A degreasing sintering method based on nanoparticle additive manufacturing of shaped parts
A nanoparticle and additive manufacturing technology, applied in the field of additive manufacturing materials, can solve the problems that the chemical degreasing process cannot be applied to nanoparticles and nanoparticle embryo defects, and achieve the effects of cost saving, carbon neutrality and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
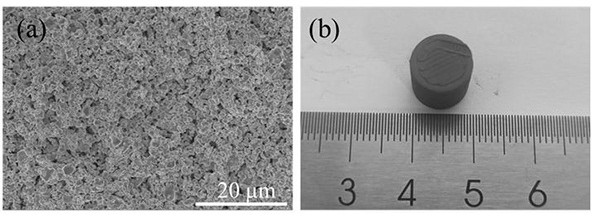
[0035]This embodiment provides a degreasing and sintering method based on nanoparticle additive manufacturing of formed parts, using tungsten-based alloy nanoparticles as the original material, and using powder extrusion printing technology to prepare tungsten-based alloy blanks. The prepared embryo is cylindrical. The process parameters of the powder extrusion printing technology are the scanning line spacing of 50 μm and the layer thickness of 20 μm. 0.5 g of sodium citrate was dissolved in 1 L of distilled water to form a solution and heated to 40°C. The tungsten-based alloy blanks were then placed in a sodium citrate solution at 40°C and stirred. The whole degreasing time was 4h, during which the solution was replaced with a new solution at 40°C every 1h. After the degreasing, the degreasing embryos were placed in an atmosphere furnace, the sintering atmosphere was hydrogen, the heating rate was kept at 3K / min, and the temperature was raised to 1400 °C for 1 h to complet...
Embodiment 2
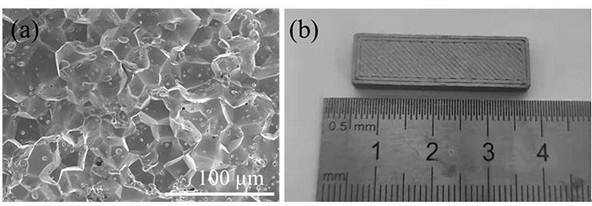
[0037] This embodiment provides a degreasing and sintering method based on nanoparticle additive manufacturing of formed parts, using tungsten-based alloy nanoparticles as the original material, and using powder extrusion printing technology to prepare tungsten-based alloy blanks. The process parameters of the powder extrusion printing technology are the scanning line spacing of 1000 μm and the layer thickness of 100 μm. The prepared prime embryo is a cuboid with a linear pattern on the surface. 20 g of sodium citrate was dissolved in 2 L of distilled water to form a solution and heated to 70°C. The tungsten-based alloy blanks were then placed in a sodium citrate solution at 70°C and stirred. The whole degreasing time was 36h, during which the solution was replaced with a new solution at 70°C every 3h. After the degreasing, the degreasing embryos were placed in an atmosphere furnace, and the atmosphere was a mixture of hydrogen and argon. The microstructure of the sintered ...
Embodiment 3
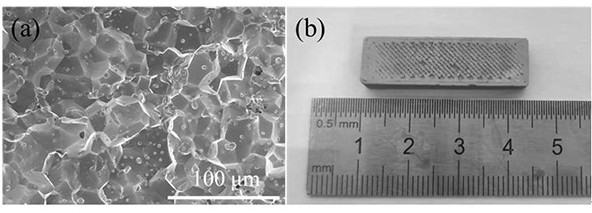
[0039] This embodiment provides a degreasing and sintering method based on nanoparticle additive manufacturing of formed parts, using tungsten-based alloy nanoparticles as the original material, and using powder extrusion printing technology to prepare tungsten-based alloy blanks. The process parameters of the powder extrusion printing technology are the scanning line spacing of 100 μm and the layer thickness of 30 μm. The prepared prime embryo is a cuboid with a linear pattern on the surface. 90 g of sodium citrate was dissolved in 3 L of distilled water to form a solution and heated to 90°C. The tungsten-based alloy blanks were then placed in a sodium citrate solution at 90°C and stirred. The whole degreasing time was 48h, during which the solution was replaced with a new solution at 90°C every 2h. After the degreasing, the degreasing embryos were placed in an atmosphere furnace, the sintering atmosphere was hydrogen, the heating rate was kept at 10 K / min, and the temperat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com