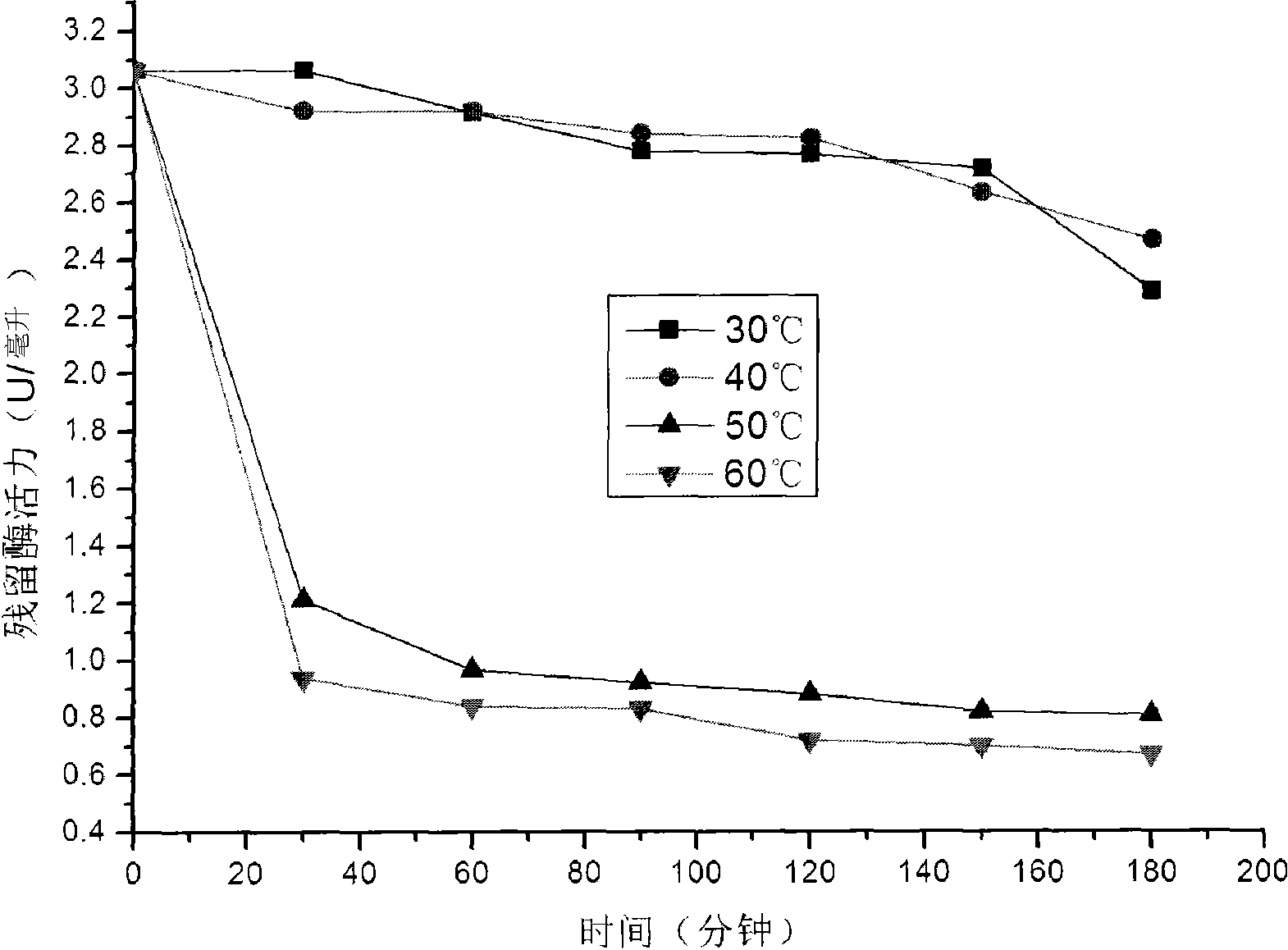
The invention provides an intelligent water-treatment microorganism machine vision identification system and a method. By using artificial intelligent technology, the system and the method can real-timely shoot microscopic images of microorganism in water and carry out the steps of automatic image pre-treatment, image segmentation, microorganism characteristic parameter extraction and selection, and microorganism classification and identification. The system and the method have the advantages that optimal segmentation threshold value can be searched automatically in HIS color space by using self-adaptive image segmentation algorithm; and the classifier is designed in a voting manner to obviate the low classification accuracy by using single classifier so as to effectively improve the entire classification accuracy and accurately identify microorganisms in drinking water and urban domestic sewage. The implementation of the method can further shorten the microorganism detection period in the water treatment process and accurately predict the condition of the water-treatment microorganisms to allow the operators to take measures in time. Accordingly, the method and the system can powerfully ensure the safety of drinking water and the normal operation of urban domestic sewage treatment facility so as to achieve considerable economic and social benefits.
Owner:吴俊 +2
Lactobacillus fermentum capable of reducing blood uric acid
ActiveCN110079476AReduce contentControl levelBacteriaSkeletal disorderMicroorganismLactobacillus fermentum
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and discloses lactobacillus fermentum capable of reducing blood uric acid. The strain is named 2644 strain, and is preserved at the China GeneralMicrobiological Culture Collection Center on 19th, November, 2018, and a microbial preservation number is CGMCC NO.16754; and the preservation authority address is NO.3 1# Courtyard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the microorganism is classified and named Lactobacillus fermentum. The strain can effectively reduce the content of the blood uric acid; and not only can intake of exogenous purines be reduced, but also discharge of internal uric acid from an intestinal tract can be promoted so that the blood uric acid level of a body can be more effectively controlled.
Owner:HANGZHOU WAHAHA TECH +1
Detection vessel for rapidly detecting moulds and yeasts and preparation method
InactiveCN105483204AImprove breathabilityImprove adsorption capacityMicrobiological testing/measurementYeastMetabolite
The invention provides a detection vessel capable of rapidly culturing and detecting moulds and yeasts at the same time. A biochemical reaction characteristic of microorganisms is utilized, types and reaction conditions of endoenzymes of the microorganisms are determined as main bases for microorganism classification and identification, a microorganism specific enzyme chromogenic substrate is added into an isolation medium or a selective medium, and when target bacteria grow on the medium, the chromogenic substrate can be degraded by specific enzymes and metabolites in special colors can be generated to realize specific colors or forms of colonies, thereby implementing culturing and detection of the microorganisms in a sample. The detection vessel has the advantages of convenience in operation, low cost, labor saving, simple judgment result, reliable detection result, short detection time and the like, and can play an important role in microorganism detection, and accuracy of a detection result reaches 90 percent or over 90 percent of a national standard detection method.
Owner:贵州勤邦食品安全科学技术有限公司
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain and its application in waste deodorization
InactiveCN106282063AStrong ability to degrade complex organic matterEasy to expand and cultivateBacteriaDispersed particle separationBacillus amyloliquefaciensLitter
The invention provides a bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain and its application in waste deodorization. The stratin is bacillus amyloliquefaciens YZ-0001, and collected at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center; the collection number is CGCC 12052 and the collection date is January 14, 2016. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain is isolated from soil; the colony characteristics shown on a screening flat panel (LB flat panel) is: the form is round, the surface is smooth and dirty white, and the gram stain is positive. Through the 16Sr DNA microorganism classification and identification, it is determined as bacillus amyloliquefaciens. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain has strong and complex organic matter degradation ability; therefore, it can be applied to the waste deodorization, and the deodorization effect is good.
