Method for combined enhanced phytoremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon polluted farmland soil
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and phytoremediation technology, applied in the field of soil organic pollution remediation, can solve problems such as low bioavailability and limited phytoremediation efficiency, and achieve the effects of weak enrichment ability, improved phytoremediation efficiency, and improved biological activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A method for uniting and strengthening phytoremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated farmland soil. This embodiment is carried out in a greenhouse for facility agriculture in Shenbei New District, Shenyang City, and includes the following steps:
[0029] S1: Level the 0-20cm surface soil of facility agriculture, discard the residues including weeds, gravel, and plastic, and continue to plow and mix; adopt the field experiment method, the area of the experimental plot is 1.5m×1.5m, and the area of the adjacent plot is 1.5m×1.5m. Set up about 50cm isolation ditch between them.
[0030] S2: Spray the prepared anion-nonionic mixed surfactant RL-TX100 solution containing rhamnolipid (RL) and Triton 100 (TX100) evenly on the polluted soil, wherein, rats in the RL-TX100 solution The mixing ratio of Liglycolipid (RL) and Triton 100 (TX100) is 1:9, the spraying concentration is 80mg / kg soil, and then the soil is turned and mixed immediately.
[0031] S3: ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Compared with Example 1, the experiment of this example is that the concentration of the RL-TX100 solution is 100 mg / kg of soil sprayed on the soil, and other steps are the same as Example 1.
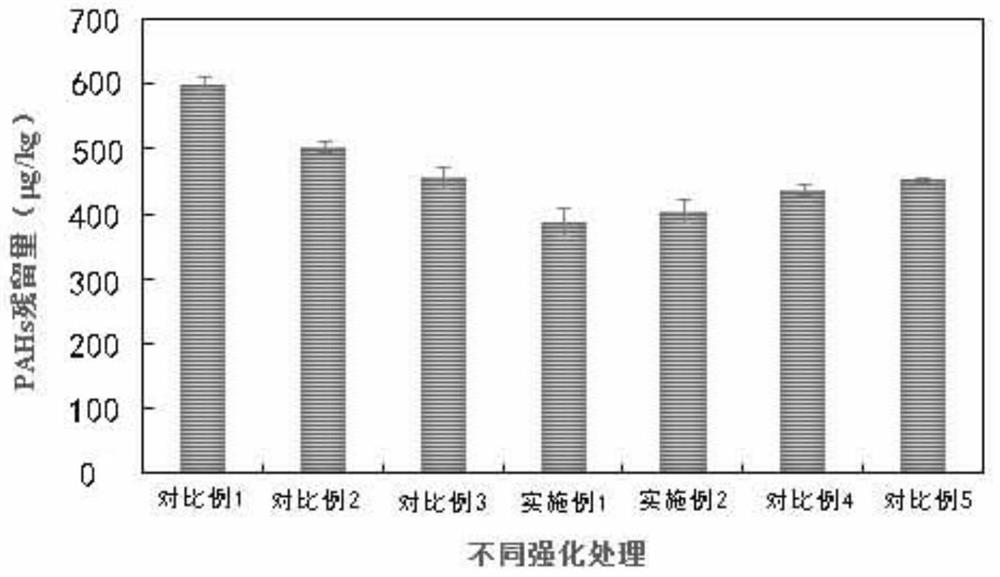
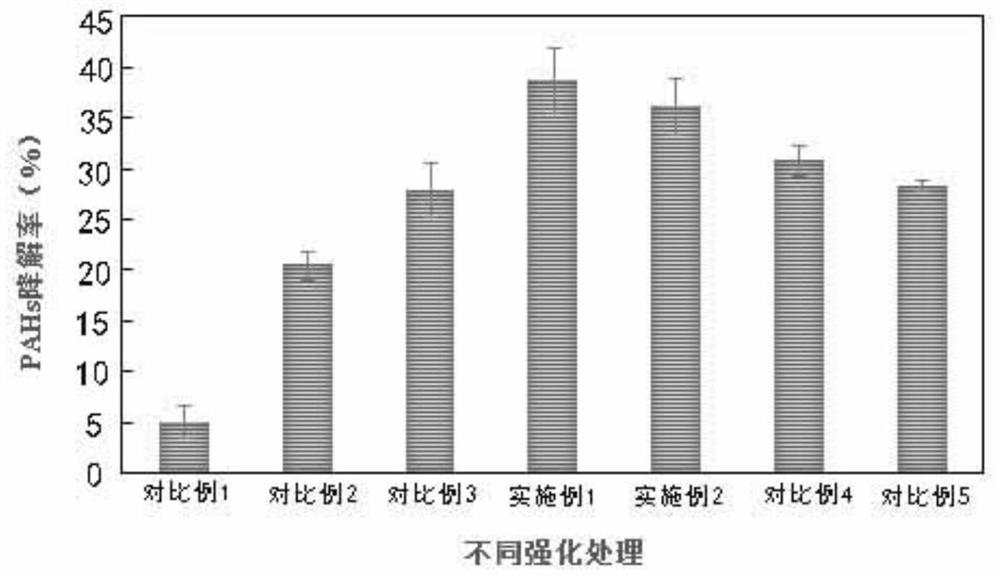
[0036] The radish was harvested when it was 3 months old, and the content of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the soil was measured, and the degradation rate was calculated, such as figure 1 As shown, under the experimental conditions, the content of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the soil is 404.47μg / kg, such as figure 2 As shown, the degradation rate of PAHs under the experimental conditions was 36.26%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com