Method of removing ammonia nitrogen in water by using electrodialysis
A technology of electrodialysis and water removal, applied in the separation method and dispersed particle separation, etc., can solve the problems of poor biochemical ammonia removal effect, many disinfection by-products, easy air pollution, etc., achieve stable operation, few influencing factors, and reduce pollution Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
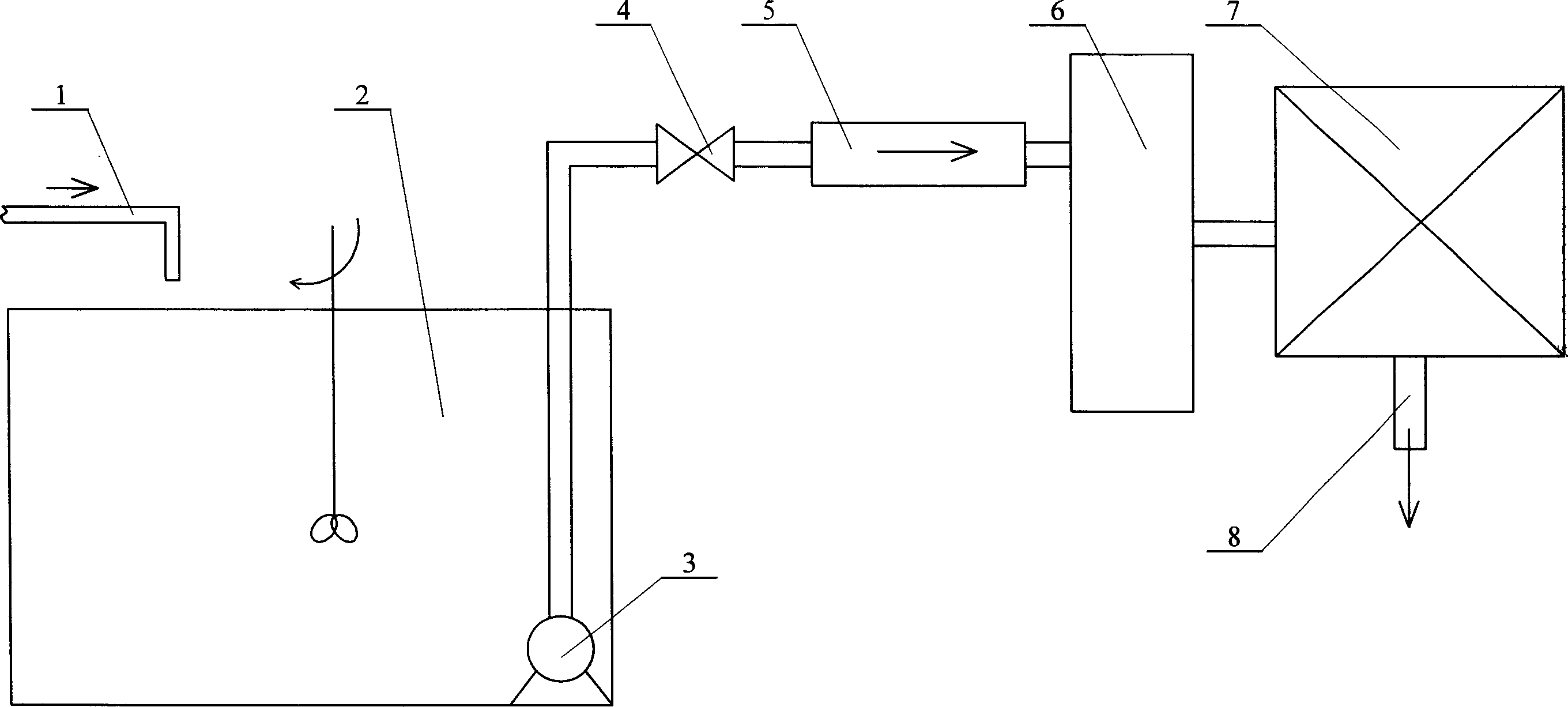
[0012] Specific embodiment one: the present embodiment adopts electrodialysis to remove the method for ammonia nitrogen in water and comprises the following steps:
[0013] Step 1. Coagulate, settle or filter the feed water or waste water output by the rotameter 5; the function of this treatment is to remove suspended components in the water, and aluminum sulfate, polyaluminum, polyaluminium-iron or polysilicon-alumina can be added (5~40mg / L) coagulant, and 1.5~5.0mg / L coagulant can also be added at the same time. The coagulant uses activated silicic acid or polyacrylamide to strengthen the removal of suspended solids in the water; sedimentation uses a sedimentation tank; Filtration measures adopt ultrafiltration membrane, the pore size of ultrafiltration membrane is 0.45μm, and quartz sand, ceramsite, anthracite, garnet, iron ore or activated carbon can also be used for filtration;
[0014] Step 2. Oxidize the water in step 1; oxidize the organic nitrogen and coexisting organ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
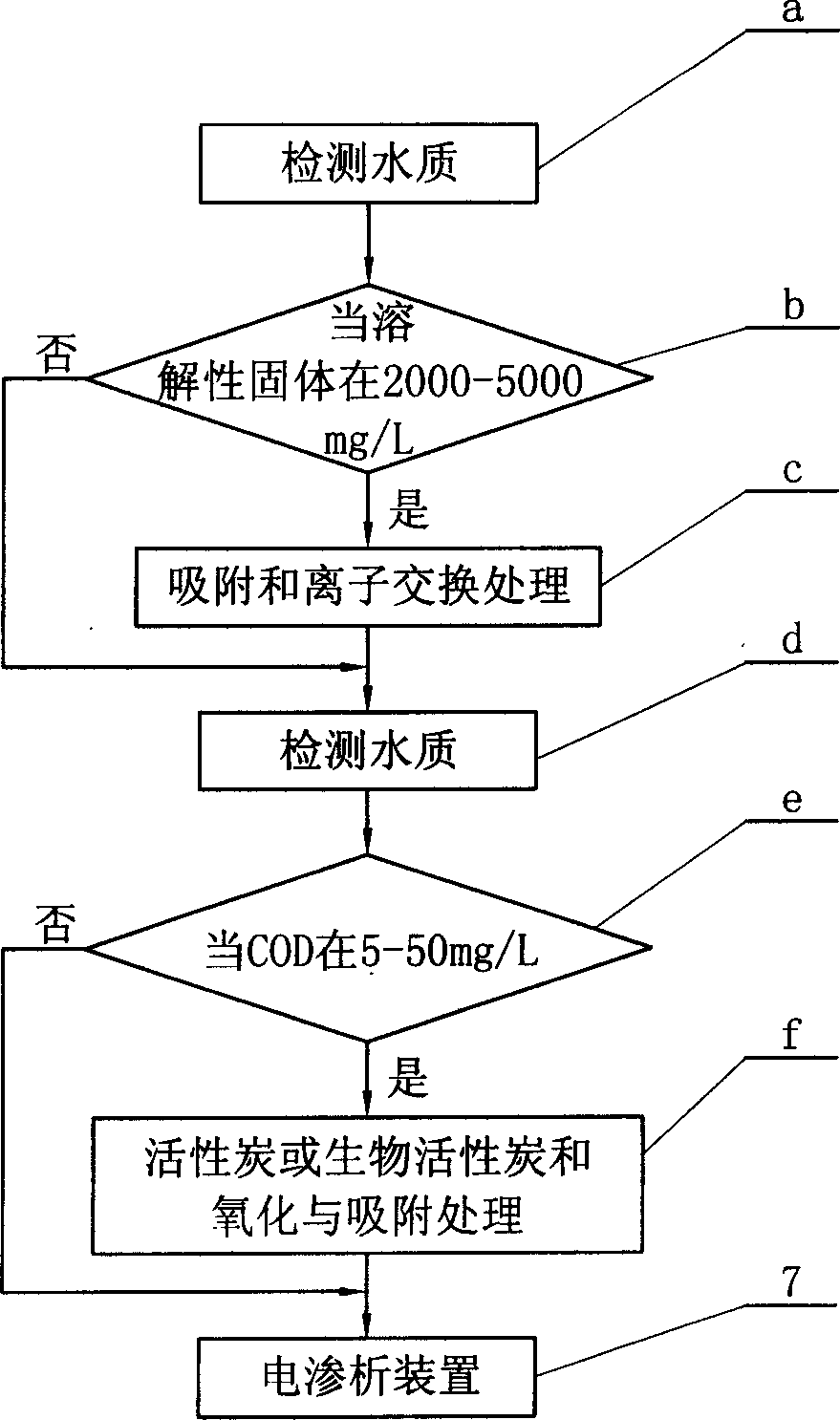
