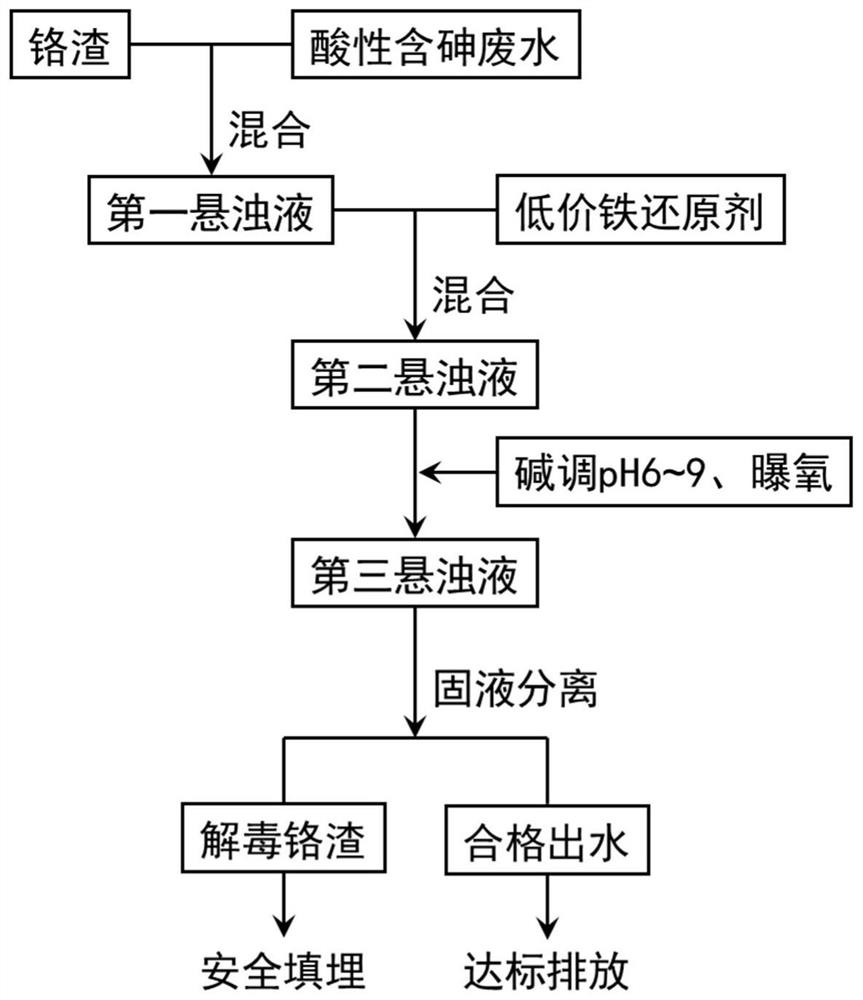
Co-treatment method for chromium slag and acidic arsenic-containing wastewater
A technology for co-processing and chromium slag is applied in the field of co-processing of chromium slag and acidic arsenic-containing wastewater, which can solve the problems of consuming a large amount of acid and consuming a large amount of alkaline chemicals, and achieves the promotion of detoxification, reduction of the use of chemicals and treatment costs, and reduction of The effect of mass transfer limitation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
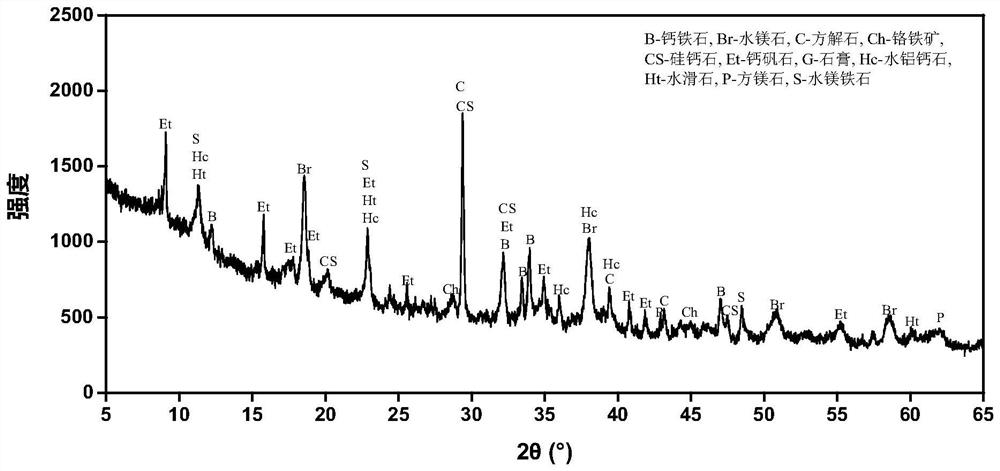
[0062] No. I chromium slag (taken from a chromium salt factory in Changsha, Hunan) and No. I arsenic-containing wastewater (taken from a sulfuric acid plant in Daye, Hubei) were co-treated. The components of the treated objects are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. The XRD spectrum of chromium slag is shown in figure 2 As shown, it can be seen that the chromium slag contains unreacted raw ore (chromite), minerals formed during high-temperature roasting (masonite, periclase, wollastonite) and environmental impact during the storage process. Minerals formed by weathering (brucite, calcite, hydrocalumite, hydrotalcite, ettringite), among which metal oxides such as chromite and layered minerals such as hydrocalumite, hydrotalcite, and ettringite have potential arsenic adsorption capacity.