Owner:NANJING RUNZHONG BIOTECH
Methods for identifying interactions amongst microorganisms
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Microorganism for producing beta-1,3-glucanase and application thereof
The invention relates to a microorganism for producing beta-1,3-glucanase and application thereof. The microorganism for producing the beta-1,3-glucanase has a category name of Mitsuaria chitosanitabida H12 and a preservation number of CGMCC 2949, and is applied to preparing the beta-1,3-glucanase. By preparing bacterial fermentation cultivating crude enzyme solution of the Mitsuaria chitosanitabida H12, a crude enzyme solution dry powder preparation of the beta-1,3-glucanase is further prepared. The beta-1,3-glucanase and the crude enzyme solution dry powder preparation of the beta-1,3-glucanase can be widely applied to the fields of brewing industry, feed industry, biological control, medicaments and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method and system for classifying environmental microorganisms by image recognition technology
InactiveCN105447527AImprove classification accuracyAvoid the problem of not being able to describe the details of the local shape of microorganismsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognition3-deoxyribose
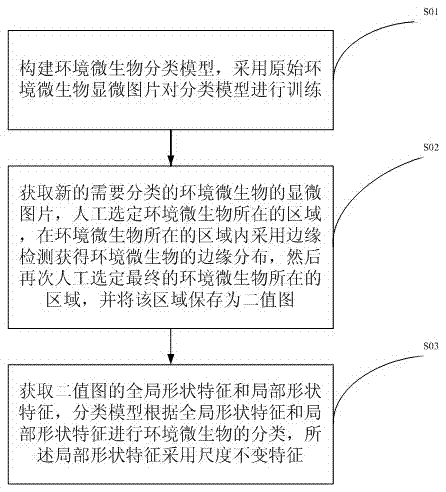
The invention relates to the technical field of environmental microorganism classification, and discloses a method for classifying environmental microorganisms by an image recognition technology. The method specifically comprises the following steps: 1) constructing an environmental microorganism classification model; 2) obtaining the micrograph of the environmental microorganism which needs to be classified, selecting an area where the environmental microorganism is positioned, and adopting edge detection to obtain the edge distribution of the environmental microorganism; and 3) obtaining global shape features and local shape features, and carrying out the environmental microorganism classification by the classification model according to the global shape features and the local shape features, wherein the local shape features adopt scale invariant features. Through the construction of the classification model, the environmental microorganism classification can be realized according to graphs, the complexity of DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) detection is avoided, the global shape features of an image are judged in a classification process, the local shape features of the image can be judged, and final microorganism classification accuracy is improved.
Owner:SICHUAN MUNIULIUMA INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
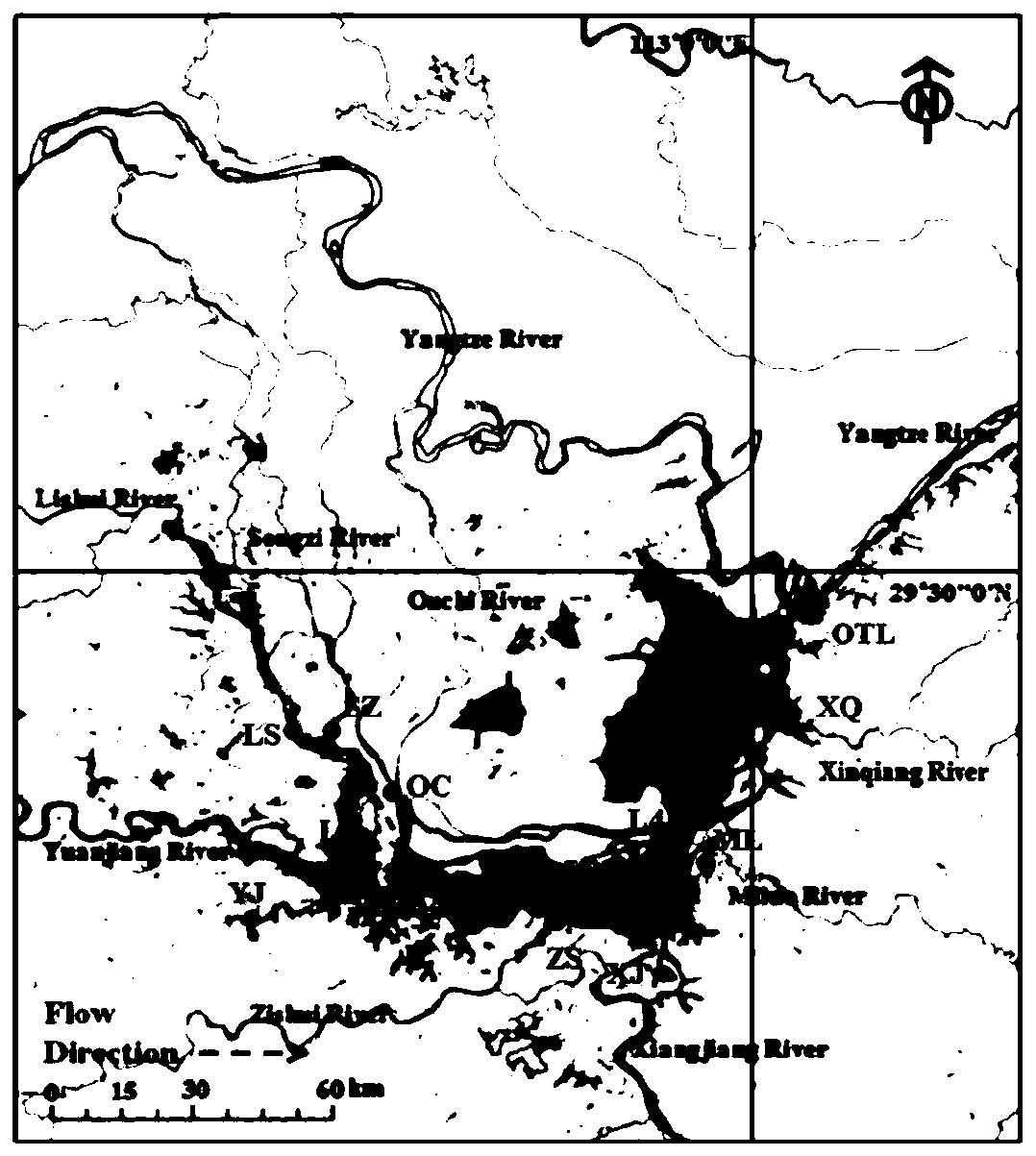
Sediment tracing method in river and lake system
InactiveCN110033133ASolve the problem that the degree of discrimination is not high and the source of sediment cannot be accurately distinguishedImprove efficiencyForecastingResourcesOrganismSediment
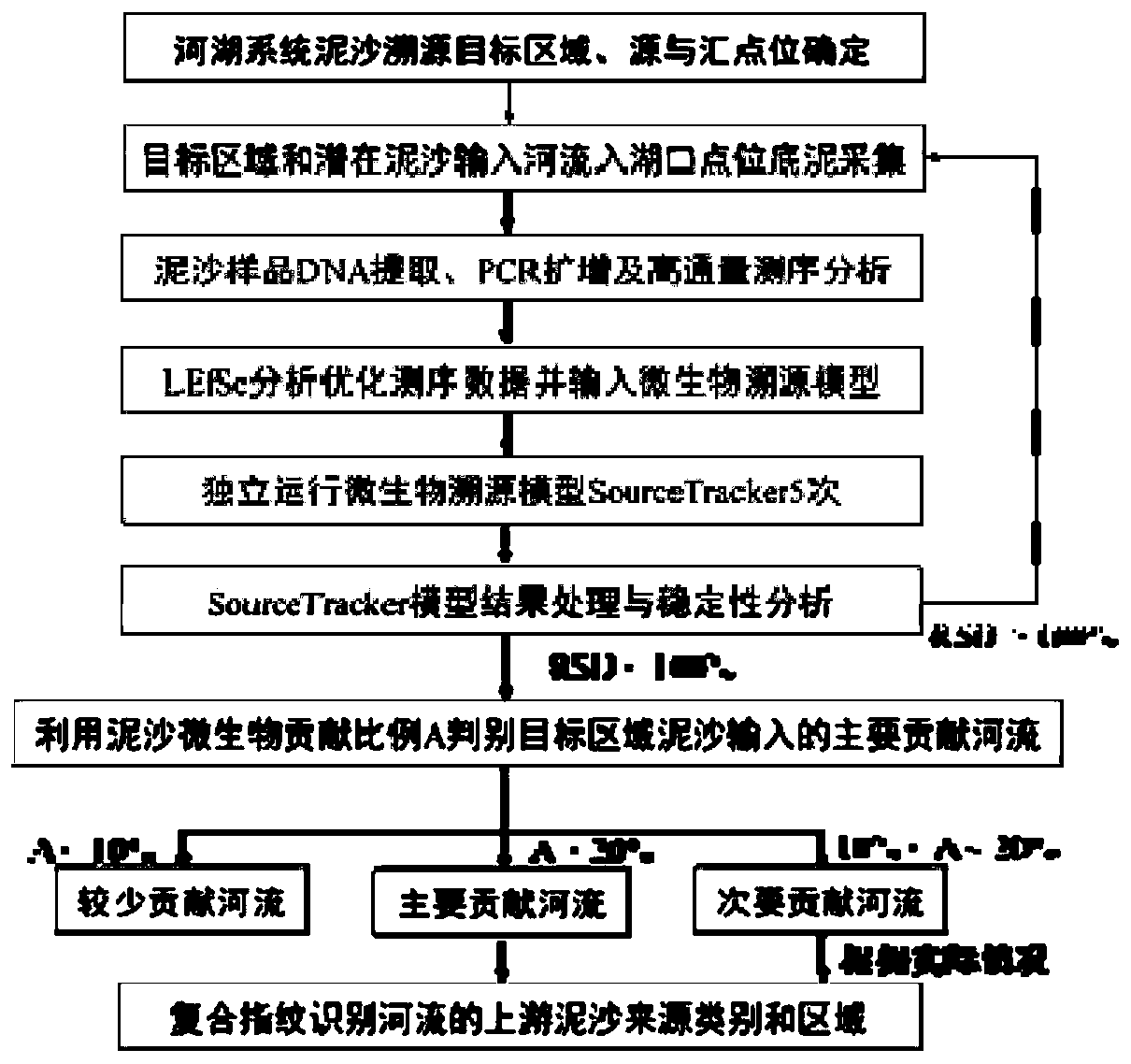
