Negative electrode of rechargeable battery
A technology for rechargeable batteries and negative electrodes, applied to battery electrodes, non-aqueous electrolyte battery electrodes, negative electrodes, etc., which can solve the problems of reduced inhibition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0045] Several examples and comparative examples of the negative electrode of the present invention are now described. However, these examples do not limit the present invention. Example 1 Preparation of negative electrode
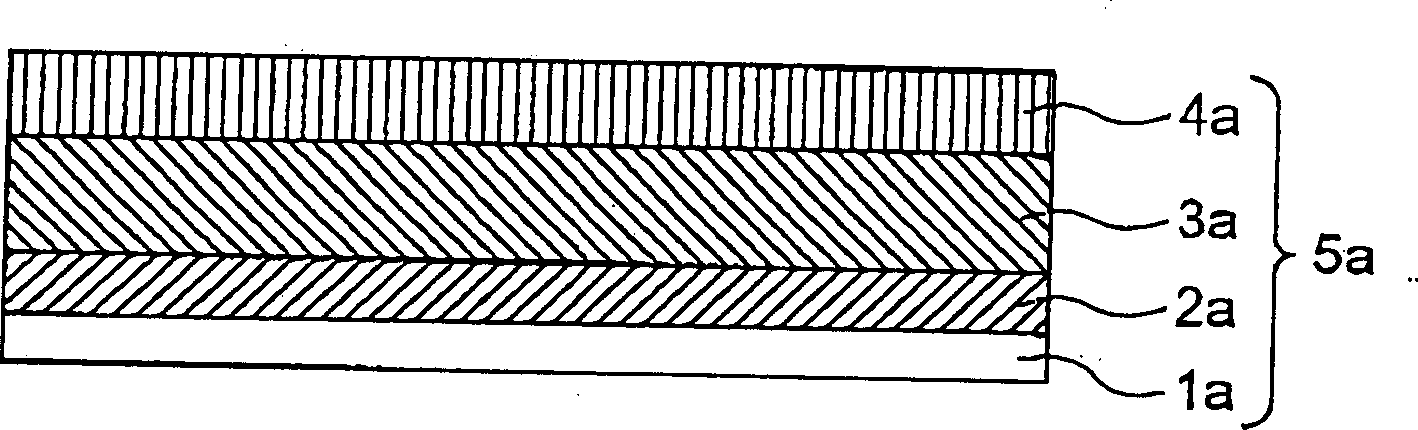
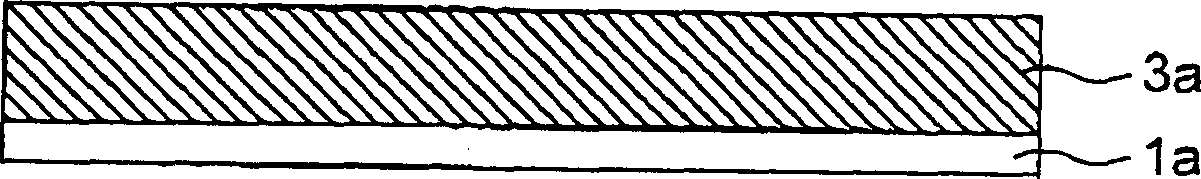
[0046] Such as figure 1 As shown, a 10 μm thick electrolytic copper foil is used as the current collector 1a. The slurry is applied to the copper foil 1a, and then dried and pressed to form the first layer 2a. The slurry is prepared by mixing graphite with polyvinylidene fluoride, and then dissolving the mixture in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone solvent. The second layer 3a and the third layer 4a are formed by vacuum evaporation deposition of lithium-silicon alloy and lithium fluoride (LiF), respectively. The equipment used for vacuum evaporation deposition of lithium-silicon alloy or LiF has a vacuum degree of 10 -6 to 10 -5 Pa, roll width 60mm, heated by electron beam or electric resistance. The capacity of the negative electrode thus formed is the sum ...
example 10
[0053] Manufacture negative electrode by the same condition as example 1, just with the LiN(C of 1M 2 f 2 SO 2 ) 2 Dissolve the electrolyte that ethylene carbonate and diethyl carbonate make to replace the electrolyte of example 1, and the material of the second layer 3a and the 3rd layer 4a is polycrystalline Li-Si alloy and LiF respectively, and these materials are obtained by adding N- (C 2 f 5 SO 2 ) 2 Introduced by reaction with lithium. The negative electrode and battery of Example 10 were evaluated as in Example 1, and the results are listed in Table 1.
[0054] As in Examples 2-9, compared with Comparative Examples 1-5, the initial charge and discharge efficiency and capacity retention rate or cycle characteristics of the battery of Example 10 were improved.
[0055] However, the initial charge and discharge efficiency and capacity retention ratio of Example 10 were lower than those of Example 1 using the amorphous Li-Si alloy. The charge and discharge reactio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| retention rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com