Method for producing pimelic acid by fermenting enterobacter hormaechei
A technology of Enterobacter horii and pimelic acid is applied in the field of Enterobacter horii fermenting and producing pimelic acid to achieve the effect of reducing the cost of industrialization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: Screening of pimelic acid-producing strains
[0038] After streaking the strains preserved in the laboratory, pick a single colony to prepare a secondary seed solution: the single colony of the inoculated strain is placed in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50 mL of LB medium, and cultured at 37°C for 12 hours at 250 r / min to prepare primary seeds. Continue to transfer the first-class seed solution to a conical flask at 2% of the inoculum, and cultivate at 37°C at 250 r / min for 12 h to prepare the second-class seed solution.
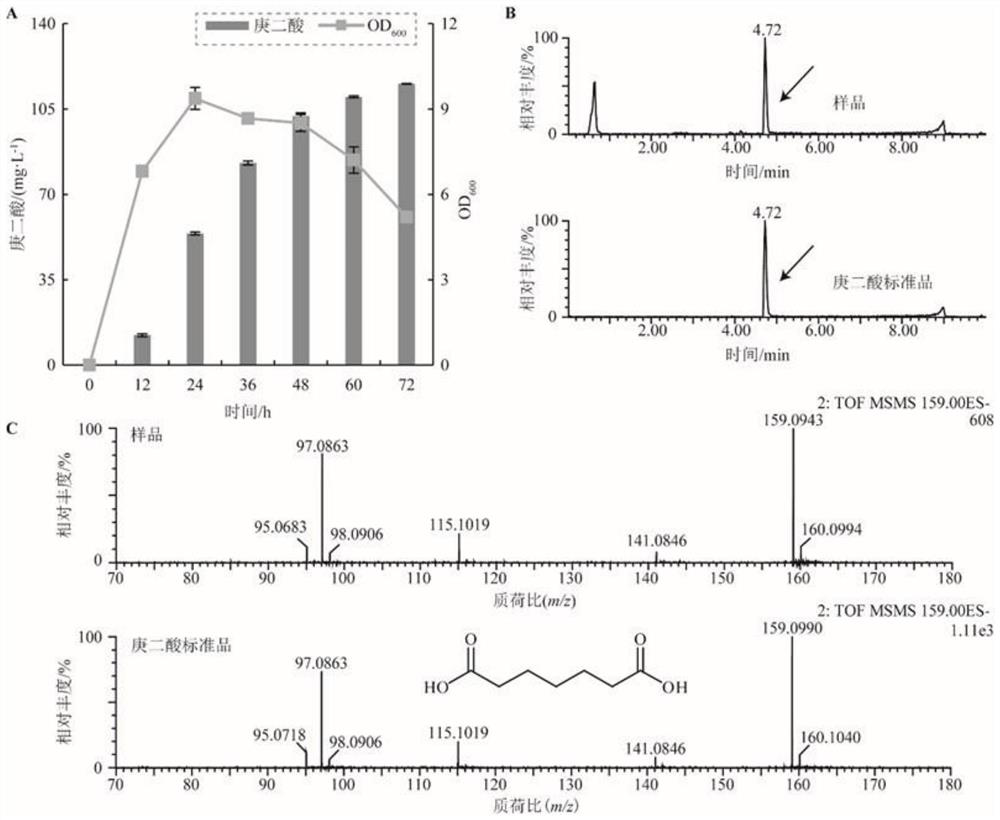
[0039] A 48-well plate was used for primary screening, fermentation was performed at 30°C, 250 r / min for 72 h, and pimelic acid in the fermentation broth was detected by HPLC. Then, the strains obtained from the primary screening were re-screened in a shaker flask, and the prepared secondary seed liquid was inoculated into a 250mL conical flask containing 50mL SOB medium with 2% inoculum, and fermented at 30°C and 250r / min for 72h. ...
