Methods and compositions for accelerating alcohol metabolism
A technology of ethanol metabolism and composition, which is applied in the field of composition to accelerate ethanol metabolism, and can solve problems such as limited effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Example 1 description.
[0068] B. Coupling regeneration of NAD
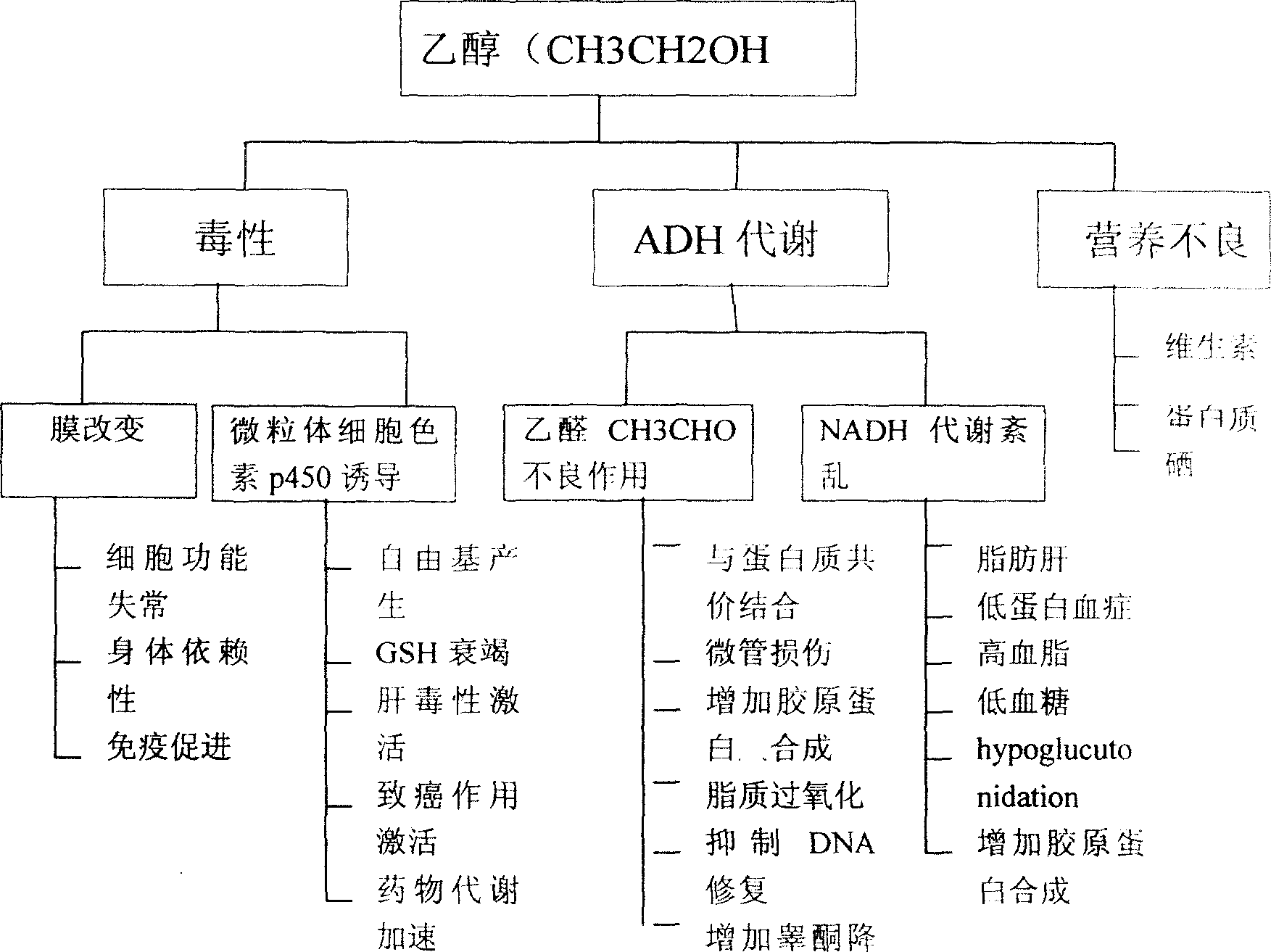
[0069] As shown in Formula 1 and Formula 2 above, the mechanism of ethanol metabolism catalyzed by ADH and ALDH enzymes requires the coenzyme NAD. Oxidation of each mole of ethanol consumes 2 moles of NAD. Since NAD is consumed, the redox ratio, that is, NAD + / NADH ratio, is reduced so that the oxidation of ethanol is limited by the limited supply of NAD. NAD thus becomes the limiting factor for ethanol metabolism.