The invention discloses a sediment tracing method in a river and lake system, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of determining a source point location and a confluence point location of a sediment tracing target area; collecting a target bottom mud sample, and inputting the area and the potential sediment into the lake port point position bottom mud; extracting and collecting the DNA of the sediment sample, carrying out PCR amplification and sequencing, and carrying out microorganism classification based on a gene database; optimizing the sequencing data on the basis ofLEfSe analysis; inputting the optimized sequencing data into a biological traceability model for detection to obtain the contribution proportions of the sediment microorganisms flowing into lakes andlakes from all potential rivers to the sediment microorganisms in the target area; carrying out stability analysis on a detection result, and judging a main contribution river for silt input in the target area according to a judgment scheme; and identifying the upstream sediment source categories and areas of rivers by combining a composite fingerprint identification method. The method has the advantages of being easy to operate, wide in application range, accurate in result and high in efficiency, and has the very important significance for treatment, development and protection of the river and lake system.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
High-adhesion-property Lactobacillus helveticus strain with immunity enhancement function and application thereof
ActiveCN111254087AExcellent Adhesive PropertiesStrong adhesionMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologySpecific immunity
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and discloses a high-adhesion-property Lactobacillus helveticus strain with an immunity enhancement function. The Lactobacillus helveticus strain is named WHH2580, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center since October 23, 2019 under the preservation number of CGMCC No. 18730. The Lactobacillus helveticus strain has a classification name of Lactobacillus helveticus. The invention further discloses application of the Lactobacillus helveticus strain. The Lactobacillus helveticus strain disclosed by the invention has excellent adhesion property in both active form and inactivated form, and is capable of enhancing body immunity by improving and regulating organ index of the body as well as nonspecific immune response and specific immune response. Moreover, the Lactobacillus helveticus strain disclosed by the invention has immunity regulation effects such that corresponding compositions can be ingested so as to improve decreased immune functions by activating the immune functions.
Owner:HANGZHOU WAHAHA TECH +1
Pichia pastoris strain for producing acid protease
PendingCN111286463AHigh acid protease production propertiesHigh in amino acidsFungiBio-organic fraction processingPichia pastorisMicrobiological culture
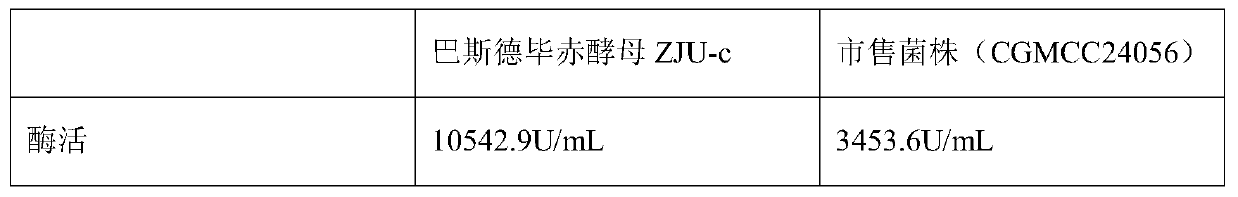
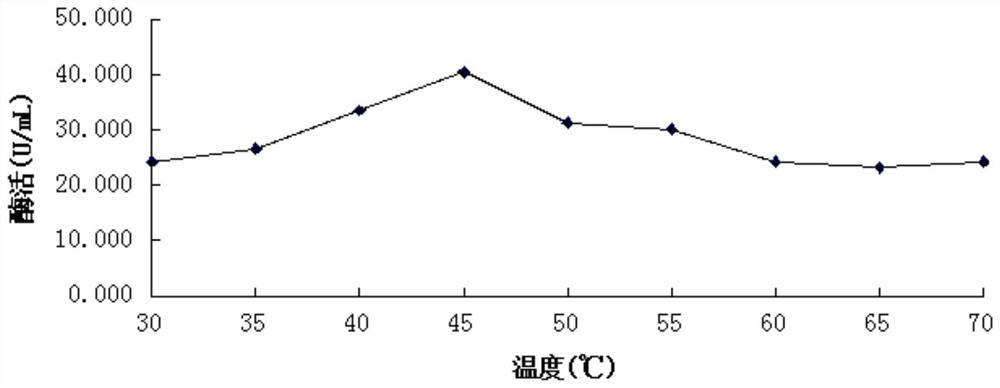
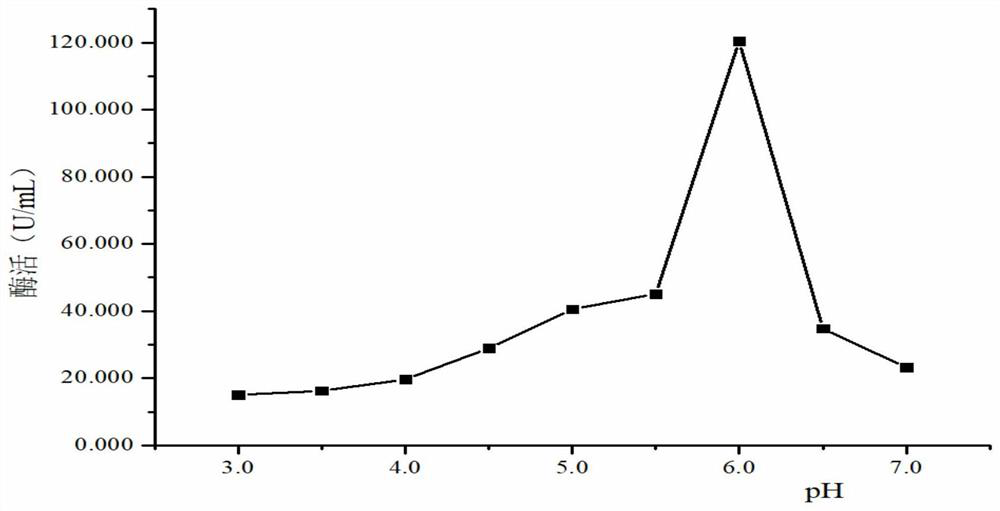
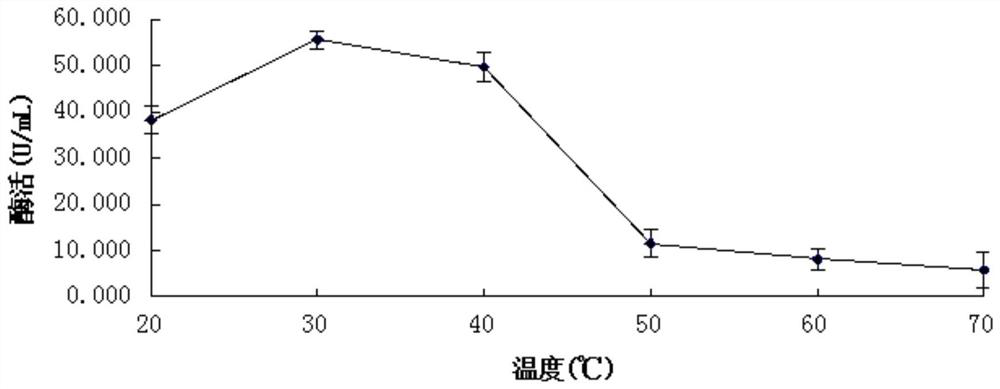
The present invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and discloses a pichia pastoris strain for producing acid protease. The pichia pastoris strain is named as ZJU-c, is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on October 12, 2018, the preservation number of the Pichia pastoris strain is CGMCC 16580, and the Pichia pastoris strain is classified and named as Pichia pastoris. Compared with other similar strains, the pichia pastoris strain disclosed by the invention has the characteristic of high yield of acid protease; the pichia pastoris strain disclosed bythe invention is applied to development of amino acid liquid fertilizer, and the content of amino acid in obtained fermentation liquor is higher.
