Staphylococcus equorum and application of staphylococcus equorum in prevention and treatment of gray mold of fruits and vegetables
A technology for staphylococcus and botrytis cinerea, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of lack of biocontrol agents, few biological strains, etc., and achieve the effects of improving the expression level of disease resistance genes, increasing enzyme activity, and excellent antagonism.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1 Isolation, screening and strain identification of Staphylococcus equisetum F1
[0047] 1. Isolation and screening of strains
[0048] Mature and healthy fruits were collected from a commercial Fuji apple orchard in Shandong, and after surface disinfection, the fruit tissue was ground, added with sterile water, and the conventional gradient dilution coating separation method was used. The colonies with obvious morphological differences were purified and stored on PDA medium, and the primary screening and repeated screening of antagonistic bacteria were carried out with the apple tree rot pathogen as the target pathogen, and a bacterial strain with bacteriostatic effect and significant control effect was finally obtained. , and name it F1.
[0049] 2. Identification of strain F1
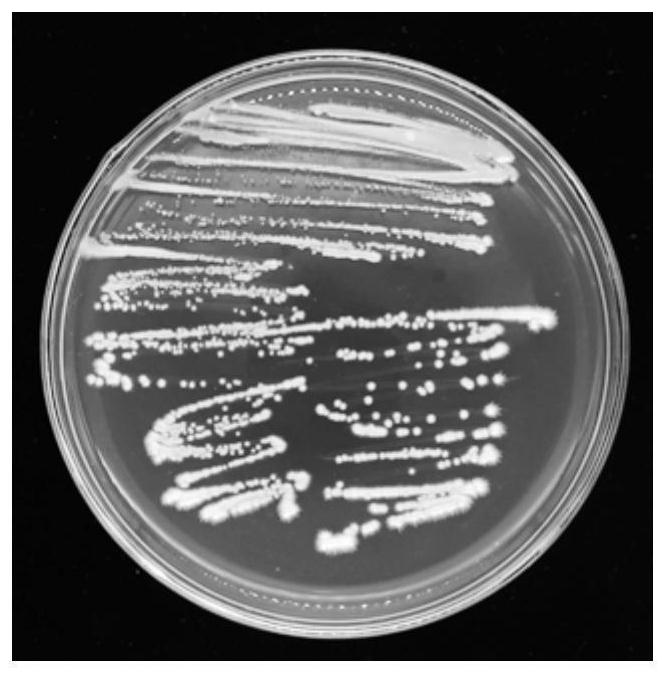
[0050] (1) Morphological characteristics
[0051] like figure 1 The results showed that the colony of strain F1 on the LB medium was small, grayish-white, rounded (slightly irregul...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2 The effect of Staphylococcus equisetum F1 on mycelial growth and spore germination of Botrytis cinerea on fruits and vegetables
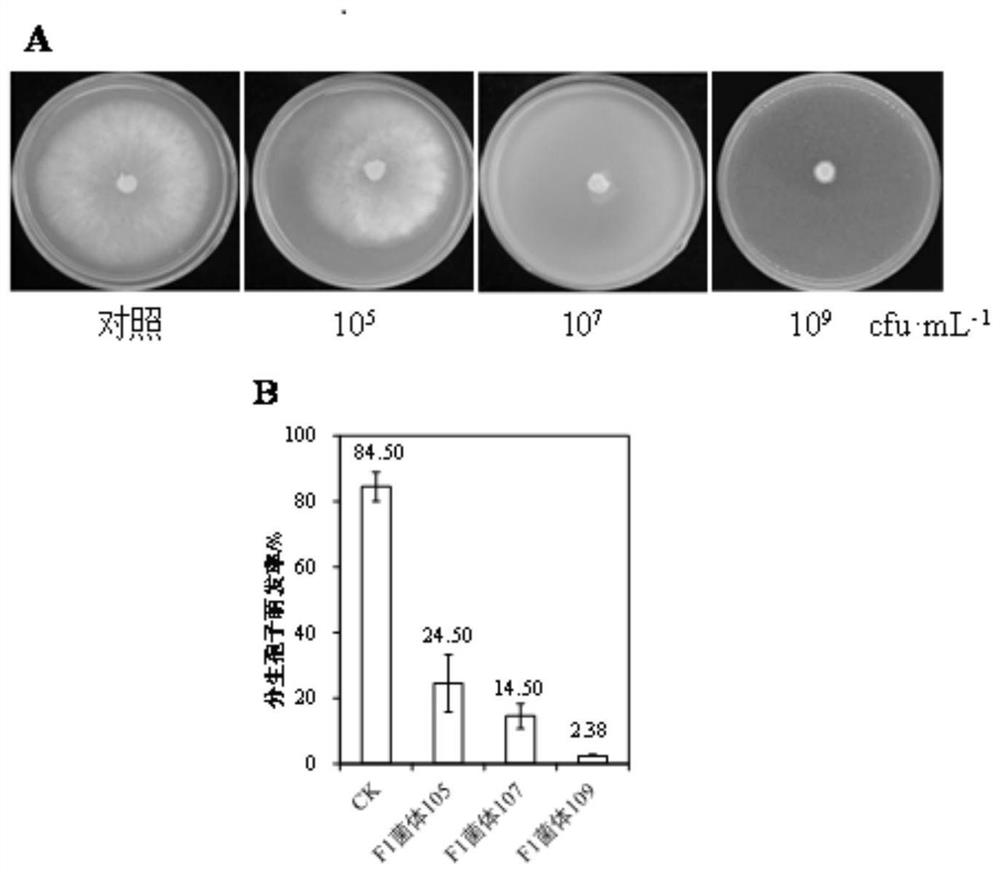
[0060] (1) The effect of strain F1 on the growth of mycelium of Botrytis cinerea
[0061] A. Experimental method: The seed fermentation broth of Staphylococcus equorum F1 was inoculated into PDB medium, and incubated at 28°C with constant temperature shaking for 48 hours to obtain the cell culture liquid of strain F1, and the cells of strain F1 were collected after centrifugation. Prepare PDA medium, add the bacterial cells of strain F1 to it, and make the final concentration of 10 5 , 10 7 and 10 9 cfu·mL -1 , with PDA without strain F1 as a control. The above-mentioned PDA medium was inoculated with activated Botrytis cinerea. The cells were cultured at 25°C in the dark for 3 days, and the colony diameter was observed and measured.
[0062] B. Results and analysis:
[0063] The results showed that the addition of different ...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3 Inhibitory effect of Staphylococcus equisetum F1 on various plant pathogens
[0070] A. Experimental method: prepare Staphylococcus equorum F1 bacterial suspension to make the final concentration 10 9 cfu·mL -1 , with PDA without strain F1 as a control, and then inoculated with activated cultured pathogens.
[0071] Bacteriostatic rate=(colony diameter of control group-colony diameter of treatment group) / colony diameter of control group×100%.
[0072] B. Results and analysis: As shown in Table 1, strain F1 has significant inhibitory effect on major plant pathogens such as Botrytis cinerea, apple tree rot, apple rot, and apple anthracnose leaf blight, showing good results. The broad-spectrum antibacterial properties of the bacteria were shown in Table 1.
[0073] Table 1 Inhibitory effect of Staphylococcus equorum strain F1 on major plant pathogens
[0074]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com