Bacteria-like nano-drug delivery system as well as preparation method and application thereof
A nano-drug and delivery system technology, applied in the directions of drug combination, pharmaceutical formulation, capsule delivery, etc., can solve the problems of weakening the targeting function, difficult to achieve a high level of tumor enrichment, improving the level and limited targeting ability, etc. Improve the effect of recognition and killing, structural stabilization, and tumor growth inhibition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Embodiment 1 A kind of preparation method of imitating bacteria nanometer drug delivery system
[0044] The preparation method comprises the following steps that are carried out in sequence:
[0045] S1. Preparation of Nanoparticle Concentrates
[0046] To contain 25g PEG 5K -PLGA 11K (biodegradable polymer) and 2.5g (2,3-dioleoyl-propyl)-trimethylamine (cationic lipid) in 0.5L chloroform, add siYthdf1 (siRNA drug) 12.5μmol aqueous solution (25mL), After the first sonication in an ice bath for 1 min, add 5 L of water to the mixture obtained after sonication, place in an ice bath environment, sonicate for the second time for 2 min, suspend and evaporate the chloroform, and concentrate to 0.5 L by ultrafiltration to obtain a nanoparticle concentrate (marker codes are NPs);
[0047] S2. Preparation of bacterial-like nano-drug delivery system
[0048]Preparation of bacterial outer membrane vesicles: Inoculate attenuated Salmonella VNP20009 into LB medium, and shake at ...
Embodiment 2~7
[0050] The preparation method of embodiment 2~7 imitated bacteria nanometer drug delivery system
[0051] Embodiments 2 to 7 are respectively a preparation method of a bacterial-like nano-drug delivery system, and the process steps in their preparation method are similar to those of embodiment 1, and the difference from embodiment 1 is only:
[0052] In Example 2, the biodegradable polymer is PEG 5K -PLA 25K ; siRNA drug is siPd-l1; cationic lipid is BHEM-cholesterol; the ratio of biodegradable polymer, cationic lipid, chloroform, siRNA drug and water is 20g:2g:0.48L:14μmol:4L.
[0053] In Example 3, the biodegradable polymer is PEG 5K -PLA 25K ; siRNA drug is siPd-l1; the ratio of biodegradable polymer, cationic lipid, chloroform, siRNA drug and water is 23g:3g:0.5L:15μmol:5L.
[0054] In Example 4, the siRNA drug was siPd-l1; the ratio of biodegradable polymer, cationic lipid, chloroform, siRNA drug and water was 30g:2.5g:0.4L:12μmol:6L.
[0055] In Example 5, the biode...
Embodiment 8
[0059] Example 8 Performance detection of imitated bacteria nanometer drug delivery system
[0060] (1) Surface potential, particle size and stability of bacterial-like nano-drug delivery systems
[0061] The surface potential, particle size and structural stability of NPs and BNMs were determined by dynamic light scattering.
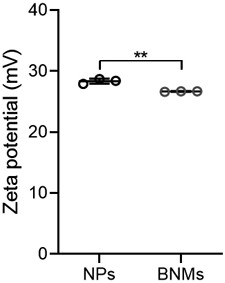
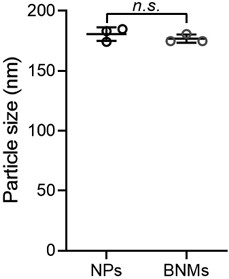
[0062] The surface potential results of NPs and BNMs are as follows figure 1 As shown, the surface potential of NPs is about 28.33mV, and the surface potential of BNMs is about 26.67mV. particle size such as figure 2 As shown, the particle sizes of both NPs and BNMs are around 180 nm.
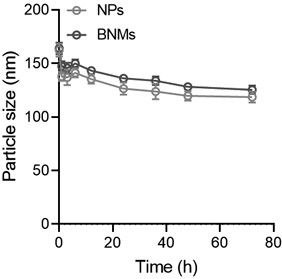
[0063] Dynamic light scattering was used to determine the particle stability of NPs and BNMs in physiological solutions (physiological saline containing 2% FBS), such as image 3 As shown, the particle size of NPs and BNMs changed little within 72 h, indicating that the bacterial-like nano-drug delivery system of the present invention has good structural stability i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com