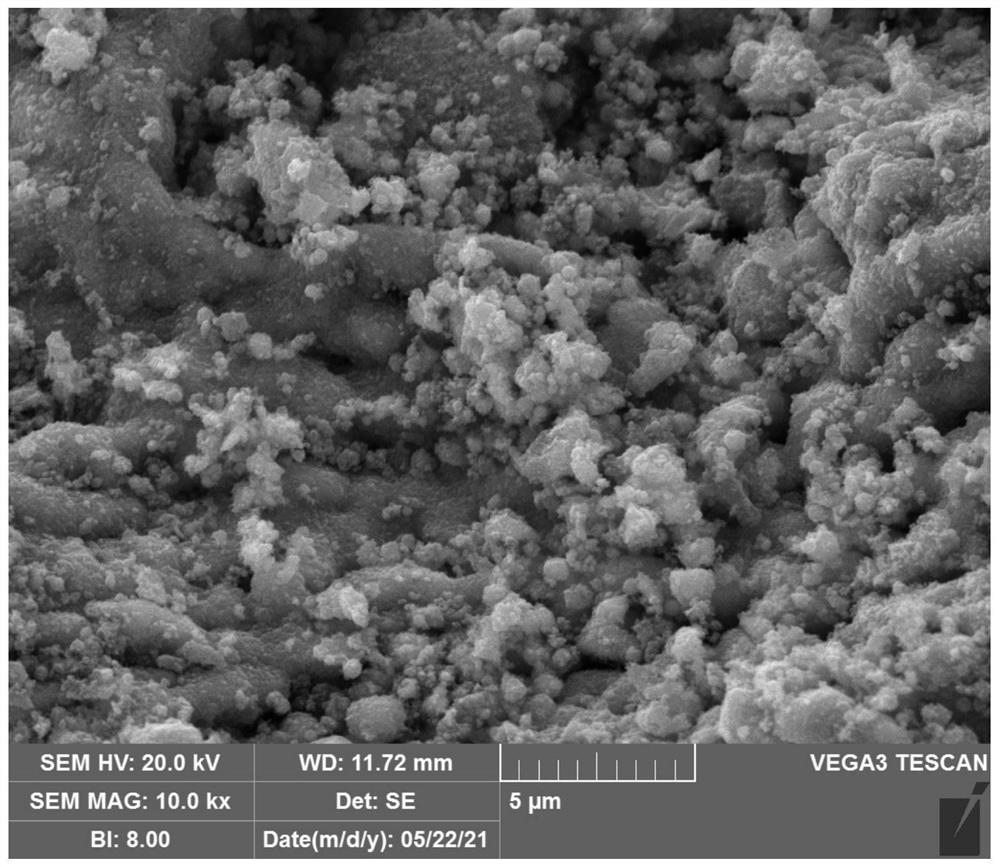
Ferroferric oxide/biomass porous carbon composite wave-absorbing material and preparation method thereof
A composite wave-absorbing material, the technology of ferroferric oxide, which is applied in the field of wave-absorbing materials, can solve problems such as easy agglomeration, poor temperature adaptability, and poor low-frequency absorption performance, and achieve the effect of solving agglomeration, strong adsorption capacity, and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
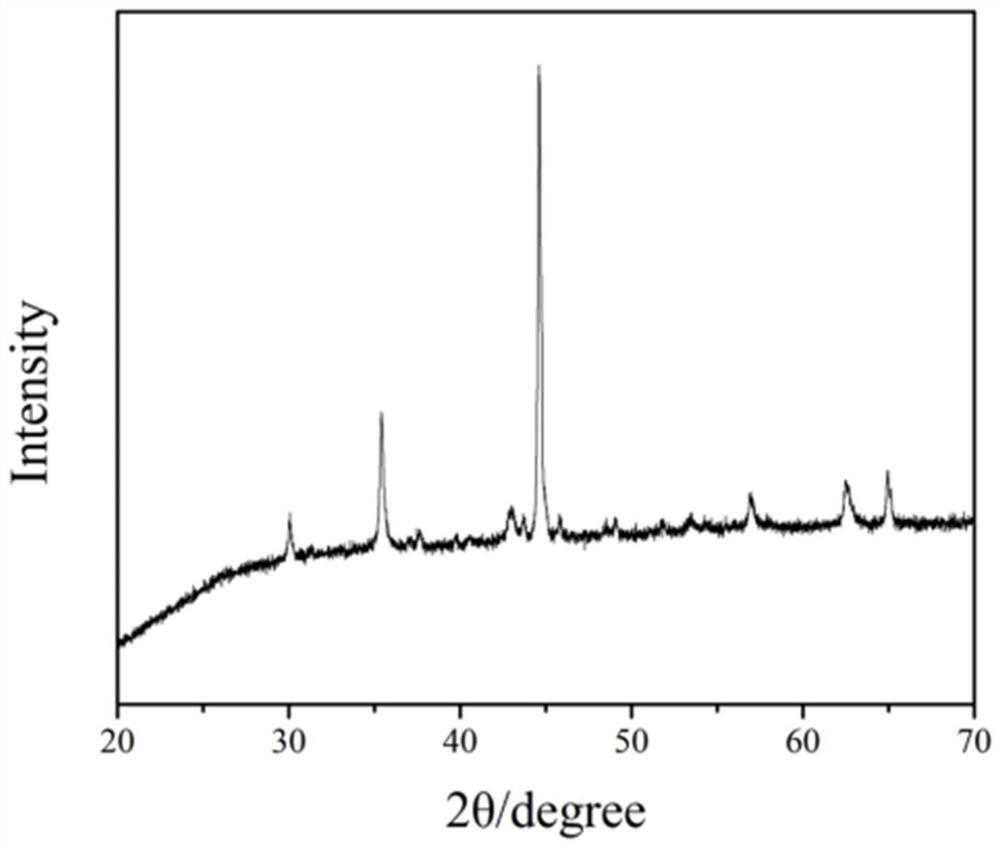
[0028] The present invention adopts the direct carbonization method to prepare the embedded Fe 3 o 4 Biomass carbon magnetic wave-absorbing material of magnetic particles, that is, ferric oxide / biomass porous carbon (Fe 3 o 4 / BPC) (BPC, biomass porous carbon) composite absorbing material. The Fe 3 o 4 The preparation method of the / BPC composite wave-absorbing material specifically includes the following steps:
[0029] (1) Clean the biomass carbon source ultrasonically in ethanol, and dry it in an oven after cleaning.
