Tumor-related gene variation pathogenicity classification method and device and storage medium
A tumor-related gene and pathogenicity technology, applied in the field of tumor-related gene variation interpretation, can solve the problems of detail and parameter specification, cumbersome data processing process, error-prone, etc., to increase standardization and uniformity, and reduce artificial duplication Work and improve work efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
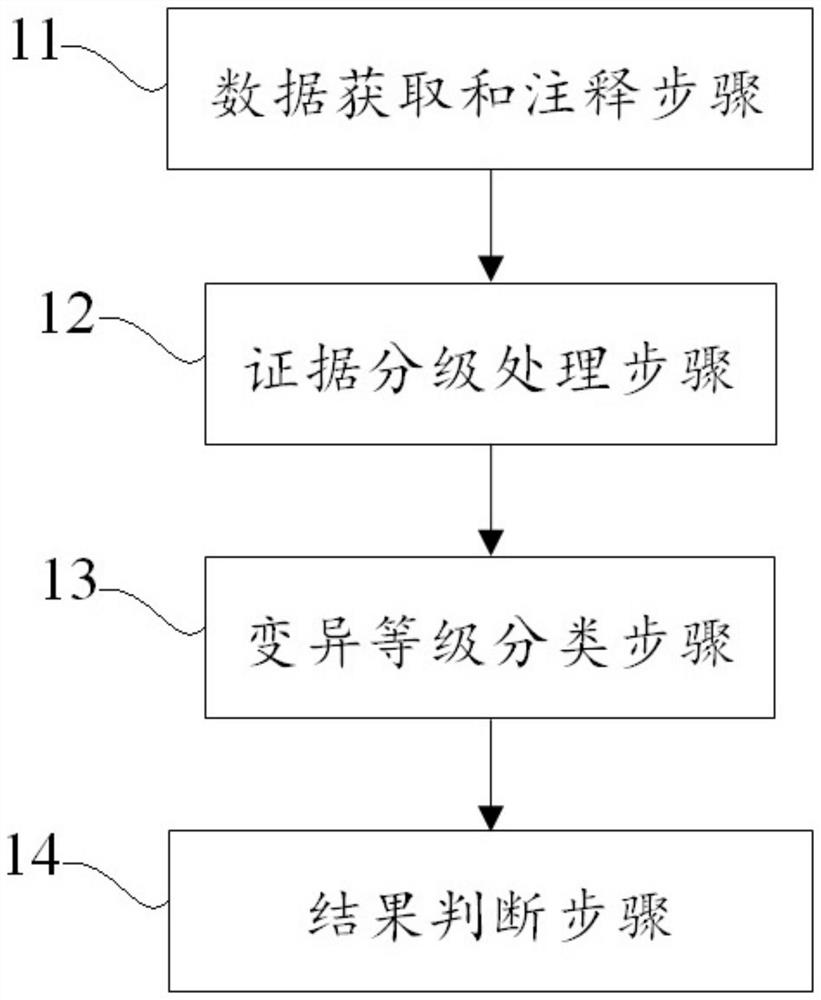
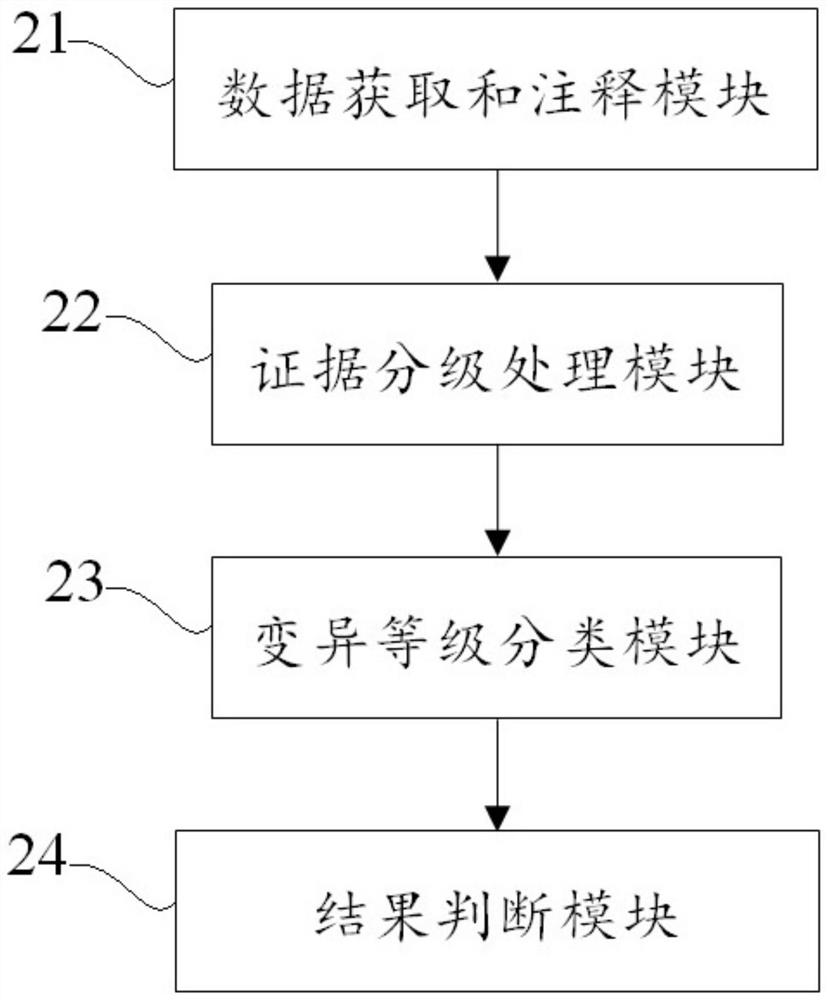
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] In this example, POLE: S2018G is used as an example to classify the pathogenicity of hereditary tumor-related gene variants, as follows:
[0082] (1) According to the specified search format, input gene: nucleotide / amino acid change, POLE: S2018G;
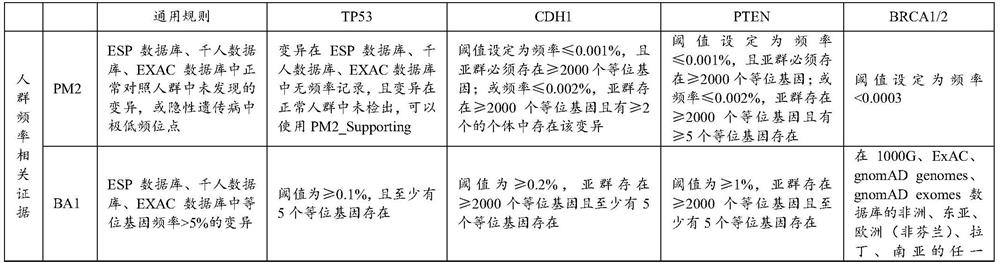
[0083] (2) Step (1) Variation description automatically output after retrieval: This variation causes the mutation of codon 2018 of the POLE gene from serine to glycine, which is a missense mutation. This variant is not documented or has a very low frequency in the population databases gnomAD / ExAC and 1000Genomes. Various statistical methods predict that the variant has no effect on the gene or gene product. According to the ACMG guidelines, this variant was judged to be of undetermined significance comprehensively.
[0084] (3) The interpretation result of automatic output is: meaning unknown (PM2+BP4).
[0085] (4) According to the improved method and device for classifying the pathogenicity of hereditary tumor-related ...
Embodiment 2
[0089] In this example, USH1C:c.238dup is used as an example to classify the pathogenicity of hereditary tumor-related gene variants, as follows:
[0090] (1) Input USH1C:c.238dup, and the automatic output variation is described as; this variation causes the USH1C gene codon 80 to be mutated from arginine to proline, and a termination signal is generated in advance at the 69th position of the new reading frame, is a frameshift mutation. This variation may cause loss of normal protein function through protein truncation or nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. This variant is not documented or has a very low frequency in the population databases gnomAD / ExAC and 1000Genomes. This variant is documented in the Clinvar database as pathogenic. According to ACMG guidelines, this variant is comprehensively judged to be pathogenic.
[0091] (2) The interpretation result of automatic output is: pathogenic (PVS1+PM2+PP5).
[0092] The entire retrieval process takes less than 5 seconds. Conf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com