Edge-emitting type laser element
A laser component and side-firing technology, which is applied to laser components, lasers, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as temperature rise, overflow, and active layer coupling efficiency reduction, so as to reduce the critical current value and improve the mode The effect of low gain and critical current value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042]
[0043] *Note: The thickness of the active layer can be designed according to the luminous wavelength range of the operating EEL element.
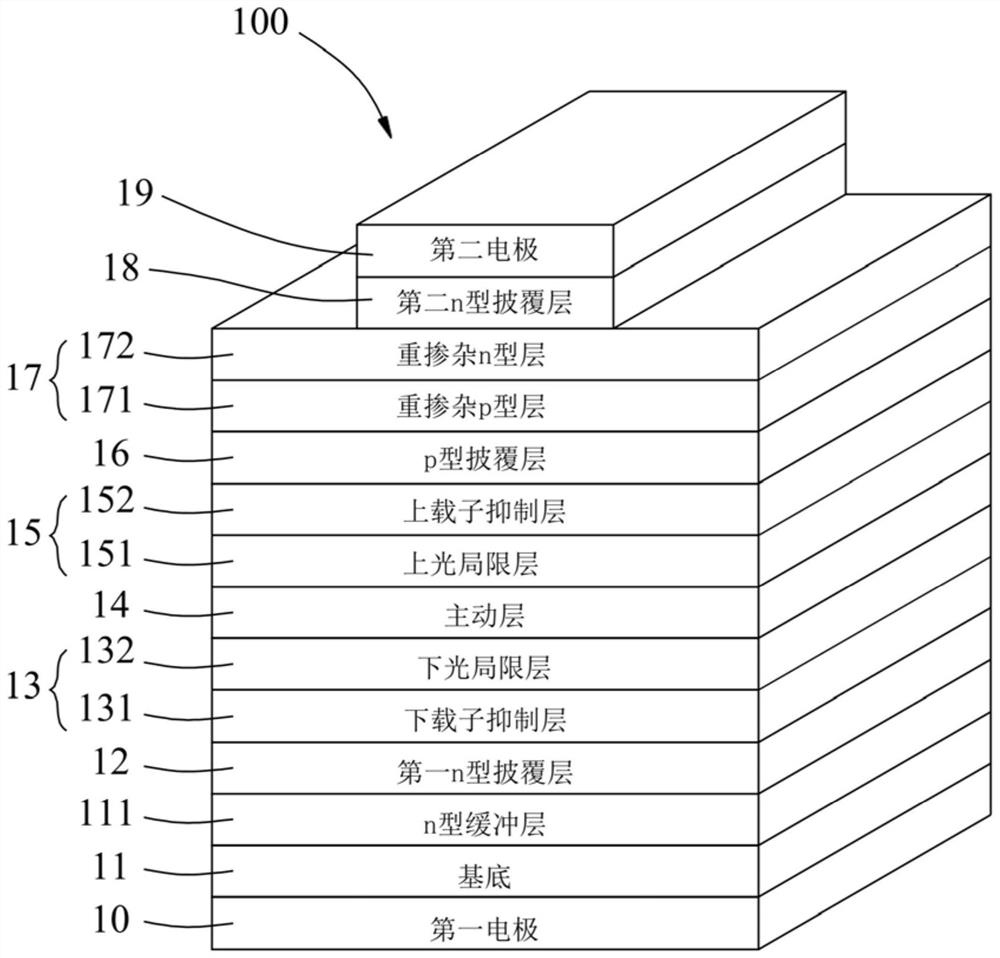
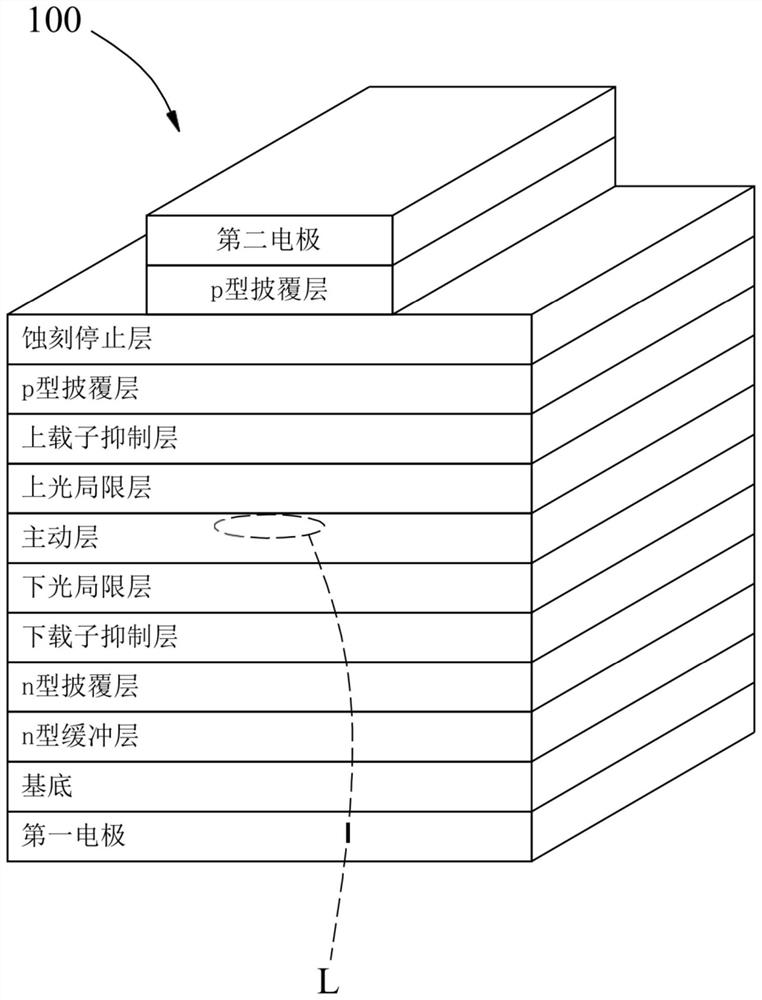
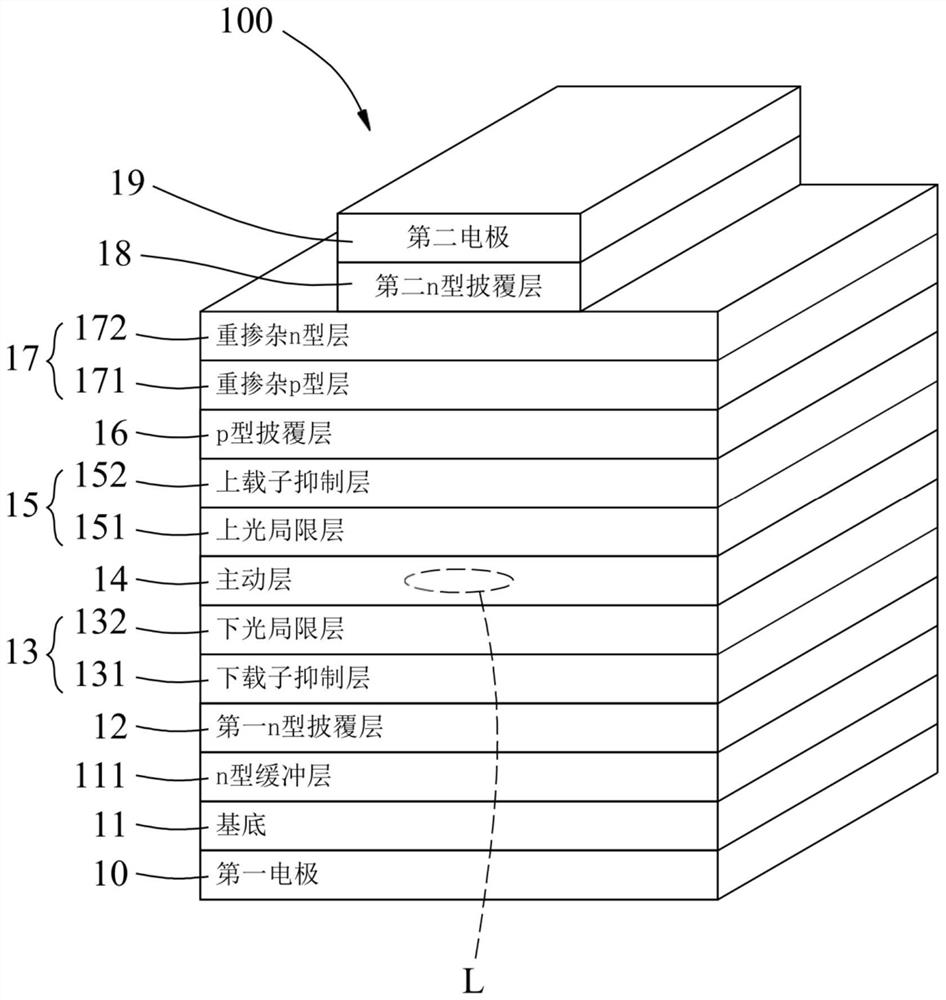
[0044] Corresponding to Comparative Example 1, Embodiment 1 produces the following advantages: (1) at the 11th layer, since Embodiment 1 adopts the tunnel junction layer 17 to combine the p-type cladding layer (12th layer) of Comparative Example 1 ) is transposed into the second n-type cladding layer 18 (the 12th layer) of embodiment 1, which makes embodiment 1 only have p-type cladding layer 16 (thickness 50nm) and the heavily doped p Type layer 171 (15nm) is a p-type semiconductor, and its total