Owner:OCEAN RES CENT OF ZHOUSHAN ZHEJIANG UNIV
Endophytic fungus Aspergillus nomius and application thereof
ActiveCN111996123AEnzyme activity is high and stableFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPectinase
The invention discloses endophytic fungus Aspergillus nomius and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The microorganism is classified and named as Aspergillus nomius z4, and is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2019946, and the preservation date is November 18, 2019. The Aspergillus nomius z4 disclosed by the invention is used for producing pectinase by adopting liquid state fermentation, and can effectively degrade pectin, hemicellulose, lignin, cellulose, waxiness and other components in bamboo wastes. The microorganism can be applied to bamboo powder degrading to obtain bamboo fibers.
Owner:武夷学院
Methods for identifying interactions amongst microorganisms
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Application of lactobacillus plantarum in preparation of composition for relieving chronic inflammation of organism
ActiveCN112190600APromote proliferationImprove the level ofMilk preparationAntipyreticBiotechnologyInflammatory factors
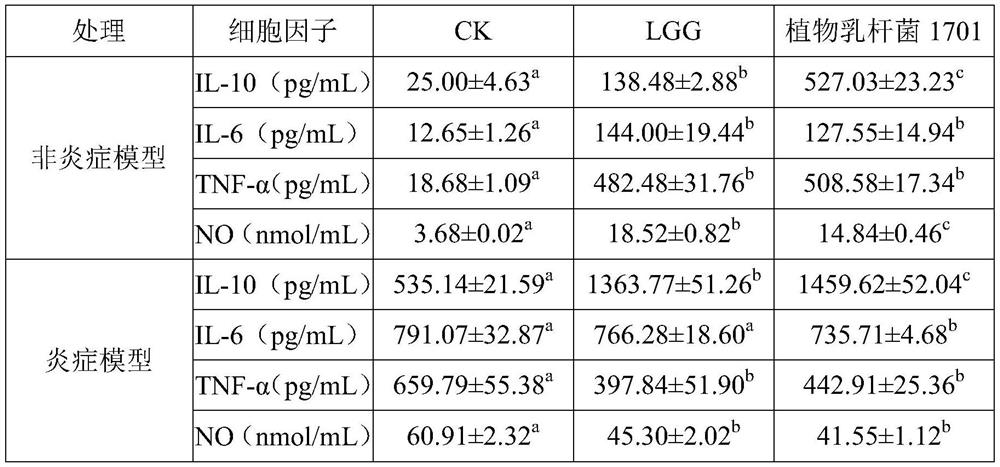
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and discloses application of lactobacillus plantarum in preparation of a composition for relieving chronic inflammation of an organism. The lactobacillus plantarum is named as 1701, is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on October 23, 2019, has a preservation number of CGMCC No.18728, and is named as lactobacillus plantarum based on classification of microbes. The adopted lactobacillus plantarum can adjust the levels of a cell factor IL-12, an anti-inflammatory factor IL-10 and a proinflammatory factor (including IL-1beta, IL-6, TNF-alpha, MCP-1 and NO) at the same time, so that the lactobacillus plantarum can adapt to chronic inflammation caused by different reasons, and diseases caused by the chronicinflammation can be prevented more comprehensively.
Owner:HANGZHOU WAHAHA TECH
Paracoccus thiooxidans capable of efficiently degrading DMF (Dimethyl Formamide) and application of Paracoccus thiooxidans in treatment of DMF-containing wastewater
PendingCN114456974AImprove toleranceEfficient mineralizationBacteriaWater contaminantsEnvironmental engineeringNitrogen source
The invention relates to the technical field of DMF (Dimethyl Formamide) degradation, and provides paracoccus thiooxidans capable of efficiently degrading DMF and application of the paracoccus thiooxidans in treatment of DMF-containing wastewater. The paracoccus thiooxidans is named as 175A1-1, has been preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on October 25, 2021, the preservation number of the paracoccus thiooxidans is CGMCC NO.23659, and the classification of the microorganisms is named as paracoccus thiooxidans. The paracoccus thiooxidans 175A1-1 disclosed by the invention has relatively high DMF (Dimethyl Formamide) tolerance and can be used for converting DMF into NH3-N by taking DMF as a unique carbon source and a unique nitrogen source, so that efficient ammonification and mineralization of DMF are realized; in addition, the strain can be efficiently and stably applied to field engineering.
Owner:浙江台州秀川科技有限公司
Classified batch culture method for soil microorganisms
ActiveCN113265319ARealize automatic shakingSpeed up coolingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSoil sciencePetri dish
The invention discloses a soil microorganism classification batch culture method. The method is characterized by comprising a sterile water generation system, a mixing system and a culture system. According to the invention, sterile water can be automatically prepared through a heating and rapid cooling method; and automatic shaking of soil and sterile water can be realized; and when sterile water is prepared, the cooling vessel can form a non-closed environment when the water is heated, but the cooling vessel can be cooled in the closed environment during cooling, so that the cooling speed is increased. Therefore, mixed soil solutions can be taken into culture dishes with different culture media respectively.
