Polysulfide iron sodium additive for strengthening low-temperature rapid reduction of refractory iron ore and application method of multi-sulfur iron sodium additive
An application method, the technology of sodium polysulfide, is applied in the field of additives for strengthening the solid-state reduction of iron ore, which can solve the problems of poor solid-state reduction effect of iron ore, complex production process of additives, and difficult treatment of metallurgical solid waste, etc. Iron ore solid-state reduction and co-processing of metallurgical solid waste, low price and reasonable composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
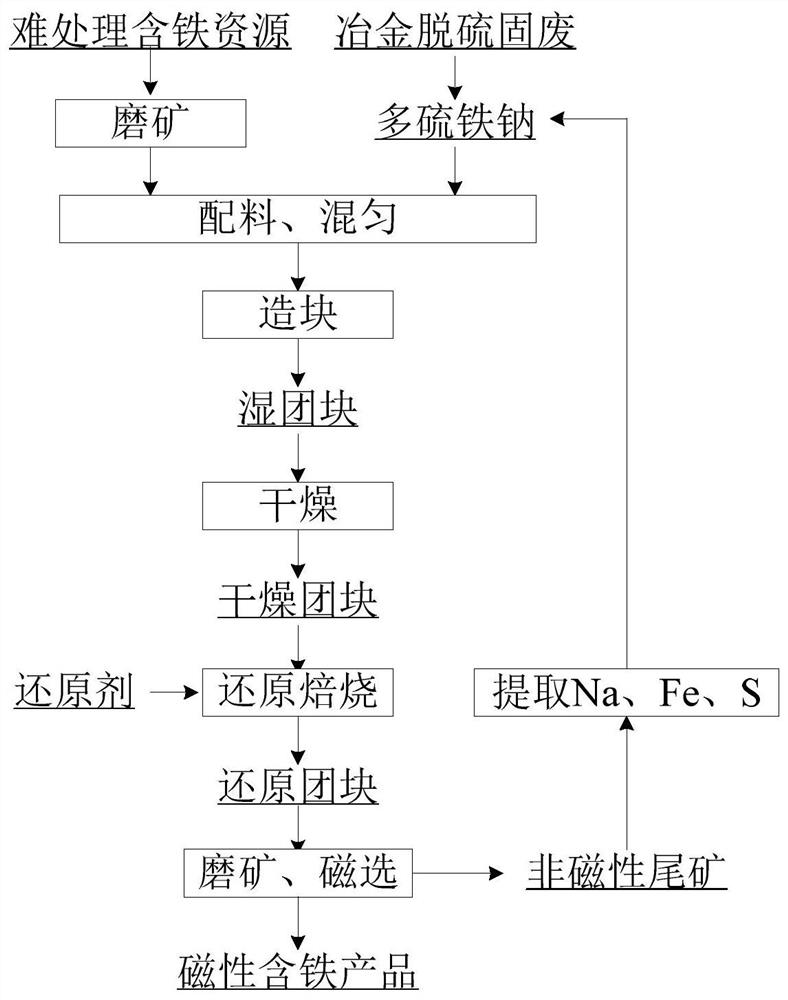
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
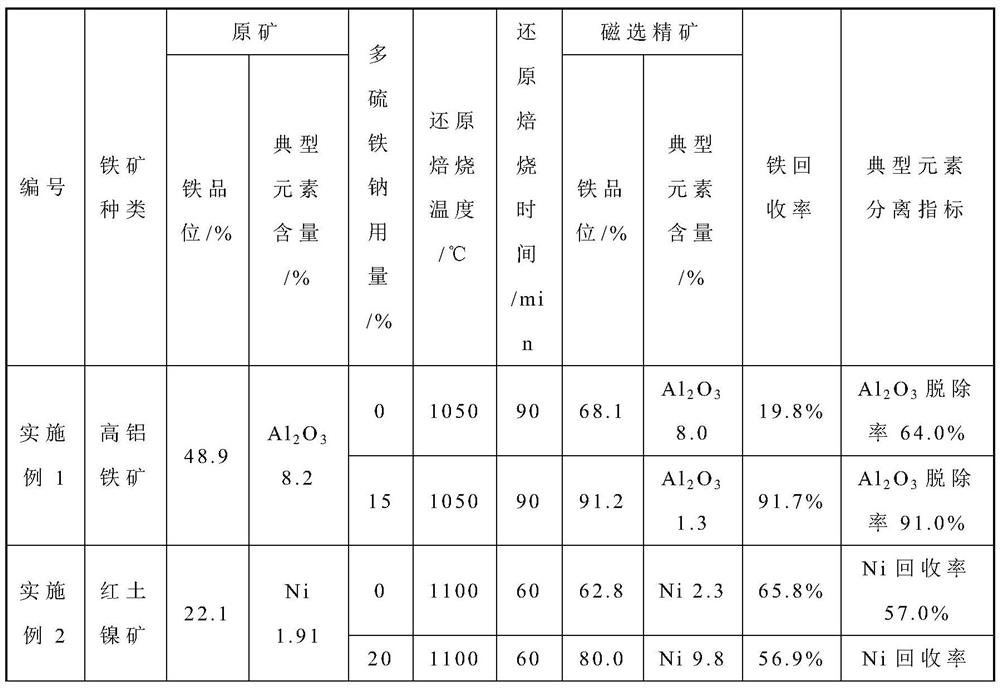
[0044] The TFe content of a certain high alumina iron ore is 48.9%, Al 2 o 3 The content is 8.2%. Mix the finely ground iron ore with 15% mass ratio of sodium polysulfide additive to form agglomerates. After the obtained agglomerates are dried, they are reduced and roasted using lignite as a reducing agent. The roasting temperature is 1050°C. The time is 90 minutes. Compared with no addition of desulfurization slag, the average particle size of metallic iron particles in roasted ore grows from 5 μm to 46 μm, which can effectively improve the subsequent iron and aluminum separation effect. The iron grade of the magnetic separation concentrate is 91.2%, Al 2 o 3 The content is 1.30%, the iron recovery is 91.7%, and the aluminum removal rate is 91.0%.
