Optical selective screening process for amidase
A selective amidase, optically selective technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as no amidase screening model, and meet the requirements of high speed, strong versatility and equipment. low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
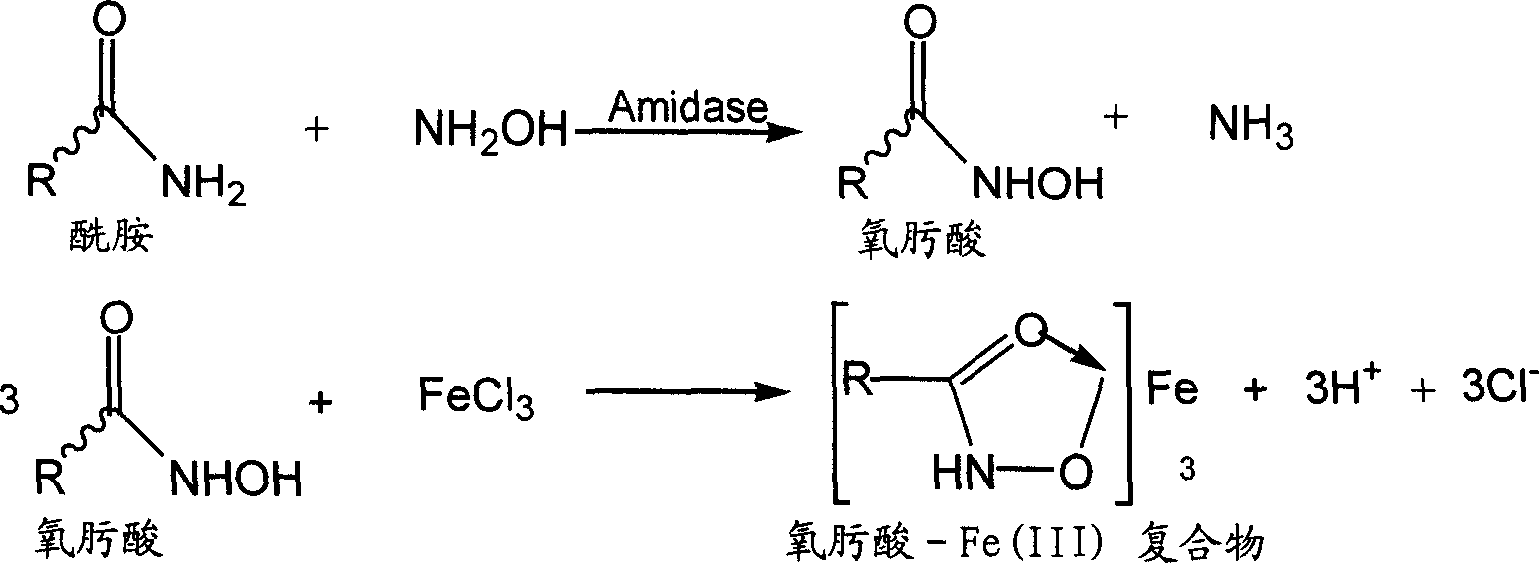
[0036] Example 1: Screening of microorganisms containing acetamide hydrolysis amidase activity After culturing each microorganism in the microbial library to be screened, centrifuge, wash with physiological saline, and evenly disperse in a phosphate buffer solution with pH=7.0 to prepare OD 600 =10.0 bacterial suspension. The enzyme-catalyzed reaction was carried out in a stoppered Erlenmeyer flask (50ml), and the reaction temperature was 30°C.
[0037] The composition of the reaction solution: (1) freshly prepared hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution, adjusted to pH 7 (5ml, 1M) with 10N NaOH before use; (2) disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer solution (5ml, 100mM); (3 ) cells dispersed in buffer solution (5ml, OD 600=10.0); (4) Acetamide solution (5ml, 100mM). Sample 2ml every 5 minutes, add 4ml FeCl 3 HCl solution (355mM FeCl 3 Soluble in 0.65M HCl). The cells were removed by centrifugation, and the absorbance value of the filtrate was measure...