Owner:山东天润和生物工程有限公司
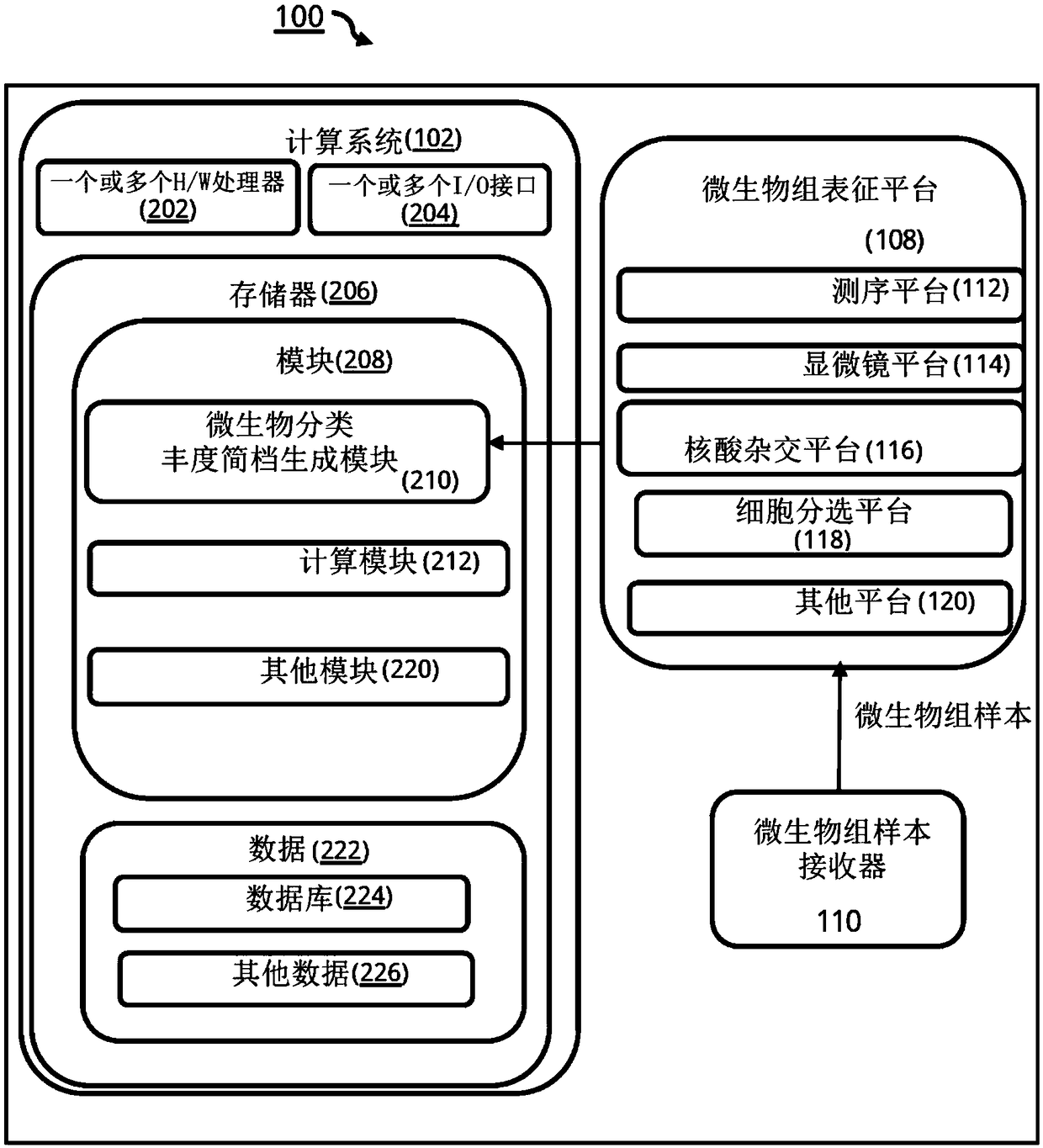
Method and system for early risk assessment of preterm delivery outcome
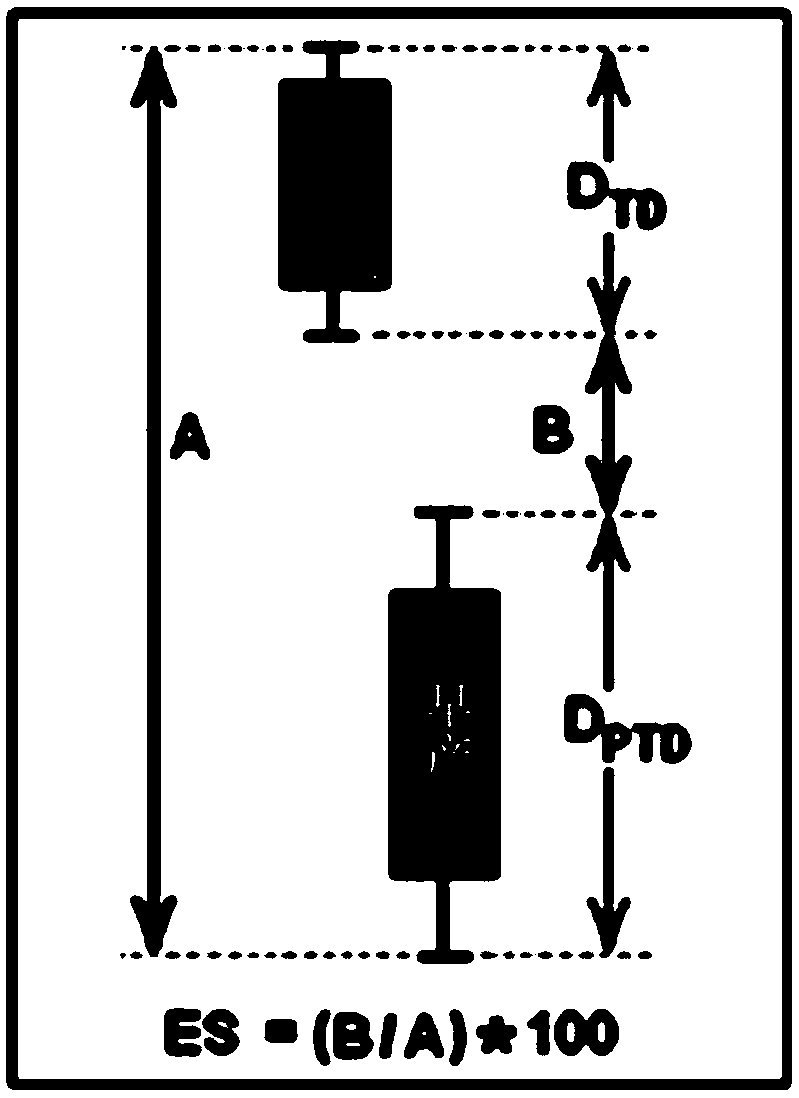
System and method for assessing preterm delivery risk for pregnant subject is disclosed. Existing preterm delivery risk assessment methods provide results in late second or third trimester of pregnancy, so little time is available for medical advice. Presently disclosed method and system predict preterm delivery risk within 15 weeks of pregnancy. Microbiome characterization data obtained from microbiome sample from pregnant subject. 'Microbial taxonomic abundance profile' generated from microbiome characterization data, contains abundance values of microbes present in the microbiome sample. 'Taxonomic Composition Skew' value, and distribution characteristic value for 'microbial taxonomic abundance profile', quantifying biases in abundance values of microbes from the microbial taxonomic abundance profile, is computed. Risk of preterm delivery is determined based on the distribution characteristic value or 'taxonomic composition skew' value of the set DSR, wherein the set DSR comprises values quantifying biases in the abundance values of microbes from the microbiome sample.
Owner:TATA CONSULTANCY SERVICES LTD
Lactococcus lactis capable of improving oral health and application of lactococcus lactis
ActiveCN112481155AGood antagonistic propertiesStrong gathering abilityMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologyOral health
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and discloses lactococcus lactis capable of improving oral health and application thereof, the lactococcus lactis is named as 2311 and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on May 25th, 2018, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 15812; wherein the microorganisms are classified and named as Lactococcus lactis subsp. Lactis. The strain disclosed by the invention has special characteristics in the aspect of oral health related application, and particularly has the characteristics of good antagonism to oralharmful bacteria, good aggregation capability, no generation of volatile sulfide and low acidification; therefore, the strain is suitable for being applied to various oral cavity improvement foods, medicines, dietary supplements, oral care products and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU WAHAHA TECH
Extremely thermophilic bacteria and application thereof in high-temperature composting fermentation
ActiveCN110819554AAccelerated putrefactionHigh activityBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyHumin
The invention relates to the fields of microbial technology and environmental engineering, and discloses extremely thermophilic bacteria and application thereof in high-temperature composting fermentation. The extremely thermophilic bacteria are named as GW-2, the preservation number of the extremely thermophilic bacteria is CGMCC 18012, and the microbial classification name is Chelativorans composti. The bacterial strain can normally metabolize and grow under the condition that the temperature is 40-105 DEG C, the pH is 5-11 and the salinity is 0-7%, and can grow by utilizing multiple carbonsources and nitrogen sources, and the substrate spectrum is very broad. The bacterial strain, supplemented by a special high-temperature composting process, can be used for high-temperature aerobic composting treatment of varieties of organic matter such as kitchen waste, agricultural-product tailings and slaughter-house waste, so that the organic matter is completely humified, dehydrated and dried, the weight is reduced by 70-92%, and finally, an organic fertilizer with excellent quality is formed.