Embodiment 2
[0050] The TFe content of a certain laterite nickel ore is 22.1%, and the Ni content is 1.91%. The finely ground laterite nickel ore is mixed with a mass ratio of 20% polysulfide sodium additive to make agglomerates. After the obtained agglomerates are dried, lignite is used as the The reducing agent is subjected to reduction roasting, the roasting temperature is 1100°C, and the roasting time is 60 minutes. Compared with no addition of desulfurization slag, the average particle size of nickel-iron alloy particles in roasted ore grows from 7 μm to 52 μm, which can effectively improve the subsequent separation effect of nickel-iron and gangue components. The iron grade of the magnetic separation concentrate is 80.0%, the nickel grade is 9.8%, the iron recovery rate is 56.9%, and the nickel recovery rate is 92%.
Embodiment 3
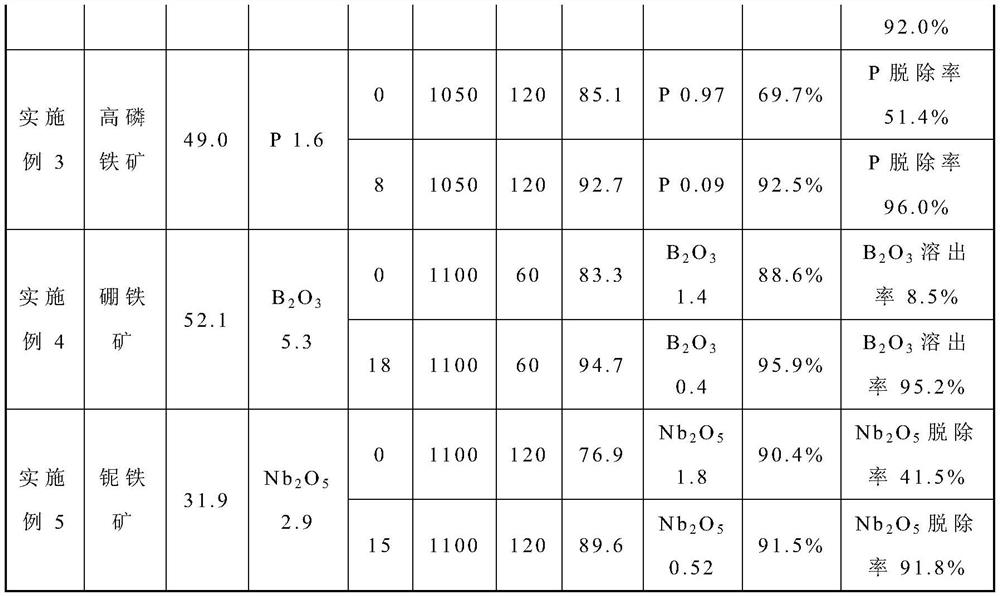
[0056] The TFe content of a certain high-phosphorus oolitic hematite is 49.0%, and the P content is 1.6%. The finely ground high-phosphorus oolitic hematite is mixed with a mass ratio of 8% polysulfide sodium additive to make agglomerates, and the obtained agglomerate After the blocks are dried, the anthracite is used as the reducing agent for reduction roasting, the roasting temperature is 1050°C, and the roasting time is 120 minutes. Compared with no addition of desulfurization slag, the average particle size of metallic iron particles in roasted ore grows from 9 μm to 48 μm, which can effectively improve the subsequent iron and phosphorus separation effect. The iron grade of the magnetic separation concentrate is 92.7%, the phosphorus content is 0.09%, the iron recovery is 92.5%, and the phosphorus removal rate is 96.1%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com