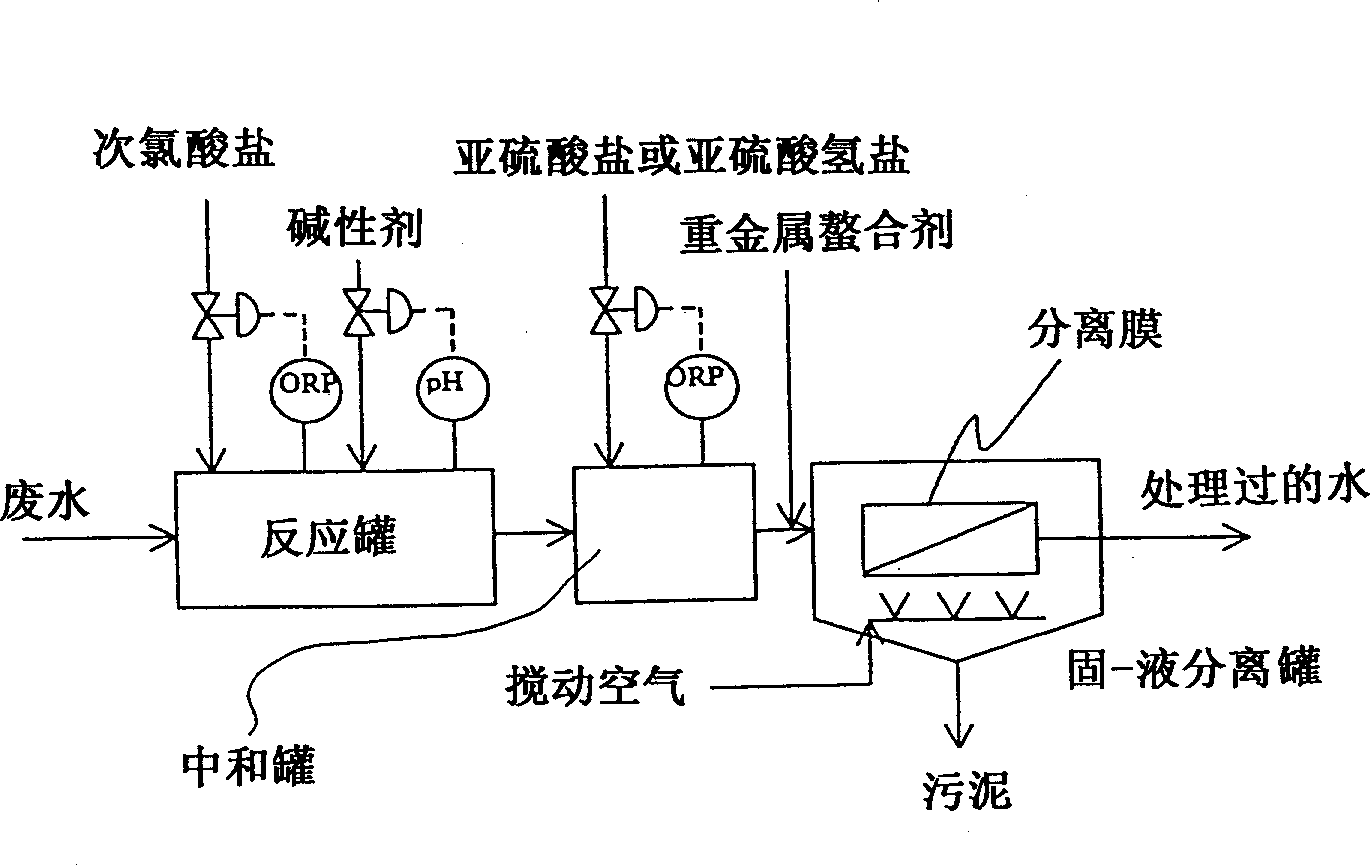
Method for flue gas desulfurization and flue gas desulfurization system
A flue gas and system technology, applied in the field of flue gas desulfurization, can solve the problems of increased operating costs, no coexisting components, complexity, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing the size of equipment, avoiding the size of equipment, and simplifying the treatment process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
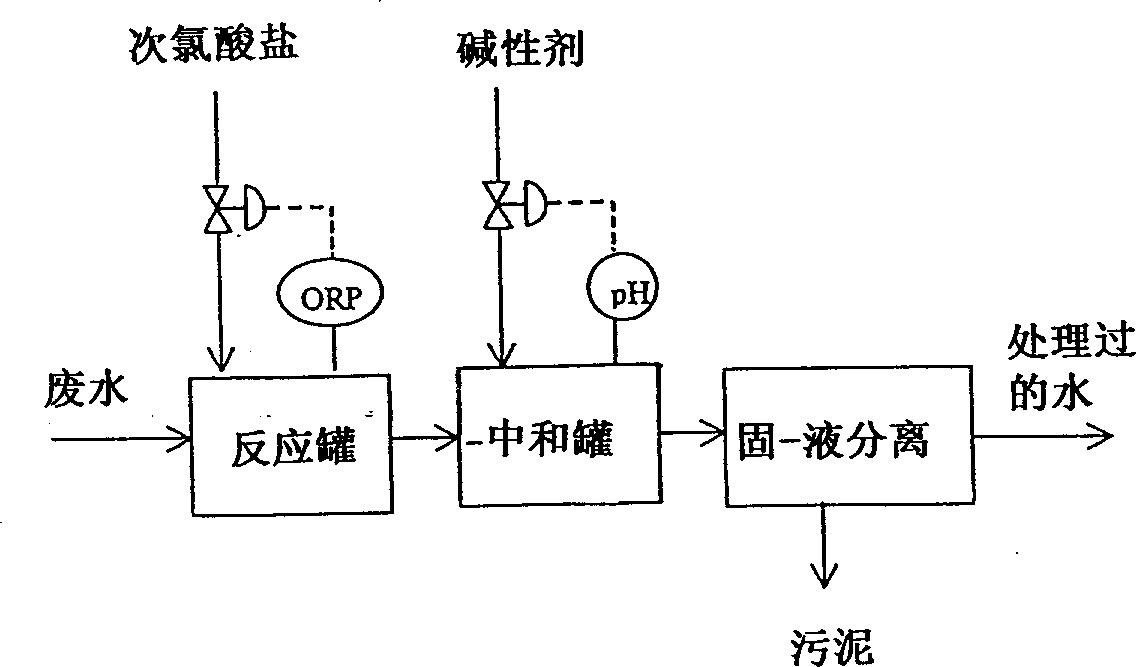
[0244] As the wastewater discharged from the desulfurizer of boiler combustion flue gas, under the treatment conditions given in Table 2, use figure 1 The scheme shown treats desulfurization wastewater having the water qualities given in Table 1 below. Table 2 gives the treated water quality and the amount of sludge generated in this treatment.
[0245] It can be seen from Table 2 that if the amount of chlorine added is 50 mg / L or greater, then manganese ions Mn in the treated water 2+ The amount is 10 mg / L or less.
[0246] pH value
