Preparation method of high-yield nucleic acid fragments
A nucleic acid fragment, high-yield technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as low economic efficiency, increased material demand, and extended production cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The construction of embodiment 1 recombinant plasmid
[0036] S1. Take the pUC57-Kan-Yh plasmid strain containing the target gene, inoculate it in LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL Kan, shake it at 37°C and 220 rpm overnight, take the overnight culture, and use the plasmid to extract a small amount The kit performs plasmid extraction to obtain the pUC57-Kan-Yh target plasmid.
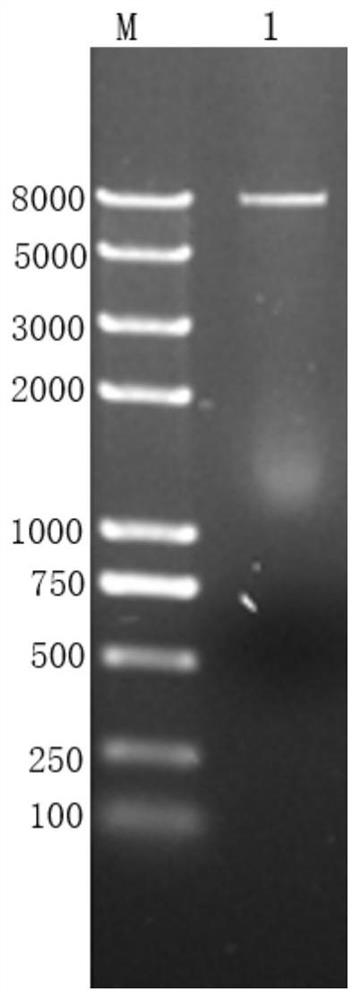
[0037] S2. Take 10 μg of the pUC57-Kan-Yh target plasmid, digest it with the restriction endonuclease KpnI, and digest it at 37°C for 40 minutes. After the reaction solution is separated by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, the target of about 3759 bp is recovered by cutting the gel. Fragment bands and 2579bp vector fragments, and then purified by DNA gel recovery kit to obtain Yh target gene fragments and vector backbone fragments, such as figure 1 shown.
[0038] S3. Add calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIAP) to the recovered carrier skeleton fragment solution for dephosphorylation trea...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Screening of high-yielding plasmid strains and analysis of the target gene fragment yield of recombinant plasmids:
[0049] 1. Screening of high-yielding plasmid strains
[0050] The 5 newly-made plasmid strains and original plasmid strains that were correctly identified were inoculated in 50 μg / mL Kan-resistant LB liquid medium, and cultured overnight at 37°C and 220 rpm with shaking. Measure the OD of each bacterial solution at 600nm with a spectrophotometer 600 value. Adjust each bacterial solution to an appropriate OD with sterile water 600 , take an appropriate volume of bacterial liquid, extract the plasmid with a plasmid mini-extraction kit, and use the same volume (100 μL) for elution. Then measure the concentration of each plasmid solution with an ultra-micro spectrophotometer, and calculate the content of the plasmid and the content of the target gene fragment in each sample. According to the content of the target gene segment, the plasmid with h...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The separation and purification analysis of the target gene fragment of embodiment 3
[0055] (1) Plasmid amplification and extraction
[0056] The above-mentioned recombinant plasmid strains and original plasmid strains were respectively inoculated in Kan-resistant LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL, and cultured overnight at 37°C and 220 rpm with shaking. Bacteria were collected by centrifugation at 8000×g for 2 min to collect the bacteria, and the plasmids were extracted respectively.
[0057] (2) Enzymatic digestion
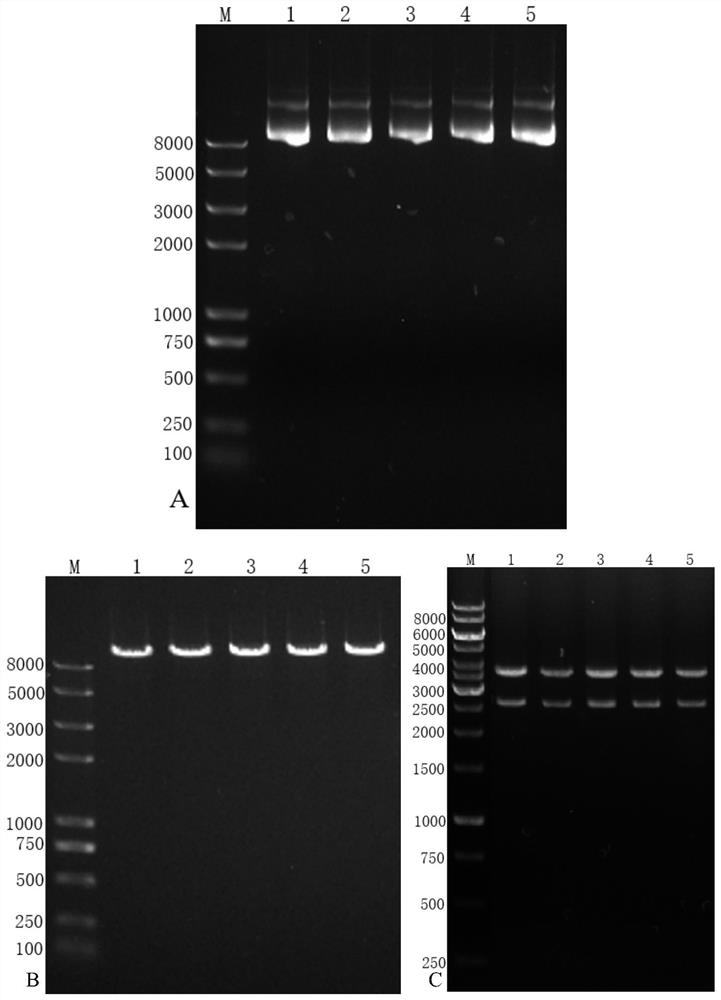
[0058] Take 1 mg of the recombinant plasmid and the original plasmid and digest them with the restriction endonuclease KpnI, and detect them by electrophoresis until the digestion is complete. Figure 7 shown.
[0059] (3) Purification of target gene fragments
[0060] Take a certain amount of digestion solution and use AKTA for sample loading analysis. Separation and purification by chromatographic column NanoQ-15L, the target peak and carrier ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com