[0070] Therefore, to maintain an efficient rate of ethanol oxidation catalyzed by ADH, regeneration of NAD from NADH is required + , and this NADH is produced by the reaction of ADH as shown in formula 1 and formula 2, so that the redox ratio, NAD + / NADH, remained relatively unchanged.
[0071] In humans and other mammals, the redox ratio NAD + / NADH is regulated by a number of enzymes, including lactate dehydrogenase (lactate dehydrogenase), β-hydroxybutyrate dehy...
Embodiment
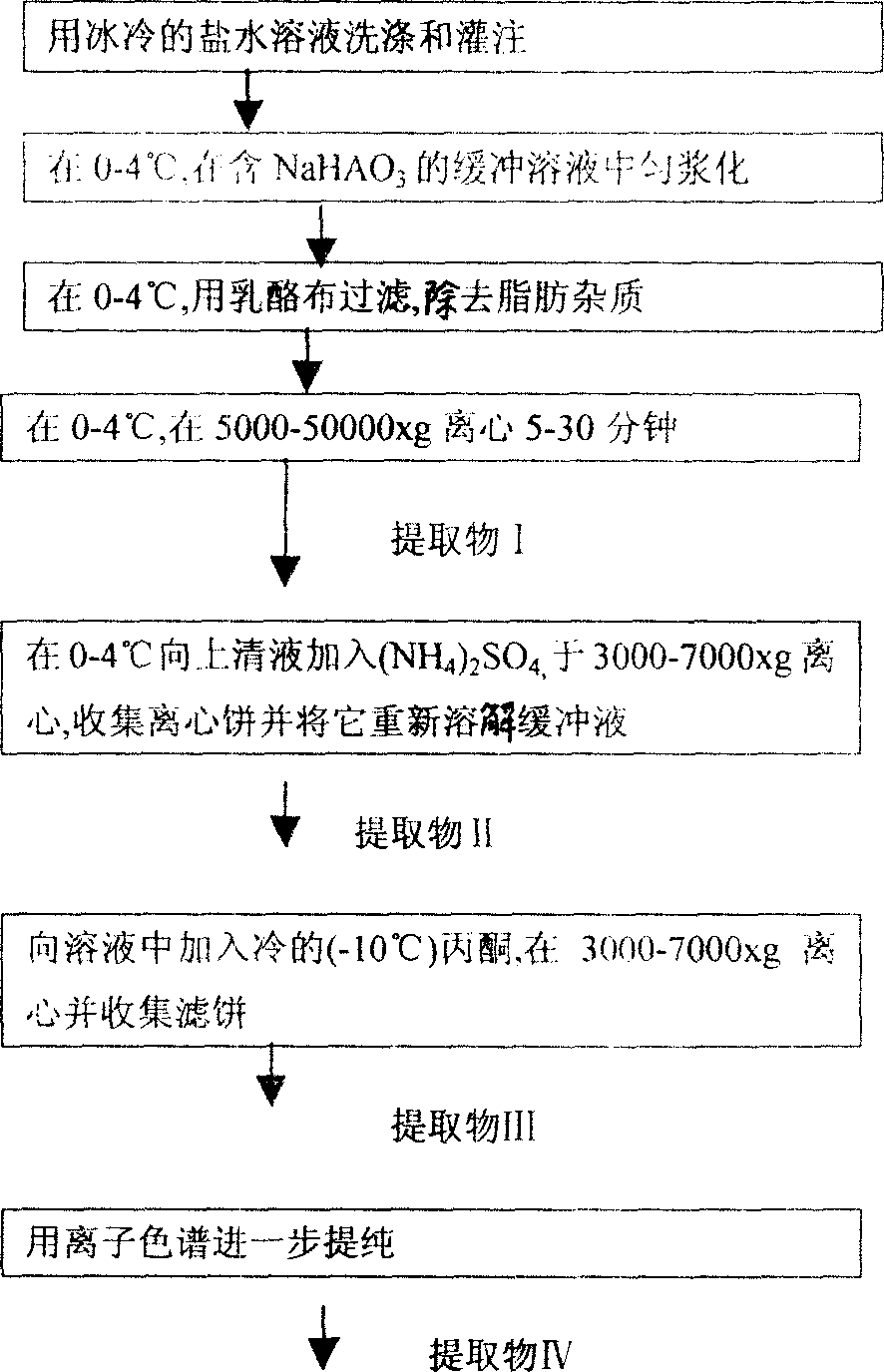
[0093] Embodiment 1. Preparation of animal gland extract
[0094] Fresh animal gland parts are washed and perfused with a liquid such as ice-cold saline, then homogenized in a kitchen homogenizer with, for example, 4 volumes of ice-cold buffer solution (0.1M potassium phosphate, pH=7.8) and 1 mM sodium bisulfite . All the following manipulations were performed at 0-4°C using the same buffer containing 0.1M sodium bisulfite. The homogenate was then centrifuged at about 20,000 g for about 30 minutes. The supernatant (extract I) was fractionated by addition of ammonium sulfate (30-50% saturation), resulting in a precipitate. The precipitate (extract II) was isolated by centrifugation at 5000g for 10 minutes. The pellet was redissolved in a small volume of buffer. Cold acetone (-10°C) was added to the solution, resulting in a precipitate (Extract III). The solid is further purified by ion exchange chromatography, gel filtration, and / or affinity chromatography (Extract IV), if...
