Method for detecting and identifying subspecies of fusobacterium nucleatum
A subspecies, nucleotide sequence technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of inability to reach the subspecies level, lack of accuracy, and technical limitations of isolation and culture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Obtaining of subspecies-specific DNA sequences
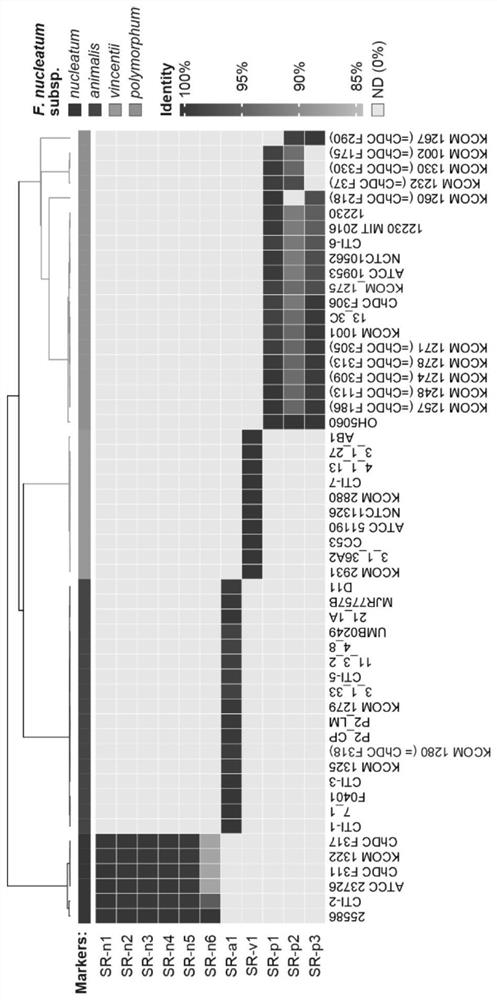
[0043] In this example, first, the subspecies-specific DNA sequence of Fusobacterium nucleatum was obtained by comparative genomics. The specific method is to download the sequenced Fusobacterium nucleatum strains from the NCBI public database (such as image 3 shown) genomes, including completed maps and drafts; kSNP software was used to construct a genome-wide phylogenetic tree to determine the strains belonging to different subspecies; PGAP software was used to perform pan-genome analysis on all included genomes. From the obtained gene clusters, genes that are conserved in all strains of a certain subspecies of Fusobacterium nucleatum but absent in other subspecies are selected. Compare the corresponding gene sequence with the NCBI nucleotide database to observe whether there are homologous sequences in other subspecies and species other than Fusobacterium nucleatum, and confirm whether it is truly specific...
Embodiment 2
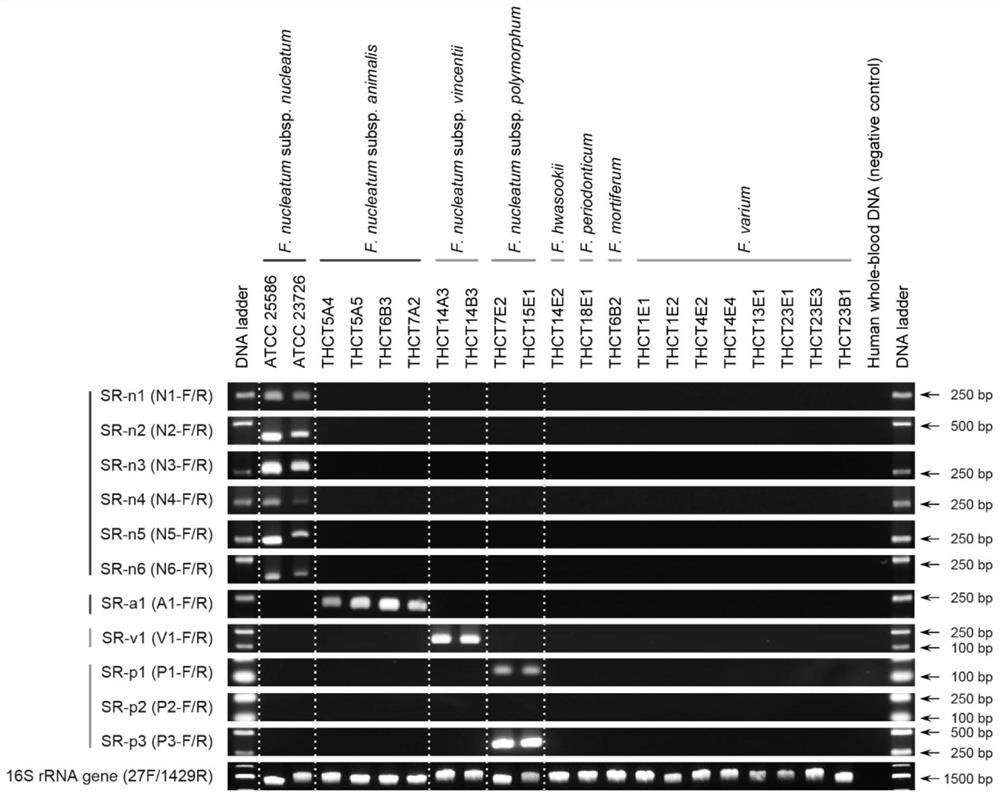
[0049] Example 2 Example of the application of subspecies-specific primers in a single strain sample