thickness is 65nm (65nm=50nm+15nm), but comparative example 1 has p-type cladding layer (50nm), etching stop layer (25nm), p-type cladding layer Layer (1500nm) and second electrode (200nm) are p-type semiconductors, and its total thickness is 1775nm (1775nm=50nm+25nm+1500nm+200nm), and the p-type semiconductor total thickness 65nm of e...
Embodiment 2
[0053]
[0054]
[0055] *Note: The thickness of the active layer can be designed according to the luminous wavelength range of the operating EEL element.
[0056] Similar to the discussion of Comparative Example 1 of the aforementioned FP laser element Table 1 and Example 1 of Table 2, corresponding to Comparative Example 2 of the DFB laser element, Example 2 also produces the following advantages: (1) on the 11th layer, Since Example 2 uses the tunnel junction layer 17 to transpose the p-type cladding layer (12th layer) of Comparative Example 2 into the second n-type cladding layer 18 (12th layer) of Example 2, this makes the implementation In Example 2, only the p-type cladding layer 16 (thickness 50nm) and the heavily doped p-type layer 171 (15nm) of the tunnel junction layer 17 are p-type semiconductors, and their total thickness is 65nm. However, Comparative Example 2 has p-type semiconductors. Coating layer (50nm), etching stop layer (25nm), p-type cladding layer ...
Embodiment 3
[0064]
[0065]
[0066] *Note: The thickness of the active layer can be designed according to the luminous wavelength range of the operating EEL element.
[0067] Similar to the discussion of Comparative Example 1 of the aforementioned FP laser element Table 1 and Example 1 of Table 2, corresponding to Comparative Example 3 of the DFB laser element, Example 3 also produces the following advantages: (1) on the 11th layer, Since Example 3 uses the tunnel junction layer 17, the p-type cladding layer (the 12th layer and the 13th layer) of Comparative Example 3 is transposed into the second n-type cladding layer 18 (the 12th layer) of Example 3. The lower second n-type cladding layer 181 and the upper second n-type cladding layer 182 of the 13th layer), which makes embodiment 3 only have the weight of the p-type cladding layer 16 (thickness 20nm) and the tunnel junction layer 17 The doped p-type layer 171 (15nm) is a p-type semiconductor with a total thickness of 35nm, but C...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com