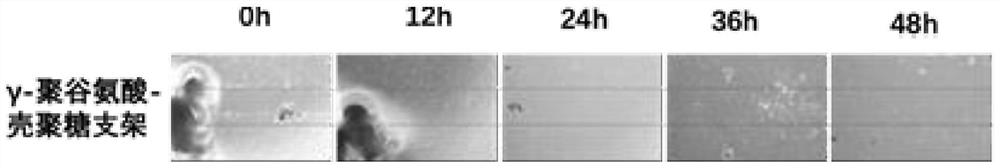
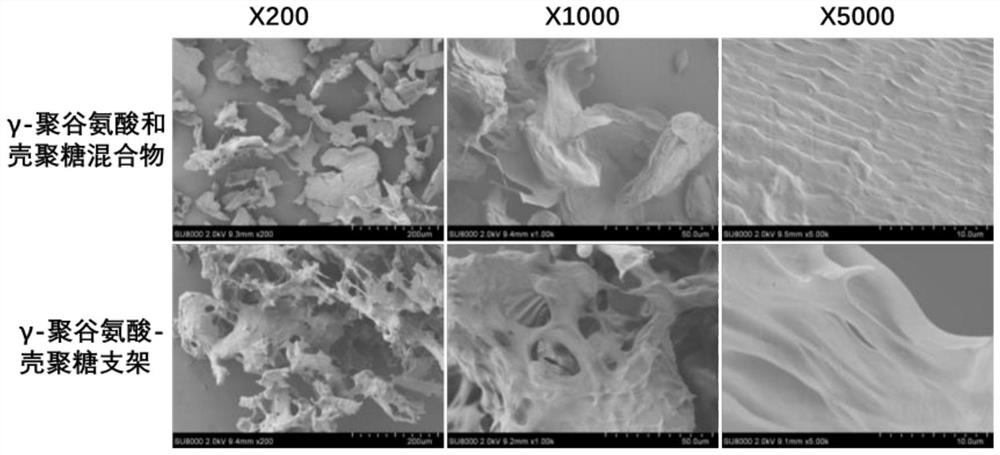
Preparation method of gamma-polyglutamic acid/chitosan microsphere scaffold
A technology of chitosan microspheres and polyglutamic acid, which is applied in the fields of medical science and prosthesis, can solve the difficulty of large-scale production and market sales of microspheres, the complicated steps of emulsification and cross-linking method, and the influencing factors of microsphere scaffolds. Many problems, to achieve the effect of excellent bone conduction performance, good biodegradability, good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] A preparation method of γ-polyglutamic acid / chitosan microsphere scaffold, comprising the following steps:
[0044] S1: Take 1L of distilled water in a beaker, calibrate the pH meter, and add NaOH to adjust to pH=9. Place the prepared NaOH solution on a magnetic stirrer, adjust the speed to 800r / min; weigh 3.5g of γ-polyglutamic acid (purity ≥95%, molecular weight>700kDa), slowly add it to the NaOH solution while stirring And placed on a magnetic stirrer and stirred for 1 hour to obtain a γ-polyglutamic acid solution;
[0045] S2: After the γ-polyglutamic acid is completely dissolved, slowly add 1.55g of chitosan to the γ-polyglutamic acid solution while stirring (the degree of deacetylation is ≥95%, the viscosity is 100-200mpa.s, the γ- The molar ratio of polyglutamic acid and chitosan is 2:1), after stirring for 6 hours, a mixed solution of chitosan-γ-polyglutamic acid is obtained, and the mixed solution is equally divided into 2 parts;
[0046] S3: Calibrate the pH...
Embodiment 2
[0052] A preparation method of γ-polyglutamic acid / chitosan microsphere scaffold, comprising the following steps:
[0053] S1: Take 1L of distilled water in a beaker, calibrate the pH meter, and add NaOH to adjust to pH=8.5. Place the prepared NaOH solution on a magnetic stirrer, adjust the speed to 800r / min; weigh 3.5g of γ-polyglutamic acid (purity ≥95%, molecular weight>700kDa), slowly add it to the NaOH solution while stirring And placed on a magnetic stirrer and stirred for 1 hour to obtain a γ-polyglutamic acid solution;
[0054] S2: After the γ-polyglutamic acid is completely dissolved, slowly add 3.1 g of chitosan (degree of deacetylation ≥ 95%, viscosity 100-200 mpa.s, γ- The molar ratio of polyglutamic acid and chitosan is 1:1), and after stirring for 6 hours, a chitosan-γ-polyglutamic acid mixed solution is obtained, and the mixed solution is equally divided into 2 parts;
[0055] S3: Calibrate the pH meter, prepare distilled water with pH=7, and dilute the 10% ac...
Embodiment 3
[0061] A preparation method of γ-polyglutamic acid / chitosan microsphere scaffold, comprising the following steps:
[0062] S1: Take 1L of distilled water in a beaker, calibrate the pH meter, and add NaOH to adjust to pH=9.5. Place the prepared NaOH solution on a magnetic stirrer, adjust the speed to 800r / min; weigh 3.5g of γ-polyglutamic acid (purity ≥95%, molecular weight>700kDa), slowly add it to the NaOH solution while stirring And placed on a magnetic stirrer and stirred for 1 hour to obtain a γ-polyglutamic acid solution;
[0063] S2: After the γ-polyglutamic acid is completely dissolved, slowly add 6.2 g of chitosan (degree of deacetylation ≥ 95%, viscosity 100-200 mpa.s, γ- The molar ratio of polyglutamic acid and chitosan is 1:2), after stirring for 6 hours, a chitosan-γ-polyglutamic acid mixed solution is obtained, and the mixed solution is equally divided into 2 parts;
[0064] S3: Calibrate the pH meter, prepare distilled water with pH=7, and dilute the 10% acetic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass volume concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com