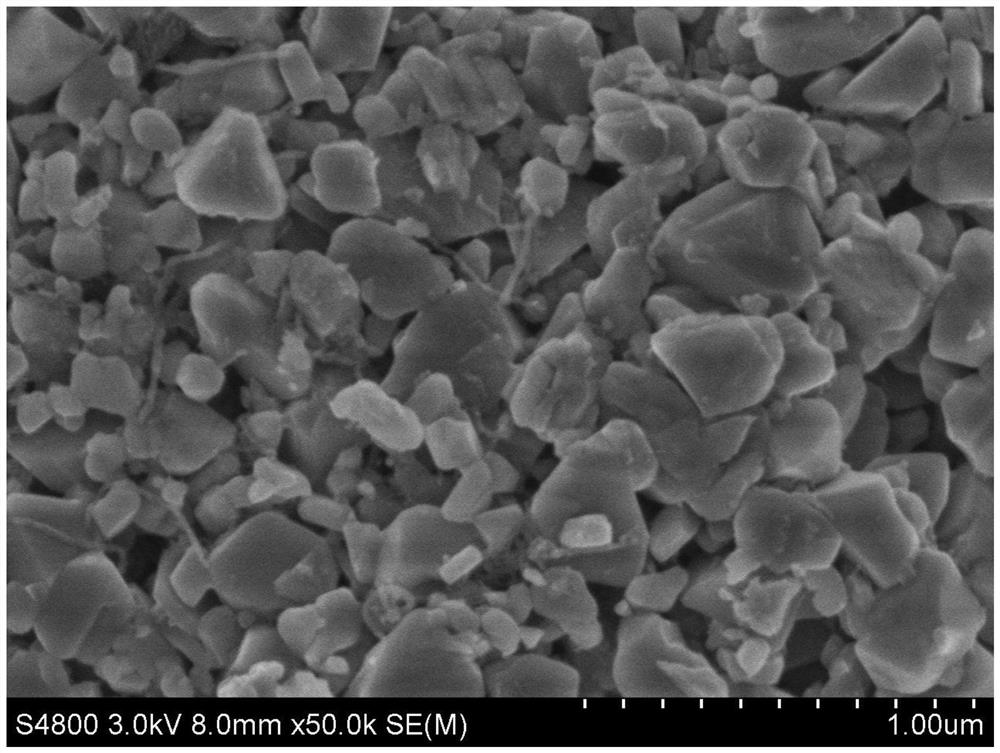
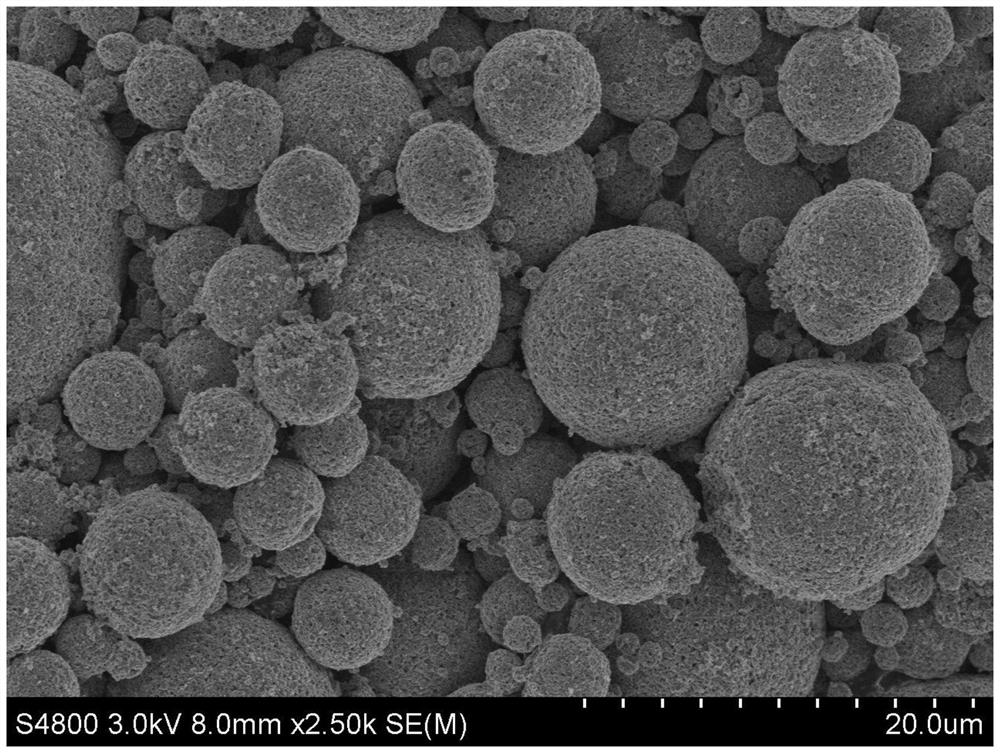
Sodium ferric phosphate-coated carbon nanotube positive electrode material with low iron-phosphorus ratio and preparation method of sodium ferric phosphate-coated carbon nanotube positive electrode material
A technology of carbon nanotubes and sodium iron phosphate, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, electrode manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and high equipment requirements, and achieve the effects of increasing cycle life, low preparation cost, and reducing diffusion distance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
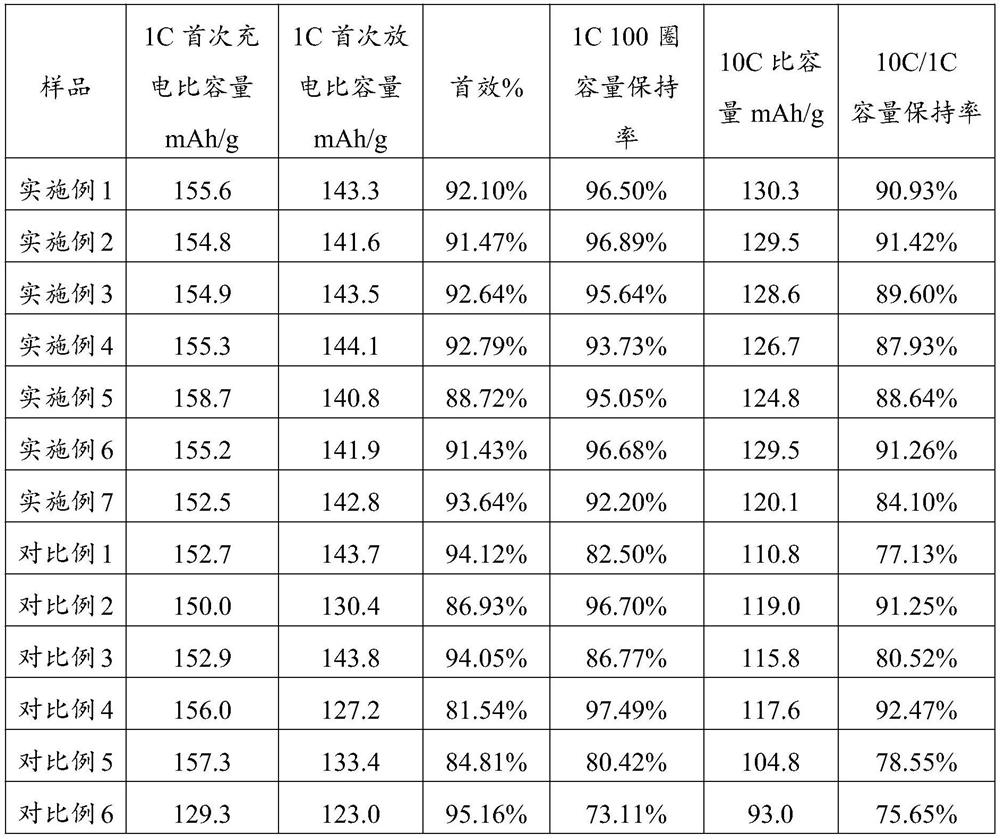
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0031] The invention provides a preparation method of a low iron-phosphorus ratio sodium iron phosphate@carbon nanotube positive electrode material, comprising the following steps:
[0032] The iron source, phosphorus source, sodium source, carbon nanotube, dispersant and water are mixed and ground to obtain a mixed slurry; the mixed slurry is spray-dried to obtain a precursor; the precursor is calcined in a protective atmosphere to obtain a low Iron phosphorus ratio sodium iron phosphate@carbon nanotube cathode material.
[0033] In the present invention, the molar ratio of Na, Fe, and P in the mixed slurry is preferably 0.95-1:0.94-1:1, more preferably 0.955-0.98:0.955-0.99:1, more preferably 0.96:0.98:1 .
[0034] In the present invention, the mass of carbon nanotubes is preferably 0.5-5%, more preferably 0.8-4.1%, and more preferably 3.2% of the mass of the low iron-phosphorus ratio sodium iron phosphate@carbon nanotube cathode material.
