High-gain photoelectric detector
A photodetector, high-gain technology, applied in circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of degraded detector response speed, limited number of photogenerated holes, high operating voltage, etc., and achieve high speed and extremely high responsivity Effects of photodetection, increased electron injection ratio, and reduced recombination loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
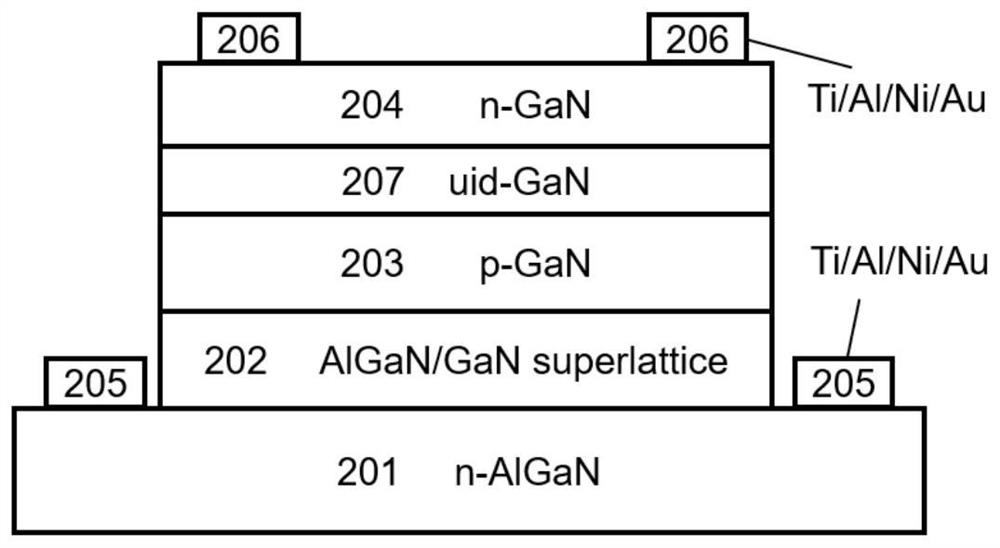
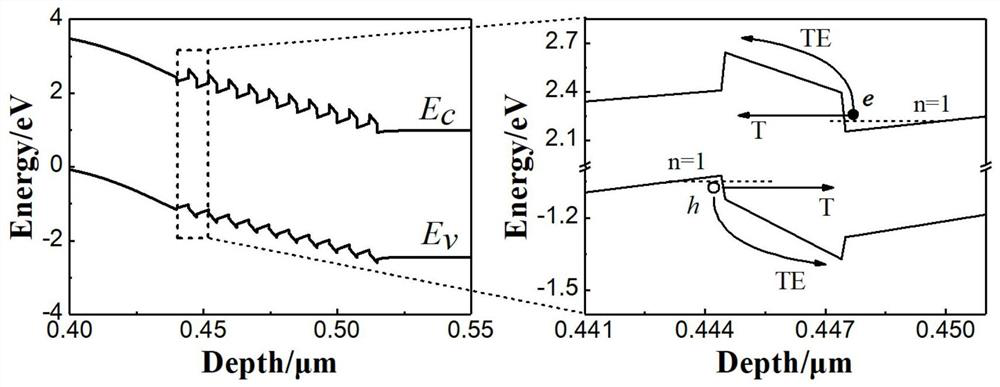
[0050] Such as figure 1 As shown, a GaN-based high-gain photodetector structure mainly includes an emitter layer 201 , a periodic quantum structure layer 202 , a base layer 203 , an absorber layer 207 and a collector layer 204 sequentially arranged from bottom to top.
[0051] In this embodiment, lower contact electrodes 205 are provided on both sides of the upper surface of the emitter layer 201 , and upper contact electrodes 206 are provided on both sides of the upper surface of the absorber layer 205 .
[0052] Wherein, the material of the emitter layer 201 is n-type AlGaN, the Al composition is 20%, and the electron concentration is 2×10 18 cm -3 , the thickness is 300nm, and the preparation method is not limited. Specifically, a substrate layer and / or a buffer layer is further provided under the emitter layer.
[0053] The periodic quantum structure layer 202 is an AlGaN / GaN superlattice structure, in which the Al component is 20%, the number of periods is 20, the thic...
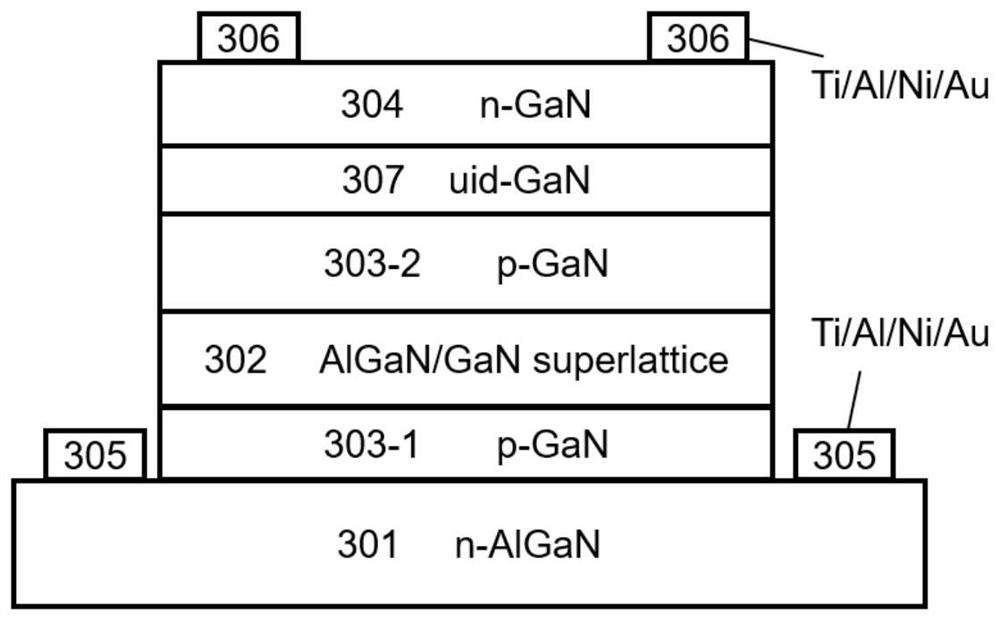
Embodiment 2
[0068] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 lies in that the material of the emitter layer is n-type GaN, the periodic quantum structure layer is AlGaN (6nm) / GaN (3nm) multiple quantum wells, and the number of periods is 10.
Embodiment 3
[0070] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 lies in that in the AlGaN / GaN superlattice layer of the periodic quantum structure layer, the Al composition of AlGaN is 15%, the thickness of AlGaN in each period is 3nm, and the thickness of GaN is 4nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com