Owner:HANGZHOU XIUCHUAN TECH CO LTD
High-temperature-resistant bacillus hisashii and high-temperature compost fermentation method
ActiveCN110862935AHeating up fastBroad substrate spectrumBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyHumin
The invention, which relates to the fields of microbial technology and environmental engineering, discloses high-temperature-resistant bacillus hisashii and a high-temperature compost fermentation method. The high-temperature-resistant bacillus hisashii is named as NH-1 and the preservation number of the high-temperature-resistant bacillus hisashii is CGMCC 17919; and the microorganism is classified and named as bacillus hisashii. According to the invention, the strain can normally metabolize and grow at a temperature of 35 to 100 DEG C under the conditions of the pH value being 6 to 11 and the salinity being 0 to 5%; growth can be realized by utilizing various carbon sources and nitrogen sources; and the substrate spectrum is wide. The bacterial strain can be used for carrying out high-temperature aerobic composting treatment on various organic matters such as kitchen wastes, agricultural product tailings, slaughter house wastes in cooperation with the special high-temperature composting process, so that the organic matter materials are processed by humification and dehydration drying ad the weight is reduced by 65 to 90% and thus an organic fertilizer with excellent quality is formed.
Owner:浙江佳河绿环境科技有限公司
Halophilic brevibacterium linum strain capable of efficiently degrading ammonia nitrogen and application of same
ActiveCN112831434AStrong ammonia nitrogen degradation abilityImprove toleranceBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyBrevibacterium sp.
The invention relates to the field of sewage treatment, and discloses a halophilic brevibacterium linum strain capable of efficiently degrading ammonia nitrogen and application of same, wherein the brevibacterium linum is named as B1, has been preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on July 2, 2019, the preservation number of the brevibacterium linum is CGMCC NO.18298, and the microorganism classification of the brevibacterium linum is named as Brevibacterium lines. The brevibacterium linum B1 has strong ammonia nitrogen degradation capability, can tolerate a high-salt environment, can grow and maintain high ammonia nitrogen removal efficiency under a salinity condition of 1%-10%, can be applied to high-salt sewage ammonia nitrogen degradation treatment, and has the advantage of short treatment time.
Owner:浙江幸双环保科技有限公司
A strain of Bacillus ornithine suitable for the treatment of cyanide-containing wastewater
The invention relates to the field of water treatment, and discloses a strain of Bacillus ornithinius that is suitable for treating cyanide-containing wastewater containing cyanide. It was preserved in the General Microbiology Center of the China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, its preservation number is CGMCC18052, and the microbial classification is named Ornithinibacillus sp.; the 16s ribosomal subunit gene sequence of the ornithine B1132 is as follows: Shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The Bacillus ornithinius B1132 of the present invention has both alkali resistance, salt resistance, cyanide resistance and the ability to degrade cyanide, fully meets the conditions for treating cyanide-containing wastewater containing thurendan, and is an ideal strain for treating cyanide-containing wastewater containing thurendan resource.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
A strain of Lactobacillus helveticus with high adhesion performance and its application for enhancing immunity
ActiveCN111254087BExcellent Adhesive PropertiesStrong adhesionMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologySpecific immunity
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The invention discloses a strain of Lactobacillus helveticus with high adhesion performance that has the function of enhancing immunity. The number is: CGMCC No.18730. The microbial taxonomy is named Lactobacillus helveticus. The invention also discloses the application of the Lactobacillus helveticus with high adhesion performance which has the function of enhancing immunity. In the present invention, both the live bacterial form and the inactivated form of the bacterial strain have excellent adhesion properties, and improve the immunity of the body by improving the organ index, non-specific immunity and specific immune response of the regulation body; the lactobacillus of the present invention has immune regulation If the corresponding composition is taken, it can improve immune function decline by invigorating immune function.
Owner:HANGZHOU WAHAHA TECH +1
A kind of endophytic fungus Aspergillus rubrum and its application
ActiveCN111996123BEnzyme activity is high and stableFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPectinase
The invention discloses an endophytic fungus Aspergillus rubrum and its application, belonging to the technical field of microorganisms. The microorganism is named as Aspergillus nomius z4, and it has been preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection with the preservation number: CCTCC NO:M 2019946 and the preservation date: November 18, 2019. Aspergillus rubrum z4 of the present invention uses liquid fermentation to produce pectinase, and can effectively degrade components such as pectin, hemicellulose, lignin, cellulose and wax in bamboo waste, and the microorganism can be applied to degrade bamboo powder Obtained in bamboo fiber.
Owner:武夷学院
An extreme thermophilic bacterium and its application in high temperature composting fermentation
ActiveCN110819554BBroad substrate spectrumImprove qualityBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaHuminEngineering
