Lactobacillus plantarum with protease production capability, and application thereof
A protease-producing technology of Lactobacillus plantarum, which is applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of weak protease-producing ability, increased production cost, and increased fermented lactose content, and achieve the effects of strong protease-producing ability, low production cost, and shortened delay period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Example 1: Acquisition and Protease Production Ability of Lactobacillus plantarum JX025073.1
[0054] 1 Screening of protease-producing strains
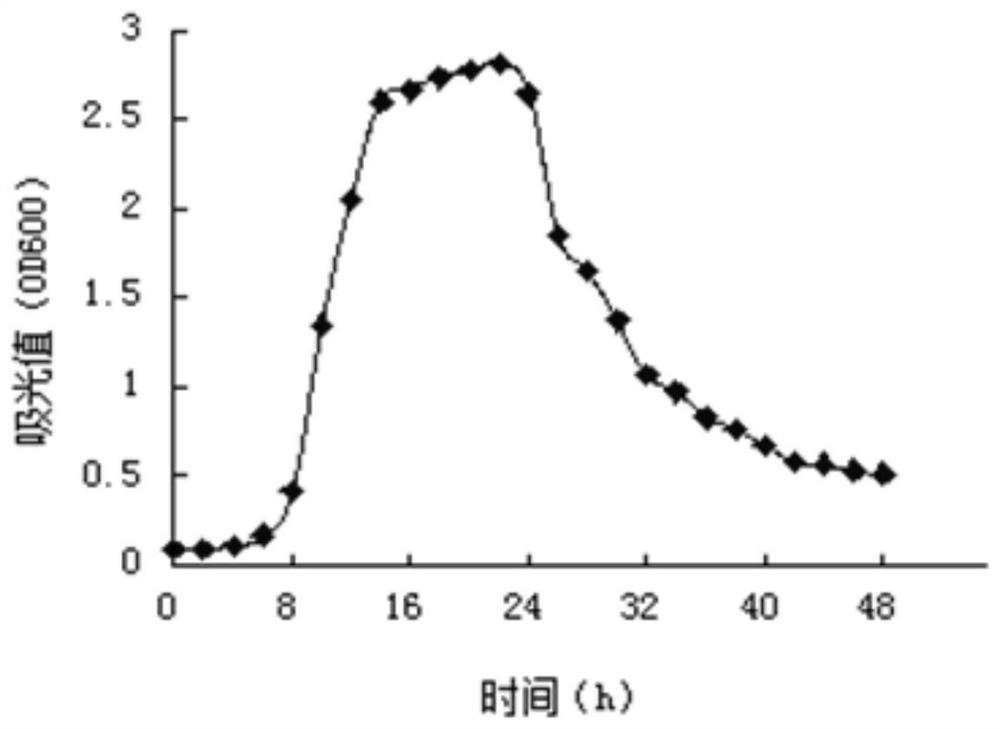
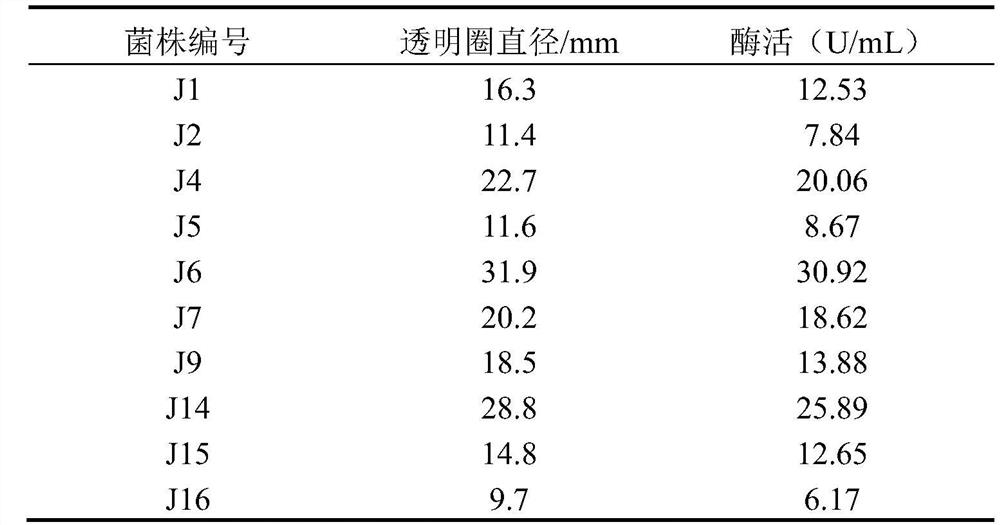
[0055] Pick and produce Ca from the acidified MRS medium by plate isolation culture 2 CO 3 Dissolving circle, milky white or yellow, colony diameter 1-3mm, smooth surface, colonies with neat edges were streaked repeatedly on MRS medium, single colonies were picked for Gram staining and microscopic examination. choose G + Bacteria, rod-shaped, solitary, paired or short-chain strains, 17 strains were isolated, marked as J1~J17, and stored on the slope. The strains J1-J17 were inoculated on the skim milk plate, and after culturing at 35°C for 48 hours, the diameter of the transparent circle produced by each strain on the plate was measured. According to the measurement results, 10 protease-producing Lactobacillus strains with larger transparent circle diameters were screened out from the 17 isolated Lactobacillus strains, and...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment 2: the preparation of fermented liquid
[0065] 1 Activation of Lactobacillus plantarum JX025073.1
[0066] The concentration of 0.5mL bacteria was 4.3×10 9 Add cfu / mL Lactobacillus plantarum JX025073.1 bacterial suspension into 10mL 12% milk (i.e. milk powder aqueous solution with a mass fraction of 12%). After culturing at 40°C for 10h, take 0.5mL of it and add it to 100mL 2% milk. Cultivate at 40°C for 10 h, and activate repeatedly in the above-mentioned manner until the concentration of the obtained bacteria is 5.8×10 9 cfu / mL activated bacterial liquid, the pH of the activated bacterial liquid is 4.2.
[0067] 2 Preparation of fermentation broth
[0068] Take 4mL of the activated bacterial liquid obtained after activation with 12% milk, add it to 100mL of milk medium (12%), and cultivate at 37°C until the cell concentration is about 9.6×10 8 cfu / mL.
[0069] The formula of the above-mentioned milk medium (12%) is as follows: milk powder 12g, distill...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3: Effect of fermentation time on sensory quality of fermented milk
[0071] Preheat fresh milk to 70°C, sterilize at 100°C for 5 minutes, and then cool to 37°C to obtain sterilized milk; add the fermented liquid prepared in Example 2 to the sterilized milk, the volume of sterilized milk and fermented liquid The ratio was 1:0.02. After culturing at 40°C for 10, 12, 14, 16, and 18 hours respectively, the sensory evaluation was performed according to the standards in Table 2. The results are shown in Table 3. It can be seen from the table that when the fermentation time is 14 hours, the fermented milk produced is milky white, moderately sour, soft and dense, soft and elastic, without bubbles, has the unique aroma of yogurt, strong smell, and good sensory properties.
[0072] Table 2 Sensory scoring criteria
[0073]
[0074] Table 3 Effect of fermentation time on sensory quality of fermented milk
[0075]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com