Recombinant Escherichia coli for efficiently producing clarified acid and application of recombinant Escherichia coli
A technology of recombinant Escherichia coli and claritic acid, applied in the fields of genetic engineering, fermentation engineering and material science, can solve problems that only focus on monosaccharide components, molecular weight and rheological properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] Example 1: Screening for high-yielding claric acid starting strains
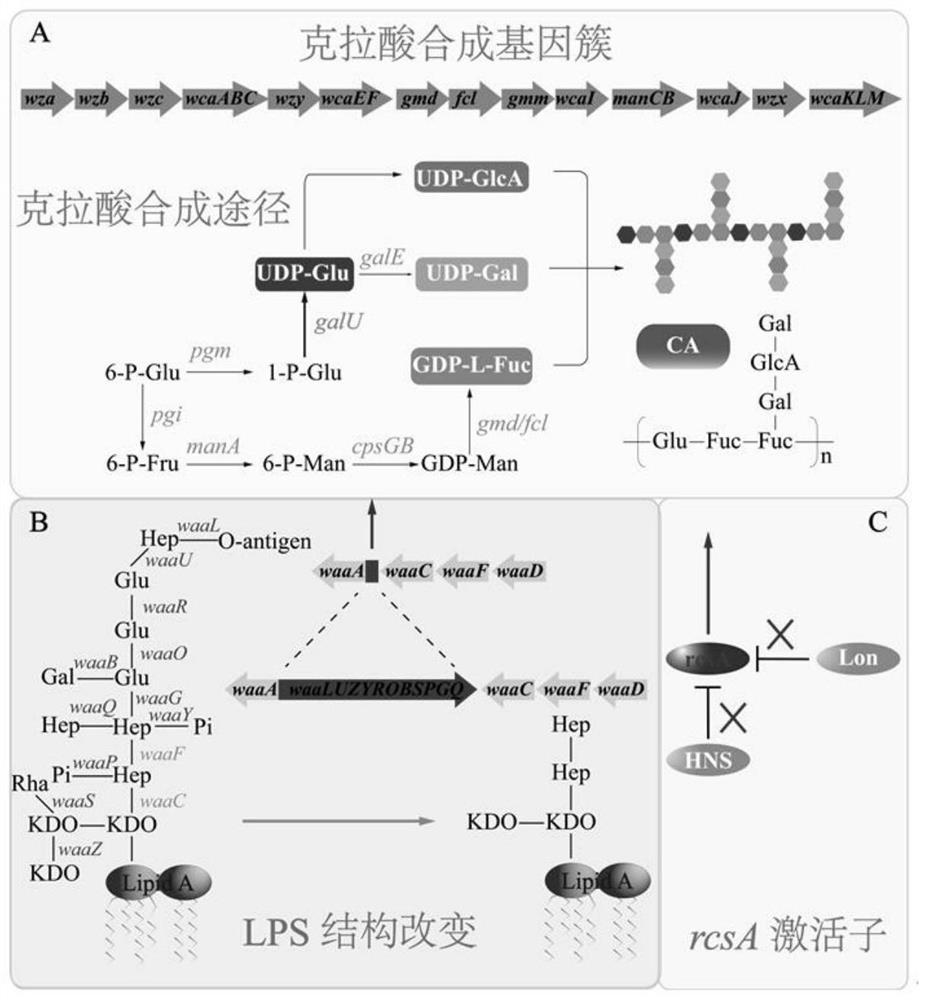
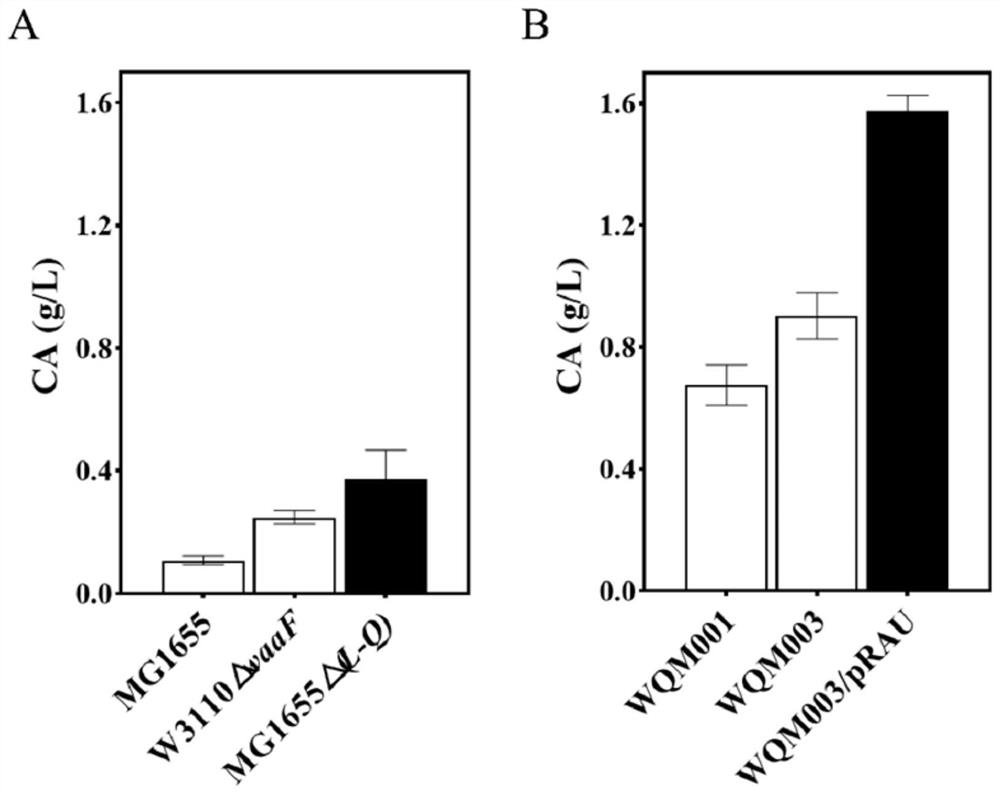
[0088] CA production can be effectively promoted by knocking out the waaF gene in E. coli W3110 or the waaL-waaQ gene cluster in MG1655, resulting in truncation of the LPS core polysaccharide (e.g. figure 1 shown in A). In the present invention, the CA production rate of W3110ΔwaaF and MG1655Δ(L-Q) were compared, and a strain with high CA production was selected as the starting strain for further optimization and transformation. Specific steps are as follows:
[0089] (1) The MG1655Δ(L-Q) strain was constructed according to the method in the SCI paper (Wang C H, Zhang H L, Wang J L, et al. Colanic acid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli