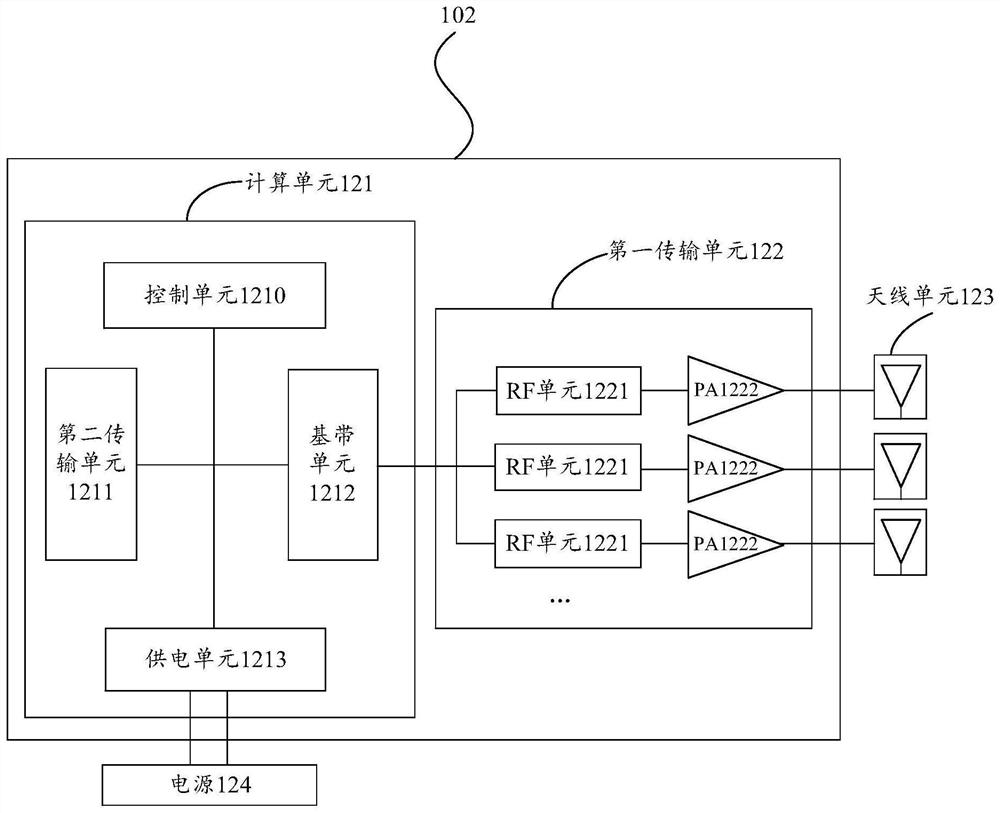
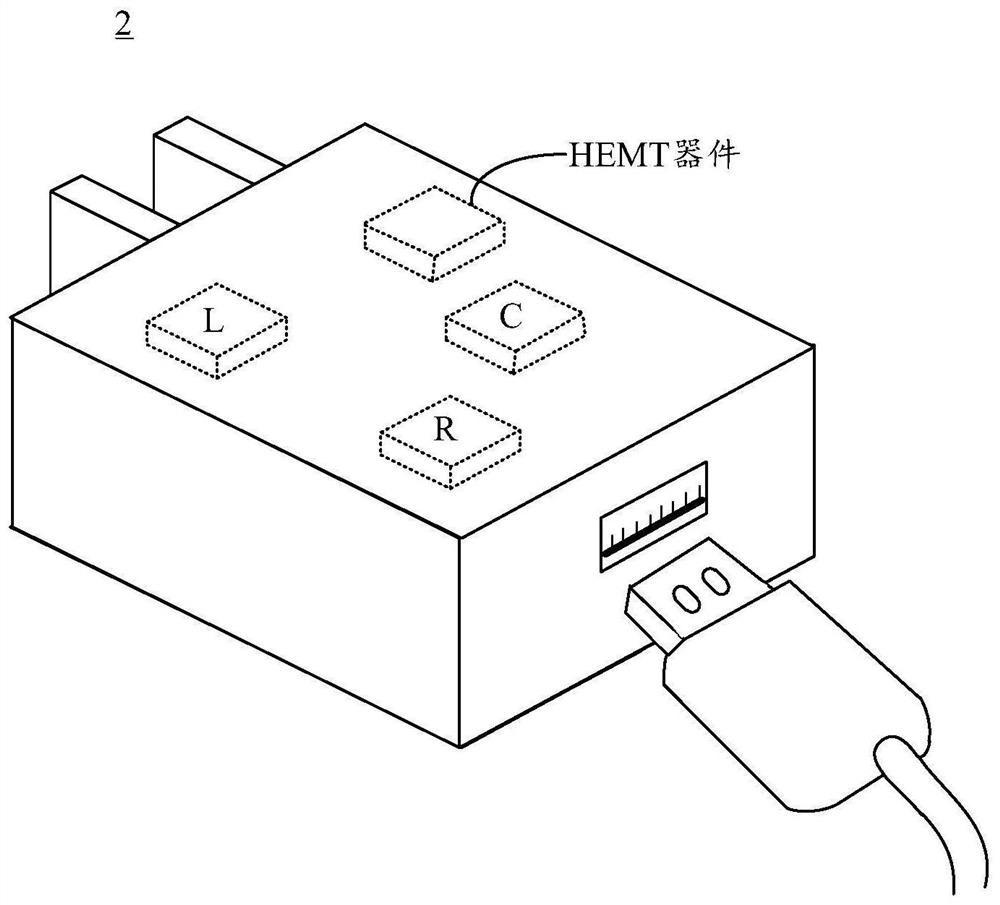
Composite substrate and preparation method thereof, semiconductor device and electronic equipment
A composite substrate and composite structure technology, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of SiC and high cost of AlxGayN-based semiconductor devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0070] Provides a method of preparing a composite substrate, first epitaxially growing the GaN single crystal layer on sapphire substrate, and then bonds to the GaN single crystal layer with the carrier substrate in which the stress compensation layer is formed, and then peel the sapphire substrate, Prepare Figure 4 The composite substrate shown. like Figure 4 As shown, the composite substrate includes a carrier substrate, a bonding dielectric layer and a GaN single crystal layer located on the carrier substrate, and a stress compensation layer in the back of the substrate.
[0071] Figure 4 The composite substrate shown, although there is an advantage of the GaN substrate, it grows in the sapphire substrate, still facing problems with high technical complexity, thickness thickness, low yield rate, etc., resulting in difficult, cost high. Moreover, the stress compensation layer is a thin film dielectric layer, and the stability is poor during subsequent processing, and the stress...
example 1
[0075] like Figure 5A As shown, the present application provides a method of preparing a composite substrate, including:
