Iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
A co-doping, biochar technology, applied in physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, etc., can solve problems such as poor removal effect, affecting the quality of advanced treatment and purification of wastewater, and achieve reusability. Wide applicability and the effect of conversion and utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
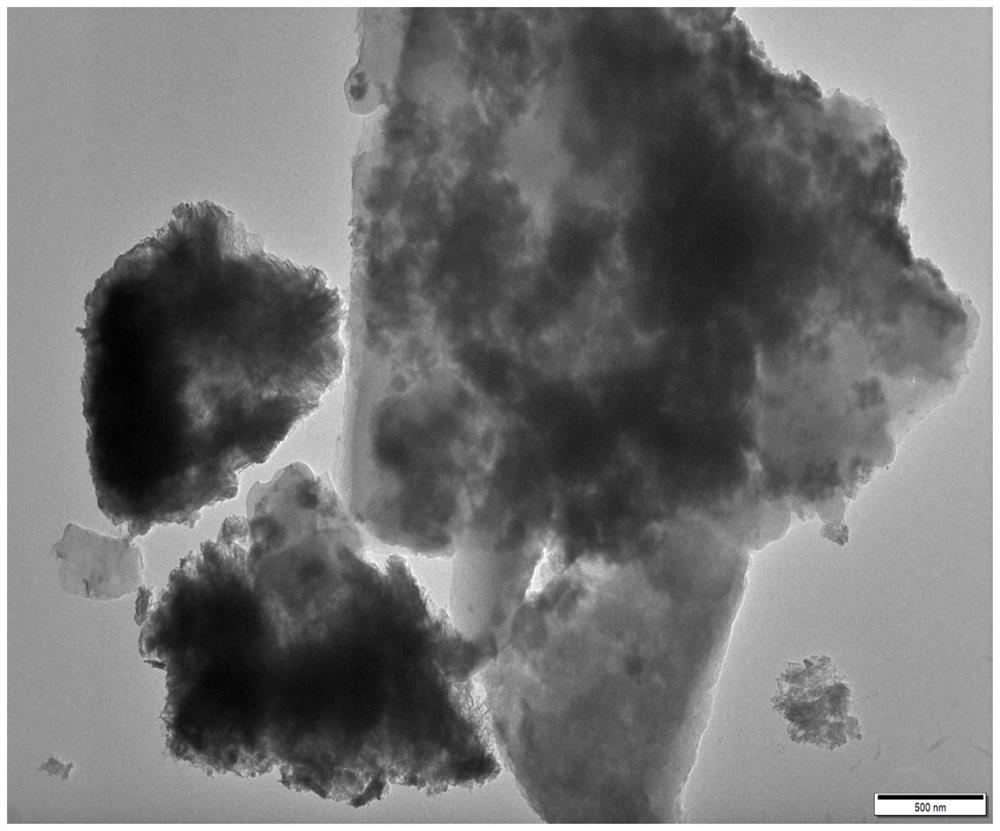
[0041] Please refer to figure 1 , this embodiment discloses an iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst, which is used to remove antibiotic pollutants that are difficult to degrade in tail water of municipal sewage treatment plants. The iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst has the following components: corn stalks, iron source, nitrogen source and reducing agent are prepared in proportion to the iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst. Wherein, the weight ratio of the iron source, nitrogen source and reducing agent is 5.56:3:2.5.
[0042] In the present embodiment, adopt FeSO with iron source 4 ·7H 2 O. The nitrogen source is urea, and the reducing agent is ascorbic acid as an example for illustration. In other embodiments, the iron source, nitrogen source, and reducing agent can be replaced according to actual conditions.
[0043] figure 1 Shown is the scanning electron microscope image of the iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst in this example. It can be seen from...
Embodiment 2
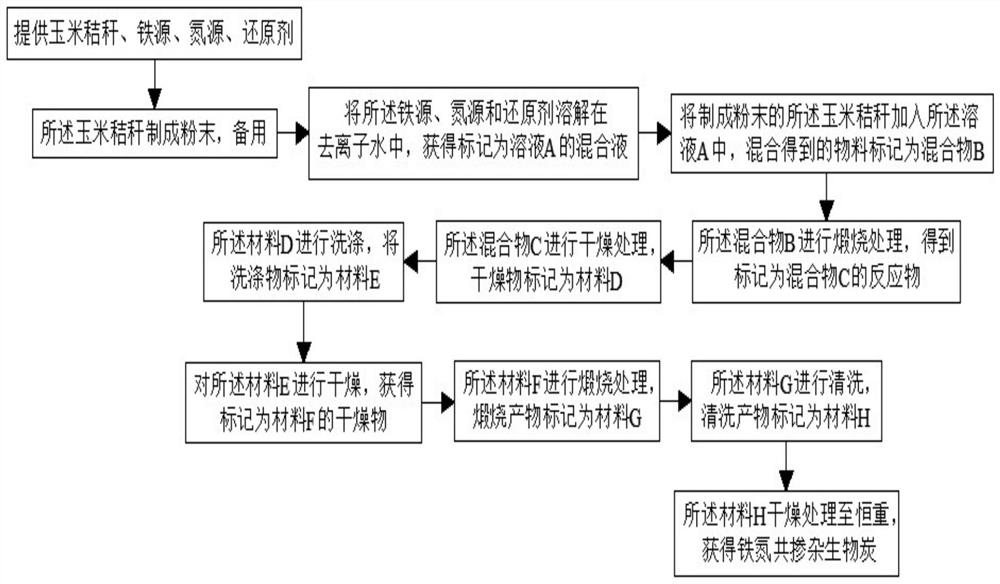
[0046] Please refer to figure 2 , this embodiment discloses a method for preparing an iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst, which is applied to the preparation of the iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst as described in Example 1, and the preparation method includes the following steps:
[0047] S1 provides corn stalks, iron source, nitrogen source and reducing agent;
[0048] The iron source uses FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O; the nitrogen source adopts urea; the reducing agent adopts ascorbic acid.
