A pesticide intermediate degrading bacterial strain, its cultivation method and its bacterial agent and application
A technology for intermediates and pesticides, applied in the field of pesticide intermediates degrading strains, can solve problems such as refractory biodegradation, accumulation, environmental and human health hazards, and achieve the effects of high-efficiency degradation capacity, simple processing technology, and low processing costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Isolation, screening and identification of degrading strain PH-1:
[0041] 1. Isolation and screening of degrading strain PH-1
[0042]The invention provides a degrading strain PH-1 for efficiently degrading pesticides, which is separated from the activated sludge of a sewage treatment plant. The specific strain culture method is as follows: take the activated sludge in the biochemical tank of the sewage treatment plant, add it to the inorganic salt medium containing CCMP for domestication and culture; Cultured with constant temperature shaking at 160 rpm; after culturing for 5 days, the inoculum of 5% (V / V) was inserted into fresh inorganic salt medium, and enriched and transferred 4 times in a row; 1 mL of enrichment solution was diluted with sterile water To different concentration gradients (10-2-10-6), take 0.2 mL of dilutions of different concentration gradients, spread them on R2A agar medium plates containing 100 mg / L CCMP, and place them in a 30°C constant tem...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Degradation effect of degrading strain PH-1:
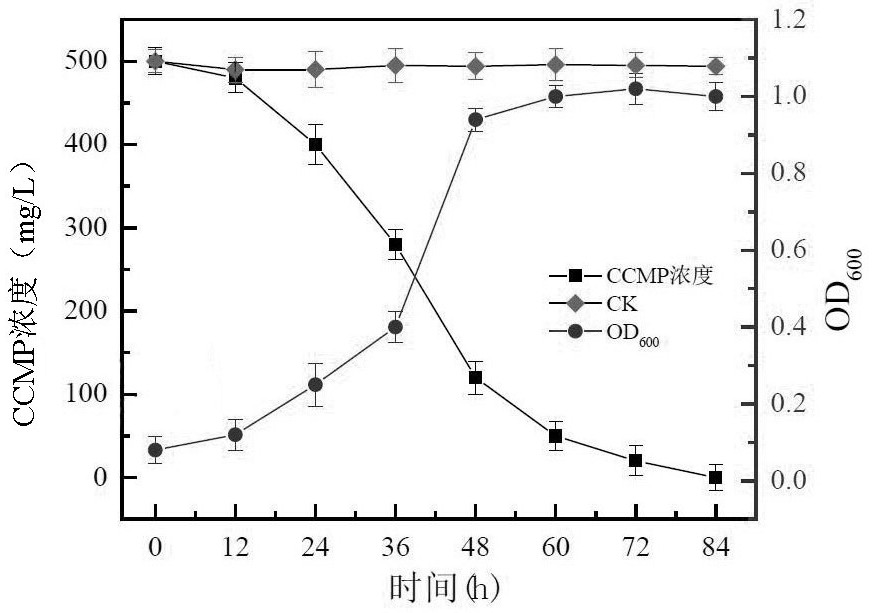
[0049] The single colony of degrading strain PH-1 obtained by screening in Example 1 was inoculated in 50 mL of LB medium, enriched and cultured to OD600=1.0 under the conditions of 30 ° C and 160 rpm, and the obtained culture solution was centrifuged at 4 ° C and 10000g for 10 min, The bacteria were collected, washed three times with sterile phosphate buffer and resuspended in phosphate buffer as a bacterial suspension. The obtained bacterial suspension was inoculated into an inorganic salt medium with CCMP as the sole carbon source at a volume ratio of 5%, the CCMP concentration in the culture solution was 500 mg / L, and the culture was incubated at 30 ° C and 160 rpm under constant temperature shaking for 84 h, and sampling was performed regularly. The corresponding OD600 value and the concentration of CCMP in the culture medium were determined, and the experiment was repeated three times. To draw the degradation and gro...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The degradation effect of degrading strain PH-1 on the downstream products of CCMP:
[0053] The inorganic salt medium of imidacloprid, fluazinam and diflufenapyr with a final concentration of 200 mg / L was prepared respectively, and the pH of the medium was adjusted to 7. Pick the single colony of degrading strain PH-1 obtained by screening in Example 1, inoculate it in 50mL LB medium, enrich and cultivate it to OD600=1.0 under the conditions of 30°C and 160rpm, and the obtained bacterial liquid is 5% by volume (V / V ) were inoculated into the medium containing different pesticides, cultured in a constant temperature shaking box at 30 °C and 160 rpm, and the degradation was detected after 72 h. The degradation effect is as follows: Figure 4 shown.
[0054] according to Figure 4 It can be seen that the strain PH-1 can effectively degrade the downstream products of 2-chloro-5-chloromethylpyridine, and the degradation rates of imidacloprid, flufenazuron and diflufenacil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com