The invention relates to the field of microbial technology and environmental engineering, and discloses an extreme thermophile and its application in high-temperature composting fermentation. The extreme thermophile is named GW-2, and its preservation number is CGMCC 18012, and the classification of microorganisms is named for Chelativorans composti . The strain of the present invention can grow normally in the range of 40-105°C, pH 5-11, and salinity 0-7%, can utilize various carbon sources and nitrogen sources for growth, and has a very broad substrate spectrum. The strain of the present invention combined with the special high-temperature composting process of the present invention can be used for high-temperature aerobic composting treatment of various organic matter such as kitchen waste, agricultural product tailings, slaughterhouse waste, etc., so that the organic matter is completely humified, dehydrated and dried, and loses weight by 70- 92%, finally forming a high-quality organic fertilizer.
Owner:HANGZHOU XIUCHUAN TECH CO LTD
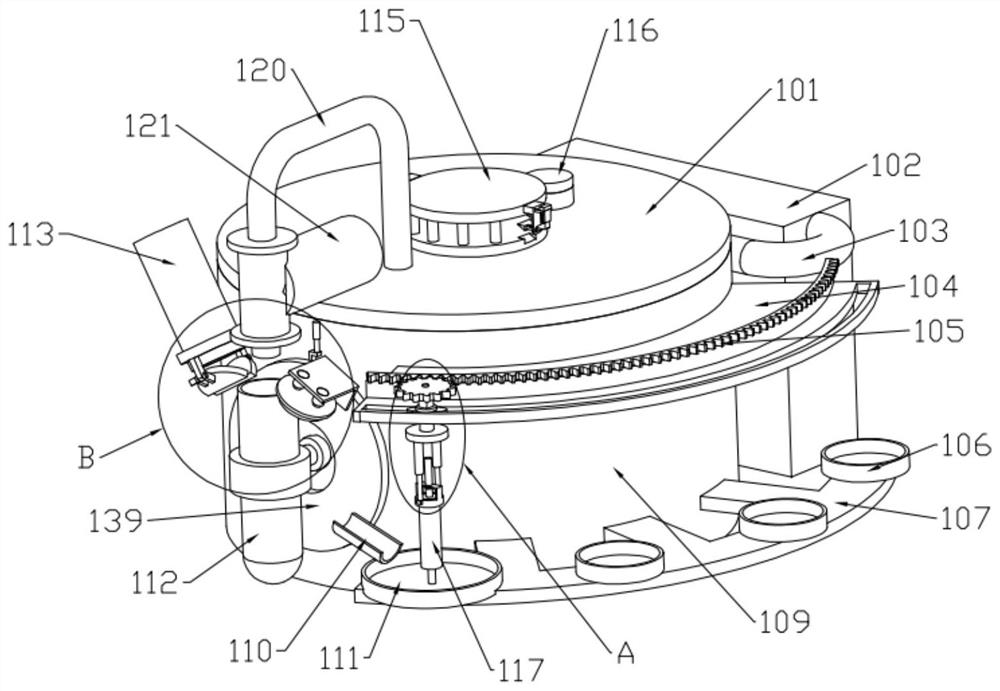
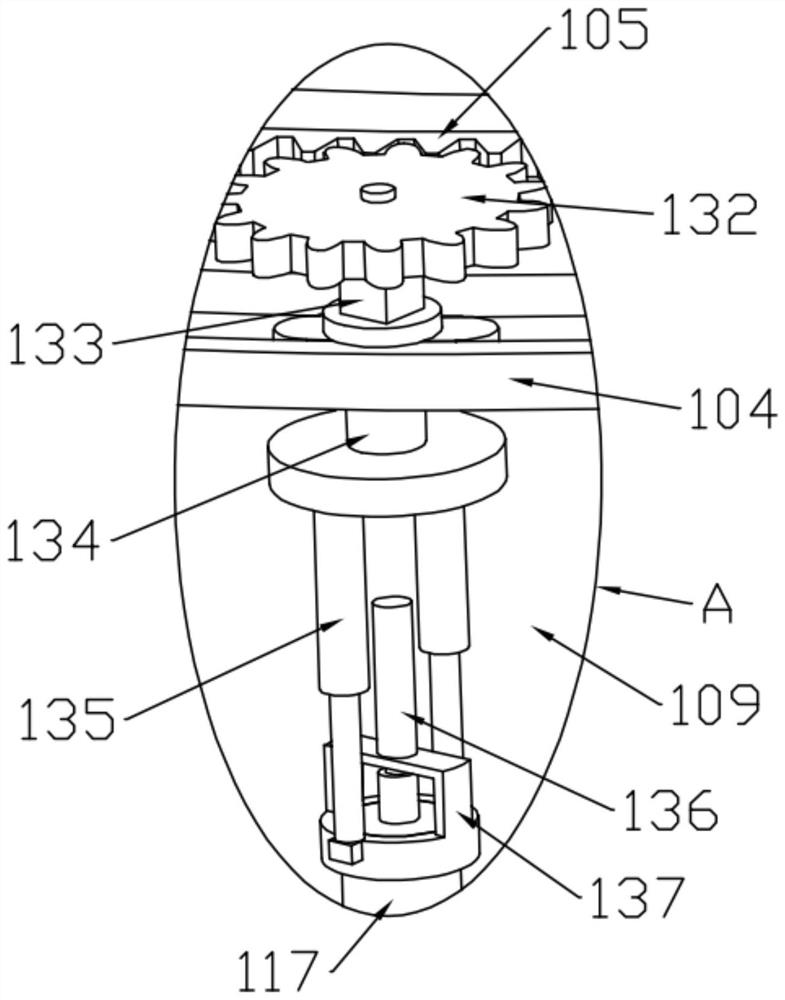
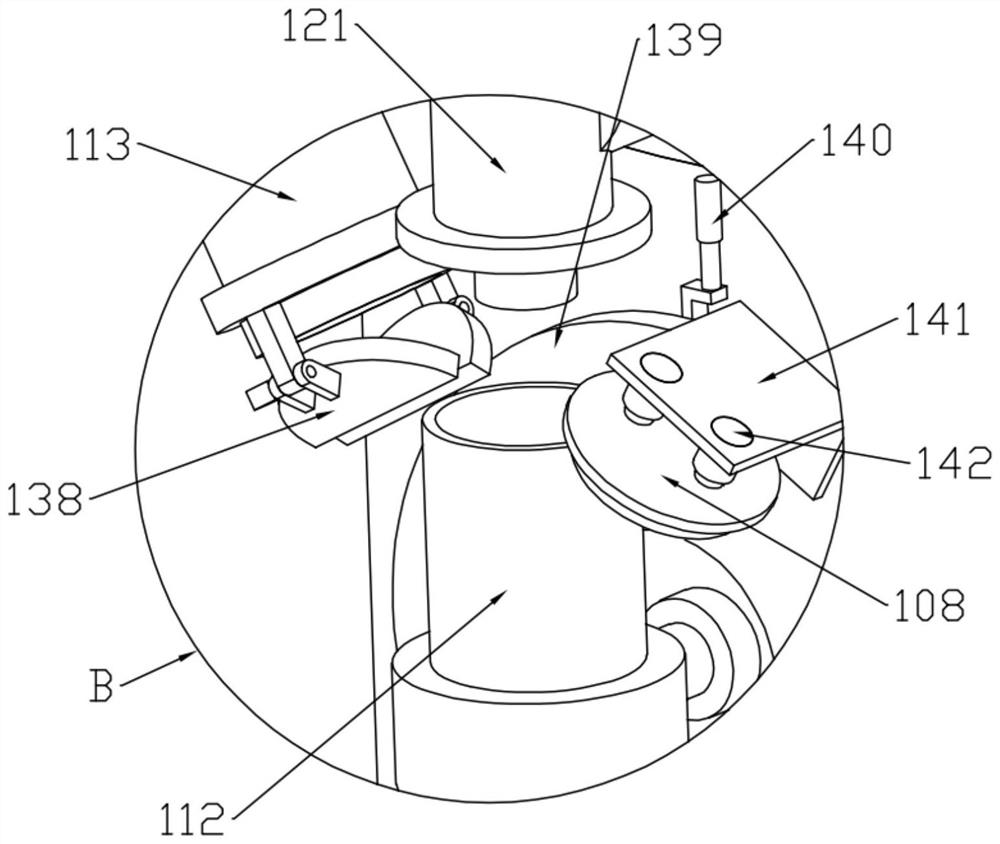
A mobile integrated device for classification, sampling, cultivation and detection of microorganisms
ActiveCN107058074BFast samplingRapid cultivationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringInfusion pump
The invention discloses a mobile-type integrated device for classified sampling, cultivation and detection of microbes. The device comprises a box body, the bottom of which is provided with universal wheels and supporting legs in a fixed mode, wherein a solution storage box, an incubator and a detection box are arranged inside an inner chamber of the box body respectively; a sampling pipe extending to the external of the box body is movably installed on one end of the solution storage box, and connected to an infusion pump; the solution storage box is interconnected with the incubator, and the incubator is connected to the detection box. The mobile-type integrated device for classified sampling, cultivation and detection of microbes has the advantages of being simple in structure, convenient in operation, capable of realizing quick sampling, cultivation and detection of microbes, low in costs, and high in work efficiency.
Owner:江苏端峰生物科技有限公司
Method for classifying the presence or absence of microorganisms in biological media
ActiveCN103764839BEasy to detectSure easyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyFluid phase
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Lactobacillus plantarum with protease production capability, and application thereof
PendingCN112063548AShorten the delay periodStrong Protease Production AbilityMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologyProbiotic bacterium
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and discloses a strain of lactobacillus plantarum with the protease production capability, and application thereof. The lactobacillus plantarum isseparated from pickled vegetables, is named as JX025073.1, is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection centre on July 6, 2020, and has a preservation number of CGMCC NO.20190; and the microorganism is classified and named as lactobacillus plantarum. The lactobacillus plantarum JX025073.1 disclosed by the invention has relatively strong protease production capability, andcan be independently fermented in cow milk without the help of proliferation factors; therefore, more probiotics can be planted in intestinal tracts under the condition of ensuring the taste of the fermented milk; furthermore, the production cost is relatively low; and the prepared fermented milk is low in sugar content.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEDICAL COLLEGE
A strain of Lactobacillus fermentum that can reduce blood uric acid
ActiveCN110079476BLower uric acid levelsEasy dischargeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLactobacillus fermentum
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and discloses a strain of Lactobacillus fermentum that can reduce blood uric acid. The strain is named: 2644 strain, which was preserved in the General Microbial Strain Preservation Center of the China Microbial Strain Collection Management Committee on November 19, 2018. Microbial The deposit number is CGMCC NO.16754; the address of the depository unit is No. 3, Yard No. 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the microbial classification is named Lactobacillus fermentum . The bacterial strain of the invention can effectively reduce the content of blood uric acid. In addition to reducing the intake of exogenous purine substances, it can also promote the excretion of uric acid in the body from the intestines, and more effectively control the body's blood uric acid level.
Owner:HANGZHOU WAHAHA TECH +1
A kind of Lactobacillus helveticus bacterial strain with effect of improving depression and application thereof
ActiveCN113430135BAlleviate depression/anxiety-like behaviorDecreased depressive-like behaviors in the tail-suspension testMilk preparationNervous disorderBiotechnologyBacterial strain
The invention discloses a strain of Lactobacillus helveticus with the function of improving depression. The Lactobacillus helveticus is named WHH1889, which is isolated from the milk dregs collected in the village of Shigatse City, Tibet Autonomous Region, my country, and has been preserved in China Microorganism on February 25, 2021. General Microbiology Center of Species Preservation Management Committee, its preservation number is CGMCC NO.21832, and the microbial classification is named Lactobacillus helveticus Lactobacillus helveticus . The Lactobacillus helveticus strain has good tolerance, adhesion, and intestinal barrier protection properties. It can effectively relieve depression / anxiety-like behaviors of depressed mice, adjust the level of depression neurological factors, and have excellent fermentation properties. It can be applied to fermented milk Among them, it can also be used as drugs, health products or health foods for the prevention and treatment of depression.