[0030] (2) Dip the dried biomass carbon source into ferric nitrate / ferric sulfate / ferric chloride / ferric acetate solution, and put it in an oven for a period of time to fully absorb iron ions.
[0031] (3) Take out the soaked biomass carbon source, ultrasonically clean it, and dry it in an oven.
[0032] (4) The soaked and dried biomass carbon source is used as a precursor under vacuum and calcined in a horizontal vacuum tube furnace to obtain a compos...
Embodiment 1
[0041] (1) The dried fungus was ultrasonically cleaned in ethanol for 1 hour, and dried in an oven at 60°C for 2 hours.
[0042] (2) Immerse 10 g of fungus into a beaker filled with 100 mL of 0.2 mol / L ferric nitrate solution, seal the beaker with plastic wrap and put it in an oven at 60°C for 6 hours to fully absorb iron ions.
[0043] (3) Take out the soaked fungus, ultrasonically clean it for 30 minutes, and dry it in an oven at 60° C. for 36 hours.
[0044] (4) The soaked and dried fungus was used as a precursor to be calcined under vacuum at a heating rate of 5 °C / min to 400 °C for 2 h to obtain a composite material of ferroferric oxide and biomass porous carbon (Fe 3 o 4 / BPC), which is Fe 3 o 4 / BPC composite absorbing material.
Embodiment 2
[0046] (1) The dried fungus was ultrasonically cleaned in ethanol for 1 hour, and dried in an oven at 60°C for 2 hours.
[0047] (2) Immerse 10 g of fungus into a beaker filled with 100 mL of 2 mol / L ferric nitrate solution, seal the beaker with plastic wrap and put it in an oven at 60°C for 6 hours to fully absorb iron ions.
[0048] (3) Take out the soaked fungus, ultrasonically clean it for 30 minutes, and dry it in an oven at 60° C. for 36 hours.
[0049] (4) The soaked and dried fungus was used as a precursor to be calcined under vacuum at a heating rate of 5 °C / min to 600 °C for 2 h to obtain a composite material of ferroferric oxide and biomass porous carbon (Fe 3 o 4 / BPC), which is Fe 3 o 4 / BPC composite absorbing material.
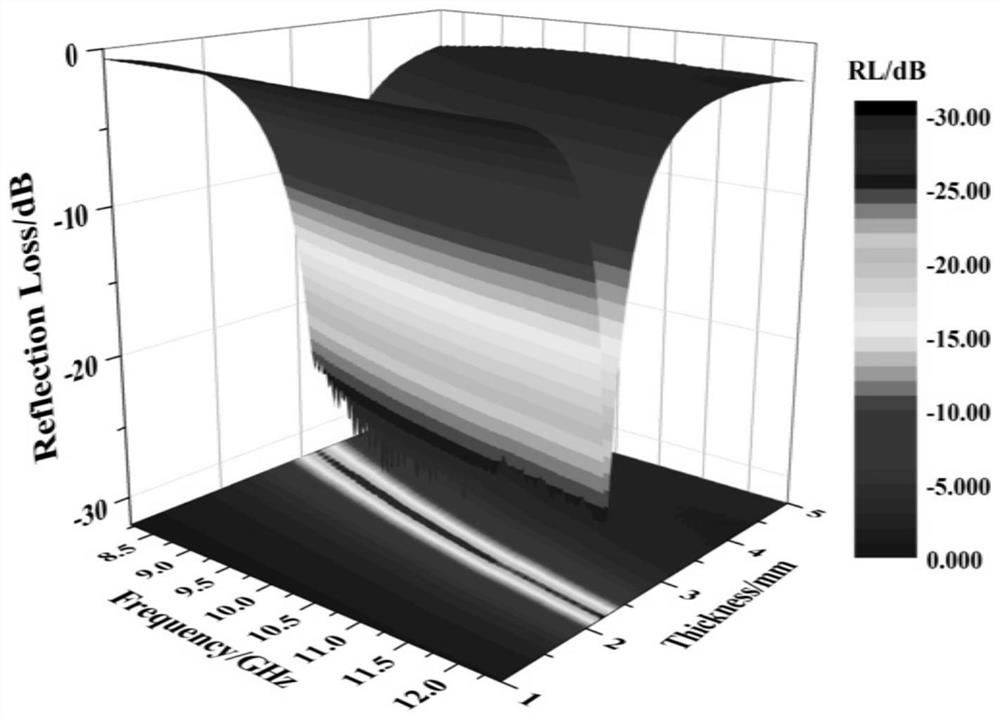
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption peak | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com