[0247] Reactor Chlorine added (mg / L) 20 50 100 ORP(mV) 450 600 780 Neutralization tank pH(-) 8 8 8 ORP(mV) 430 580 750 Residual Chlorine (mg / L) >0.05 12 17 treated water mn 2+ (mg / L) 30 8 >1 Amount of sludge (mg / L): SS 10 45 60
Embodiment 2
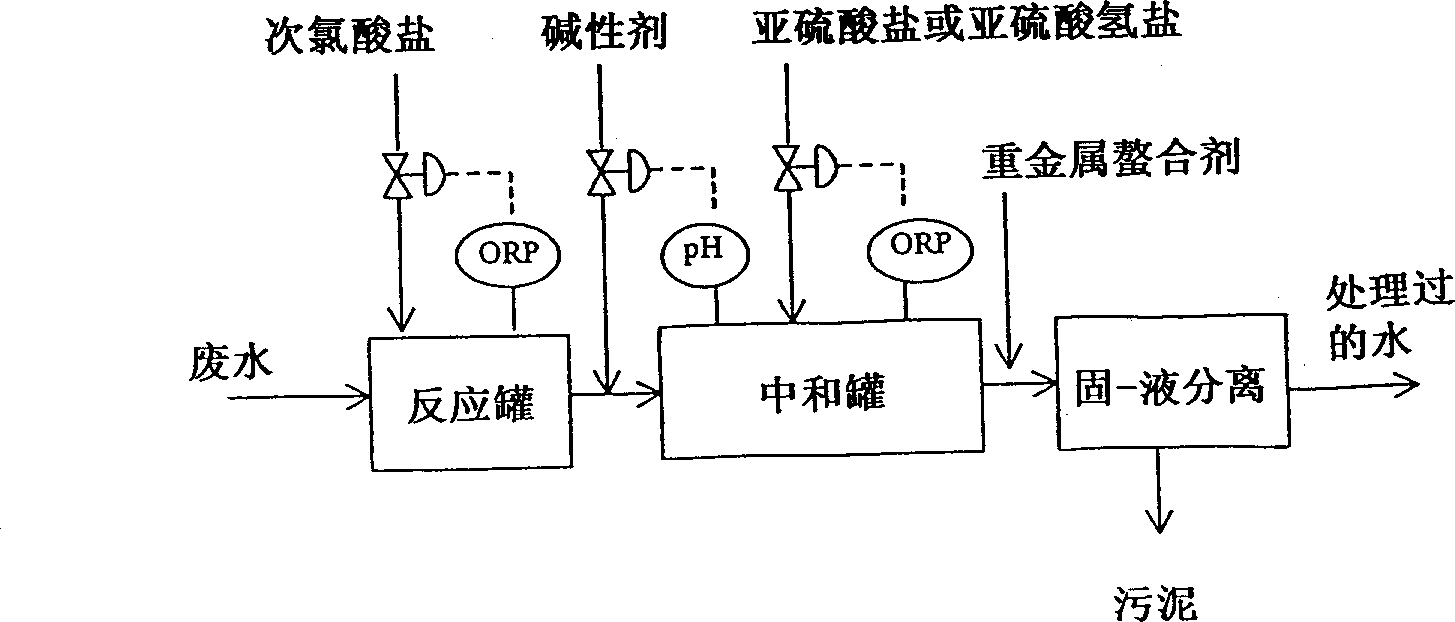
[0251] As in the case of Working Example 1, under the treatment conditions given in Table 3 with figure 2 The process shown treats desulfurization wastewater with the water quality given in Table 1. The treated water quality and the amount of sludge generated in this treatment are listed in Table 3.
[0252] As can be seen from Table 3, the amount of manganese ions in the treated water is 1 mg / L or less, but if there is residual chlorine in the neutralization tank, cadmium cannot be removed at all; Or sulfite ion excess treatment conditions, cadmium is removed.
[0253] Reactor Chlorine added (mg / L) 100 100 100 ORP(mV) 780 780 780 Neutralization tank PH(-) 8 8 8 Added bisulfite (mg / L) 0 50 100 ORP(mV) 750 350 200 Residual Chlorine (mg / L) 17 <0.05 <0.05 residual So 3 2- (mg / L) - <1 <1 Added heavy metal chelating agent (mg / L) 30 30 30 treated water mn 2+ (mg / L) <1 <1 <1 Cd 2+ (mg / L) 0...
Embodiment 3
[0255] As in the case of Working Example 1, under the treatment conditions given in Table 4, with figure 2 The flow shown treats desulfurization wastewater with the water qualities given in Table 1. The treated water quality and the amount of sludge generated in this treatment are listed in Table 4.
[0256] Reactor Chlorine added (mg / L) 100 100 100 ORP(mV) 750 750 750 PH(-) 9 9 9 Neutralization tank Added bisulfite (mg / L) 0 50 100 ORP(mV) 750 350 170 Residual Chlorine (mg / L) 17 <0.05 <0.05 residual So 3 2 (mg / L) - <1 7 Added heavy metal chelating agent (mg / L) 30 30 30 treated water mn 2+ (mg / L) <1 <1 1.6 Cd 2+ (mg / L) 0.5 <0.1 <0.1 Amount of sludge (mg / L) 70 70 70
[0257] As can be seen from Table 4, when residual chlorine was present in the neutralization tank (OPR 750 mV), the amount of manganese ions in the treated water was 1 mg / liter or less, but cadmium could not...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com