An environmental DNA method to detect the distribution of giant salamanders
A giant salamander and environmental technology, applied in the molecular field, can solve the problems of small number of natural populations, ineffective survey methods, time-consuming and labor-intensive costs, etc., and achieve the effect of high amplification efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: Primer Sensitivity Verification
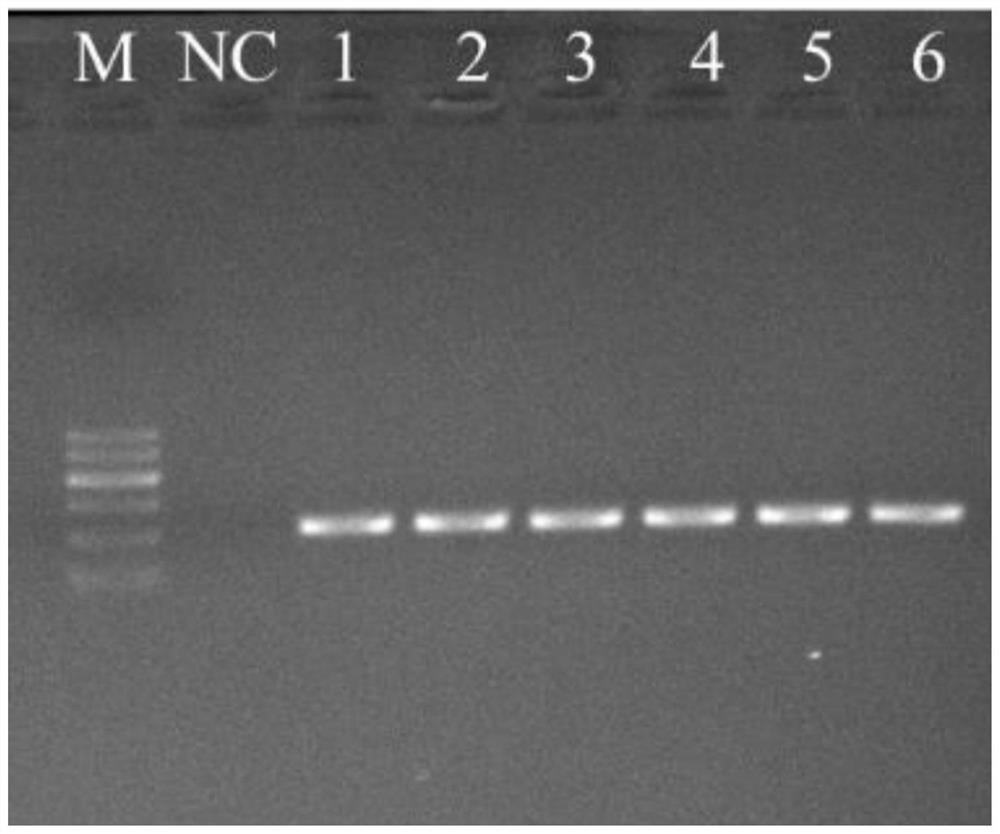
[0026] 1. Chinese giant salamander tissue sample DNA was extracted using TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit. DNA from tissue samples of 22 Chinese giant salamanders captured from Gutian Mountain, Zhejiang Province (concentration: 1.55 ng / μL, numbers 1-22) were amplified by PCR using the 5 pairs of primers described above. Amplification results showed only clear band after agarose gel electrophoresis, and the sequence length of the band was between 150-250bp.
[0027] According to the brightness of the amplified bands, that is, the amplification efficiency, it was judged that the amplification effects of the primers Ad_Cytb_E1, Ad_Cytb_E3, Ad_Cytb_E5 were better than those of Ad_Cytb_E2, Ad_Cytb_E4.
[0028] 2. Select 6 DNA samples with slightly poor amplification effects, dilute the DNA stock solution 20 times (sample concentration 0.0775ng / μL), and use the above-mentioned 3 pairs of primers with better amplification effects to carry o...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2: Primer Specificity Verification
[0032] Two methods were used for primer specificity verification:
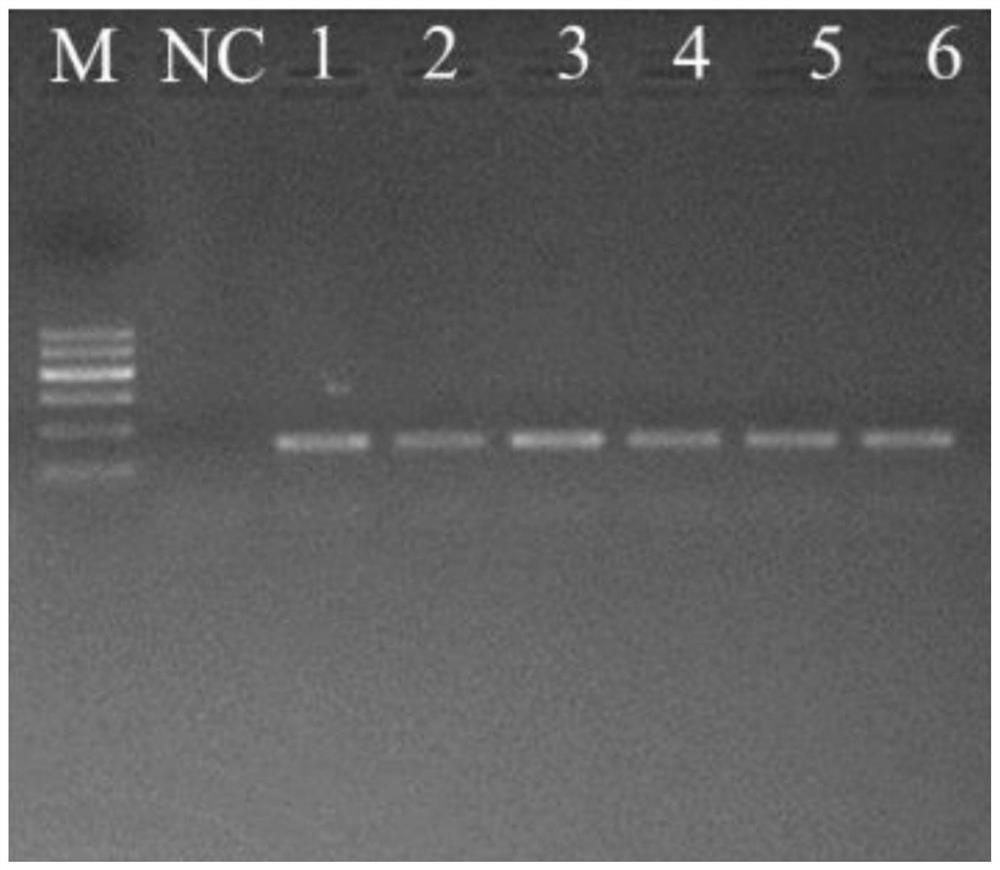
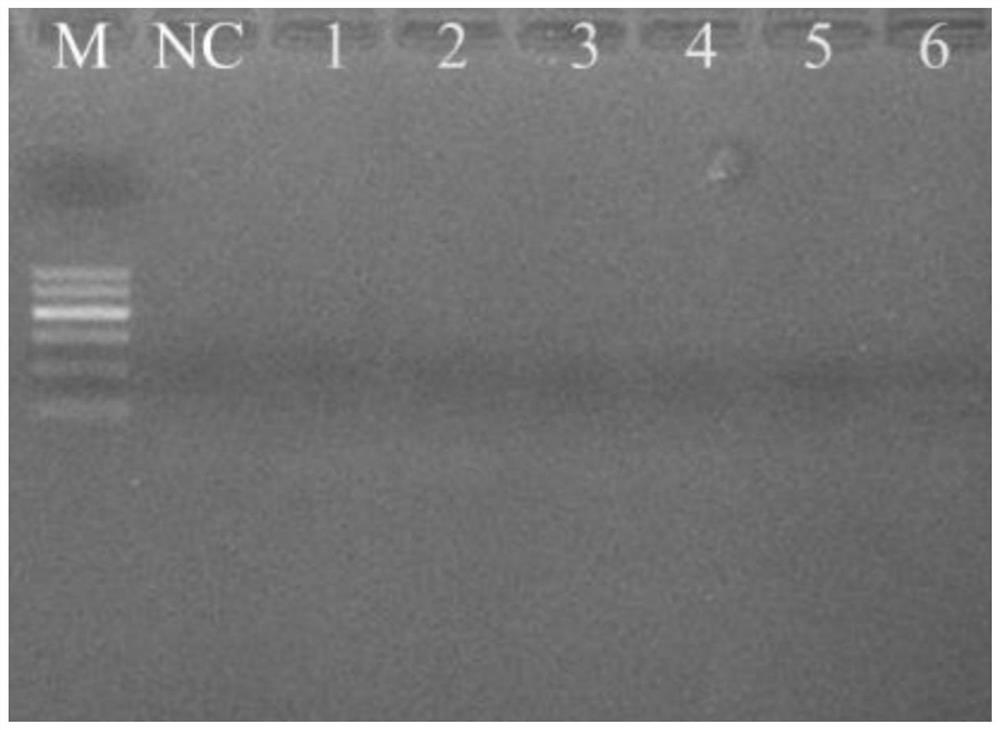
