Photoacoustic microfluidic detection system and detection method
A detection system and microfluidic technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, measurement devices, material analysis by optical means, etc., can solve the problems of narrow bandwidth, insufficient sensitivity of small size, single frequency band, etc. The effect of small size, simple structure and wide detection band
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
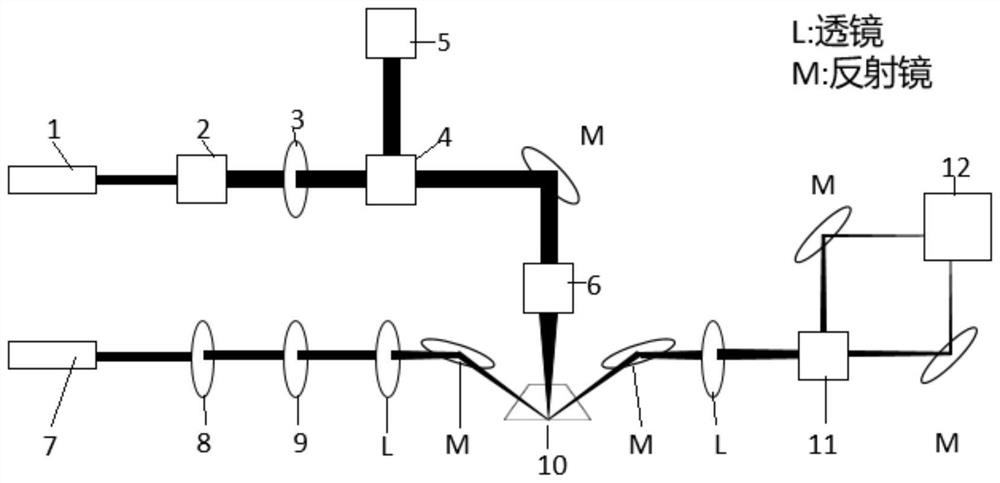
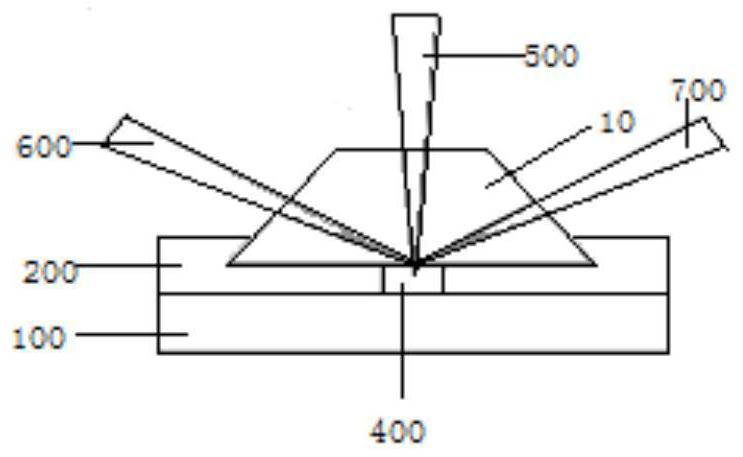
[0046] Such as figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, the laser excitation module includes a pulse excitation light source 1, a beam expander 2, a filter 3, a beam splitter 4, a mirror M, an objective lens 6 and a photoelectric probe. A pulsed laser light is emitted from the pulsed excitation light source 1, collimated and amplified by the beam expander 2, filtered by the filter 3, and split by the beam splitter 4, and one beam of light enters the photoelectric probe 5 as a subsequent signal processing module trigger signal. Another beam of light 500 is reflected by the mirror M and enters the objective lens 6, and is focused on the sample in the microfluidic channel 400 of the microfluidic chip to excite the sample to emit ultrasonic waves.
[0047] The laser detection module includes a continuous laser light source 7 , a polarizer 8 , a 1 / 4 wave plate 9 , a lens L, a mirror M, a polarization beam splitter 11 and a balanced light detector 12 . The continuous laser light source ...
Embodiment 2
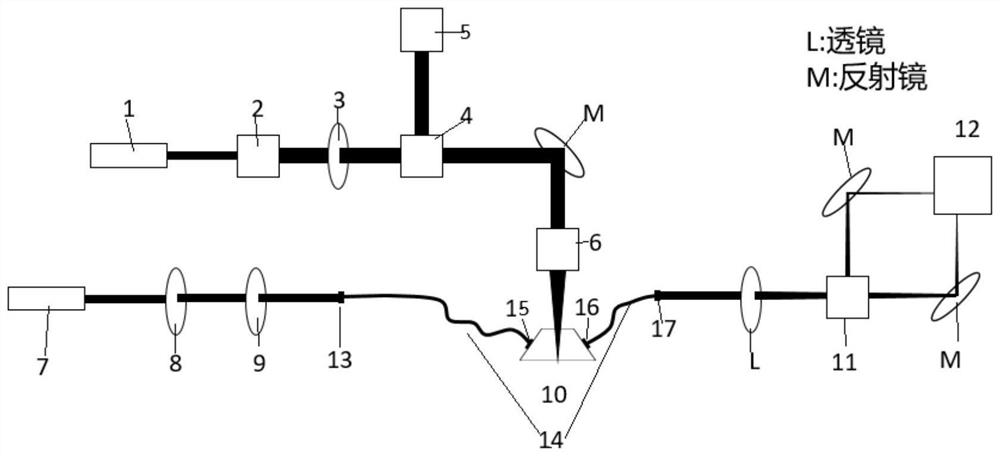
[0058] The laser excitation module in this example includes a pulse excitation light source 1, a beam expander 2, an optical filter 3, a beam splitter 4, a mirror M, an objective lens 6 and a photoelectric probe. A pulsed laser light is emitted from the pulsed excitation light source 1, collimated and amplified by the beam expander 2, filtered by the filter 3, and split by the beam splitter 4, and one beam of light enters the photoelectric probe 5 as a subsequent signal processing module trigger signal. Another beam of light 500 is reflected by the mirror M and enters the objective lens 6, and is focused on the sample in the microfluidic channel 400 of the microfluidic chip to excite the sample to emit ultrasonic waves.
[0059] The laser detection module of this example includes a continuous laser light source 7, a polarizer 8, a 1 / 4 wave plate 9, an optical fiber 14, fiber collimating mirrors 13, 15, 16, 17, a lens L, a polarization beam splitter 11 and a balanced light dete...
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0069] Such as Figure 5 As shown, in this embodiment, the pulse excitation light source 1 uses a 532nm pulse laser, the continuous laser light source 7 uses a HeNa laser, the polarizer 8 uses a polarizer, and the sample uses black tape. Black tape is attached to the tubes on the underside of the prisms in the microfluidic chip. The thickness of the pipes in the microfluidic chip is about 500 microns. The photoacoustic signal of the black tape in the 500 micron pipe displayed in the oscilloscope of the signal processing module is as follows: Image 6 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com