Method for treating n-butyl isocyanate kettle residues
A technology for treating butyl isocyanate residues and isocyanate residues, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of amino compounds, preparation of organic compounds, etc. The effect of added value, reduction of three waste emissions, and high product purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
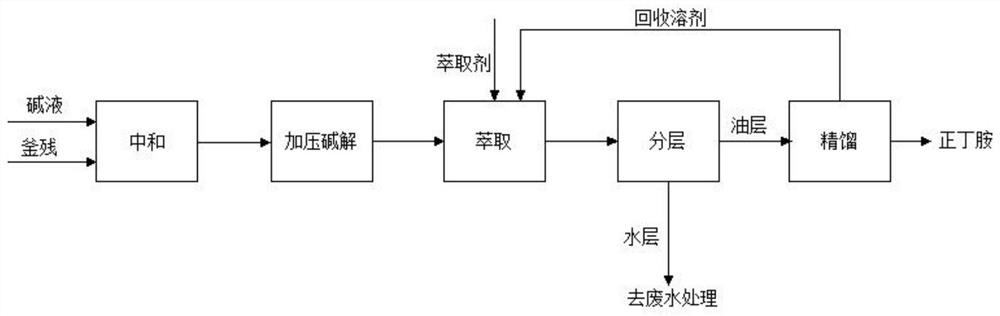
[0026] As can be seen from the above technical scheme, a kind of n-butyl isocyanate still residue treatment method comprises the steps:
[0027] S1: Add n-butyl isocyanate residue in a clean reactor;
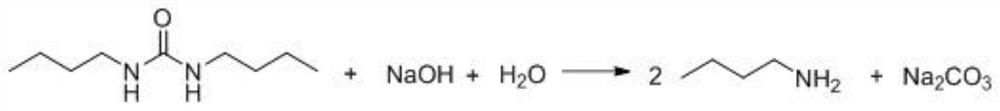
[0028] S2: Maintain the temperature of the reaction system at 20-50°C, add dilute lye to the reactor and continue to stir for 3-5 hours, so that the pH in the reactor is kept at 13-14, and the neutralization reaction will remove the n-butane in the residue Amine hydrochloride is neutralized to n-butylamine;
[0029] S3: After nitrogen replacement in the system, the system is boosted to 2-5MPa, and the system is raised to 100-200°C, and the alkali hydrolysis reaction is performed for 1-20 hours. The alkali hydrolysis reaction converts the trimer into n-butylamine. This process Add a certain amount of alkali to maintain the alkali concentration at 1%-50%;
[0030] S4: After cooling down the system and releasing the pressure, add an extractant for extraction, layer the extract, a...
Embodiment 2
[0039] As can be seen from the above technical scheme, a kind of n-butyl isocyanate still residue treatment method comprises the steps:
[0040] S1: Add n-butyl isocyanate residue in a clean reactor;
[0041] S2: Maintain the temperature of the reaction system at 20-50°C, add dilute lye to the reactor and continue to stir for 3-5 hours, so that the pH in the reactor is kept at 13-14, and the neutralization reaction will remove the n-butane in the residue Amine hydrochloride is neutralized to n-butylamine;
[0042] S3: After nitrogen replacement in the system, the system is boosted to 2-5MPa, and the system is raised to 100-200°C, and the alkali hydrolysis reaction is performed for 1-20 hours. The alkali hydrolysis reaction converts the trimer into n-butylamine. This process Add a certain amount of alkali to maintain the alkali concentration at 1%-50%;
[0043] S4: After cooling down the system and releasing the pressure, add an extractant for extraction, layer the extract, a...
Embodiment 3
[0052] As can be seen from the above technical scheme, a kind of n-butyl isocyanate still residue treatment method comprises the steps:
[0053] S1: Add n-butyl isocyanate residue in a clean reactor;
[0054] S2: Maintain the temperature of the reaction system at 20-50°C, add dilute lye to the reactor and continue to stir for 3-5 hours, so that the pH in the reactor is kept at 13-14, and the neutralization reaction will remove the n-butane in the residue Amine hydrochloride is neutralized to n-butylamine;
[0055] S3: After nitrogen replacement in the system, the system is boosted to 2-5MPa, and the system is raised to 100-200°C, and the alkali hydrolysis reaction is performed for 1-20 hours. The alkali hydrolysis reaction converts the trimer into n-butylamine. This process Add a certain amount of alkali to maintain the alkali concentration at 1%-50%;
[0056] S4: After cooling down the system and releasing the pressure, add an extractant for extraction, layer the extract, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com