[0035] In the present invention...
Embodiment 1
[0050] This embodiment provides a low iron-phosphorus ratio sodium iron phosphate@carbon nanotube cathode material, wherein the molar ratio of Na, Fe, and P is 0.96:0.955:1;
[0051] The preparation method includes the following steps:
[0052] (1) Disperse 18.0g polyethylene glycol in 1800mL ultrapure water, shear and disperse for 5min, then add 13.0g of carbon nanotubes, continue shearing and dispersing for 2h to form a uniformly dispersed conductive paste; mix 452.6g Fe, P Ferric phosphate with a molar ratio of 0.955:1 and 156.6 g of sodium carbonate were added to the conductive slurry in turn, transferred to a sand mill, and ground for 6 hours at a linear speed of 20 m / s (the grinding medium was zirconia balls with a particle size of 0.6 mm). ) to obtain a mixed slurry with a median particle size of 200 nm;
[0053] (2) carrying out two-fluid spray drying of the mixed slurry, controlling the temperature of the spray inlet to 240°C and the temperature of the outlet to 100°...
Embodiment 2
[0056] This embodiment provides a low iron-to-phosphorus ratio sodium iron phosphate@carbon nanotube positive electrode material, wherein the molar ratio of Na, Fe, and P is 0.97:0.95:1;
[0057] See Example 1 for the preparation method, except that in step (1), 452.6 g of Fe, iron phosphate with a P molar ratio of 0.95:1, and 154.2 g of sodium carbonate were added to the conductive paste.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com