Embodiment 2
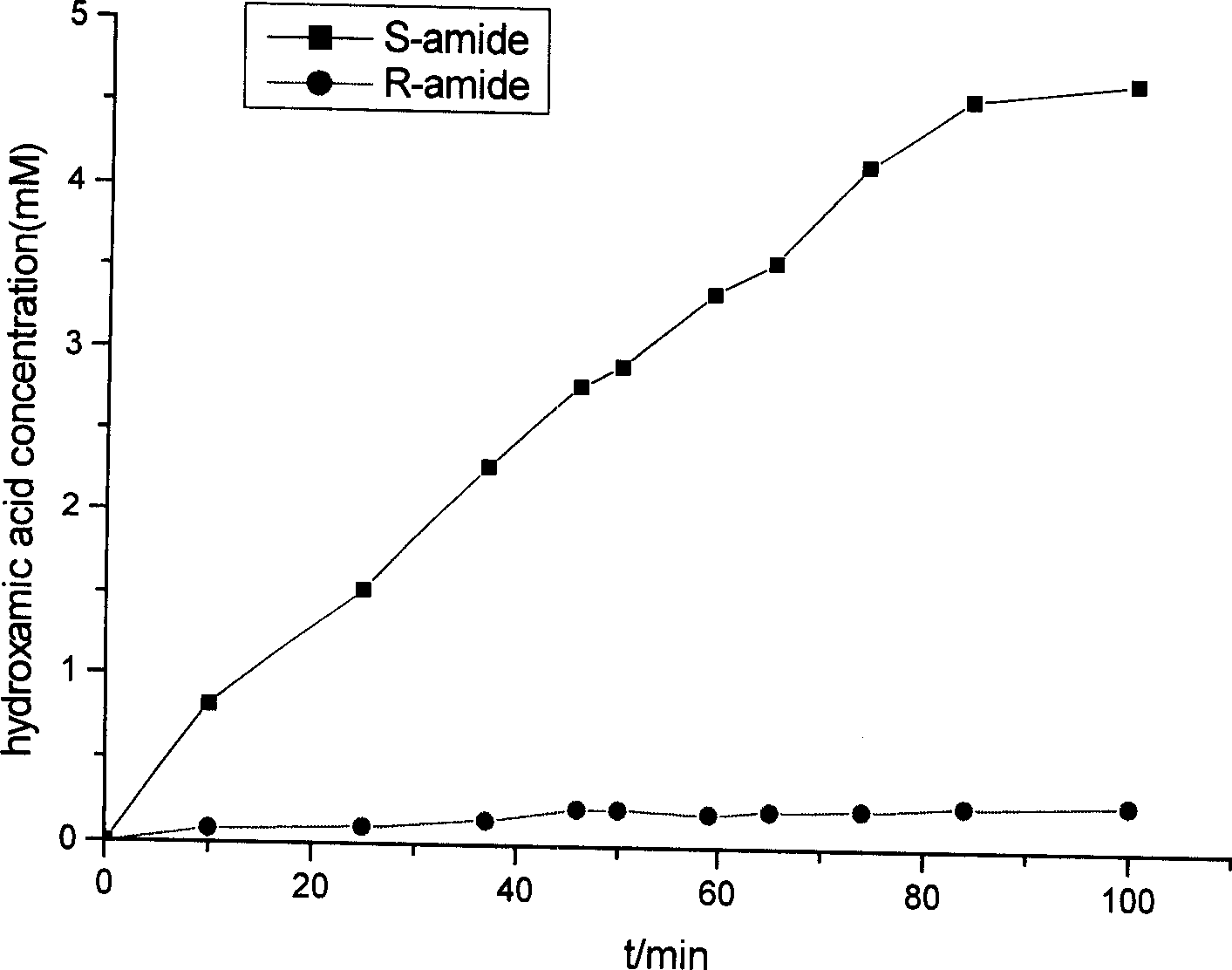
[0040] The strain Rhodococcus erythropolis A21 preserved in the laboratory is a known S-selective amidase strain consistent with the report in the literature (Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. (1997) 47:668-674). After the strain is cultivated, a bacterial suspension is made. The composition and detection method of the reaction solution are the same as in Example 1. The substrates were R-2-phenylpropanamide and S-2-phenylpropanamide (10 mM). These two catalytic reactions proceed simultaneously. React for 1h, take a sample, add FeCl 3 After the color development of the HCl solution, it was found that the conversion solution using R-2-phenylpropanamide as the substrate was light yellow, while the conversion solution using S-2-phenylpropanamide as the substrate was reddish brown, indicating that the amide The chiral selectivity of the enzyme is S type.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3: Contain the screening of R-amidase activity microorganism
