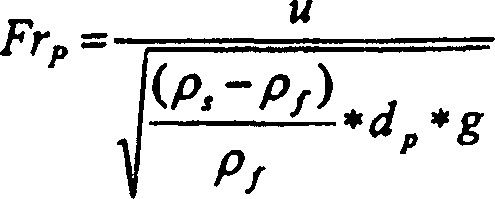Method and plant for removing gaseous pollutants from exhaust gases
A pollutant and waste gas technology, applied in the field of removal of gaseous pollutants, can solve the problems of control operation, low utilization rate of reaction reagents, residence time limitation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
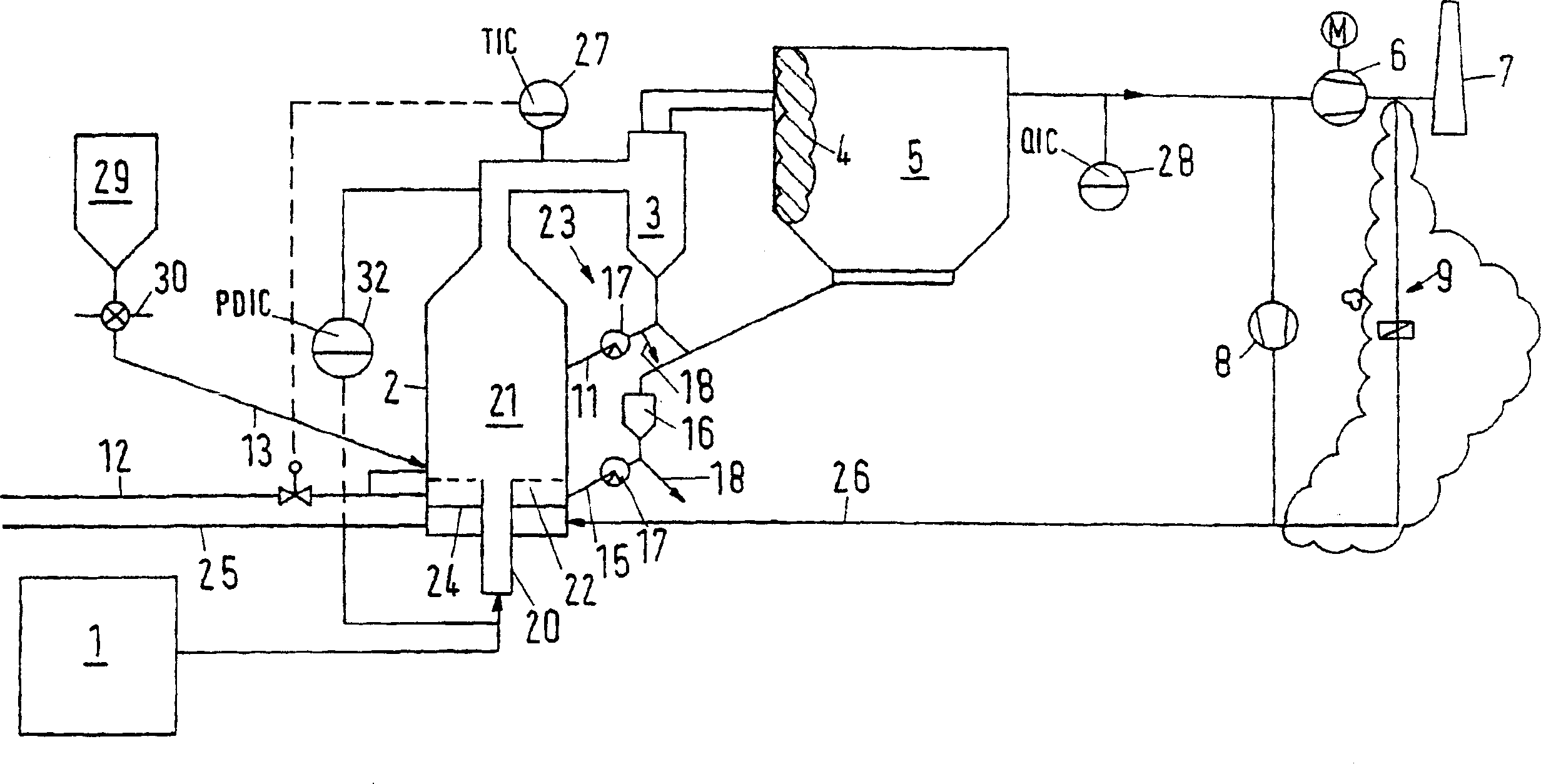
[0055] When the electrolytic aluminum is melted, a large amount of gaseous hydrogen fluoride (HF) is released. This pollutant enters the furnace exhaust, from which it must be removed before it is released into the atmosphere.