Embodiment 2
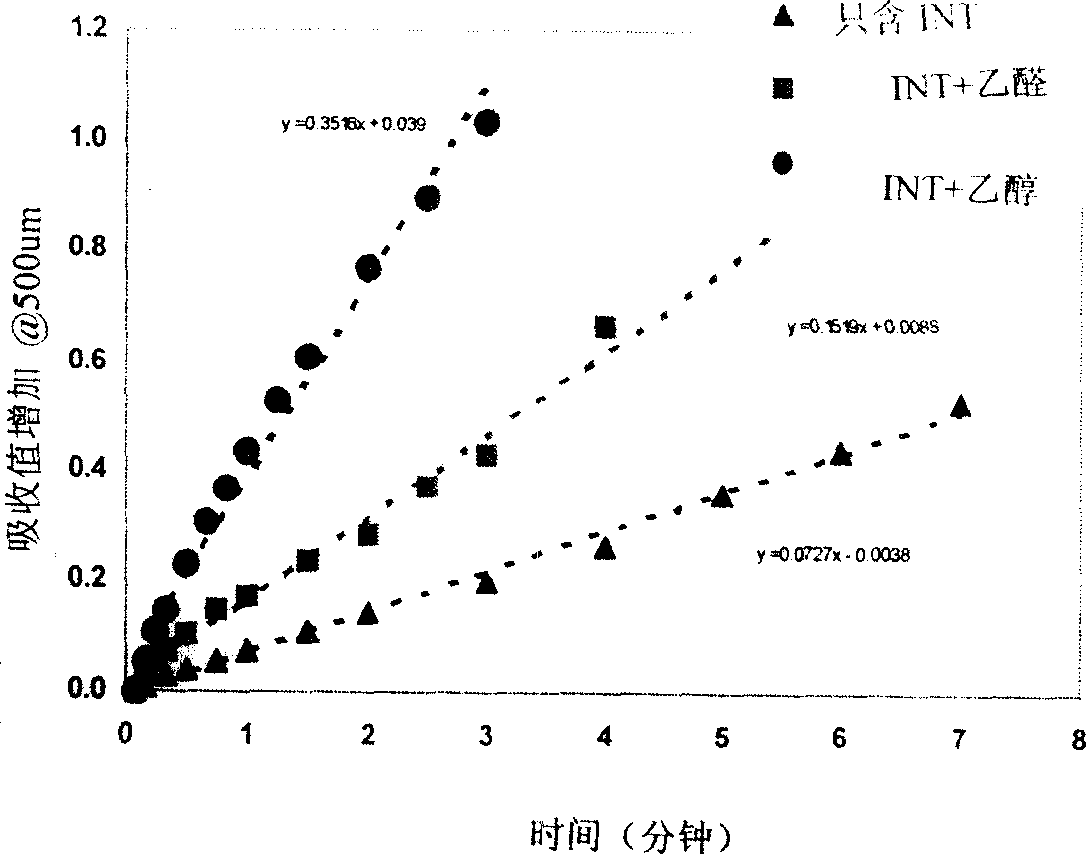
[0097] Example 2. Enzyme activity of pig liver extract
[0098] The animal gland extract prepared in Example 1 was tested for various enzyme activities: alcohol dehydrogenase, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, lactate dehydrogenase, sorbitol dehydrogenase and diaphorase, as follows.
[0099] a. Alcohol dehydrogenase
[0100] The activity of alcohol dehydrogenase (catalyses the conversion of ethanol to acetaldehyde, Formula 1) was determined spectrophotometrically. As shown in Formula 1, the reaction at pH=9 (such as Tris or phosphate buffer) is favorable for the formation of acetaldehyde, and the formed acetaldehyde is coupled with a capture agent. NADH has a maximum absorption at 340nm. A unit of enzyme activity is defined as an increase in absorbance per minute at 35°C (1 unit). In each test, 3.0 mL " ADH Cocktail Solution". Changes in absorbance at 340 nm were followed after addition of 10 or 20 μL of animal gland extract. Reported activity is the average of at least 6 dete...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com