Sound-proof floor and its manufacturing method
A floor, elastic foaming technology, used in sound insulation, floor covering, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low productivity, low production rate, high manufacturing cost, etc., achieve simple installation, absorb and block noise, excellent footing sense of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
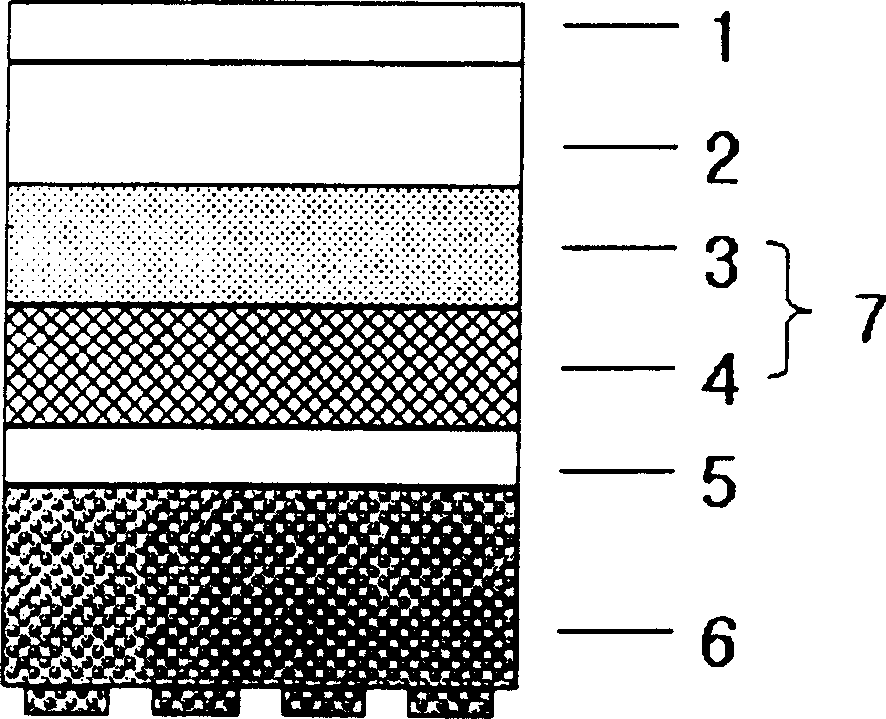
[0045] All layers except the dimension-enhancing layer 4 are formed by calendering.
[0046] (Forming the middle resin layer)
[0047] Use 100 parts by weight of polyvinyl chloride with a degree of polymerization of 1,000, 50 parts by weight of dioctyl phthalate, 2 parts by weight of epoxidized soybean oil, 1.8 parts by weight of barium zinc stabilizer and 60 parts by weight of calcium carbonate as the intermediate resin Layer 5 ingredients.
[0048] The above mixture was mixed in a Banbury-Limi heavy-duty twin-screw mixer at 150°C, followed by a first mixing and a second mixing in a two-roll mill at 150°C. Subsequently, the resulting mixture was formed into a sheet having a thickness of 0.3 mm using a calender.
[0049] (forming the printing layer)
[0050] Using 100 parts by weight of polyvinyl chloride with a degree of polymerization of 1,000, 50 parts by weight of dioctyl phthalate, 2 parts by weight of epoxidized soybean oil, 10 parts by weight of titanium dioxide, 2 p...
Embodiment 2
[0065] All layers except the elastic foam layer 6 were formed in the same manner as in Example 1. The elastic foam layer 6 is formed according to the method described below.
[0066] (form elastic foam layer)
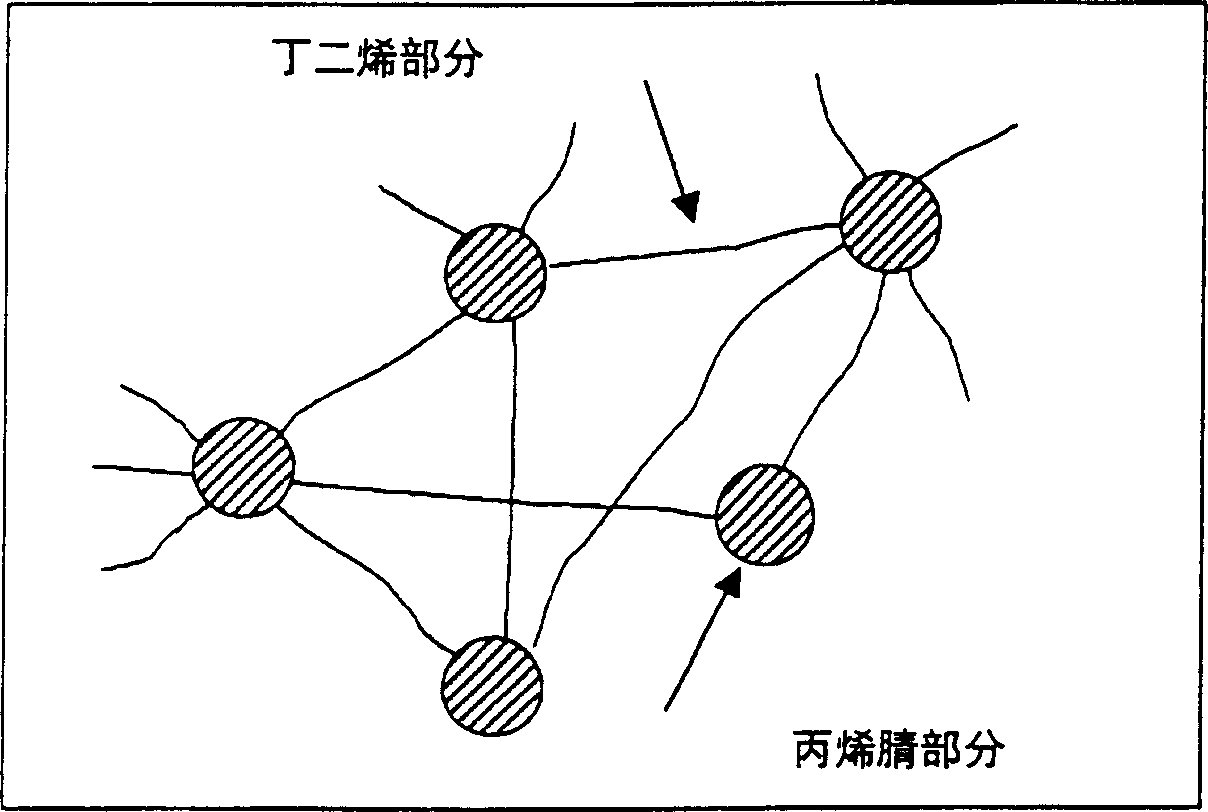
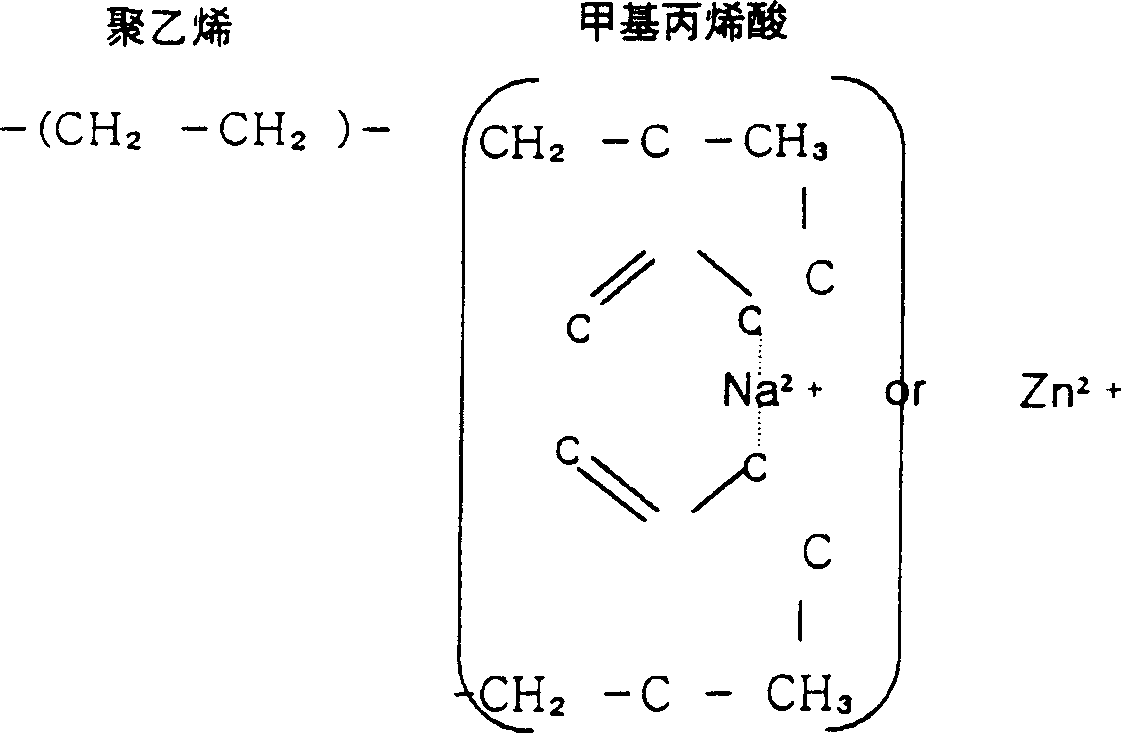