[0076] S10, such as Figure 5b As shown, hydrogen ion injection is performed to the silicon carbide single crystal ingot 10 from the back surface A1 of the silicon carbide single crystal ingot 10 such that the injection ion reaches the preset depth X, and the defect layer 20 is formed at the preset depth, the defect layer 20 The silicon carbide layer 11 is formed on one side of the silicon carbide single crystal ingot 10 back surface A1.
[0077] That is, the silicon carbide single crystal ingot 10 is located on the side of the defect layer 20 toward the side of the silicon carbide single crystal ingot 10 as the silicon carbide layer 11.
[0078] In some embodiments, the lattage direction of the silicon carbide single crystal ingot 10 is deflected in the of the lattice direction in a section greater than or equal to 0 ° and less than or equal to 8 °.
[0079] ...
example 2
[0168] Example II and examples are in that the silicon carbide layer 11 and the carrier layer 30 are bonded through the transition layer 42.
[0169] The present application example also provides a method of preparing a composite substrate, such as Figure 7A As shown, including:
[0170] S100, such as Figure 7b As shown, hydrogen ion injection is performed to the silicon carbide single crystal ingot 10 from the back surface A1 of the silicon carbide single crystal ingot 10 such that the injection ion reaches the preset depth X, and the defect layer 20 is formed at the preset depth, the defect layer 20 The silicon carbide layer 11 is formed on one side of the silicon carbide single crystal ingot 10 back surface A1.
[0171] That is, the silicon carbide single crystal ingot 10 is located on the side of the defect layer 20 toward the side of the silicon carbide single crystal ingot 10 as the silicon carbide layer 11.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com