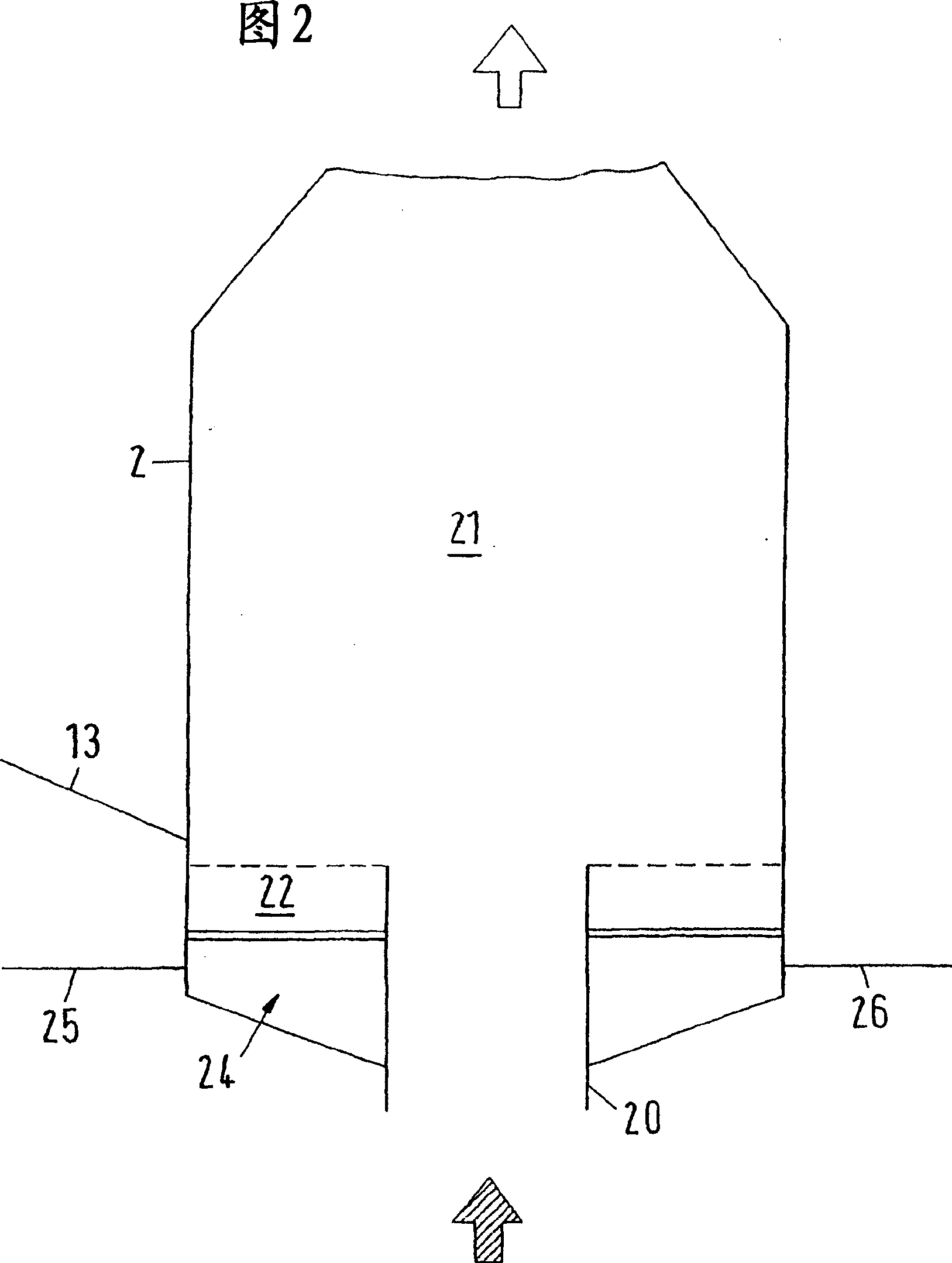
[0056] The combined off-gas stream from the electrolytic cell 1 enters a central pipe 20 surrounded by an annular fluidized bed 22 at a temperature of 50-150°C. The annular chamber of the reactor 2 with the annular fluidized bed 22 is fed with recirculated clean gas or particle-free off-gas from the parallel pipe flow, if available. The best reaction effect can be obtained by adjusting the optimum temperature in the annular fluidized bed 22 by spraying water 12 or evaporating water. The water spray 12 takes place directly in the annular fluidized bed 22 .
[0057] Particle Froude number Fr in central tube 20 p About 36, the particle Froude number Fr in the annular fluidized bed 22 p About 0.36, the particle Froude number Fr in the mixing chamber 21...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2 (removal of acid gas from the flue gas flow of combustion plant)
[0064] During the combustion process, the sulfur, fluorine and chlorine compounds in the fuel are basically converted into sulfur dioxide (SO) through various equilibrium reactions 2 , hydrogen fluoride HF and hydrogen chloride HCl. This occurs, for example, in power plants and incineration plants for waste or special waste. These gaseous compounds exit the combustion zone 1 with the exhaust gas, from which they must be removed before being released into the atmosphere.
[0065] For the removal of acidic components from exhaust gases (flue gases), various wet, dry and semi-dry methods have been developed. What all methods have in common is the simultaneous removal of acidic components with alkaline reagents.
[0066] The exhaust gas flow discharged from the combustion device 1 is supplied to the center pipe 20 (central tuyeres). The temperature at the inlet of the central tube 20 is abou...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3 (removal of sulfur dioxide, hydrogen fluoride and hydrogen chloride from the exhaust gas stream of the heat generating process)
[0074] In some production processes, such as glass production, cement production, sintering devices and metallurgical processes, clean harmful gases are released during the production process. For cleaning the gas, a method substantially similar to that described above for the combustion device is used. But in many industrial fields, lower efficiencies or higher emissions are allowed.
[0075] In this example, the exhaust gas stream discharged during the production process is supplied to the central pipe 20 of the reactor 2 . The temperature at the inlet of the central tube is about 200-600°C. The annular fluidized bed 22 is supplied with recirculated clean gas or particle-free off-gas from parallel ducted gas streams, if available.
[0076] Particle Froude number Fr in central tube 20 p About 77, the particle Froude number Fr i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com