Lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and strain, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as weak inhibition ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] The screening of embodiment 1 acid resistance and bile salt lactobacillus plantarum
[0048] Dilute 100 µL of freshly collected healthy human intestinal flora suspension with a 10-fold gradient, spread it on MRS agar medium, put it into an anaerobic culture tank, and use ternary mixed gas (80% nitrogen, 10% hydrogen) and carbon dioxide 10%) to replace the gas in the tank so that the final oxygen concentration in the culture tank was ≤5%, and the culture tank was cultivated in a 37°C incubator for 48 hours. Select independent, bright, and full-bodied colonies, and use Matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time–of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS, referred to as flight mass spectrometry) technology for high-throughput bacterial colonies. a preliminary identification.
[0049] The colonies initially identified as Lactobacillus plantarum by MALDI-TOF MS equipment were picked into liquid MRS medium and cultured at 37°C for 12 hours, and then placed on MRS agar m...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2 Preservation of bacterial strains
[0055] After the screened Lactobacillus plantarum NKK20 was streaked on the MRS agar medium for 48 hours, a single colony was selected and placed in a 10ml liquid medium, which was MRS liquid containing 4.5% soybean lecithin and 2% calcium carbonate Medium. Place the culture medium at a constant temperature of 37°C for 12h-16h, and measure the OD of the culture medium 600 When the value is greater than or equal to 1.2, add glycerol solution to the culture medium at a volume ratio of 1:1. The concentration of the glycerol solution is 30%-40%. Pre-cool at 4°C for 2 hours, then place at -20°C for 4 hours, and finally transfer to -80°C refrigerator or store in liquid nitrogen.
Embodiment 3
[0056] Example 3 Intestinal Mucosa Adhesion Experiment
[0057] Lactobacillus plantarum NKK20, Lactobacillus plantarum 229v and Lactobacillus plantarum LP-115 were selected for intestinal mucosal adhesion experiment.
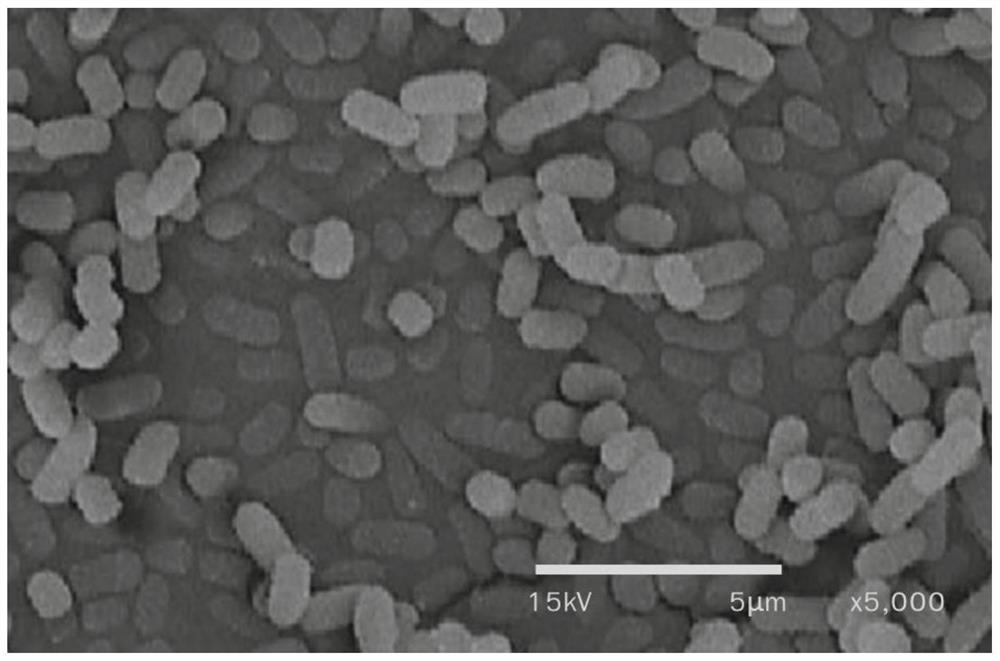
[0058] After each strain was cultured at 37°C for 3 hours, scanning electron microscope analysis showed that all the strains adhered to the intestinal mucosa, and the adhesion rate of Lactobacillus plantarum NKK20 to the intestinal mucosa was basically the same as that of LP-115, about 81%. significantly higher than Lactobacillus plantarum 229v, and the adhesion rate of each strain to the intestinal mucosa is shown in Table 2.
[0059] Scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of intestinal mucoadhesive Lactobacillus plantarum NKK20, see Figure 4 .
[0060]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com