[0050] extract as figure 1 Total DNA of known Fusobacterium nucleatum strains of the subspecies listed in . PCR amplification was performed using the subspecies-specific primers in Table 1. In addition, human whole blood DNA was used as negative control for PCR, and 16S rRNA gene amplification primers (27F and 1429R) were used as positive control for bacterial DNA template. Agarose gel electrophoresis results ( figure 1 ) shows that each specific primer has a single specific amplification band at the corresponding position in the corresponding subspecies of Fusobacterium nucleatum strains, and there is no amplification in other subspecies and other Fusobacterium strains. In the detection of 10 Fusobacterium nucleatum strains covering 4 subspecies, the detection results were completely consistent with the strain subspecies classification, and the accuracy was 100%.
Embodiment 3
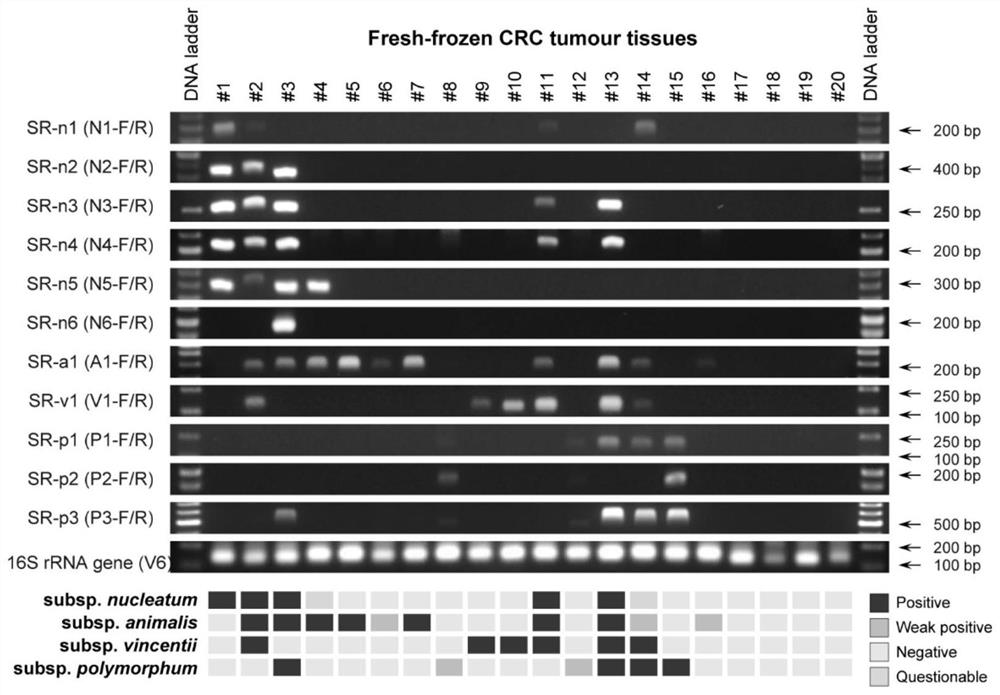
[0051] Example 3 Application example of subspecies-specific primers in samples containing mixed bacteria
[0052] Take the tumor tissue of 20 colorectal cancer patients as an example. Tissue DNA was extracted and PCR amplified using the subspecies-specific primers in Table 1. In addition, a universal primer for the V6 region of the 16S rRNA gene was used as a DNA template positive control. The results of agarose gel electrophoresis were as follows: figure 2 shown. The results of 6 pairs of primers in nucleatum subspecies were different, but they were relatively consistent, and the results of N3-F / R and N4-F / R were completely consistent. The positive amplification of other primers could not completely cover the strains with positive amplification of N3-F / R and N4-F / R, it is speculated that they may have differences in sensitivity under the background of complex flora; another individual primer (N1 -F / R and N5-F / R) were positively amplified in strains where other primers wer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com