Owner:HANGZHOU WAHAHA TECH +1
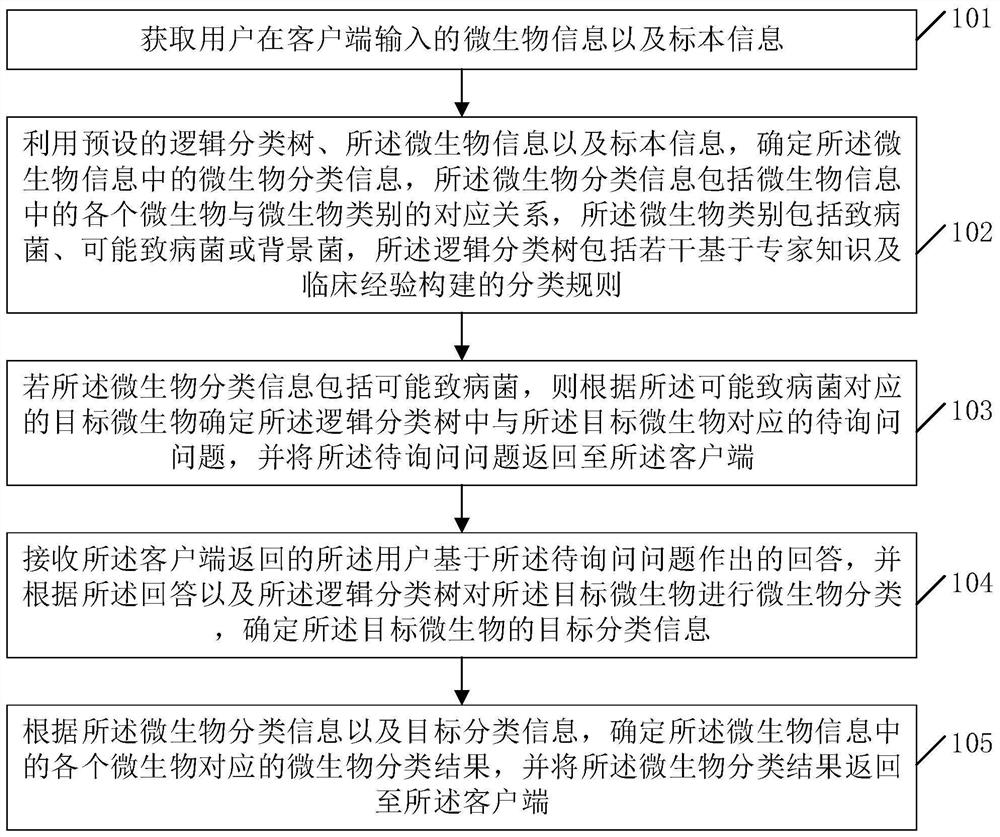
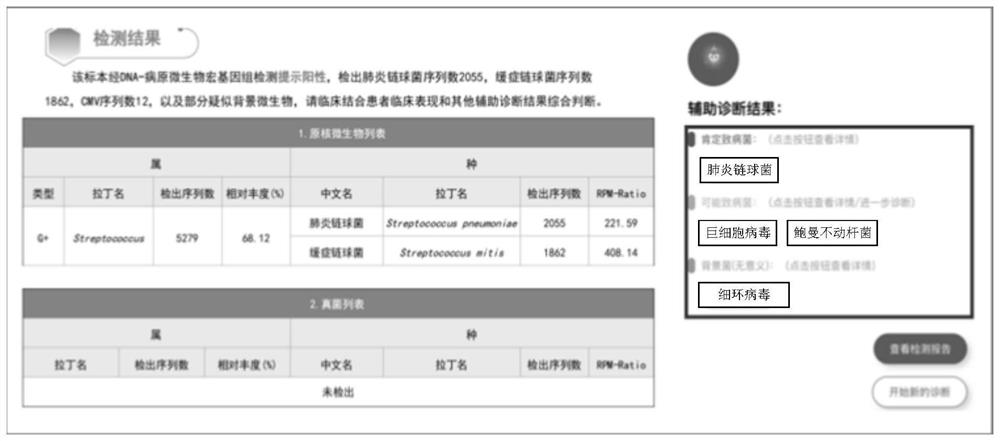
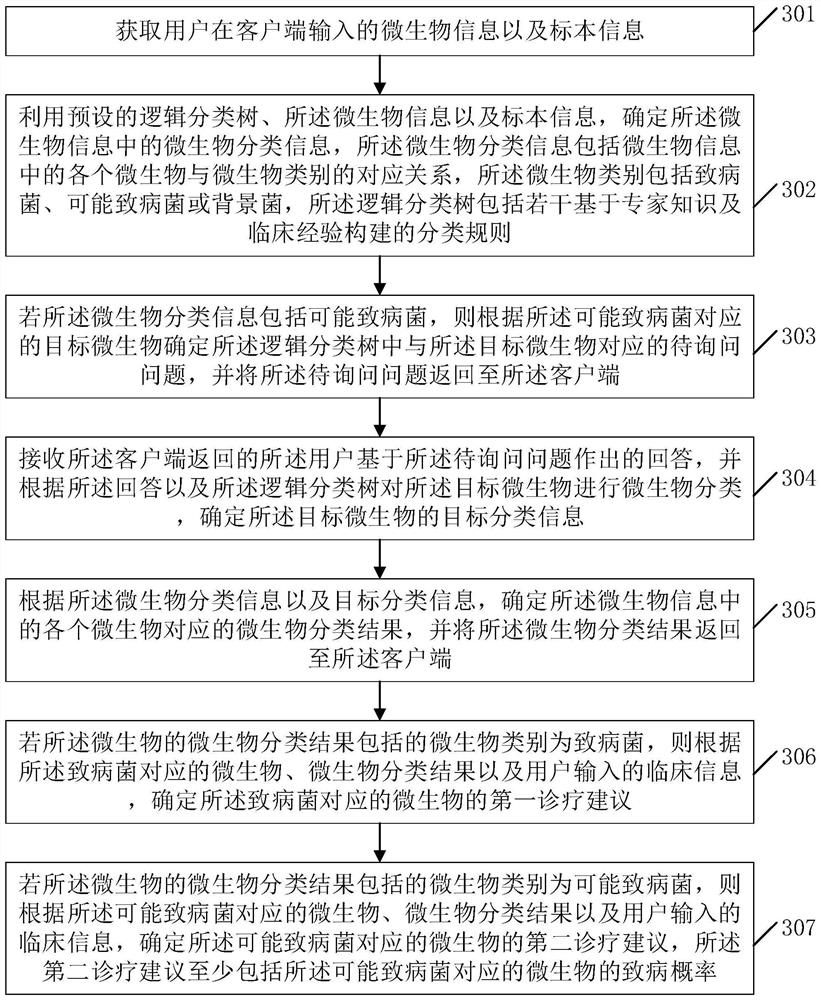
Microbial information interpretation method and device, equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114783525AImprove accuracyImprove report interpretation abilityBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringPathogenic bacteria
The embodiment of the invention discloses a microbiological information interpretation method and device, equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring microbiological information and specimen information input by a user at a client; determining microorganism classification information in the microorganism information by utilizing a preset logic classification tree, the microorganism information and the specimen information; if the microorganism classification information comprises the possible pathogenic bacteria, determining to-be-inquired questions corresponding to target microorganisms in the logic classification tree according to the target microorganisms corresponding to the possible pathogenic bacteria, and returning the to-be-inquired questions to the client; performing microorganism classification on the target microorganisms according to the answers and the logic classification tree, and determining target classification information of the target microorganisms; and according to the microorganism classification information and the target classification information, determining a microorganism classification result corresponding to each microorganism in the microorganism information, and returning the microorganism classification result to the client. By means of the method, the accuracy of microorganism classification can be improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KINGMED DIAGNOSTICS CENT +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com