Multi-organ chip and application thereof in drug evaluation
A multi-organ and chip technology, applied in the measurement/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical instruments, biomass post-processing, etc., can solve problems such as powerlessness, and achieve the effect of simple oxygen control methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
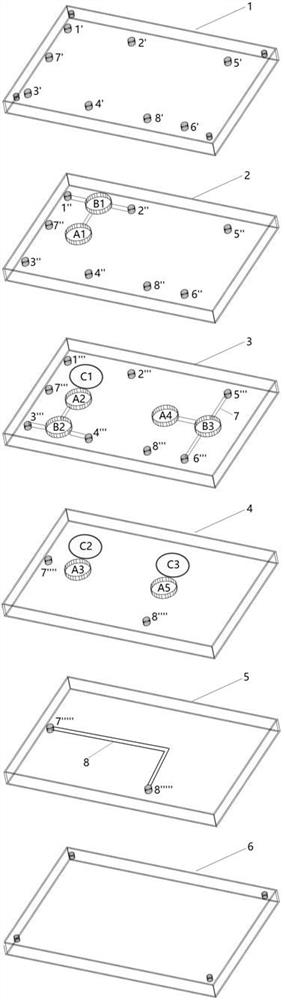
[0052] Example 1: Construction of microalgae-gut-liver-tumor organ chip
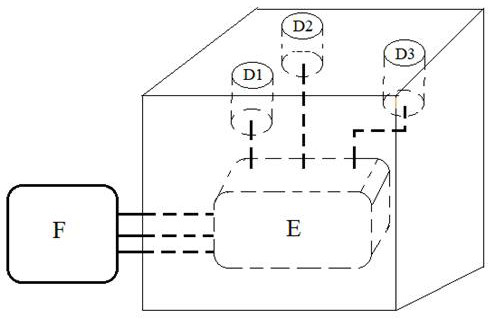
[0053]Intestine-liver-tumor organ chip is the latest in vitro platform for oral anti-tumor drug screening. It can investigate the anti-tumor effect of drugs after intestinal absorption and liver metabolism at one time, which is more advanced than conventional in vitro anti-tumor drug screening platforms. In vivo, the liver is oxygen-rich, the intestine is oxygen-free, and the tumor is hypoxic. However, in the intestinal-liver-tumor organ-on-a-chip reported so far, the oxygen content in each organ is the same, which is not consistent with the situation in vivo. This will lead to insufficient biomimeticity, thereby reducing the reference value of drug evaluation results.
[0054] The difficulty in oxygen control of intestine-liver-tumor organ chip lies in: constructing oxygen-enriched area, anaerobic area and hypoxic area at the same time in one chip, adopting any traditional oxygen control method will ca...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2: Application of microalgae-gut-liver-tumor organ chip in evaluating the antitumor activity of cyclophosphamide
[0069] The broad-spectrum antineoplastic drug cyclophosphamide itself is a weakly active drug. After being metabolized by CYP450 enzymes (mainly CYP2B6) in the body, it is transformed into the active substance aldophosphamide, and then transported into the tumor tissue to form phosphoramide mustard to inhibit cancer. effect on cell growth.
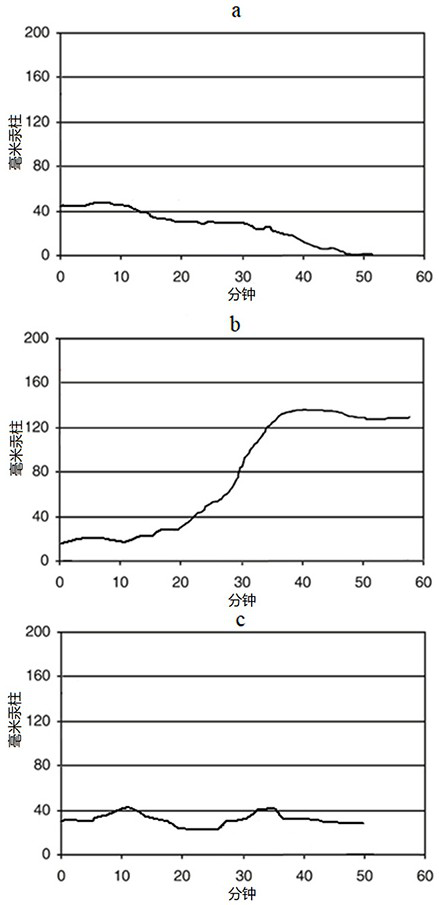
[0070] Cells and green algae were inoculated on the microalgae-intestine-liver-tumor organ chip according to the previously described method, and cultured in an incubator equipped with an LED system and an oxygen content monitoring system for 24 hours, waiting for the cells to completely adhere to the wall, and using Oxygen sensors monitor each chamber until a physiological oxygen concentration is reached in each chamber. The control group removed the light source and green algae, and was placed in an ordinary ...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3: Application of Microalgae-Intestine-Liver-Tumor Organ Chip in Evaluation of Paclitaxel Antitumor Activity
[0076] The anti-cancer mechanism of paclitaxel is that the compound itself can induce and promote tubulin polymerization, inhibit microtubule depolymerization, induce cell cycle arrest and promote apoptosis, thereby exerting an anti-tumor effect. It will be blocked by CYP3A4 in the liver in vivo. Enzyme metabolism into metabolites with weak anticancer activity.
[0077] Cells and green algae were inoculated on the microalgae-intestine-liver-tumor organ chip according to the previously described method, and cultured in an incubator equipped with an LED system and an oxygen content monitoring system for 24 hours, waiting for the cells to completely adhere to the wall, and using Oxygen sensors monitor each chamber until a physiological oxygen concentration is reached in each chamber. The control group removed the light source and green algae, and was plac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com