is dependent on lipopolysaccharide structure and glucose availability. Microbiological Research, 2021.243.), using The CRISPR / Cas9 knockout system was used to knock out the genes of E. coli. First, the pCas9 plasmid was electrotransfected into E. coli Escherichia coli ...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Embodiment 2: the construction of high-yielding claritic acid bacterial strain
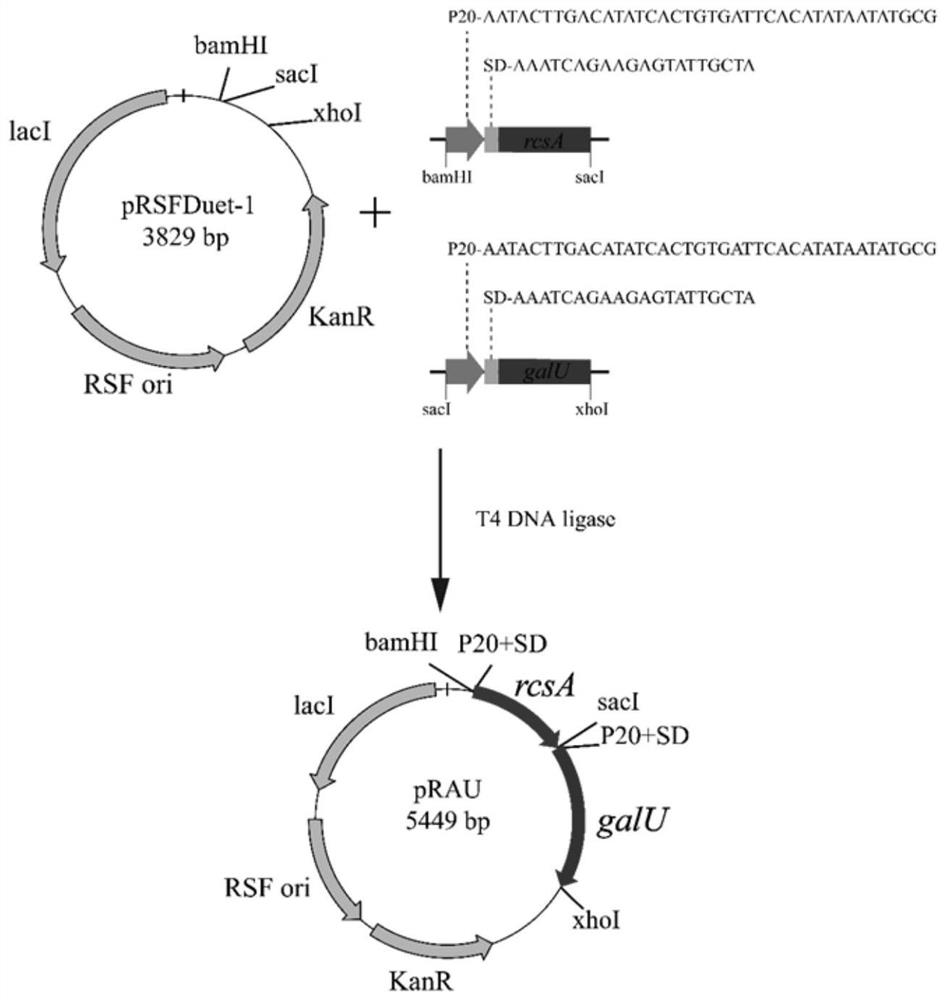
[0094] The activator RcsA can be degraded and inhibited by Lon and HNS proteins in MG1655Δ(L-Q) (eg figure 1 C shown). Therefore, the lon and hns genes need to be knocked out from the MG1655Δ(L-Q) genome.
[0095] Specific steps are as follows:
[0096] 1. Construction of WQM001 strain
[0097]The lon gene on the genome of the MG1655Δ(L-Q) strain prepared in Example 1 was knocked out. The specific method was the same as that in Example 1. The Escherichia coli MG1655Δ(L-Q) strain was knocked out using the CRISPR / Cas9 knockout system. Bacillus MG1655Δ(L-Q) strain was electroporated into pCas9 plasmid, and L-arabinose was added to induce the expression of recombinase Gam, Bet, and Exo to obtain MG1655Δ(L-Q) / pCas9 strain
[0098] Using the Escherichia coli MG1655 genome as a template, use F1-lon / R1-lon and F2-lon / R2-lon to amplify the upstream and downstream homology arms of the knockout lo...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Embodiment 3: CA medium composition and fermentation condition optimization
[0123] 1. Single factor experiment to optimize medium composition
[0124] According to the results of exopolysaccharide staining in step 5 of Example 2, it can be seen that the composition of the medium has a significant impact on the production of exopolysaccharides. Compared with LB and LBG medium, WQM003 / pRAU was cultured in M9 medium at 30°C The exopolysaccharide production was the highest at this time. Therefore, media optimization was therefore performed in M9 media. The effects of carbon source, nitrogen source, phosphate, and NaCl on CA production were investigated using a single factor test to determine approximate variable ranges. The experiment studied 4g / L glucose, 4g / L fructose, 4g / L galactose, 4g / L mannose and 4g / L sucrose to select the best carbon source for CA biosynthesis; The nitrogen source is selected from 10g / L NH 4 Cl, peptone of 10g / L, yeast extract of 10g / L and cor...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com