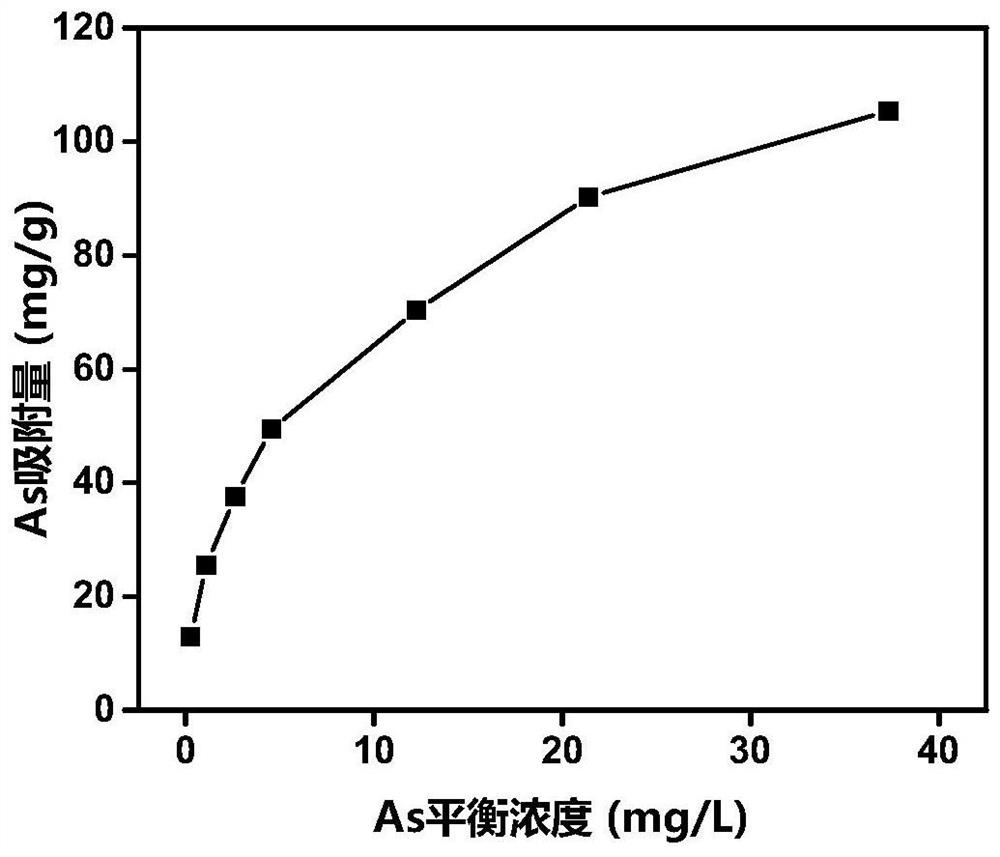
[0063] Weigh 10g of chromium slag sample, add 150mL of waste water sample according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 0.67:10, stir for 24 hours to obtain the first suspension, and the pH of its su...
Embodiment 2
[0070] In order to compare the difference in chemical dosage and cost between co-treatment and separate treatment, No. I chromium slag and No. I arsenic-containing wastewater were treated separately. The required sulfuric acid consumption of processing No. I chromium slag alone is 750g / kg, and the required ferrous sulfate heptahydrate consumption is 380g / kg, and the Cr(VI) leaching concentration of chromium residue after processing is less than 0.1mg / L, reaches " chromium residue pollution Governance Environmental Protection Technical Specifications (HJ / T 301-2007) "requirements. To treat No. I arsenic-containing wastewater separately, the required lime consumption is 60kg / m 3 , the required ferrous sulfate heptahydrate is 36kg / m 3 , the pH of the treated wastewater is 8.5, and the concentration of As is 0.3mg / L, meeting the requirements of the "Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard (GB8978-1996)". And as described in embodiment 1, No. I chromium slag and No. I arsenic-co...
Embodiment 3
[0072] The No. II chromium slag sample (taken from a chromium salt factory in Jinan, Shandong) and the No. II arsenic-containing wastewater sample (taken from a sulfuric acid plant in Daye, Hubei) were co-treated. The components of the treated objects are shown in Table 3 and Table 4. Weigh 10g of chromium slag sample, add 1200mL of waste water sample according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 0.083:10, stir for 24 hours to obtain the first suspension, and the pH of the supernatant is 6.8; then press 3.1kg / m 3 Add ferrous chloride tetrahydrate, stir and react for 24 hours to obtain the second suspension; then press 0.6kg / m 3 Add milk of lime and react with oxygen for 12 hours to obtain the third suspension, the pH of the supernatant is 7.5. The third suspension is filtered to separate the solid and liquid phases to obtain treated chromium residue and waste water. The leaching toxicity test results of the treated chromium slag show that the leaching concentration of Cr(VI) is 0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com