Method for determining bioavailability and bioavailability of cadmium in boletus cinereus
A bioavailability, bolete technology, applied in the direction of bacteria, color/spectral property measurement, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc. good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
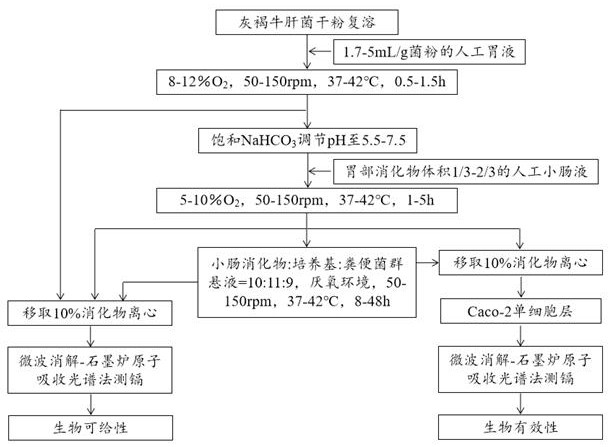
[0035] Example 1: as figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment utilizes the in vitro full biomimetic digestion and absorption method to measure the bioavailability and bioavailability of cadmium in Boletus boletus as follows:
[0036] Gray-brown boletus dry powder: The gray-brown boletus collected from various places is dried, crushed, and passed through a 40-mesh sieve by conventional drying methods, and the material under the sieve is taken. After microwave digestion-graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry, the cadmium content varies, and three samples of Boletus taupe with different cadmium content were selected (low: 7.31mg / kgDW; medium: 24.20mg / kgDW; high: 41.64mg / kgDW) for the following implementation process.
[0037] 1. Stomach physical and chemical digestion process: Accurately weigh 3g dry powder of boletus taupe into a 100mL anaerobic bottle, add 27mL deionized water, swell and rehydrate at room temperature. Add 10 mL of commercially available artificial...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2: At the same time in this embodiment, the standard substance GBW10025 (GSB-16) Spirulina is used for the recovery rate of cadmium in the detection method and the repeatability of the measurement results, and the steps are as follows:
[0051] The standard material for biological component analysis GBW10025 (GSB-16) Spirulina (developed by: Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences) was purchased, and the standard value of cadmium content was 0.37±0.03mg / kgDW.
[0052] 1. Stomach physical and chemical digestion process: Accurately weigh 3g of spirulina powder into a 100mL anaerobic bottle, add 27mL of deionized water, and swell and rehydrate at room temperature. Add 10mL of commercially available artificial gastric juice (Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd., product number: R41110), in a solution containing 10% CO 2 In the anaerobic box of 37℃, 100rpm water bath shaking for 1h. Pipette 4 mL of the mixtu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com