[0033] (1) On the NCBI website, use the primer BLAST function (https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / tools / primer-blast / ) to perform simulation verification of the Ad_Cytb_E1 primer specificity against the GenBank database. Ad_Cytb_E1 was proved by primer BLAST: the specificity is high, and the 202 sequences that completely match it are all from the Chinese giant salamander, and the sequences from other species cannot be completely matched, and the number of mismatched bases is 4 to 10, and the giant salamander is closely related The species Japanese giant salamander had a sequence mismatch of 1 base, indicating that it might also be possible to amplify this sample.
[0034] (2) The Chinese giant salamander and 7 other amphibians in the same area: Chinese salamander (Paramesotritonchinesis), Tibetan mountain stream salamander (Batrachuperus tibetanus), light-shoulder...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: Verification of Primer Versatility
[0039] 1. To test the amplification of each branch of Chinese giant salamander with Ad_Cytb_E1 primer. The test method is as follows: select 7 representative individuals from the 4 genetic branches of Chinese giant salamander (as shown in Table 2), extract the DNA of these 7 individuals, use Ad_Cytb_E1 primers for PCR amplification, and all can be seen after gel electrophoresis The target band was verified to be the cytochrome b gene sequence of Chinese giant salamander by next-generation sequencing, which showed that the Ad_Cytb_E1 primer had good amplification efficiency for different genetic lines of Chinese giant salamander.
[0040] Table 2 Sample information of giant salamander from different clades
[0041]
[0042] 2. In order to further verify whether the environmental DNA of different clades of giant salamander can be simultaneously amplified, next-generation sequencing is carried out. The DNA of each sample i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com