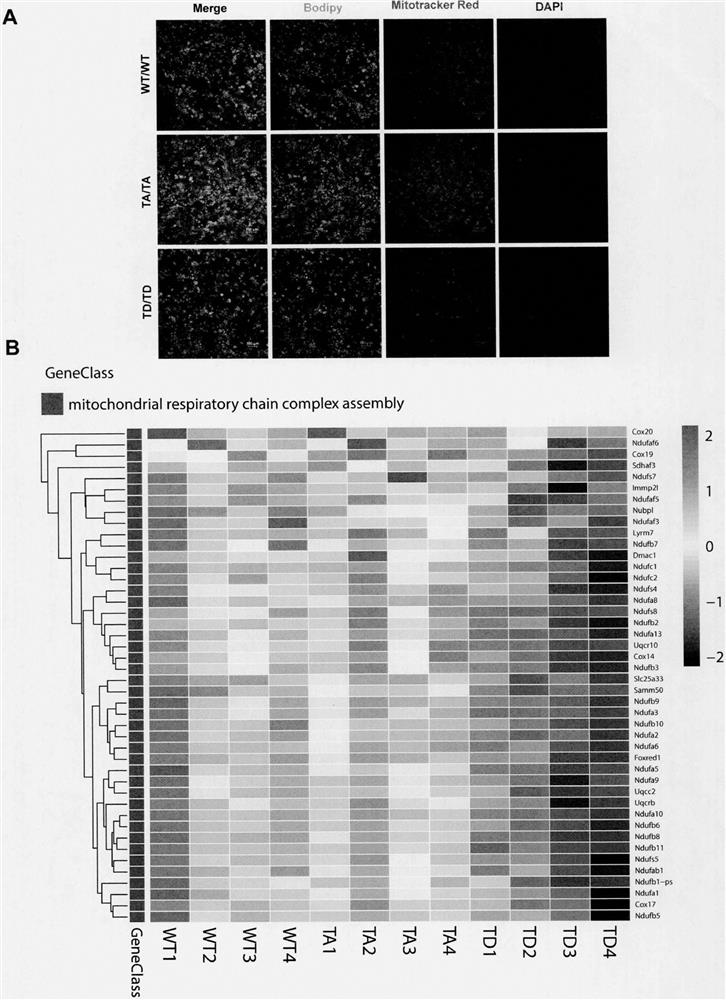
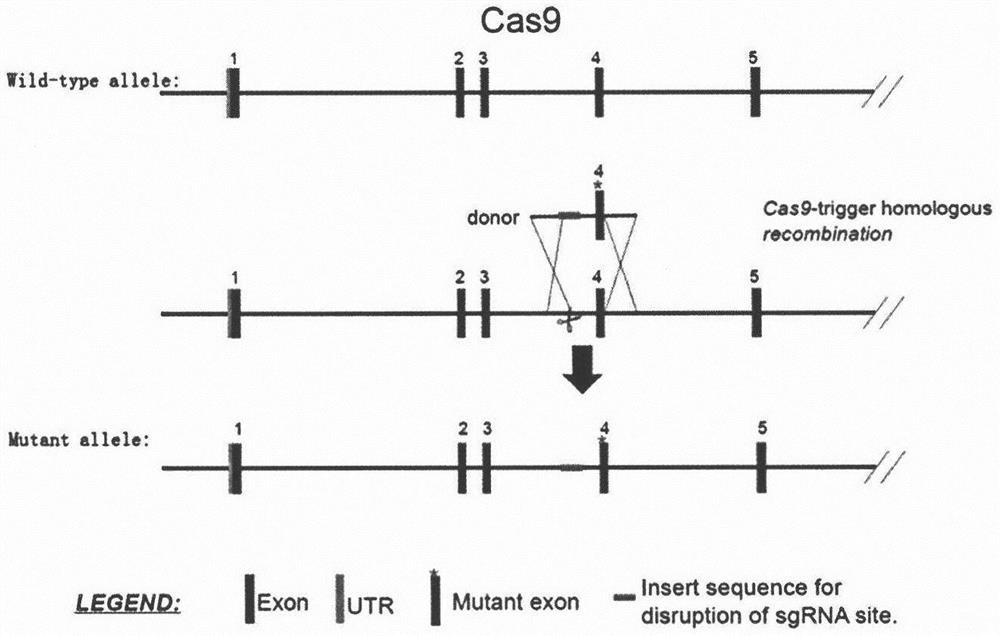
Construction and application of Pparg gene site-directed mutagenesis mouse model
A gene site-directed mutation, mouse model technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Construction method of mouse model of Pparg gene site-directed mutation, the principle is as follows figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0044] 1. Design of CRISPR / Cas9 gRNA for Pparg gene:
[0045] According to the Pparg gene sequence and the mutations T166A (ACC→GCT) and T166D (ACC→GAT) to be introduced, two gRNA sequences were designed. For the specific sequences, see SEQ ID NO.1 (T166A mutation) and NO.2 (T166D mutation) in the sequence table. )
[0046] 2. Construction of Donor vector:
[0047] The Donor vector construction method is to first artificially synthesize target sequence oligonucleotide primers with different restriction enzyme cleavage site recognition sequences at the 5′ end, and directly anneal the two pairs of primers by PCR to synthesize target sequence DNA carrying different sticky ends. A short fragment was inserted into the vector to construct a Donor vector (CRISPR / Cas9 targeting vector) targeting the...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2: 8-week-old TA and TD mice were subjected to adipose tissue sectioning and H&E staining. By analyzing the morphological characteristics of adipose tissue, it was found that adipocytes in the adipose tissue of TA mice were smaller and more numerous, and single adipocytes accumulated lipids; conversely, adipocytes in TD mice were larger and less numerous, and individual adipocytes accumulated more lipids ( image 3 .A); Simultaneously, using fluorescence quantitative PCR to analyze the changes of metabolism-related genes in adipose tissue, it can be found that the adipose tissue of TA mice is characterized by high fatty acid metabolism, while the fatty acid catabolism of TD mice is blocked ( image 3 .B). Subsequently, the two point mutant mice were fed high-fat for 3 months, and the liver and muscle tissues were isolated to analyze their pathological status. steatosis ( Figure 4 .A-B). Simultaneous analysis of insulin sensitivity, substance and energy metab...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3: point mutant mice and wild-type mice were fed with high-fat (60% fat content) for 3 months. Subsequently, the visceral fat of the mice was isolated and paraffin sectioned, and the tissue sections were analyzed by H&E pathological staining; the results showed that a large number of inflammatory immune cells were infiltrated in the visceral adipose tissue of wild-type mice, and the adipose tissue presented a state of chronic inflammation , while the visceral adipose tissue of TA mice contained less immune cell infiltration ( Figure 5 .A). At the same time, sorting mouse primary macrophages and performing quantitative PCR analysis showed that TA mutations reduced the classical activation of macrophages (M1 polarization) and enhanced the alternative activation phenotype of macrophages (M2 polarization). ). Conversely, TD mutations reduce macrophage alternative activation phenotype (M2 polarization) and instead enhance classical activation (M1 polarization) ( ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com