[0049] The corn stalks described in S2 are made into powder for later use;
[0050]Wash the corn stalks with deionized water and dry them to a constant weight. The dried corn stalks are made into powder. The process of making corn stalks into powder is carried out in a plant crusher, and finally the powder is passed through a 80-mesh sieve. The mesh is finely sieved to obtain corn stover powder.
[0051] S3 dissolving the iron source, nitrogen source and reducing agent in deionized...
Embodiment 3
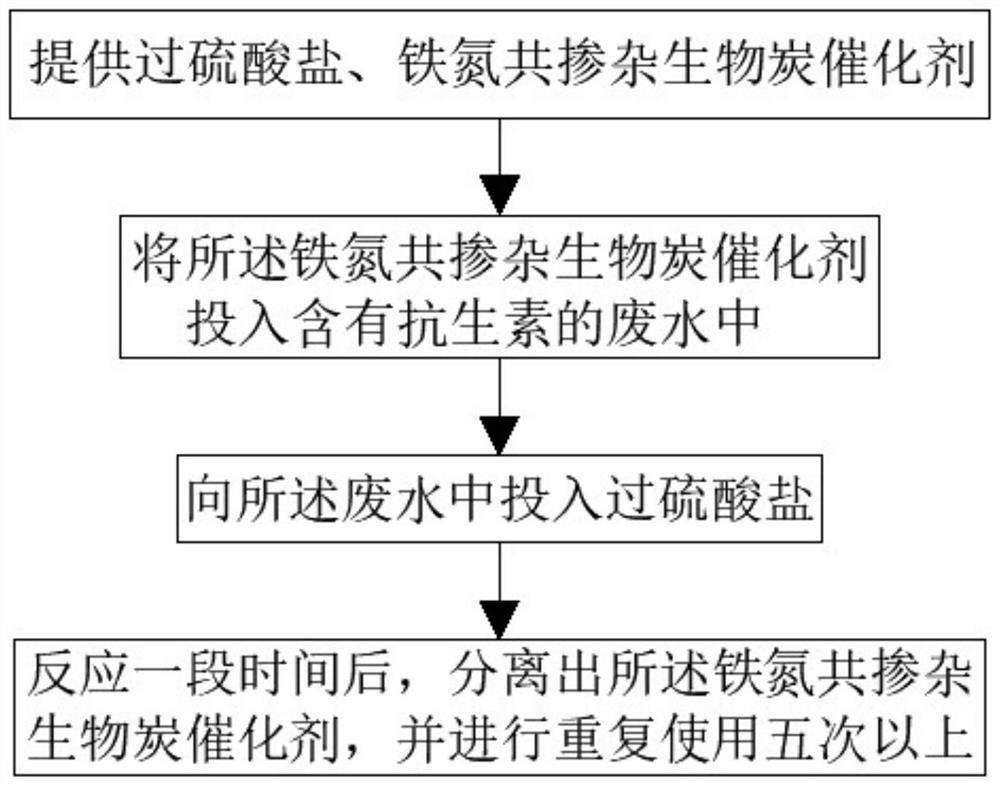
[0071] Please refer to image 3 , this example discloses the application of an iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst in the efficient removal of antibiotics in water. The operation of the application is as follows:
[0072] Provide persulfate, the iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst as described in Example 1, and the iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst is prepared by the preparation method of the iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst as described in Example 2 get.
[0073] The iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst is dropped into waste water containing (norfloxacin) antibiotics;
[0074] The dosage standard of iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst is 0.1g / L.
[0075] Drop into persulfate in described waste water;
[0076] The dosage standard of persulfate is 10mmol / L.
[0077] After reacting for a period of time, the iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst is separated and reused more than five times;
[0078] The iron-nitrogen co-doped biochar catalyst a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com