Method for producing bacterial cellulose through coconut milk pre-fermentation
A technology of bacterial cellulose and pre-fermentation, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation, etc., can solve the problem of slow growth and reproduction of Acetobacter xylinum, high transportation cost of coconut water, hard coconut tissue structure, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of omitting the embrittlement step, solving the shortage of raw material resources and making the taste crisp and tender
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
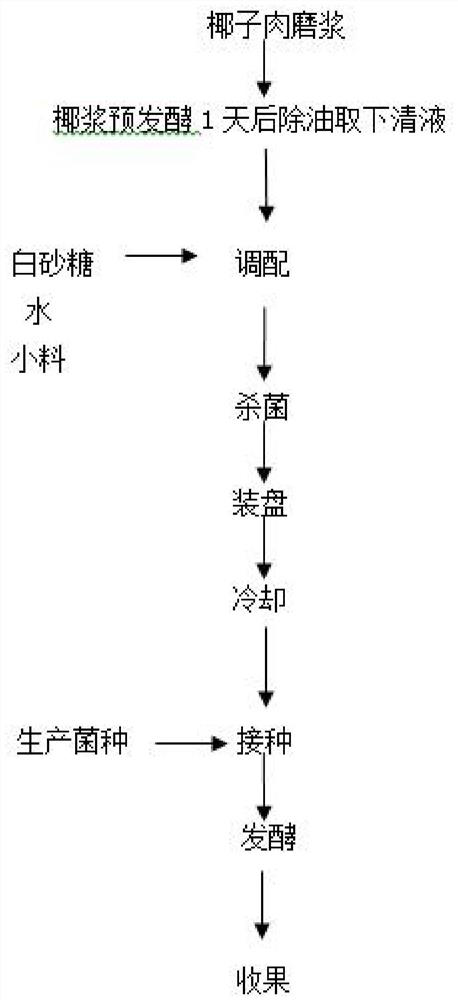
[0030] S1, first fresh coconut meat is defibrinated to obtain fresh coconut milk, and fresh coconut meat is to obtain fresh coconut meat by peeling and scraping the coconut fruit picked for 2 days;
[0031] S2. Pour the fresh coconut milk obtained in step S1 into cooking equipment, boil and sterilize the coconut milk, then remove it and cool it to room temperature, then transfer it to a fermenter and insert yeast for fermentation. After 24 hours of fermentation, the coconut milk oil will float. Stratification occurs, remove the floating oil with a scraper tool, and collect the supernatant;
[0032] S3. Transfer the supernatant liquid obtained in step S2 to the batching equipment, and then respectively prepare white granulated sugar, small ingredients and water in corresponding weight ratios through the batching equipment, and mix the supernatant liquid, white granulated sugar, small ingredients and water of the batching Pour water into the mixing equipment one by one, start th...
Embodiment 2
[0036] S1, first fresh coconut meat is defibrinated to obtain fresh coconut milk, and fresh coconut meat is to obtain fresh coconut meat by peeling and scraping the coconut fruit picked for 1 day;
[0037] S2. Pour the fresh coconut milk obtained in step S1 into cooking equipment, boil and sterilize the coconut milk, then remove and air-cool to room temperature, then transfer to a fermenter and insert yeast for fermentation. After 23 hours of fermentation, the coconut milk oil floats, Stratification occurs, remove the floating oil with a scraper tool, and collect the supernatant;
[0038] S3. Transfer the supernatant liquid obtained in step S2 to the batching equipment, and then respectively prepare white granulated sugar, small ingredients and water in corresponding weight ratios through the batching equipment, and mix the supernatant liquid, white granulated sugar, small ingredients and water of the batching Pour water into the mixing equipment one by one, start the mixing e...
Embodiment 3
[0042] S1, at first the fresh coconut meat is refined to obtain fresh coconut milk, and the fresh coconut meat is obtained by peeling and scraping the coconut fruit picked for 3 days;
[0043] S2, pour the fresh coconut milk obtained in step S1 into the cooking equipment, boil the coconut milk to sterilize, then remove and air-cool to room temperature, then transfer to the fermenter and insert yeast to ferment, after 25 hours of fermentation, the coconut milk grease floats, Stratification occurs, remove the floating oil with a scraper tool, and collect the supernatant;
[0044]S3. Transfer the supernatant liquid obtained in step S2 to the batching equipment, and then respectively prepare white granulated sugar, small ingredients and water in corresponding weight ratios through the batching equipment, and mix the supernatant liquid, white granulated sugar, small ingredients and water of the batching Pour water into the mixing equipment one by one, start the mixing equipment and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com