Embodiment 2
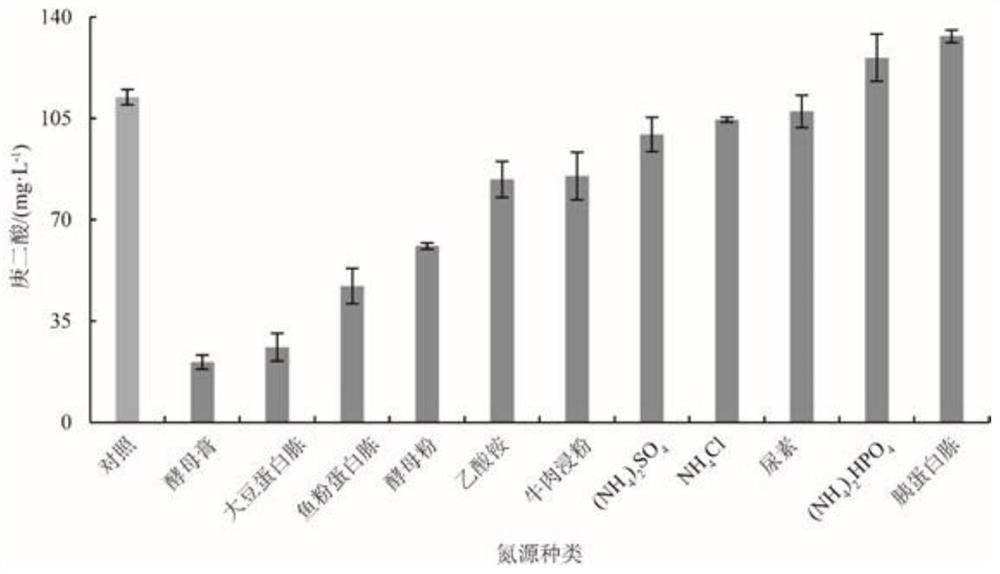
[0041] Example 2: Optimization of media composition
[0042] Preparation of secondary seed solution: inoculate a single colony of strain Bpa-3 in a 250 mL conical flask containing 50 mL of LB medium, and cultivate at 37°C for 12 hours at 250 r / min to prepare primary seed solution; inoculate the primary seed solution with 2% Continue to transfer the amount to the Erlenmeyer flask, cultivate at 37°C, 250r / min for 12h to prepare secondary seed solution (OD 600 =4±0.5).
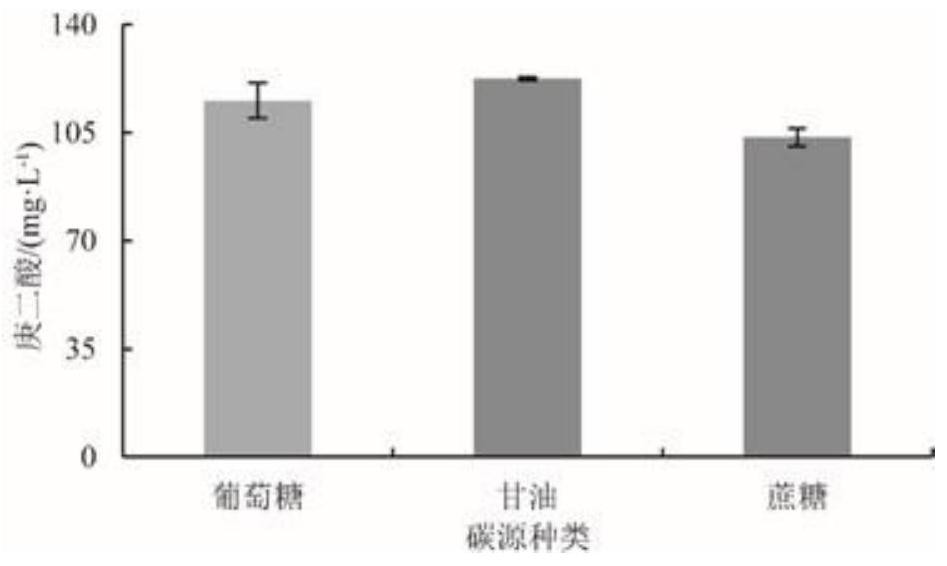
[0043] (1) Optimization of carbon source species: 4g / L sucrose and 4g / L glycerol were used to replace glucose in SOB medium, respectively, and the secondary seed solution of strain Bpa-3 was treated with an inoculum of 2% (v / v). It was inoculated into the medium, fermented at 30°C, 250r / min for 72h, sampling every 12h, and the fermentation broth was analyzed by HPLC. The result is as figure 2 As shown, after 72 h of fermentation, when the carbon source was glycerol, the yield of pimelic acid was 122.5 mg / L as...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Optimization of inoculum size
[0048] The secondary seed liquid of strain Bpa-3 was transferred with the inoculum of 1%, 2%, 4%, 6%, 8% and 10% (v / v) respectively, and the optimal composition medium was used for shake flask fermentation , 30 ℃, 250r / min fermentation 72h, sampling every 12h, using HPLC to analyze the fermentation broth. The result is as Figure 5 As shown, when the inoculation amount is 4%, the yield of pimelic acid can reach a maximum of 149.2 mg / L, and when the inoculation amount is 1%, 2%, 6%, 8%, and 10%, the yield of pimelic acid is respectively were 113.4 mg / L, 123.5 mg / L, 140.3 mg / L, 140.8 mg / L, and 124.0 mg / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com