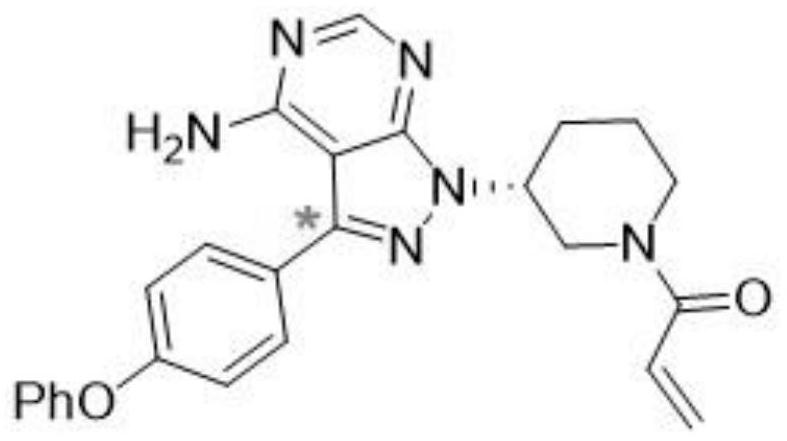
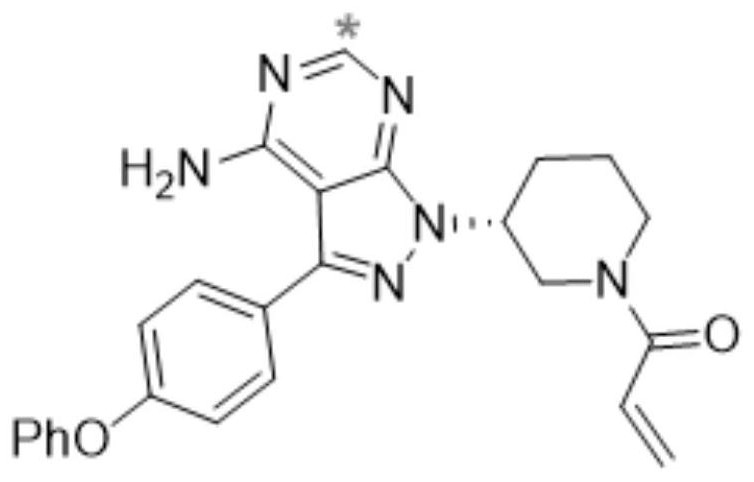
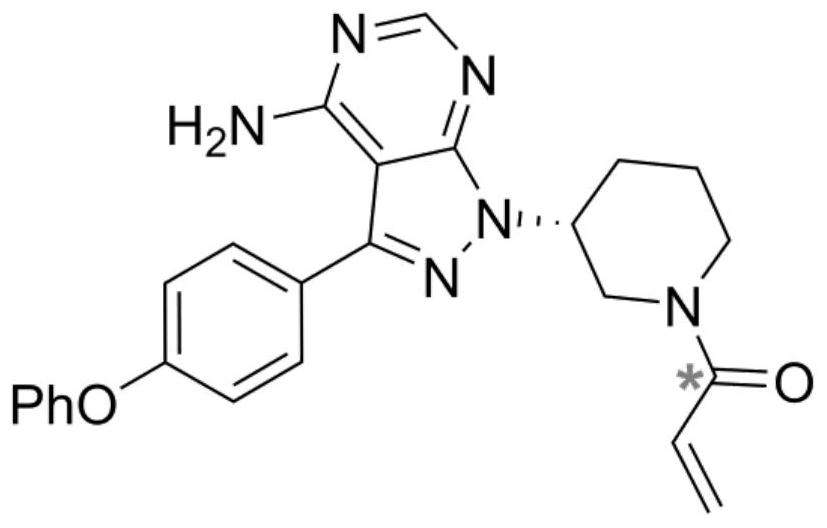
Radioisotope carbon-14 labeled ibrutinib and synthesis method thereof
A radioactive isotope and ibrutinib technology, applied in the field of radiochemical synthesis, can solve the problem of high cost of labeling and synthesis, and achieve the effect of low raw material cost and high operational safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] S1: Slowly drop concentrated sulfuric acid (5mL, 18.4M) into the radioactive material under argon protection at -78°C[ 14 C] In barium carbonate (28.8μCi, 0.5mmol), escape [ 14 C]CO 2 A solution (5 mL) of the metal reagent 4-phenoxyphenyllithium (0.55 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran was introduced through a thin glass tube. After stirring for 30 minutes, the reaction was completed. The system was slowly raised to room temperature, and water (5 mL) was added to quench the reaction under ice-water bath cooling. The aqueous phase was extracted with dichloromethane, and the remaining aqueous phase was adjusted to pH 4 with dilute hydrochloric acid (1M). Methane (4mL) was extracted 5 times, the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered with suction, concentrated under reduced pressure, and dried to obtain 4-phenoxybenzene[ 14 C] Formic acid (2, 25.9 μCi, 96 mg, radiochemical yield 90%). 1 H NMR (400MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ: 12.82(s, 1H), 7.94(d, J=8.7H...
Embodiment 2
[0053] S1: Slowly drop concentrated sulfuric acid (5mL, 18.4M) into the radioactive material under the protection of argon at room temperature[ 14 C] In barium carbonate (28.8μCi, 0.5mmol), escape [ 14 C]CO 2 A solution (5 mL) of the metal reagent 4-phenoxyphenylmagnesium iodide (0.55 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran was introduced through a thin glass tube. After stirring for 30 min, the reaction was completed. The system was slowly raised to room temperature, and water (5 mL) was added to quench the reaction under cooling in an ice-water bath. The aqueous phase was extracted with dichloromethane, and the remaining aqueous phase was adjusted to pH 4 with dilute hydrochloric acid (1M). Methane (4mL) was extracted 5 times, the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered with suction, concentrated under reduced pressure, and dried to obtain 4-phenoxybenzene[ 14 C] formic acid (2, 24.7μCi, radiochemical yield 86%). 1 H NMR (400MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ: 12.82(s...
Embodiment 3
[0062] S1: Slowly drop concentrated sulfuric acid (5mL, 18.4M) into the radioactive material under the protection of argon at room temperature[ 14 C] In barium carbonate (28.8μCi, 0.5mmol), escape [ 14 C]CO 2A solution (5 mL) of the metal reagent 4-phenoxyphenylmagnesium bromide (0.55 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran was introduced through a thin glass tube. After stirring for 30 minutes, the reaction was completed. The system was slowly raised to room temperature, and water (5 mL) was added to quench the reaction under ice-water bath cooling. The aqueous phase was extracted with dichloromethane, and the remaining aqueous phase was adjusted to pH 4 with dilute hydrochloric acid (1M). Methane (4mL) was extracted 5 times, the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered with suction, concentrated under reduced pressure, and dried to obtain 4-phenoxybenzene[ 14 C] formic acid (2,27.4μCi, radiochemical yield 95%). 1 H NMR (400MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ: 12.82(s, 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com