[0067] The elastic foamed layer 6 is formed in the same manner as the intermediate resin layer 5 except for the components and contents of the raw materials. The raw materials used to form the elastic foam layer 6 are 100 parts by weight of polyvinyl chloride with a polymerization degree of 1,000-1,700, 30 parts by weight of pre-crosslinked acrylonitrile-butadiene-polyvinyl chloride copolymer resin, 10 parts by weight of ion Cross-linked polymer (Surlyn, Dupont) as modified olefin resin, 15 parts by weight of thermoplastic polyurethane resin, 60 parts by weight of dioctyl phthalate as plasticizer, 3 parts by weight of barium as foam stabilizer Zinc stabilizer, 6 parts by weight of azobisdicarbonamide as blowing agent, 10 parts by weight of calcium carbonate and 1 part...
Embodiment 3
[0069] All layers except the elastic foam layer 6 were formed in the same manner as in Example 1. The elastic foam layer 6 is formed according to the method described below.
[0070] (form elastic foam layer)
[0071] The raw materials used to form the elastic foam layer 6 are 100 parts by weight of polyvinyl chloride with a polymerization degree of 1,000-1,700, 30 parts by weight of pre-crosslinked acrylonitrile-butadiene-polyvinyl chloride copolymer resin, 60 parts by weight as Dioctyl phthalate of plasticizer, 3 parts by weight of barium zinc stabilizer as foaming stabilizer, 6 parts by weight of azodicarbonamide as foaming agent, 10 parts by weight of calcium carbonate and 1 part by weight Parts of paint. The above mixture was mixed in a Banbury-Limi heavy-duty twin-screw mixer at 120°C, followed by a first mixing and a second mixing in a two-roll mill at 150°C. Subsequently, the resulting mixture was formed into a sheet having a thickness of 1 mm using a calender.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com