[0017] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 2 The difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment 1 is that the method also includes: detecting the water quality of the water after the treatment in the first step and the second step of the specific embodiment, and then entering the b step for judgment, and when the judgment result, the dissolved matter in the water When it is in the range of 2000-5000mg / L, carry out the c-step adsorption and ion exchange treatment, the adsorbent treatment uses activated carbon, the ion-exchanger treatment uses zeolite or anion exchange resin, and the treated water goes to the d-step to test the water quality; when the b-step If the judgment result is no, go directly to step d to test the water quality, and then go to step e to make a judgment. When the COD in the water is within the range of 5-50 mg / L, go to step f to carry out activated carbon or biological activated carbon and oxidation and adsorption treatment...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0018] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiments 1 and 2 is that the NH in the feed water needs to be treated 3 -N concentration is 9.86mg / L, pH is 7.86, calcium ion is 34.43mg / L, magnesium ion is 7.61mg / L, conductivity is 430mS / m, water temperature is 17.8℃, water flow is controlled at 58.85mL / s, water The flow rate is 10cm / s, the current in the electrodialysis device 7 is 0.40A, and the applied voltage is 220V. After being treated by the electrodialysis device 7 , the ammonia nitrogen content in the water outlet pipe 8 was detected to be 0.86 mg / L, and the ammonia nitrogen removal rate was 91.28%. Other steps are the same as in the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com