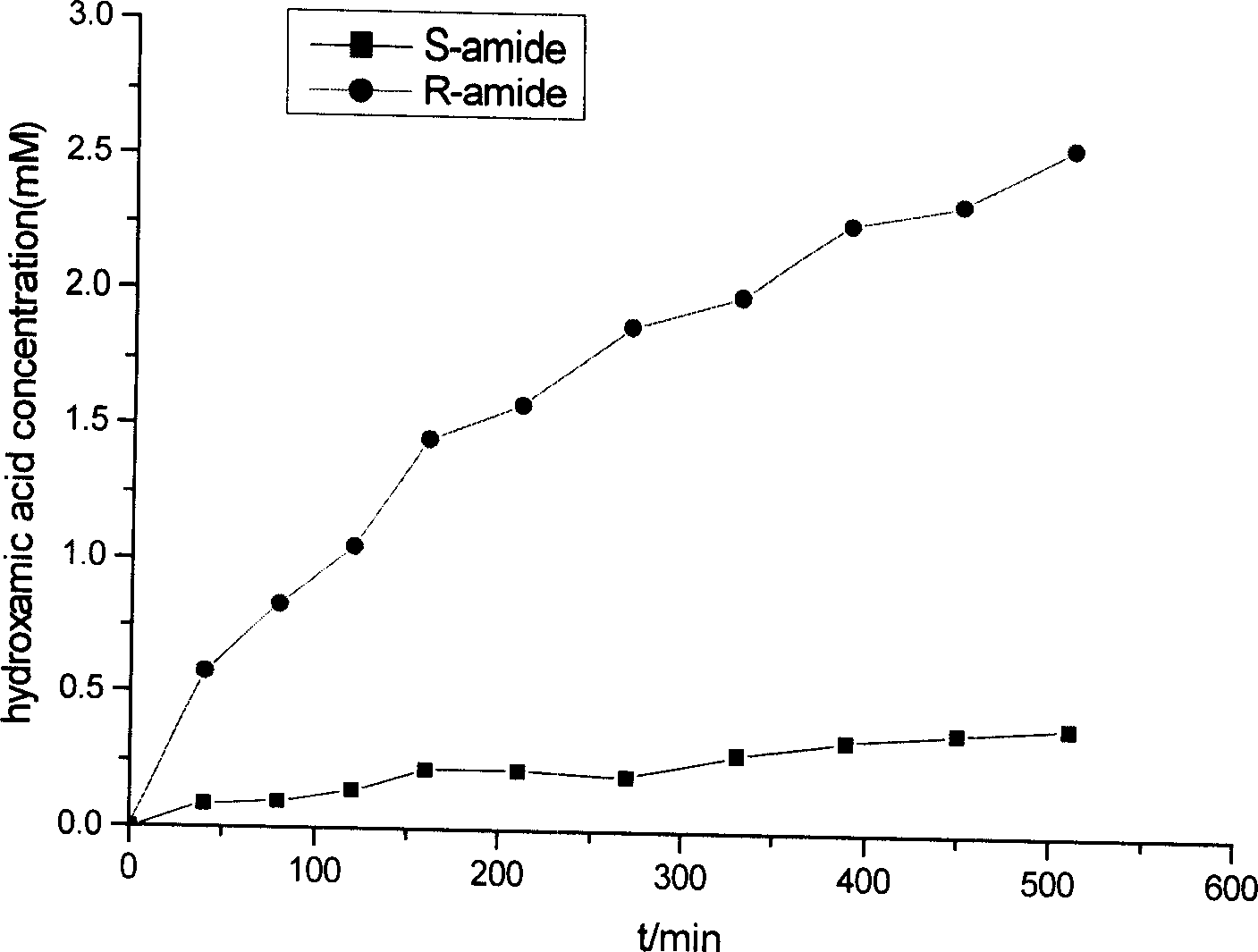
[0042] The composition and detection method of the reaction solution are the same as in Example 1. Just replace the substrate with an amide with the α carbon atom as the chiral center, such as R-(-)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropylcarboxamide and S-(+)-2,2-dimethyl Cyclopropylcarboxamide (20 mM). These two catalytic reactions are carried out at the same time, and samples are taken every 10 minutes to detect the content of hydroxamic acid generated, and the initial reaction rate r can be calculated respectively 1 , r 2 , r 1 / r 2 The magnitude of the value reflects the stringency of amidase selectivity. Delftia sp. uses the above two enantiomers as substrates respectively, and the generation curve of hydroxamic acid in the reaction solution is as follows: figure 1 ;
[0043] From figure 1 It can be seen that the amount of generated R-hydroxamic acid is much greater than that of S-hydroxamic acid, i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com