Hard alloy waste recovery method
A technology for recycling cemented carbide and waste materials, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of high tungsten content in slag, large loss of raw and auxiliary materials, low recovery rate, etc., and achieve low chemical consumption, low decomposition cost, large The effect of promoting meaning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
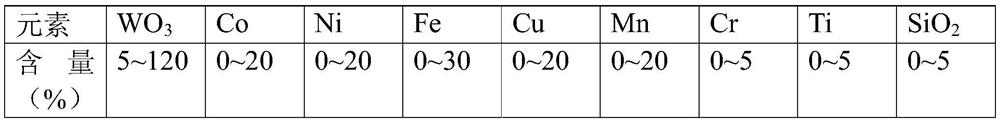
[0033] A method for recycling cemented carbide scraps, comprising:
[0034] Step 1: Take 2Kg of cemented carbide waste (the mass content of tungsten oxide is 5%), and mix it with 0.36Kg calcium carbonate and 0.15Kg sodium silicate to obtain a mixture;
[0035] Step 2: Put the mixture obtained in Step 1 into a roasting furnace for roasting at a roasting temperature of 900°C and a roasting time of 1 hour;
[0036] Step 3: Soak the calcined material obtained in Step 2 in water. After water immersion, the feed liquid is filtered out by solid-liquid separation equipment to obtain sodium tungstate solution, and the recovery rate of tungsten is 98.18%.
Embodiment 2
[0038] A method for recycling cemented carbide scraps, comprising:
[0039] Step 1: Take 2.5Kg of cemented carbide waste (the mass content of tungsten oxide is 30%), and mix it with 1.12Kg of calcium oxide and 0.98Kg of sodium silicate glass to obtain a mixture;
[0040] Step 2: put the mixture obtained in step 1 into a roasting furnace for roasting, the roasting temperature is 800°C, and the roasting time is 16 hours;
[0041] Step 3: Soak the calcined material obtained in Step 2 in water. After water immersion, the feed liquid is filtered out by solid-liquid separation equipment to obtain sodium tungstate solution, and the recovery rate of tungsten is 98.32%.
Embodiment 3
[0043] A method for recycling cemented carbide scraps, comprising:
[0044] Step 1: Take 2Kg of cemented carbide waste (the mass content of tungsten oxide is 50%), and mix it with 0.95Kg calcium hydroxide and 1.05Kg sodium silicate to obtain a mixture;
[0045] Step 2: Put the mixture obtained in Step 1 into a roasting furnace for roasting, the roasting temperature is 1000°C, and the roasting time is 8 hours;
[0046] Step 3: Soak the calcined material obtained in Step 2 in water. After water immersion, the feed liquid is filtered out by solid-liquid separation equipment to obtain sodium tungstate solution, and the recovery rate of tungsten is 98.63%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com