Heavy metal chelating agent for waste incineration fly ash and preparation method of chelating agent
A technology of heavy metal chelating agent and waste incineration fly ash, which is applied in the direction of protection device against harmful chemical agents, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the chelating stability of the chelating agent, easily separating out heavy metal ions, and poor chelating performance of hydroxycarboxylic acid, etc. Achieve the effect of limiting the migration and leaching of heavy metals, reducing the permeability coefficient, and improving the chelation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
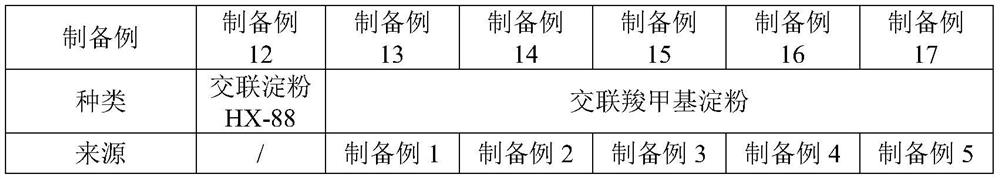
preparation example 1
[0040] Preparation examples 1-5 provide a cross-linked carboxymethyl starch, and preparation example 1 is taken as an example for illustration below.
[0041] The cross-linked carboxymethyl starch that preparation example 1 provides, its preparation steps are:
[0042] S1. Take 200g of cross-linked starch and add it to 500mL of ethanol, stir and dissolve completely, then add dropwise 50mL of sodium hydroxide aqueous solution with a concentration of 2mol / L, and after the dropwise addition is complete, perform an alkalization reaction at 30°C for 2 hours;
[0043] S2. Add 800 g of chloroacetic acid ethanol solution with a mass fraction of 15 wt % to the reaction solution obtained in the step S1, etherify at 70° C. for 4 h, and adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 7 with 0.1 mol / L hydrochloric acid after the etherification is completed. Suction filtration, washing the upper layer solid with absolute ethanol until there is no chloride ion in the filtrate, and drying at 60°C t...
preparation example 6
[0051] Preparation examples 6-17 provide a cross-linked starch-grafted polyacrylamide, and preparation example 6 is taken as an example to illustrate below.
[0052] The cross-linked starch grafted polyacrylamide that preparation example 6 provides, its preparation steps are:
[0053] (1) 200g of cross-linked starch was gelatinized at 70°C for 4 hours, cooled to 40°C, 0.3g of initiator was added, and 400g of acrylamide monomer was added. 2 Under the atmosphere, react at 40°C for 3 hours, wash with absolute ethanol after the reaction until no white viscous substance is precipitated in the reaction solution, and the crude product is obtained;
[0054] (2) adding the crude product obtained in the step (1) into acetone, extracting and removing the acrylamide homopolymer by reflux, and drying at 60° C. to obtain cross-linked starch-grafted polyacrylamide;
[0055] Wherein, the model of the cross-linked starch is HX-88;
[0056] The initiator is potassium persulfate.
[0057] Pre...
preparation example 8、11-12
[0061] The quality of table 4 preparation example 8,11-12 acrylamide monomer and initiator
[0062] Preparation example Preparation example 8 Preparation Example 11 Preparation Example 12 Initiator 0.3g 0.4g 0.35g Acrylamide Monomer 400g 600g 500g
[0063] Preparation Examples 13-17 differ from Preparation Example 12 only in that the type and source of the cross-linked starch are different, see Table 5 for details.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com